1 简介
Sankalap Arora和Satvir Singh两位学者,通过观察蝴蝶觅食行为而受到启发,提出了一种新的群智能优化算法——蝴蝶优化算法(Butterfly Optimization Algorithm)。该算法的主要思想是模拟蝴蝶的觅食和求偶行为实现对目标问题的求解。
具体原理如下:





2 部分代码
%% Monarch Butterfly Optimization (MBO)
% % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % %%
%% Notes:
% Different run may generate different solutions, this is determined by
% the the nature of metaheuristic algorithms.
%%
function [MinCost] = MBO(ProblemFunction, DisplayFlag, RandSeed)
% Monarch Butterfly Optimization (MBO) software for minimizing a general function
% The fixed Function Evaluations (FEs) is considered as termination condition.
% INPUTS: ProblemFunction is the handle of the function that returns
% the handles of the initialization, cost, and feasibility functions.
% DisplayFlag = true or false, whether or not to display and plot results.
% ProbFlag = true or false, whether or not to use probabilities to update emigration rates.
% RandSeed = random number seed
% OUTPUTS: MinCost = array of best solution, one element for each generation
% Hamming = final Hamming distance between solutions
% CAVEAT: The "ClearDups" function that is called below replaces duplicates with randomly-generated
% individuals, but it does not then recalculate the cost of the replaced individuals.
tic
if ~exist('ProblemFunction', 'var')
ProblemFunction = @Ackley;
end
if ~exist('DisplayFlag', 'var')
DisplayFlag = true;
end
if ~exist('RandSeed', 'var')
RandSeed = round(sum(100*clock));
end
[OPTIONS, MinCost, AvgCost, InitFunction, CostFunction, FeasibleFunction, ...
MaxParValue, MinParValue, Population] = Init(DisplayFlag, ProblemFunction, RandSeed);
nEvaluations = OPTIONS.popsize;
% % % % % % % % % % % % Initial parameter setting % % % % % % % % % % % %%%%
%% Initial parameter setting
Keep = 2; % elitism parameter: how many of the best habitats to keep from one generation to the next
maxStepSize = 1.0; %Max Step size
partition = OPTIONS.partition;
numButterfly1 = ceil(partition*OPTIONS.popsize); % NP1 in paper
numButterfly2 = OPTIONS.popsize - numButterfly1; % NP2 in paper
period = 1.2; % 12 months in a year
Land1 = zeros(numButterfly1, OPTIONS.numVar);
Land2 = zeros(numButterfly2, OPTIONS.numVar);
BAR = partition; % you can change the BAR value in order to get much better performance
% % % % % % % % % % % % End of Initial parameter setting % % % % % % % % % % % %%
%%
% % % % % % % % % % % % Begin the optimization loop % % % % % % % % % %%%%
% Begin the optimization loop
GenIndex = 1;
% for GenIndex = 1 : OPTIONS.Maxgen
while nEvaluations< OPTIONS.MaxFEs
% % % % % % % % % % % % Elitism Strategy % % % % % % % % % % % %%%%%
%% Save the best monarch butterflis in a temporary array.
for j = 1 : Keep
chromKeep(j,:) = Population(j).chrom;
costKeep(j) = Population(j).cost;
end
% % % % % % % % % % % % End of Elitism Strategy % % % % % % % % % % % %%%%
%%
% % % % % % % % % % % % Divide the whole population into two subpopulations % % % %%%
%% Divide the whole population into Population1 (Land1) and Population2 (Land2)
% according to their fitness.
% The monarch butterflis in Population1 are better than or equal to Population2.
% Of course, we can randomly divide the whole population into Population1 and Population2.
% We do not test the different performance between two ways.
for popindex = 1 : OPTIONS.popsize
if popindex <= numButterfly1
Population1(popindex).chrom = Population(popindex).chrom;
else
Population2(popindex-numButterfly1).chrom = Population(popindex).chrom;
end
end
% % % % % % % % % % % End of Divide the whole population into two subpopulations % % %%%
%%
% % % % % % % % % % % %% Migration operator % % % % % % % % % % % %%%%
%% Migration operator
for k1 = 1 : numButterfly1
for parnum1 = 1 : OPTIONS.numVar
r1 = rand*period;
if r1 <= partition
r2 = round(numButterfly1 * rand + 0.5);
Land1(k1,parnum1) = Population1(r2).chrom(parnum1);
else
r3 = round(numButterfly2 * rand + 0.5);
Land1(k1,parnum1) = Population2(r3).chrom(parnum1);
2
SavePopSize = OPTIONS.popsize;
OPTIONS.popsize = numButterfly2;
% Make sure each individual is legal.
NewPopulation2 = FeasibleFunction(OPTIONS, NewPopulation2);
% Calculate cost
NewPopulation2 = CostFunction(OPTIONS, NewPopulation2);
% the number of fitness evaluations
nEvaluations = nEvaluations + OPTIONS.popsize;
OPTIONS.popsize = SavePopSize;
% % % % % % % % % % % % End of Evaluate NewPopulation2 % % % % % % % % % % % %%
%%
% % % % % % % Combine two subpopulations into one and rank monarch butterflis % % % % % %
%% Combine Population1 with Population2 to generate a new Population
Population = CombinePopulation(OPTIONS, NewPopulation1, NewPopulation2);
% Sort from best to worst
Population = PopSort(Population);
% % % % % % End of Combine two subpopulations into one and rank monarch butterflis % %% % %
%%
% % % % % % % % % % % % Elitism Strategy % % % % % % % % % % % %%% %% %
%% Replace the worst with the previous generation's elites.
n = length(Population);
for k3 = 1 : Keep
Population(n-k3+1).chrom = chromKeep(k3,:);
Population(n-k3+1).cost = costKeep(k3);
end % end for k3
% % % % % % % % % % % % End of Elitism Strategy % % % % % % % % % % % %%% %% %
%%
% % % % % % % % % % Precess and output the results % % % % % % % % % % % %%%
% Sort from best to worst
Population = PopSort(Population);
% Compute the average cost
[AverageCost, nLegal] = ComputeAveCost(Population);
% Display info to screen
MinCost = [MinCost Population(1).cost];
AvgCost = [AvgCost AverageCost];
if DisplayFlag
disp(['The best and mean of Generation # ', num2str(GenIndex), ' are ',...
num2str(MinCost(end)), ' and ', num2str(AvgCost(end))]);
end
% % % % % % % % % % % End of Precess and output the results %%%%%%%%%% %% %
%%
%% Update generation number
GenIndex = GenIndex+1;
end % end for GenIndex
Conclude2(DisplayFlag, OPTIONS, Population, nLegal, MinCost, AvgCost);
toc
% % % % % % % % % % End of Monarch Butterfly Optimization implementation %%%% %% %
%%
function [delataX] = LevyFlight(StepSize, Dim)
%Allocate matrix for solutions
delataX = zeros(1,Dim);
%Loop over each dimension
for i=1:Dim
% Cauchy distribution
fx = tan(pi * rand(1,StepSize));
delataX(i) = sum(fx);
end
3 仿真结果
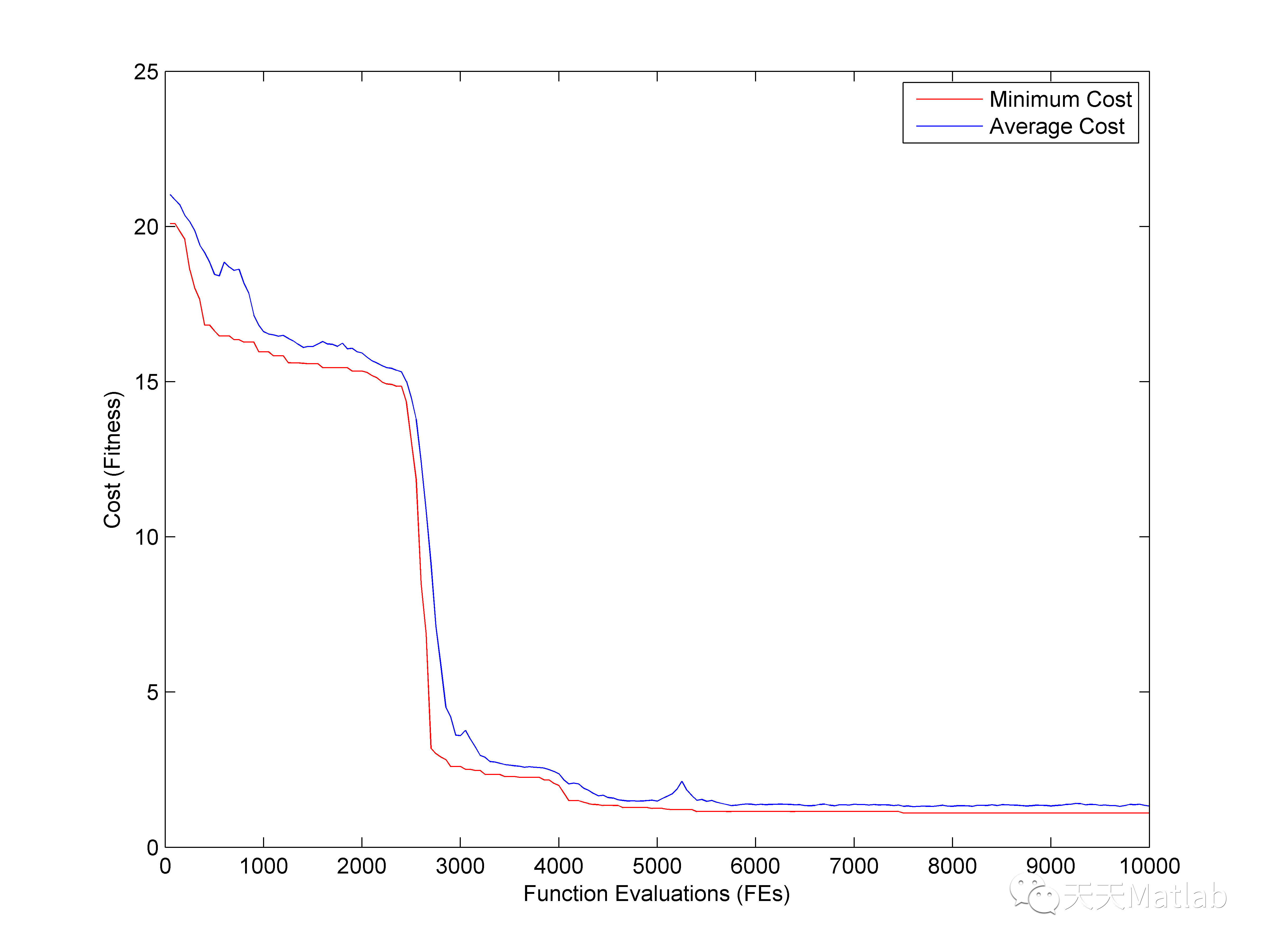
4 参考文献
[1]王希彤. 基于MBO的约束满足问题求解算法研究[D]. 吉林大学.
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。
5 MATLAB代码与数据下载地址
见博客主页
最后
以上就是超级百褶裙最近收集整理的关于【优化求解】基于蝴蝶算法MBO求解最优目标matlab源码的全部内容,更多相关【优化求解】基于蝴蝶算法MBO求解最优目标matlab源码内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。


![高斯分布+柯西-洛伦兹分布+三种光谱线型函数(洛伦兹线型函数+多普勒[高斯]线型函数+vogit 线型函数)一、两种分布二、光谱线型函数](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg3.png)





发表评论 取消回复