sr锁存器和rs锁存器
锁存器 (Latch)
The word latch means "to lock". A Latch is an example of a bistable multivibrator (the device which has two stable states). In the first stable state is the high-output and the second one is low-output. A Latch contains a feedback path from which the information can be retained by any device. So, we can conclude that latches are memory devices that are capable to store one bit of data when the power supply is provided. Designing of latches will be similar to flip-flops, but they do not have clocks.
闩锁一词的意思是“锁定” 。 锁存器是双稳态多谐振荡器(具有两个稳定状态的设备)的示例。 在第一个稳定状态下为高输出,第二个为低输出。 锁存器包含一个反馈路径,任何设备都可以通过该路径保留信息。 因此,我们可以得出结论, 锁存器是在提供电源时能够存储一位数据的存储设备 。 锁存器的设计将类似于触发器,但它们没有时钟。
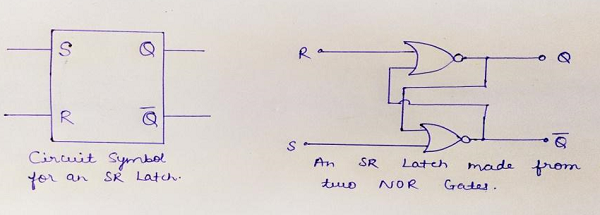
SR Latch的施工和建造 (SR Latch working and construction)
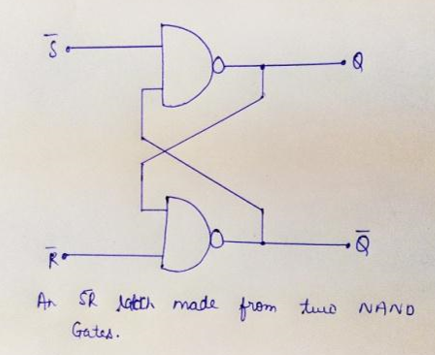
SR latch (Set/Reset) works independently of clock signals and depends only upon S and R inputs, so they are also called as asynchronous devices. SR latch can be created in two ways- by using NAND gates and also can be implemented using NOR gates. SR latch created by NAND gates is sometimes called an inverted SR latch.
SR锁存器 (设置/复位)与时钟信号无关,并且仅取决于S和R输入,因此它们也称为异步设备。 SR锁存器可以通过两种方式创建- 使用“与非”门 ,也可以使用“或非”门实现。 由“与非”门创建的SR锁存器有时也称为反向SR锁存器。
Working of SR NOR latch:
SR NOR锁存器的工作:
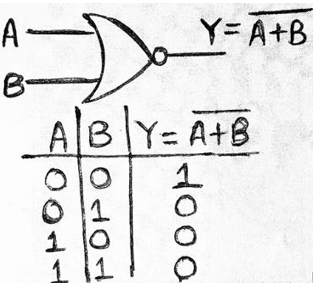
For understanding the working of SR NOR latch, we need to have a look at the truth table of the NOR gate (given below) which shows if any of the input is 'high' output becomes 'low', irrespective of the other input.
为了理解SR NOR锁存器的工作原理,我们需要查看NOR门的真值表(如下所示),该表显示任何输入是否为“高”输出都变为“低”,而与其他输入无关。
Case 1: When R=0 and S=0
情况1:当R = 0和S = 0时
Let us suppose, initially the value of Q be 0 then, both the inputs of lower NOR gate becomes zero, and output of that gate becomes 1 i.e., Q'=1, now in the upper gate inputs provided will be 0 and 1, so from truth table of NOR gate we know the output will be low hence Q=0.
让我们假设,最初Q的值为0,那么下或非门的输入都为零,并且该门的输出为1,即Q'= 1 ,现在在所提供的上门的输入中将为0和1。因此,根据“或非”门的真值表,我们知道输出将较低,因此Q = 0。
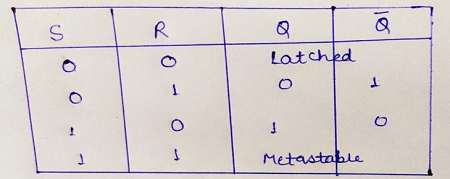
From this observation, we can conclude that output in the next state remains the same as the output in the previous state. This condition of the latch is known as Memory condition / Hold state / Latched state.
从这个观察结果,我们可以得出结论,下一个状态的输出与前一个状态的输出保持相同。 锁存器的这种状态称为存储状态/保持状态/锁存状态 。
Case 2: When R=1, S=0
情况2:当R = 1时,S = 0
When R=1 and S=0, then at the upper NOR gate, we will receive output as 0 i.e., Q=0, now at the lower NOR gate we have both inputs as 0, so the output Q’=1. Thus, this condition of the latch is known as Reset Condition.
当R = 1且S = 0时,在上或非门,我们将接收输出为0,即Q = 0,现在在下或非门,我们两个输入均为0,因此输出Q'= 1。 因此,锁存器的这种状态称为复位状态。
Case 3: When R=0, S=1
情况3:当R = 0时,S = 1
In this case, output at the second NOR gate will be 0 i.e., Q’=0, now at first NOR gate inputs provided will be both 0, so the output will be Q=1. Thus, this condition of latch is known as Set Condition.
在这种情况下,第二个NOR门的输出将为0,即Q'= 0,现在在第一个NOR门处提供的输入将均为0,因此输出将为Q = 1。 因此,该锁存条件称为置位条件。
Case 4: When R=1, S=1
情况4:当R = 1时,S = 1
At both gates, we will gate output Q and Q'=0, which is absurd and does not follow the basic working of latch, both Q and Q' must be complementary to each other. So, this condition of latch is known as Invalid state/Race-Around condition/Forbidden state.
在两个门处,我们将对输出Q和Q'= 0进行门操作,这是荒谬的,并且不遵循锁存器的基本工作,因此Q和Q'必须彼此互补。 因此,锁存器的这种状态称为无效状态/绕圈状态/禁止状态。
Thus, above all cases of the latch can be summarized in a truth table as:
因此,最重要的是,在真值表中可以将闩锁的所有情况总结为:
Working of SR NAND latch:
SR NAND锁存器的工作:
To understand the working of SR NAND latch, we need to have a look at the truth table of NAND gate given below.
要了解SR NAND锁存器的工作原理,我们需要查看下面给出的NAND门的真值表。
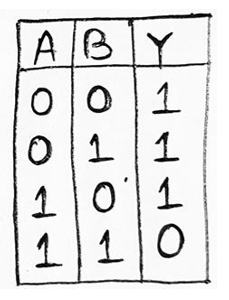
Case 1: When S=0, R=0
情况1:当S = 0时,R = 0
Let us suppose, the value of Q at the start of the circuit be 1, then inputs at the lower gate will be 1, thus from truth table of NAND gate, we can say that output of the lower gate will be 0 i.e., Q’=0, as a result, input at the upper gate will be 0 & 1. We know, if any of the inputs of the NAND gate is low, the output will always be high, thus Q=1.
让我们假设,电路开始时Q的值为1,那么下门的输入将为1,因此从与非门的真值表中,我们可以说下门的输出将为0,即Q '= 0,因此,上门的输入将为0&1。我们知道,如果“与非”门的任何输入为低,则输出将始终为高,因此Q = 1。
Therefore, we can observe the output in the next state to be the same as in the previous state. So, this condition of the latch is known as Memory state/Hold condition.
因此,我们可以观察到下一个状态的输出与上一个状态的输出相同。 因此,锁存器的这种状况称为“ 内存状态/保持状况” 。
Case 2: When S=0, R=1
情况2:当S = 0时,R = 1
The inputs provided to the lower gate is 0, thus output will be high i.e., Q'=1. Now, at the upper gate inputs provided are 1, thus output Q=0. This condition of latch is known as Reset Condition.
提供给下栅极的输入为0,因此输出将为高,即Q'= 1。 现在,在上栅极处提供的输入为1,因此输出Q = 0。 锁存器的这种条件称为复位条件。
Case 3: When S=1, R=0
情况3:当S = 1时,R = 0
In this case, one of the outputs at upper gate will be 0, thus we will get Q=1, similarly inputs at lower gate are 1 and 1, so we get output Q'=0. This condition of latch is known as Set Condition.
在这种情况下,上栅极的输出之一将为0,因此我们将得到Q = 1,下栅极的类似输入将为1和1,因此我们将获得输出Q'= 0。 锁存器的这种条件称为置位条件。
Case 4: When S=1, R=1
情况4:当S = 1时,R = 1
In this case, one of the inputs of each gate will be low, and we know if any of the inputs of the NAND gate is low its output will be high, so both Q and Q'=1, which is not possible, thus we neglect this condition. This condition of the latch is known as Invalid state / Race-Around condition / Forbidden state.
在这种情况下,每个门的输入之一将为低,并且我们知道“与非”门的任何输入是否为低,其输出将为高,因此Q和Q'= 1都是不可能的,因此我们忽略了这种情况。 锁存器的这种情况称为无效状态/比赛状态/禁止状态 。
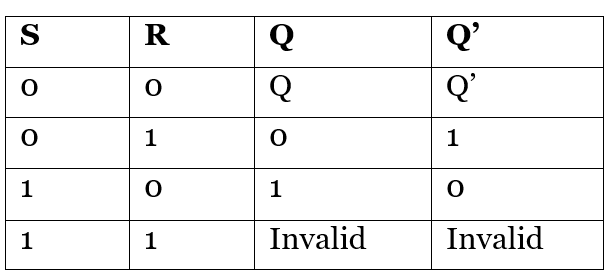
All the above cases of the latch can be summarized in the table as:
锁存器的所有上述情况可以在表中总结为:
翻译自: https://www.includehelp.com/basics/sr-latch-in-digital-electronics.aspx
sr锁存器和rs锁存器
最后
以上就是想人陪眼睛最近收集整理的关于sr锁存器和rs锁存器_数字电子产品中的SR锁存器的全部内容,更多相关sr锁存器和rs锁存器_数字电子产品中内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复