横向控制 | Pure Persuit(纯跟踪)算法
- 1. 算法简介
- 2. 源码解析
- 3. 效果演示
参考链接: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/48117381
Github链接: https://github.com/chanchanchan97/ROS
1. 算法简介
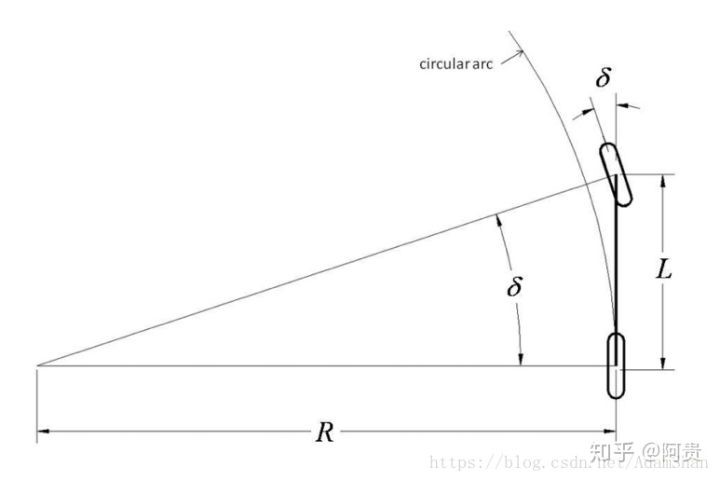
单车模型(Bicycle Model)实际上是对阿克曼转向几何的一个简化,使用单车模型需做如下假设:
- 不考虑车辆在Z轴方向的运动,只考虑XY水平面的运动;
- 左右侧车轮转角一致,这样可将左右侧轮胎合并为一个轮胎,以便于搭建单车模型;
- 车辆行驶速度变化缓慢,忽略前后轴载荷的转移;
- 车身及悬架系统是刚性的。
采用单车模型的一大好处就在于它简化了前轮转向角与后轴将遵循的曲率之间的几何关系,其关系如下式所示:
t
a
n
(
δ
)
=
L
R
tan(δ)=frac{L}{R}
tan(δ)=RL 其中
δ
δ
δ表示前轮的转角,
L
L
L为轴距,
R
R
R则为在给定的转向角下后轴遵循着的圆的半径。
从自行车模型出发,纯跟踪算法以车后轴为切点,车辆纵向车身为切线,通过控制前轮转角,使车辆可以沿着一条经过目标路点(goal point)的圆弧行驶,如下图所示:
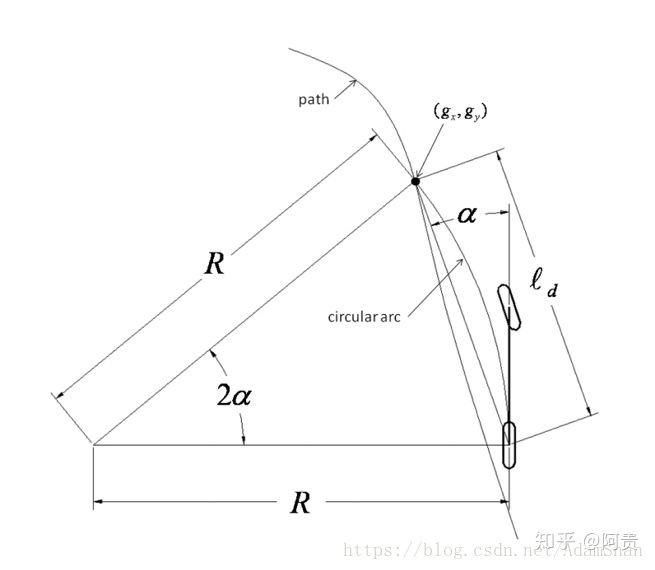
图中 ( g x , g y ) (g_x,g_y) (gx,gy)是我们下一个要追踪的路点,它位于我们已经规划好的全局路径上,现在需要控制车辆的后轴经过该路点, l d l_d ld表示车辆当前位置(即后轴位置)到目标路点的距离, α α α表示目前车身姿态和目标路点的夹角,那么根据正弦定理我们可以推导出如下转换式: l d s i n ( 2 α ) = R s i n ( π 2 − α ) frac{l_d}{sin(2α)}=frac{R}{sin(frac{pi}{2}-α)} sin(2α)ld=sin(2π−α)R l d 2 s i n α c o s α = R c o s α frac{l_d}{2sinαcosα}=frac{R}{cosα} 2sinαcosαld=cosαR l d s i n α = 2 R frac{l_d}{sinalpha}=2R sinαld=2R因为道路的曲率 κ = 1 R {κ}=frac{1}{R} κ=R1上式也可以表示为 κ = 2 s i n ( α ) l d κ=frac{2sin(α)}{l_d} κ=ld2sin(α)则由式子 t a n ( δ ) = L R tan(δ)=frac{L}{R} tan(δ)=RL可得 δ = a r c t a n ( L R ) = a r c t a n ( κ L ) = a r c t a n ( 2 L s i n ( α ) l d ) δ=arctan(frac{L}{R})=arctan(κL)=arctan(frac{2Lsin(α)}{l_d}) δ=arctan(RL)=arctan(κL)=arctan(ld2Lsin(α))
2. 源码解析
(1) 初始化函数
def __init__(self):
rospy.init_node('pure_persuit', log_level=rospy.DEBUG)
rospy.Subscriber('/rear_pose', PoseStamped, self.pose_cb, queue_size = 1)
rospy.Subscriber('/velocity', TwistStamped, self.vel_cb, queue_size = 1)
rospy.Subscriber('/final_waypoints', Lane, self.lane_cb, queue_size = 1)
self.left_vel_pub =rospy.Publisher('/rear_left_velocity_controller/command', Float64, queue_size = 10)
self.right_vel_pub = rospy.Publisher('/rear_right_velocity_controller/command', Float64, queue_size = 10)
self.left_steer_pub = rospy.Publisher('/left_bridge_position_controller/command', Float64, queue_size = 10)
self.right_steer_pub = rospy.Publisher('/right_bridge_position_controller/command', Float64, queue_size = 10)
self.currentPose = None
self.currentVelocity = None
self.currentWaypoints = None
self.loop()
说明:
rospy.Subscriber('/rear_pose', PoseStamped, self.pose_cb, queue_size = 1)
rospy.Subscriber('/velocity', TwistStamped, self.vel_cb, queue_size = 1)
rospy.Subscriber('/final_waypoints', Lane, self.lane_cb, queue_size = 1)
- 上面这三段函数创建了三个ROS话题订阅者,分别向ROS系统订阅/rear_pose、/velocity和/final_waypoints三种话题消息,即小车后轮轴中心点坐标、小车速度和局部路径点信息,而这三种话题消息对应的回调函数分别为pose_cb、vel_cb和lane_cb。
self.left_vel_pub =rospy.Publisher('/rear_left_velocity_controller/command', Float64, queue_size = 10)
self.right_vel_pub = rospy.Publisher('/rear_right_velocity_controller/command', Float64, queue_size = 10)
self.left_steer_pub = rospy.Publisher('/left_bridge_position_controller/command', Float64, queue_size = 10)
self.right_steer_pub = rospy.Publisher('/right_bridge_position_controller/command', Float64, queue_size = 10)
- 上面这四段函数创建了四个ROS话题发布者,分别发布/rear_left_velocity_controller/command、/rear_right_velocity_controller/command、/left_bridge_position_controller/command和/right_bridge_position_controller/command四种话题消息,即小车后轮的纵向速度指令和前轮的横向角度指令。
(2) loop()函数
def loop(self):
rate = rospy.Rate(20)
rospy.logwarn("pure persuit starts")
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
if self.currentPose and self.currentVelocity and self.currentWaypoints:
self.calculateTwistCommand()
rate.sleep()
说明:
- rate = rospy.Rate(20)设置该函数的循环频率为20Hz。
- while not rospy.is_shutdown():表示若ROS未被关闭,则进行以下操作。
- if self.currentPose and self.currentVelocity and self.currentWaypoints:表示若self.currentPose、self.currentVelocity和self.currentWaypoints均为非空时,则进行以下操作。
(3) 回调函数
def pose_cb(self,data):
self.currentPose = data
def vel_cb(self,data):
self.currentVelocity = data
def lane_cb(self,data):
self.currentWaypoints = data
说明:
- 这三个回调函数分别将/rear_pose、/velocity和/final_waypoints的话题消息内容提取出来,赋给self.currentPose、self.currentVelocity和self.currentWaypoints。
(4) 阿克曼(Ackermann)转向函数
def ackermann_steering_control(self, velocity, radian):
global left_angle, left_speed, right_angle, right_speed
if radian > 0:
inside_radius = L / math.tan(radian) - T / 2
outside_radius = L / math.tan(radian) + T / 2
else:
outside_radius = L / math.tan(radian) - T / 2
inside_radius = L / math.tan(radian) + T / 2
outside_speed = velocity * ( 1 + T * math.tan(abs(radian)) / ( 2 * L ) )
inside_speed = velocity * ( 1 - T * math.tan(abs(radian)) / ( 2 * L ) )
inside_angle = math.atan( L / inside_radius )
outside_angle = math.atan( L / outside_radius )
if radian > 0:
left_angle = outside_angle
left_speed = outside_speed
right_angle = inside_angle
right_speed = inside_speed
else:
right_angle = outside_angle
right_speed = outside_speed
left_angle = inside_angle
left_speed = inside_speed
说明:
- 该函数以小车的期望转角(单位:弧度)和期望速度为输入,分别根据阿克曼转向模型控制小车两个前轮的转角和两个后轮的转速。
(5) calculateTwistCommand()函数part.1
def calculateTwistCommand(self):
lad = 0.0 #look ahead distance accumulator
targetIndex = len(self.currentWaypoints.waypoints) - 1
for i in range(len(self.currentWaypoints.waypoints)):
if((i+1) < len(self.currentWaypoints.waypoints)):
this_x = self.currentWaypoints.waypoints[i].pose.pose.position.x
this_y = self.currentWaypoints.waypoints[i].pose.pose.position.y
next_x = self.currentWaypoints.waypoints[i+1].pose.pose.position.x
next_y = self.currentWaypoints.waypoints[i+1].pose.pose.position.y
lad = lad + math.hypot(next_x - this_x, next_y - this_y)
if(lad > HORIZON):
targetIndex = i+1
break
targetWaypoint = self.currentWaypoints.waypoints[targetIndex]
targetSpeed = self.currentWaypoints.waypoints[0].twist.twist.linear.x
说明:
- lad = 0.0设置的是前瞻距离。
- targetIndex = len(self.currentWaypoints.waypoints) – 1的作用是获取局部路径的长度(局部路径点的数量),并设置列表的大小,其中len(self.currentWaypoints.waypoints)的值就等于waypoints_updater.py中设置的LOOKAHEAD_WPS。
- for i in range(len(self.currentWaypoints.waypoints)):此处是遍历整个局部路径点列表。
- this_x和this_y表示当前最近的局部路径点横、纵坐标,next_x和next_y表示下一个路径点的横、纵坐标。计算当前路径点与下一个路径点的距离,并累加到前瞻距离lad。当前瞻距离lad达到阈值HORIZON时,将该点设置为目标路径点,即targetWaypoint。
(6) calculateTwistCommand()函数part.2
targetX = targetWaypoint.pose.pose.position.x
targetY = targetWaypoint.pose.pose.position.y
currentX = self.currentPose.pose.position.x
currentY = self.currentPose.pose.position.y
说明:
- targetX和targetY表示目标路径点的横、纵坐标,currentX和currentY表示小车当前的坐标点横、纵坐标。
(7) calculateTwistCommand()函数part.3
#get vehicle yaw angle
quanternion = (self.currentPose.pose.orientation.x, self.currentPose.pose.orientation.y, self.currentPose.pose.orientation.z, self.currentPose.pose.orientation.w)
euler = tf.transformations.euler_from_quaternion(quanternion)
yaw = euler[2]
说明:
- euler = tf.transformations.euler_from_quaternion(quanternion)的作用是将小车当前的姿态信息由四元数格式转换到欧拉角的格式,即以roll、pitch和yaw轴偏向角的形式存储在列表euler中。
(8) calculateTwistCommand()函数part.4
#get angle difference
alpha = math.atan2(targetY - currentY, targetX - currentX) - yaw
l = math.sqrt(math.pow(currentX - targetX, 2) + math.pow(currentY - targetY, 2))
if(l > 0.5):
theta = math.atan(2 * 0.16 * math.sin(alpha) / l)
self.ackermann_steering_control(targetSpeed, -theta)
#get twist command
left_steer = Float64()
right_steer = Float64()
left_vel = Float64()
right_vel = Float64()
left_steer.data = left_angle
right_steer.data = right_angle
left_vel.data = left_speed
right_vel.data = right_speed
else:
left_steer = Float64()
right_steer = Float64()
left_vel = Float64()
right_vel = Float64()
left_steer.data = 0
right_steer.data = 0
left_vel.data = 0
right_vel.data = 0
self.left_vel_pub.publish(left_vel)
self.right_vel_pub.publish(right_vel)
self.left_steer_pub.publish(left_steer)
self.right_steer_pub.publish(right_steer)
说明:
- alpha = math.atan2(targetY - currentY, targetX - currentX) – yaw的作用是计算小车当前的yaw角与目标点之间的角度偏差。
- l = math.sqrt(math.pow(currentX - targetX, 2) + math.pow(currentY - targetY, 2))用于计算小车当前位置点与目标路径点的距离。
- 当l < 0.5,即小车快要到达全局路径的终点时,直接将小车速度设置为0。反之,则通过Pure Persuit算法得到前轮转向角度,再将该角度作为Ackermann算法的输入,从而实现对小车横向和纵向控制,使其能够沿着全局路径行驶。
3. 效果演示
ROS|平平无奇路径跟踪仿真(Pure Persuit)
最后
以上就是清新翅膀最近收集整理的关于横向控制 | Pure Persuit(纯跟踪)算法1. 算法简介2. 源码解析3. 效果演示的全部内容,更多相关横向控制内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复