什么是overlay
Squashfs(.sfs)是一套供Linux核心使用的GPL开源只读压缩文件系统。Squashfs能够为文件系统内的文件、inode及目录结构进行压缩。
Squashfs的设计是专门为一般的只读文件系统的使用而设计,它可应用于数据备份,或是系统资源紧张的电脑上使用。
OpenWRT 一般使用的文件系统是 SquashFS ,建议下载固件的时候也下载这种固件。
这个文件系统的特点就是:只读、压缩。
一个只读的文件系统,是怎么做到保存设置和安装软件的呢?用/overlay分区。固件中已经写入了有个/overlay分区,但它的指向可以更改。
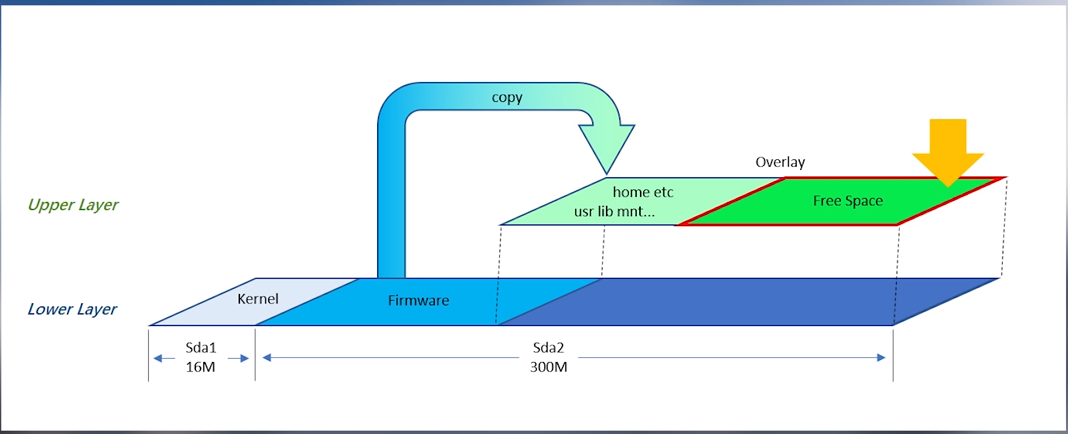
虽然原来的文件不能修改,但我们把修改的部分放在 overlay 分区上,然后映射到原来的位置,读取的时候就可以读到我们修改过的文件了。当系统故障,reset的时候,把固件中配置文件拷贝到overlay层,就恢复到最初设置了。
由于/overlay本身的指向配置也在overlay层,所以可以新建一个更大的分区,然后把overlay指向这个新分区,就相当于把overlay扩容了。这个可能有点绕。
命令行工具
lsblk
blkid
fdisk
mkswap
swapon
其实还有一些查看挂载点的命令:比如df,mount -l,查看/etc/mtab文件内容,后两者是结果是一样。
首先lsblk是列出block。结果如下:
root@OpenWrt:~# lsblk
NAME
MAJ:MIN RM
SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
loop0
7:0
0 41.8M
0 loop /mnt/loop0
sda
8:0
1
3.8G
0 disk
├─sda1
8:1
1
16M
0 part /mnt/sda1
└─sda2
8:2
1
160M
0 part /rom
这是一个U盘做的软路由,只有4G。但可以分出其他几个区。一个用来扩容overlay,剩下当swap,准备安装transmission和docker、samba。挂载一个硬盘做网络共享。
增加分区:fdisk命令。这个命令需要参数,是一个硬盘设备,比如/dev/sda。然后就进入fdisk程序中的命令,直到退出fdisk。这和其他命令不同。
root@OpenWrt:~#
fdisk /dev/sda
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.33).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): m
Help:
DOS (MBR)
a
toggle a bootable flag
b
edit nested BSD disklabel
c
toggle the dos compatibility flag
Generic
d
delete a partition
F
list free unpartitioned space
l
list known partition types
n
add a new partition
p
print the partition table
t
change a partition type
v
verify the partition table
i
print information about a partition
Misc
m
print this menu
u
change display/entry units
x
extra functionality (experts only)
Script
I
load disk layout from sfdisk script file
O
dump disk layout to sfdisk script file
Save & Exit
w
write table to disk and exit
q
quit without saving changes
Create a new label
g
create a new empty GPT partition table
G
create a new empty SGI (IRIX) partition table
o
create a new empty DOS partition table
s
create a new empty Sun partition table
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sda: 3.8 GiB, 4026531840 bytes, 7864320 sectors
Disk model: ProductCode
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xd56b2d42
Device
Boot Start
End Sectors
Size Id Type
/dev/sda1
*
512
33279
32768
16M 83 Linux
/dev/sda2
33792 361471
327680
160M 83 Linux
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p
primary (2 primary, 0 extended, 2 free)
e
extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p): 2
Value out of range.
p
primary (2 primary, 0 extended, 2 free)
e
extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p): p
Partition number (3,4, default 3): 3
First sector (33280-7864319, default 362496):
Last sector, +/-sectors or +/-size{K,M,G,T,P} (362496-7864319, default 7864319): +1G
Created a new partition 3 of type 'Linux' and of size 1 GiB.
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sda: 3.8 GiB, 4026531840 bytes, 7864320 sectors
Disk model: ProductCode
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xd56b2d42
Device
Boot
Start
End Sectors
Size Id Type
/dev/sda1
*
512
33279
32768
16M 83 Linux
/dev/sda2
33792
361471
327680
160M 83 Linux
/dev/sda3
362496 2459647 2097152
1G 83 Linux
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p
primary (3 primary, 0 extended, 1 free)
e
extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default e): p
Selected partition 4
First sector (33280-7864319, default 2459648):
Last sector, +/-sectors or +/-size{K,M,G,T,P} (2459648-7864319, default 7864319):
Created a new partition 4 of type 'Linux' and of size 2.6 GiB.
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sda: 3.8 GiB, 4026531840 bytes, 7864320 sectors
Disk model: ProductCode
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xd56b2d42
Device
Boot
Start
End Sectors
Size Id Type
/dev/sda1
*
512
33279
32768
16M 83 Linux
/dev/sda2
33792
361471
327680
160M 83 Linux
/dev/sda3
362496 2459647 2097152
1G 83 Linux
/dev/sda4
2459648 7864319 5404672
2.6G 83 Linux
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered.
Syncing disks.
这时分区就都完成了,并且写入分区表了。
然后将新加的分区/dev/sda3和/dev/sda4格式化。
将sda3格式化为ext4,将sda4格式化为swap,并打开swap。
root@OpenWrt:~# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sda3
mke2fs 1.44.3 (10-July-2018)
Creating filesystem with 262144 4k blocks and 65536 inodes
Filesystem UUID: 13105391-0ee0-43e9-b6d9-c2d75053b951
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (8192 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
root@OpenWrt:~# mkswap /dev/sda4
Setting up swapspace version 1, size = 2767187968 bytes
root@OpenWrt:~# swapon /dev/sda4
重启reboot。
下一步需要将/overlay中内容拷贝到sda3中。但不能直接用/dev/sda3来拷贝,这只是一个硬盘设备文件,不是文件系统。所以需要将其挂载到某个目录下面,通常挂载的时候会要求标识文件系统,这样把一个设备挂载在文件系统下面,同时标识了该文件系统,这样整个系统就能看到里面的文件了。
/dev/sda3挂载到一个目录,之前可以df -h命令查看一下,原来都挂载在什么地方。看到原来都在/mnt下面。
mount -t ext4 /dev/sda3 /mnt/sda3
如果没有/mnt/sda3,可以使用mkdir /mnt/sda3创建。
然后看看loop0指向的是哪个目录,发现overlay在rom中,
root@OpenWrt:/# df -h
Filesystem
Size
Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/root
118.3M
118.3M
0 100% /rom
tmpfs
487.3M
1.9M
485.4M
0% /tmp
/dev/loop0
36.4M
1.9M
31.6M
6% /rom/overlay
overlayfs:/overlay
36.4M
1.9M
31.6M
6% /
/dev/sda1
15.7M
3.7M
11.7M
24% /boot
/dev/sda1
15.7M
3.7M
11.7M
24% /boot
tmpfs
512.0K
0
512.0K
0% /dev
cgroup
487.3M
0
487.3M
0% /sys/fs/cgroup
overlayfs:/overlay
36.4M
1.9M
31.6M
6% /opt/docker
/dev/loop0
36.4M
1.9M
31.6M
6% /mnt/loop0
/dev/sda1
15.7M
3.7M
11.7M
24% /mnt/sda1
/dev/sda3
975.9M
2.5M
906.2M
0% /mnt/sda3
然后把overlay的内容全部拷贝到sda3
root@OpenWrt:/rom/overlay# cp -r /rom/overlay/* /mnt/sda3
然后umount /dev/sda3 。再用df -h看看挂载点,就没有/mnt/sda3
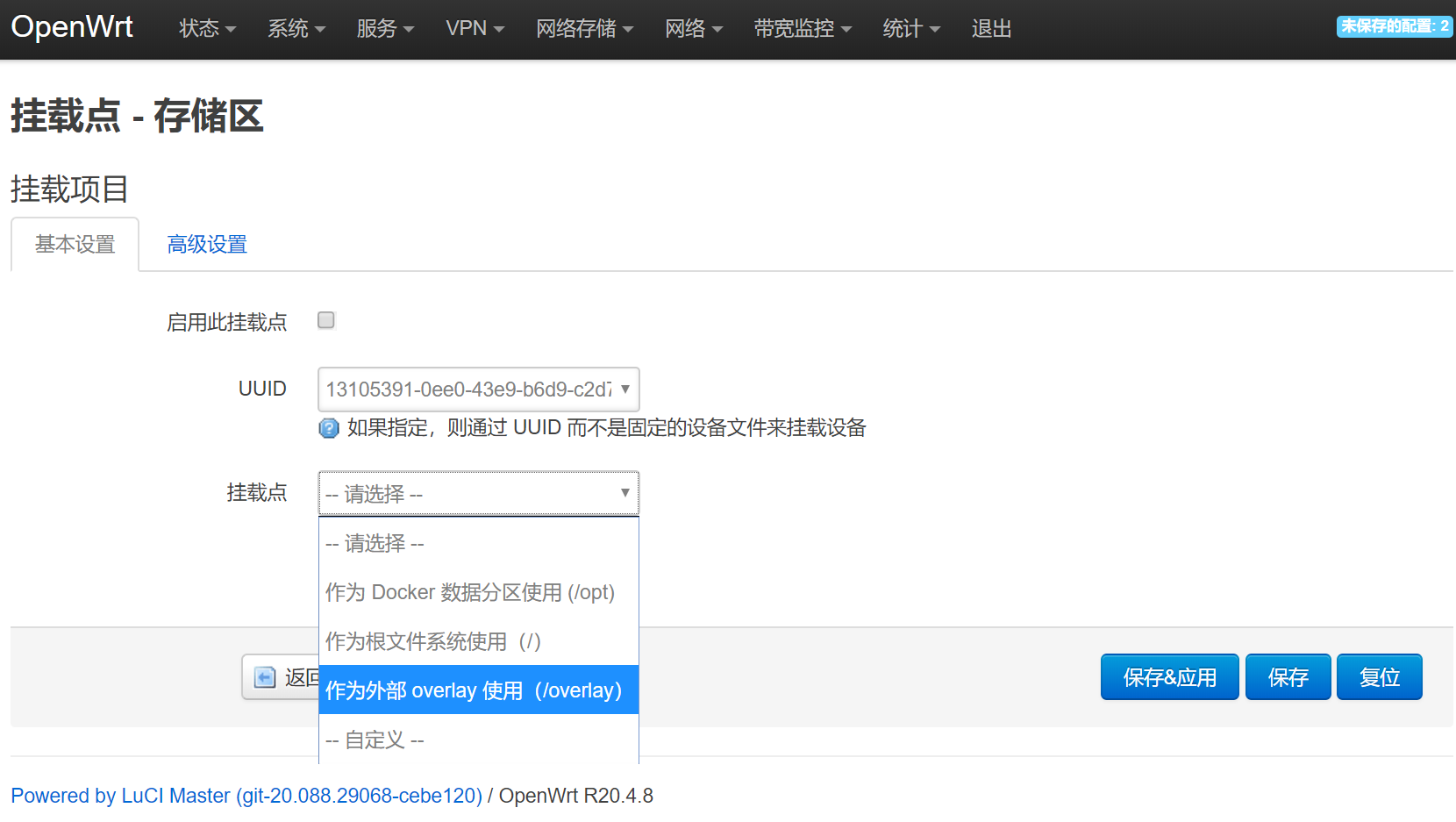
退出shell。来到路由器web界面:【系统】-【挂载点】-【添加】进入下面界面。选择1G的那块盘,挂载成overlay。这就扩容了。

最后
以上就是踏实金毛最近收集整理的关于openwrt下面扩容overlay并开启swap什么是overlay命令行工具的全部内容,更多相关openwrt下面扩容overlay并开启swap什么是overlay命令行工具内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复