Simulink仿真入门到精通(十) S函数
- 10.1. S函数的概述
- 10.2 S函数的类型
- 10.3 S函数的要素
- 10.4 S函数的组成及执行顺序
- 10.5 使用不同的语言编写S函数
- 10.5.1 Level1 M S函数
- 10.5.2 Level2 M S函数
- 1. Setup子方法
- 2. PostPropagationSetup子方法
- 3. InitializeConditions/Start子方法
- 4. InitializeConditions/Start子方法
- 5. Updata子方法
- 6. Derivatives子方法
- 7. Terminate子方法
- 10.5.3 C Mex S函数
- 1. C Mex S函数的构成
- 1) mdlInitializeSizes
- 2) mdlOutputs
- 2. C Mex S函数的编译
- 3. C Mex S函数的应用
- 1)示例1
- 2)示例2
- 10.6 C Mex S函数的自动生成
- 10.6.1 S-Function Builder
- 10.6.2 Legacy Code Tool
10.1. S函数的概述
S函数(System function)
也称为Simulink中的系统函数,是用来描述模块的Simulink宏函数,支持M,C等多种语言。当Simulink默认提供的模块不能够满足用户的需求时,用户可以通过S函数自己打造一个模块,实现自定义的算法或期待的动作。也就是说S函数能拓展Simulink模块,为满足用户需求提供无限可能。
10.2 S函数的类型
S函数有多种类型:
- 按照语言分类,有M语言、C、C++、Fortran等编写;
- 按照支持功能分类,包括Level1和Level2;
- 按照执行方式分类,可分为直接解释运行的M S函数和编译为Mex文件后执行的C Mex 函数;
几种常用的S函数区别和使用场景如下:
| 分类 | 区别 |
|---|---|
| Level1 M S | Level1 M S函数输入输出端口最多为1且数据维数固定 |
| Level2 M S | Level2 M S函数输入输出端口可以为多个,数据维数可以动态改变 |
| C Mex S | C Mex S 同Level2,并且可以包含已有的C算法,并在Output子方法中调用既有C函数。 |
另外需要注意的是:
- 编写能用于仿真和代码生成的算法时,要用Level2 M S函数或C Mex S函数,并且需要给S函数编写同名的tlc文件;
- 使用C Mex S函数,运行速度比M语言编写的S函数要快,因为M语言的S函数需要调用MTLAB解释器;
- M语言编写的S函数,用pcode指令可以讲m文件转为p文件,p文件不可读,p文件和m文件同时存在的情况下,p文件优先被调用。C Mex S函数,将c文件通过mex
xxx.c编译后发布为mex32/64文件,也是不可读。发布为p文件或mex文件后,原m文件和c文件可以删除,可以保护知识产权。
10.3 S函数的要素
Simulink包含一组输入、一组状态和一组输出。其中,输出时采样时间、输入和块状态的函数。
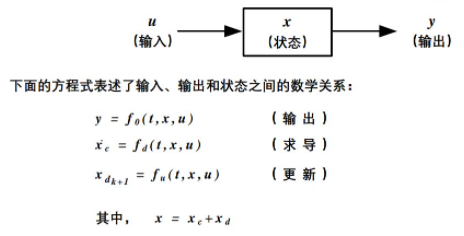
模块的构成要素有:
- 时间量t: 随着Simulink解算器运行而记录当前时间。
- 输入量u:通常为前一个模块的输出量,当作为信号源时,可以没有输入量。
- 状态量x: 根据系统性质分为连续系统中的微分量和离散系统中的差分量,通过前后不同时刻的输入值计算得到。
- 输出量y: 可以没有输出量。
10.4 S函数的组成及执行顺序
S函数执行顺序:
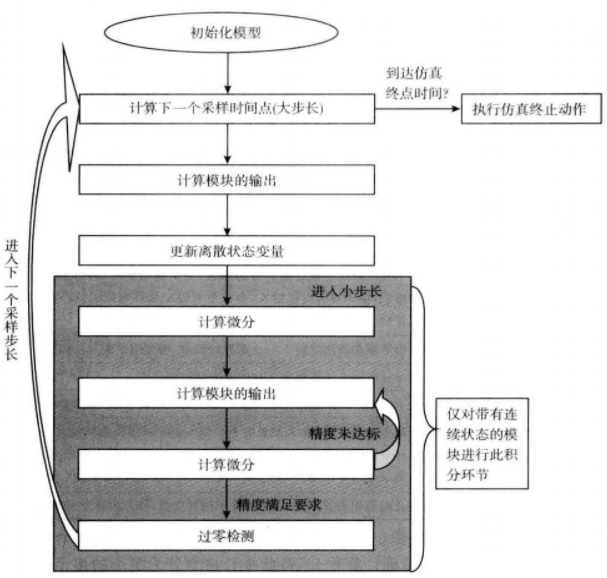
用程序的方法可表示为:
main
{
初始化模型;
计算下一个采样时间点(大步长);
while(未到达仿真终止时间)
{
计算模块的输出;
更新离散状态量;
if(此模型带有连续状态模块)
{
here:计算微分;
计算模块的输出;
if(精度未达标)
goto here;
过零检测;
计算下一个采样时间点(大步长);
}
}
执行仿真终止动作;
}
仿真运行时,模型首先要对模块进行初始化,这个过程包括模块的实例化:输入/输出端口、信号唯独、端口数据类型及采样时间等的确定,模块参数的获取及个数检查,并决定模块的执行顺序等。
- 实例化:Simulink标准库中提供的模块类似于C++等面向对象语言中的一个类,每当模块被拷贝或拖曳到模型中时,就相当于创建了这个类的一个对象,继承了这个类的属性并载入了默认的构造函数方法对其参数、端口等各个属性进行了初始化工作。
- 信号维度:一根信号线传递的数据不仅可以是标量,也可以是一个向量或矩阵,一个模块的输出端口将具有这个数据维度的信号传递给相连的信号线然后再传递给下一个模块的输入端口,这些都是需要在初始化阶段确定下来的。
- 端口数据类型:模块的输出/输出数据是浮点数还是固定点数,是8为、16位、32为或64位,有无符号,内建类型或者用户自定义类型,这些也在初始化阶段指定。
- 采样时间:对于Simulink模型来说,解算器中的一个步长决定了整个模型最小的采样时间间隔。
- 模型中模块的执行顺序:当众多模块同时存在于一个模型中时,Simulink是有明确的顺序优先度的。
- S函数方法表如下:
| 子方法 | 作用说明 |
|---|---|
| 初始化 | 在第一个采样时间的仿真之前运行的函数,用来初始化模块,包括设定输入/输出端口的个数和维数,输入是否直接馈入,参数个数设定采样时间,当使用工作向量时还需要为其分配存储空间 |
| 下一个采样时间点计算 | 根据模型解算器的算法求得下一个采样时间点,通常用于变步长模块 |
| 输出函数计算 | 在每一个major step计算模型所有的输出口的输出值 |
| 离散状态更新 | 在每一个major step都进行一次离散状态的更新计算,在输出函数之后 |
| 积分计算 | 如果模型具有连续状态,才采取此方法。将major step分隔为数个minor step,在每一个minor step里进行一次输出函数与积分计算。积分计算主要用来更新连续状态。当模型中存在非采样过零检测时,还会在minor step中进行过零检测 |
| 模型终止 | 当模型终止仿真时调用的子函数,用于清除不用的变量,释放内存空间等动作 |
| 注意: |
- minor step与major step的区别
minor step与major step是变步长解算器相关的知识点,后者表示两个采样点之间的步长;前者表示major
step内为了精确计算积分,将此步长划分为更小的多个步长。
- 过零检测
- 一般定义
过零检测指的是在交流系统中,当波形从正半周向负半周转换时,经过零位时,系统作出的检测。可作开关电路或者频率检测。
- MATLAB中的过零检测
当SIMULINK仿真一个动态系统的时候,其在每一个时间步使用过零检测技术来检测系统状态变量的间断点。如果检测到不连续的点(前后两个采样点的值变化大),则找到发生不连续的精确时间点,并且在该时间点前后增加附加的时间步(缩小采样步长)。
即:可变步长求解器可动态调整时间步大小,使其在某个变量缓慢变化时增加,在该变量迅速变化时减小。此行为使求解器在不连续点的附近执行许多小的时间步,因为该变量在此区域中迅速变化。这可以提高精确性,但可能会导致过多的仿真时间。
作用: Simulink使用过零检测技术来精确定位不连续点,以免仿真时步长过小导致仿真时间太长,一般情况下能够提高仿真速度,但有可能使得仿真到达规定时间长度之前就停止。当采用变步长解算方法仿真时,如果遇到步长自动变得很小导致仿真时间很长或基本没有进度,可以考虑勾选开启过零检测功能。
一句话概括: Simulink® 使用一种称为过零检测的技术来准确定位不连续性,无需借助于过小的时间步。通常这种方法可以缩短仿真运行时间,但它可能会导致某些仿真在预期完成时间之前停止。
- Simulink中过零检测的工作原理
一个模块能够通过Simulink注册一些列的过零变量,每一份变量就是一个状态变量(含有不连续点)的函数。当相应的不连续发生之后,过零函数从正值或负值传递零值。每一个仿真步结束时,Simulink通过调用每一个注册了过零变量的模块来更新变量。然后Simulink检测是否有变量的符号发生改变(相对于上一仿真时间点的结果),如果有改变就说明当前时间步有不连续发生。如果检测到零点,
Simulink
就会在每一个发生符号改变的变量的前一时刻值和当前值之间插入新值以评估过零点的个数,然后逐步增加内插点数目并使其值依次越过每一个过零点。
可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43229030/article/details/110499075
10.5 使用不同的语言编写S函数
不同S函数的特点:
| S函数 | 特点 |
|---|---|
| Level1 M | 支持简单的MATLAB接口及少数的API |
| Level2 M | 支持扩展的S函数API及代码生成功能,使用场合更加广泛 |
| C MEX | 提供更灵活的编程方式,即可手写C代码也可以调用既存的C/C++或Fortran代码。要求掌握很多C MEX S函数API用法及TLC代码编写方法,才能够制定具有代码生成功能的C MEX S函数 |
10.5.1 Level1 M S函数
Level1 M S函数介绍:
[sys,x0,str,ts]=f(t,x,u,flag,p1,p2,…)
其中f是S函数的函数名,Simulink会在仿真过程中的每个步长内多次调用f。
flag的值随着仿真过程自动变化,其值对应的S函数子方法如下:
| flag值 | Level1 M S函数子方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | mdlInitializeSizes | 定义S函数的基本属性,如输入/输出维数、连续/离散状态变量个数、采样时间、以及输入是否为直接馈入等 |
| 1 | mdlDerivatives | 连续状态变量的微分函数,这里通常通过给定的微分计算表达式,通过积分计算得到状态变量的值 |
| 2 | mdlUpdate | 更新离散状态变量 |
| 3 | mdlOutputs | 计算S函数的输出 |
| 4 | mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit | 仅在变离散采样时间情况下使用,用于计算下一个采样时时刻的绝对时间,若模块不是变步长此函数不会执行 |
| 9 | mdlTerminate | 在仿真结束时执行一些必要的动作,如清除临时变量,或显示提示信息等 |
| 直接馈入: |
如果S函数的输出y或采样时间t与输入u有直接联系,就是直接馈入;否则不存在直接馈入情况。如果若干直接馈入的模块通过反馈构成了一个环形,就会出现所谓的代数环。
注:
模块是否直接馈入的简单判断方法是查看mdlOutputs和mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit两个子方法中有没有用到输入u。如果用到了,这个输入端口的直接馈入direct feedthrough就必须设为1。
Level1 M S输入参数表:
| Level1 M S函数输入参数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| t | 当前时刻仿真时间 |
| x | 状态变量向量 |
| u | 输入向量 |
| pn,n=1,2,3… | 用户自定义参数,数目不定 |
| Level1 M S输出参数表: | |
| Level1 M S函数输出参数 | 功能 |
| – | – |
| sys | 通用输出参数,根据flag的值来决定返回值,比如flag=3时返回S函数的输出信号;flag=2时则返回更新后的离散状态变量的值;flag=1时根据设置的微分值积分计算出连续状态变量的值 |
| x0 | 状态变量的初始值,仅在flag=0时有效,其余情况被忽略 |
| str | 保留变量,将来版本可能使用,用户只能将其初始化为[ ] |
| ts | S函数的采样时间,由一个二维的数组表示 |
| Level1 M S采样时间表: | |
| 采样时间表示 | 意义 |
| – | – |
| [0 0 ] | 连续采样时间 |
| [-1 0] | 继承S函数输入信号或父层模型的采样时间 |
| [0.5 0.1] | 离散采样时间,从0.1s开始每0.5s采样一次 |
| [0.25 0; 1 0.1] | 采样时刻为[0 0.1 0.25 0.5 0.75 1.0 1…] |
| 示例1(连续状态): | |
 | |
| 该方程可以表示为: |
x’ = Ax +Bu;
y = Cx;
由方程可知:
A=[-0.5572,-0.7814;0.7814,0];
B=[1,-1;0,2];
C=[1.9691,6.4493];
显然,输入有两个,u1和u2,由于Level1只有一个输入,因此输入要设为2维。状态量也有两个,x1和x2,输出有一个y,而且输出和输入u没有关系,因此直接馈入为0。
function [sys,x0,str,ts,simStateCompliance] = sfun_state01(t,x,u,flag,A,B,C)
switch flag,
case 0,
[sys,x0,str,ts,simStateCompliance]=mdlInitializeSizes;
case 1,
sys=mdlDerivatives(t,x,u,A,B);
case 2,
sys=mdlUpdate(t,x,u);
case 3,
sys=mdlOutputs(t,x,u,C);
case 4,
sys=mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit(t,x,u);
case 9,
sys=mdlTerminate(t,x,u);
otherwise
DAStudio.error('Simulink:blocks:unhandledFlag', num2str(flag));
end
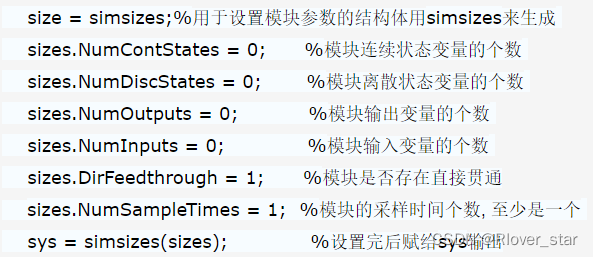
function [sys,x0,str,ts,simStateCompliance]=mdlInitializeSizes
sizes = simsizes;
sizes.NumContStates
= 2;
sizes.NumDiscStates
= 0;
sizes.NumOutputs
= 1;
sizes.NumInputs
= 2;
sizes.DirFeedthrough = 0;
sizes.NumSampleTimes = 1;
sys = simsizes(sizes);
x0
= [0,0]';
str = [];
ts
= [0 0];
simStateCompliance = 'UnknownSimState';
function sys=mdlDerivatives(t,x,u,A,B)
sys = A*x + B*u;
function sys=mdlUpdate(t,x,u)
% update state variable
sys = [];
function sys=mdlOutputs(t,x,u,C)
% update output
sys = C * x;
function sys=mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit(t,x,u)
sampleTime = 1;
sys = t + sampleTime;
function sys=mdlTerminate(t,x,u)
sys = [];
有几个地方需要注意:
- 输入维数为2时,输入初始化矩阵需要转置为[2x1]矩阵
- 由于需要引用外部变量A、B、C,所以在函数调用时不能漏掉
- 连续状态方程用到了A,B,所以在mdlDerivatives中要使用A和B。
- 同理Output中需要用到C
结果如下:
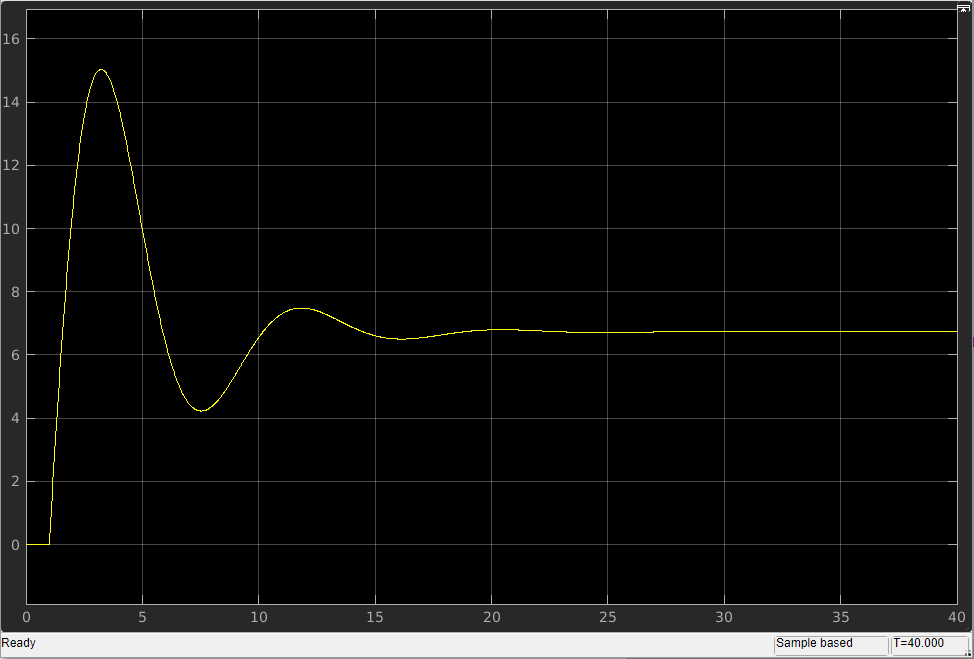
示例2(离散状态):
- mdlUpdate和mdlDerivatives分别用在离散和连续系统中,可以参考上述介绍。mdlUpdate更新的是下一时刻的状态x(k+1);
连续状态方程为:
x’ = Ax +Bu;
y = Cx;
对应的离散状态方程为:
( x(k+1)-x(k) )/Ts = A * x(k) +B * u;
y = C * x(k);
因此可以得到:
x(k+1)= (A * x(k) +B * u) * Ts + x(k);
y = C * x(k);
此处Ts为采样时间
对应的程序为:
function [sys,x0,str,ts,simStateCompliance] = sfun_state02(t,x,u,flag,A,B,C,Ts)
switch flag,
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Initialization %定义S函数的基本属性,如输入/输出维数、连续/离散状态变量个数、采样时间、以及输入是否为直接馈入等
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
case 0,
[sys,x0,str,ts,simStateCompliance]=mdlInitializeSizes;
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Derivatives % 连续状态变量的微分函数,这里通常通过给定的微分计算表达式,通过积分计算得到状态变量的值
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
case 1,
sys=mdlDerivatives(t,x,u);
%%%%%%%%%%
% Update %更新离散状态变量
%%%%%%%%%%
case 2,
sys=mdlUpdate(t,x,u,A,B,Ts);
%%%%%%%%%%%
% Outputs %计算S函数的输出
%%%%%%%%%%%
case 3,
sys=mdlOutputs(t,x,u,C);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% GetTimeOfNextVarHit %仅在变离散采样时间情况下使用,用于计算下一个采样时时刻的绝对时间,若模块不是变步长此函数不会执行
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
case 4,
sys=mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit(t,x,u);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Terminate %在仿真结束时执行一些必要的动作,如清除临时变量,或显示提示信息等
%%%%%%%%%%%%%
case 9,
sys=mdlTerminate(t,x,u);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Unexpected flags %
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
otherwise
DAStudio.error('Simulink:blocks:unhandledFlag', num2str(flag));
end
% end sfuntmpl
%
%=============================================================================
% mdlInitializeSizes
% Return the sizes, initial conditions, and sample times for the S-function.
%=============================================================================
%
function [sys,x0,str,ts,simStateCompliance]=mdlInitializeSizes
sizes = simsizes;
sizes.NumContStates
= 0;
sizes.NumDiscStates
= 2;
sizes.NumOutputs
= 1;
sizes.NumInputs
= 2;
sizes.DirFeedthrough = 0;
sizes.NumSampleTimes = 1;
% at least one sample time is needed
sys = simsizes(sizes);
%
% initialize the initial conditions/状态变量的初始值,仅在flag=0时有效,其余情况被忽略
%
x0
= [0 0]';
%
% str is always an empty matrix/保留变量,将来版本可能使用,用户只能将其初始化为[ ]
%
str = [];
%
% initialize the array of sample times/S函数的采样时间,由一个二维的数组表示
%
ts
= [0 0];
% Specify the block simStateCompliance. The allowed values are:
%
'UnknownSimState', < The default setting; warn and assume DefaultSimState
%
'DefaultSimState', < Same sim state as a built-in block
%
'HasNoSimState',
< No sim state
%
'DisallowSimState' < Error out when saving or restoring the model sim state
simStateCompliance = 'UnknownSimState';
% end mdlInitializeSizes
%
%=============================================================================
% mdlDerivatives
% Return the derivatives for the continuous states.
%=============================================================================
%
function sys=mdlDerivatives(t,x,u)
sys = [];
% end mdlDerivatives
%
%=============================================================================
% mdlUpdate
% Handle discrete state updates, sample time hits, and major time step
% requirements.
%=============================================================================
%
function sys=mdlUpdate(t,x,u,A,B,Ts)
sys = x + (A * x + B * u) *Ts;
% end mdlUpdate
%
%=============================================================================
% mdlOutputs
% Return the block outputs.
%=============================================================================
%
function sys=mdlOutputs(t,x,u,C)
sys = C * x;
% end mdlOutputs
%
%=============================================================================
% mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit
% Return the time of the next hit for this block.
Note that the result is
% absolute time.
Note that this function is only used when you specify a
% variable discrete-time sample time [-2 0] in the sample time array in
% mdlInitializeSizes.
%=============================================================================
%
function sys=mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit(t,x,u)
sampleTime = 1;
%
Example, set the next hit to be one second later.
sys = t + sampleTime;
% end mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit
%
%=============================================================================
% mdlTerminate
% Perform any end of simulation tasks.
%=============================================================================
%
function sys=mdlTerminate(t,x,u)
sys = [];
% end mdlTerminate
离散和连续状态的结果对比如下:
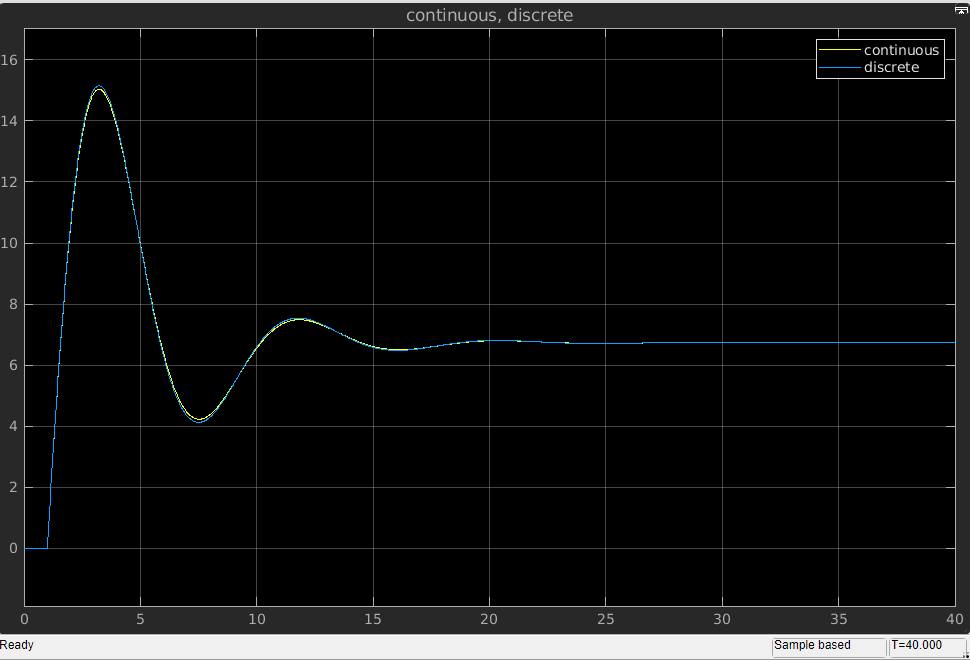
注意:孙忠潇-Simulink仿真入门到精通此处有误
示例3(离散积分):
积分连续状态方程为:
x’ = u;
y = x;
对应的离散状态方程为:
x(k+1) = u*Ts + x(k);
y = x(k);
对应的程序为:
function [sys,x0,str,ts,simStateCompliance] = DisInteg02(t,x,u,flag,Ts)
switch flag,
case 0,
[sys,x0,str,ts,simStateCompliance]=mdlInitializeSizes;
case 1,
sys=mdlDerivatives(t,x,u);
case 2,
sys=mdlUpdate(t,x,u,Ts);
case 3,
sys=mdlOutputs(t,x,u);
case 4,
sys=mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit(t,x,u);
case 9,
sys=mdlTerminate(t,x,u);
otherwise
DAStudio.error('Simulink:blocks:unhandledFlag', num2str(flag));
end
function [sys,x0,str,ts,simStateCompliance]=mdlInitializeSizes
sizes = simsizes;
sizes.NumContStates
= 0;
sizes.NumDiscStates
= 1;
sizes.NumOutputs
= 1;
sizes.NumInputs
= 1;
sizes.DirFeedthrough = 1;
sizes.NumSampleTimes = 1;
sys = simsizes(sizes);
x0
= [0];
str = [];
ts
= [0 0];
simStateCompliance = 'UnknownSimState';
function sys=mdlDerivatives(t,x,u)
sys = [];
function sys=mdlUpdate(t,x,u,Ts)
% update state variable
% x(k+1) - x(k) = u*Ts
% x(k+1) = x(k) + u*Ts
sys = x+u*Ts;
function sys=mdlOutputs(t,x,u)
% update output
sys = x;
function sys=mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit(t,x,u)
sampleTime = 1;
sys = t + sampleTime;
function sys=mdlTerminate(t,x,u)
sys = [];
和Simulink自带模块结果对比如下:
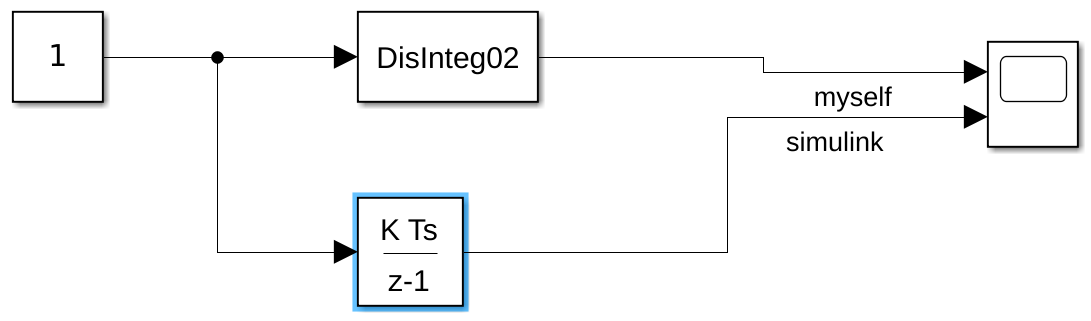
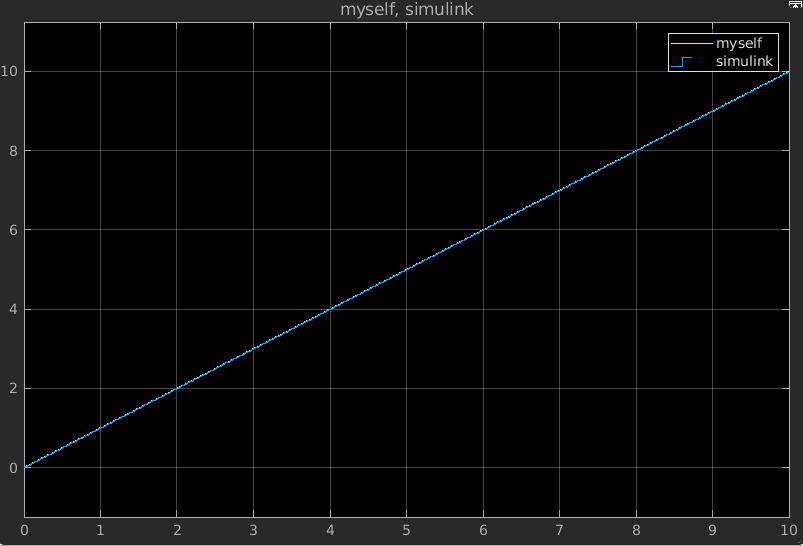
示例4(离散微分):
求导连续状态方程为:
x’ = (u - x)/Ts; //Δx/Δt
y = x;
对应的离散方程为:
(x(k+1) - x(k))/Ts = (u - x(k))/Ts;
y = x;
从而有:
x(k+1) = u ;
y = x;
因此可以得到程序为:
function [sys,x0,str,ts,simStateCompliance] = Derivative(t,x,u,flag)
switch flag,
case 0,
[sys,x0,str,ts,simStateCompliance]=mdlInitializeSizes;
case 1,
sys=mdlDerivatives(t,x,u);
case 2,
sys=mdlUpdate(t,x,u);
case 3,
sys=mdlOutputs(t,x,u);
case 4,
sys=mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit(t,x,u);
case 9,
sys=mdlTerminate(t,x,u);
otherwise
DAStudio.error('Simulink:blocks:unhandledFlag', num2str(flag));
end
function [sys,x0,str,ts,simStateCompliance]=mdlInitializeSizes
sizes = simsizes;
sizes.NumContStates
= 0;
sizes.NumDiscStates
= 1;
sizes.NumOutputs
= 1;
sizes.NumInputs
= 1;
sizes.DirFeedthrough = 1;
sizes.NumSampleTimes = 1;
sys = simsizes(sizes);
x0
= [0];
str = [];
ts
= [0 0];
simStateCompliance = 'UnknownSimState';
function sys=mdlDerivatives(t,x,u)
sys = [];
function sys=mdlUpdate(t,x,u)
% update state variable
% (x(k+1) - x(k))/Ts = (u - x(k))/Ts;
% x(k+1) = u ;
sys = u;
function sys=mdlOutputs(t,x,u)
% update output
sys = x;
function sys=mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit(t,x,u)
sampleTime = 1;
sys = t + sampleTime;
function sys=mdlTerminate(t,x,u)
sys = [];
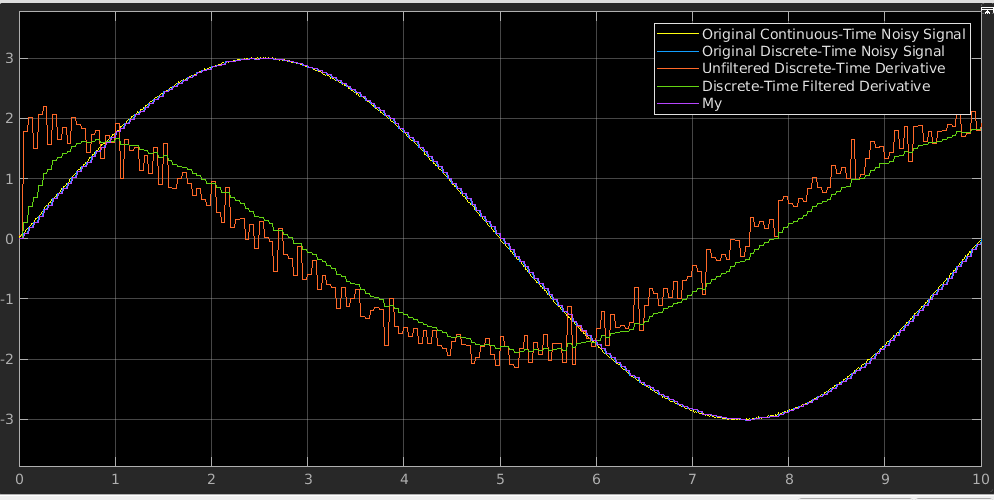
结果如下:
模型参考:openExample(‘simulink/FloatingPointDiscreteDerivativeBlockExample’)
10.5.2 Level2 M S函数
Level2 M S函数介绍:
Level2 M S函数使得用户能够使用MATLAB语言来编写支持多个输入/输出端口的自定义模块,并且每个端口都能够支持包括矩阵在内的Simulink支持的所有数据类型。
1. Setup子方法
Setup子方法是Level2 M S函数体中唯一调用的语句,对模块的属性和其他子方法进行初始化,Setup子方法类似Level1 M S函数中mdlInitializeSizes子方法的功能,并且相比之下功能更加强大,在Setup中不仅可以设置多输入多输出,而且每个输出的端口信号的维数可以是标量数或矩阵甚至是可变维数,另外S函数的其他子方法也是通过Setup子方法进行注册的,因此Setup可以成为Level2 M S函数的根本。
Setup子方法实现以下功能:
- 设定模块输入输出端口的个数;
- 设定每一个端口的数据类型、数据维度、实数复数性和采样时间等;
- 规定模块的采样时间;
- 设定S函数参数的个数;
- 注册S函数的子方法(将子方法函数的句柄传递到实时对象的RegBlockMethod函数的对应属性中)。
Setup子方法的参数是block,其属性成员如下:
| 实时对象属性成员 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| NumDialogPrms | 模块GUI参数个数 |
| NumInputPorts | 输入端口数 |
| NumOutputPorts | 输出端口数 |
| BlockHandle | 模块句柄,只读 |
| CurrentTime | 当前仿真时间,只读 |
| NumContStates | 连续状态变量数目 |
| NumDworkDiscStates | 离散状态变量数目 |
| NumRuntimePrms | 运行时参数个数 |
| SampleTimes | 产生输出的模块的采样时间 |
| NumDworks | 离散工作向量个数 |
| 通过block结构体方式来操作属性: |
block.NumDialogPrms = 0;
模块的输入输出也有自己的属性:
| 属性端口名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 端口数据维度 |
| DatatypeID/Datatype | 端口数据类型,可以通过ID号指定也可以直接指定数据类型名 |
| Complexity | 端口数据是否为复数 |
| DirectFeedthrough | 端口数据是否直接馈入 |
| DimensionsMode | 端口维数是固定或可变的(fixed/variable) |
| 当存在多个端口时,需要对每一个进行设定,设定方式如下: |
block.InputPort(1).Dimensions = 1;
Setup子方法中,可以通过block实时对象域操作符访问模块属性:
| 实时对象方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ContStates | 获取模块的连续状态 |
| DataTypeIsFixedPoint | 判断数据类型是否为固定点数 |
| DatatypeName | 获取数据类型的名称 |
| DatatypeSize | 获取数据类型大小 |
| Derivatives | 获取连续状态的微分 |
| DialogPrm | 获取GUI中的参数 |
| Dwork | 获取Dwork向量 |
| FixedPointNumericType | 获取固定点数据类型的操作 |
| InputPort | 获取输入端口 |
| OutputPort | 获取输出端口 |
| RuntimePrm | 获取运行时参数 |
| Setup子方法中,还可以通过子方法获取模块对象的信息: | |
| 子方法名 | 说明 |
| – | – |
| PostPropagationSetup | 设置工作向量及状态变量的函数(可选) |
| InitializeConditions | 在仿真开始时被调用的初始化函数(可选) |
| Start | 在模型运行仿真时调用一次,用来初始化状态变量和工作向量(可选) |
| Outputs | 在每个步长里计算模型输出 |
| Update | 在每个步长里更新离散状态变量的值(可选) |
| Derivatives | 在每个步长里更新连续状态变量的微分值(可选) |
| Terminate | 在仿真结束时调用,用来清除变量内存 |
2. PostPropagationSetup子方法
- PostPropagationSetup子方法是用来初始化Dwork工作向量的方法,规定Dwork向量的个数及每个向量的维数、数据类型、离散状态变量的名字和虚拟性,以及是否作为离散变量使用。
- Dwork向量是Simulink分配给模型中每个S函数实例的存储空间块。当不同S函数块之间需要通过全局变量或者静态变量进行数据交互时,必须在S函数中使用Dwork向量来进行变量存储。
Dwork属性列表:
| 名称 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Name | 名字 |
| Dimensions | 数据维数 |
| DatetypeID | 数据类型 |
| Complexity | 是否复数 |
| UsedAsDiscState | 是否作为离散变量使用 |
| 使用方法: |
function DoPostProSetup(block)
%% setup Dwork
block.NumDworks
= 1;
block.Dwork(1).Name
= 'x0';
block.Dwork(1).Dimensions = 1;
block.Dwork(1).DatetypeID = 1;
block.Dwork(1).Complexity = 'Real';
block.Dwork(1).UsedAsDiscState = true;
Dwork向量的数据类型,通常使用DatetypeID 表示,具体如下:
| 数据类型 | ID |
|---|---|
| ingerited | -1 |
| double | 0 |
| single | 1 |
| int8 | 2 |
| uint8 | 3 |
| int16 | 4 |
| uint16 | 5 |
| int32 | 6 |
| uint32 | 7 |
| boolean或定点类型 | 8 |
3. InitializeConditions/Start子方法
- InitializeConditions子方法可以用来初始化状态变量或者Dwork工作向量的值。
- Start子方法跟InitializeConditions子方法功能一致,但仅仅在仿真开始的时候初始化一次,而S函数模块放置在是能子系统中时其InitializeConditions子方法在每次子系统被使能时都会被调用。
4. InitializeConditions/Start子方法
Output子方法跟Level1 M S函数的mdlOutputs子方法作用一样,用于计算S函数的输出。
5. Updata子方法
Updata子方法跟Level1 M S函数中mdlUpdata子方法作用相同,用于计算离散状态变量的值。
6. Derivatives子方法
Derivatives子方法跟Level1 M S函数中的mdlDerivatives子方法作用相同,用于计算并更新连续状态变量的值。
7. Terminate子方法
S函数的收尾工作放在Terminate子方法中进行,如存储空间的释放,变量的删除等。
示例1(两张图片融合):
% Level2 m Sfunction
%% 图片处理
%%
% m1 = imread('阿布罗狄.jpg');
% m1 = m1(:,:,1);
% m2 = imread('艾欧里亚.jpg');
% m2 = m2(:,:,1);
%%
%%
function Sfcn_L2(block)
% Level-2 MATLAB file S-Function for unit delay demo.
%
Copyright 1990-2009 The MathWorks, Inc.
setup(block);
%endfunction
function setup(block)
block.NumDialogPrms
= 0;
%% Register number of input and output ports
block.NumInputPorts
= 2;
block.NumOutputPorts = 0;
%% Setup functional port properties to dynamically
%% inherited.
block.SetPreCompInpPortInfoToDynamic;
block.InputPort(1).Dimensions
= [375 500];
block.InputPort(1).DatatypeID
= 3;
%uint8
block.InputPort(1).Complexity
= 'real';
block.InputPort(1).DirectFeedthrough = false;
block.InputPort(2).Dimensions
= [375 500];
block.InputPort(2).DatatypeID
= 3;
%uint8
block.InputPort(2).Complexity
= 'real';
block.InputPort(2).DirectFeedthrough = false;
%% Set block sample time
block.SampleTimes = [0 0];
%% Set the block simStateCompliance to default (i.e., same as a built-in block)
block.SimStateCompliance = 'DefaultSimState';
%% Register methods
block.RegBlockMethod('Outputs',
@Output);
%endfunction
function Output(block)
imshow((block.InputPort(1).data + block.InputPort(2).data)/2);
%endfunction
注意:
书上是在terminate处绘图,这里是在output处,结果一样。
结果:

10.5.3 C Mex S函数
C Mex S函数的特点:
- 运行速度和效率高。使用C语言编写S函数成为C Mex S函数,相比于解释运行的M S函数,在仿真过程中不需要反复调用MATALB解释器,而是在运行前将.c文件编译成mexw32/mexw64类型的可执行文件,运行速度和效率上有明显优势;
- 灵活。采用C语言拥有编程语言上的灵活性优势;
- C Mex S-function能够支持硬件外设驱动的自定义功能,可以构建自己的算法库和驱动块库。
- 资源重用。可以直接使用已有C代码。
C Mex S函数访问模块采用C Mex宏函数实现,M S函数采用结构体方式进行访问,两种函数子方法对比:
| C Mex S函数子方法 | Level2 M S函数子方法 | 子方法功能 |
|---|---|---|
| mdlInitializeSizes | Setup | 模块属性初始化 |
| mdlDerivatices | Derivatives | 更新连续状态变量的微分值 |
| mdlInitializeConditions | InitializeConditions | 初始化工作向量的状态值 |
| mdlOutputs | Outputs | 计算模块的输出 |
| mdlSetWorkWidths | PostPropagationSetup | 当S函数模块存在于使能子系统中时,每次子系统被使能均进行工作向量属性的初始化工作 |
| mdlStart | Start | 在仿真开始时初始化工作向量及状态变量的属性 |
| mdlTerminate | Terminate | 在仿真终止时所调用的子方法 |
| mdlUpdate | Update | 更新离散状态变量的子方法 |
| mdlRTW | WriteRTW | 将S函数中获取到的GUI参数变量值写入到rtw文件中以使TLC文件用来生成代码的子方法 |
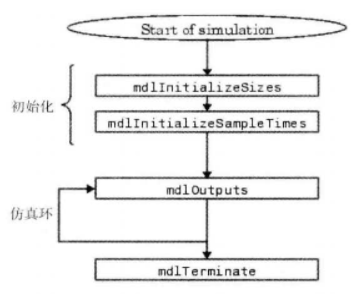
| C Mex S函数按照下面方式执行: | ||
 |
1. C Mex S函数的构成
- 最开头必须定义的两个宏:C Mex S函数名及C Mex S函数的等级。
- 头文件包含部分C Mex S函数核心数据结构simstruct类型的声明及其他库文件,另外用户根据使用需要也可以包含其他头文件。
- 参数对话框访问宏函数的定义。
- 紧接着定义C Mex S函数的各个子方法。
- S函数必须根据使用情况包含必要的源文件和头文件,从而将该S函数文件与Simulink或Simulink Coder产品进行连接。
1) mdlInitializeSizes
mdlInitializeSizes中用到一些C Mex S函数的宏函数,常用的宏函数的首个参数均为simstruct类型对象S,代表当前S函数模块,常用的API如下:
| SimStruct宏函数名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| ssSetNumSFcnParams | 设定模块参数个数,第二个参数表示个数 |
| ssGetNumSFcnParams | 获取S函数期待的参数个数 |
| ssGetSFcnParamsCount | 获取S函数实际拥有的参数个数 |
| ssSetNumInputPorts | 设置输入端口的个数 |
| ssSetInputPortWidth | 设定某个输入端口的维数,通过第二个参数指定端口号,端口号从0开始;第三个参数表示维数,DYNAMICALLY_SIZED表示维数是动态的 |
| ssSetInputPortDirectFeedThrough | 设置某个输入端口是否是直接馈入,通过第二个参数指定端口号,端口号从0开始;第三个参数1表示存在直接馈入,0则相反 |
| ssSetNumOutputPorts | 设置输入端口的个数,参数同 ssSetNumInputPorts |
| ssSetOutputPortWidth | 设定某个输入端口的维数,参数同 ssSetInputPortWidth |
| ssSetNumContStates | 设置连续状态变量个数,第二个参数表示连续状态变量个数 |
| ssSetNumDiscStates | 设置离散状态变量个数,第二个参数表示离散状态变量个数 |
| ssSetNumSampleTimes | 设置采样时间的个数,第二个参数表示采样时间的个数 |
| ssSetOptions | 设置S函数的选项,一般情况下使用SS_OPTION_EXCEPTION_FREE_CODE选项,可加速S函数执行 |
| ssSetInputPortDataType | 设置输入端口数据类型,第二个参数为端口号,第三个参数为数据类型 |
| ssSetOutputPortDataType | 设置输出端口数据类型,参数同 ssSetInputPortDataType |
C Mex S函数中的数据类型列表如下
| Simulink内建类型 | ID | SimStruct数据类型宏 |
|---|---|---|
| double | 0 | SS_DOUBLE |
| single | 1 | SS_SINGLE |
| int8 | 2 | SS_INT8 |
| uint8 | 3 | SS_UINT8 |
| int16 | 4 | SS_INT16 |
| uint16 | 5 | SS_UINT16 |
| int32 | 6 | SS_INT32 |
| uint32 | 7 | SS_UINT32 |
| boolean | 8 | SS_BOOLEAN |
2) mdlOutputs
mdlOutputs子方法尝试用的C Mex S函数API如下:
| 宏函数名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| ssSetInputPortRequiredContiguous | 设定输入端口的数据是否占据连续的存储空间,第二个参数代表输入端口序列号,从0开始;第三个参数为0或1,代表存储空间连续或不连续 |
| ssGetInputPortRealSignalPtrs | 获取输入端口各元素的指针,第二个参数表示输入端口的序号,从0开始,返回值为指向此端口各维数据的指针数组 |
| ssGetInputPortSignalPtrs | 用于获取非连续存储的输入端口数据,第二个参数表示输入端口的序号,从0开始,返回值为指向端口信号的指针数组的指针 |
| ssGetInputPortSignal | 获取存储空间连续的输入端口的地址,第二个参数表示输入端口的序号,从0开始,返回值为一个指向指定输入端口的指针 |
| ssGetOutputPortWidth | 获取输出端口的维度,第二个参数表示输入端口的序号,从0开始 |
| ssGetOutputPortRealSignal | 返回参数为一个,是指向模块输出端口的指针向量,适用于存储空间连续的输出,对其解引用之后获得端口第一维输出数据,此指针++之后获取其相邻存储单元的指针,即指向端口下一维的指针。输入参数有2个,第二个参数表示输入端口的序号,从0开始 |
| ssGetOutputPortSignal | 返回一个指向输出信号的指针 |
2. C Mex S函数的编译
编译型语言编写的程序执行之前,需要一个专门的编译过程,把程序编译成为机器语言的文件,如exe文件或mexw32/menw64文件,运行时不需要重新翻译。

3. C Mex S函数的应用
1)示例1
y = Sum(u):
/*
* sfuntmpl_basic.c: Basic 'C' template for a level 2 S-function.
*
* Copyright 1990-2018 The MathWorks, Inc.
*/
/*
* You must specify the S_FUNCTION_NAME as the name of your S-function
* (i.e. replace sfuntmpl_basic with the name of your S-function).
*/
#define S_FUNCTION_NAME
sfun_c_add
#define S_FUNCTION_LEVEL 2
/*
* Need to include simstruc.h for the definition of the SimStruct and
* its associated macro definitions.
*/
#include "simstruc.h"
/* Error handling
* --------------
*
* You should use the following technique to report errors encountered within
* an S-function:
*
*
ssSetErrorStatus(S,"Error encountered due to ...");
*
return;
*
* Note that the 2nd argument to ssSetErrorStatus must be persistent memory.
* It cannot be a local variable. For example the following will cause
* unpredictable errors:
*
*
mdlOutputs()
*
{
*
char msg[256];
{ILLEGAL: to fix use "static char msg[256];"}
*
sprintf(msg,"Error due to %s", string);
*
ssSetErrorStatus(S,msg);
*
return;
*
}
*
*/
/*====================*
* S-function methods *
*====================*/
/* Function: mdlInitializeSizes ===============================================
* Abstract:
*
The sizes information is used by Simulink to determine the S-function
*
block's characteristics (number of inputs, outputs, states, etc.).
*/
static void mdlInitializeSizes(SimStruct *S)
{
ssSetNumSFcnParams(S, 0);
/* Number of expected parameters */
if (ssGetNumSFcnParams(S) != ssGetSFcnParamsCount(S)) {
/* Return if number of expected != number of actual parameters */
return;
}
if (!ssSetNumInputPorts(S, 1)) return; //只有一个输入
ssSetInputPortWidth(S, 0, DYNAMICALLY_SIZED);//输入是动态的
/*
* Set direct feedthrough flag (1=yes, 0=no).
* A port has direct feedthrough if the input is used in either
* the mdlOutputs or mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit functions.
*/
ssSetInputPortDirectFeedThrough(S, 0, 1); //输入是直接馈入的
if (!ssSetNumOutputPorts(S, 1)) return; //只有一个输出
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 0, 1);
//输出只有一维
ssSetNumSampleTimes(S, 1);
//采样时间只有一个
/* Specify the operating point save/restore compliance to be same as a
* built-in block */
ssSetOperatingPointCompliance(S, USE_DEFAULT_OPERATING_POINT);
ssSetOptions(S,
SS_OPTION_WORKS_WITH_CODE_REUSE |
SS_OPTION_EXCEPTION_FREE_CODE |
SS_OPTION_USE_TLC_WITH_ACCELERATOR);
}
/* Function: mdlInitializeSampleTimes =========================================
* Abstract:
*
This function is used to specify the sample time(s) for your
*
S-function. You must register the same number of sample times as
*
specified in ssSetNumSampleTimes.
*/
static void mdlInitializeSampleTimes(SimStruct *S)
{
ssSetSampleTime(S, 0, INHERITED_SAMPLE_TIME);
ssSetOffsetTime(S, 0, 0.0);
ssSetModelReferenceSampleTimeDefaultInheritance(S);
}
#define MDL_INITIALIZE_CONDITIONS
/* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_INITIALIZE_CONDITIONS)
/* Function: mdlInitializeConditions ========================================
* Abstract:
*
In this function, you should initialize the continuous and discrete
*
states for your S-function block.
The initial states are placed
*
in the state vector, ssGetContStates(S) or ssGetRealDiscStates(S).
*
You can also perform any other initialization activities that your
*
S-function may require. Note, this routine will be called at the
*
start of simulation and if it is present in an enabled subsystem
*
configured to reset states, it will be call when the enabled subsystem
*
restarts execution to reset the states.
*/
static void mdlInitializeConditions(SimStruct *S)
{
}
#endif /* MDL_INITIALIZE_CONDITIONS */
#define MDL_START
/* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_START)
/* Function: mdlStart =======================================================
* Abstract:
*
This function is called once at start of model execution. If you
*
have states that should be initialized once, this is the place
*
to do it.
*/
static void mdlStart(SimStruct *S)
{
}
#endif /*
MDL_START */
/* Function: mdlOutputs =======================================================
* Abstract:
*
In this function, you compute the outputs of your S-function
*
block.
*/
static void mdlOutputs(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)
{
//获取输入尽量都这样写,其他方式有时候结果会错
InputRealPtrsType u1 = ssGetInputPortRealSignalPtrs(S,0);
int_T
width = ssGetInputPortWidth(S,0); //获取输入维数
real_T
*y1 = ssGetOutputPortSignal(S,0);
real_T Sum=0;
int_T
i;
for(i=0;i<width;i++)
{
Sum = Sum+(*u1[i]);
}
y1[0] = Sum;
//
int_T
width = ssGetInputPortWidth(S,0);
//
y1[0] = (*u1[0])*width;
}
#define MDL_UPDATE
/* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_UPDATE)
/* Function: mdlUpdate ======================================================
* Abstract:
*
This function is called once for every major integration time step.
*
Discrete states are typically updated here, but this function is useful
*
for performing any tasks that should only take place once per
*
integration step.
*/
static void mdlUpdate(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)
{
}
#endif /* MDL_UPDATE */
#define MDL_DERIVATIVES
/* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_DERIVATIVES)
/* Function: mdlDerivatives =================================================
* Abstract:
*
In this function, you compute the S-function block's derivatives.
*
The derivatives are placed in the derivative vector, ssGetdX(S).
*/
static void mdlDerivatives(SimStruct *S)
{
}
#endif /* MDL_DERIVATIVES */
/* Function: mdlTerminate =====================================================
* Abstract:
*
In this function, you should perform any actions that are necessary
*
at the termination of a simulation.
For example, if memory was
*
allocated in mdlStart, this is the place to free it.
*/
static void mdlTerminate(SimStruct *S)
{
}
/*=============================*
* Required S-function trailer *
*=============================*/
#ifdef
MATLAB_MEX_FILE
/* Is this file being compiled as a MEX-file? */
#include "simulink.c"
/* MEX-file interface mechanism */
#else
#include "cg_sfun.h"
/* Code generation registration function */
#endif
2)示例2
使用C Mex S函数编写一个简单的滤波器:
y1 = u1[0] + u1[1]
y2 = u1[0] - u1[1]
/*
* sfuntmpl_basic.c: Basic 'C' template for a level 2 S-function.
*
* Copyright 1990-2018 The MathWorks, Inc.
*/
/*
* You must specify the S_FUNCTION_NAME as the name of your S-function
* (i.e. replace sfuntmpl_basic with the name of your S-function).
*/
#define S_FUNCTION_NAME
sfun_c_add
#define S_FUNCTION_LEVEL 2
/*
* Need to include simstruc.h for the definition of the SimStruct and
* its associated macro definitions.
*/
#include "simstruc.h"
/* Error handling
* --------------
*
* You should use the following technique to report errors encountered within
* an S-function:
*
*
ssSetErrorStatus(S,"Error encountered due to ...");
*
return;
*
* Note that the 2nd argument to ssSetErrorStatus must be persistent memory.
* It cannot be a local variable. For example the following will cause
* unpredictable errors:
*
*
mdlOutputs()
*
{
*
char msg[256];
{ILLEGAL: to fix use "static char msg[256];"}
*
sprintf(msg,"Error due to %s", string);
*
ssSetErrorStatus(S,msg);
*
return;
*
}
*
*/
/*====================*
* S-function methods *
*====================*/
/* Function: mdlInitializeSizes ===============================================
* Abstract:
*
The sizes information is used by Simulink to determine the S-function
*
block's characteristics (number of inputs, outputs, states, etc.).
*/
static void mdlInitializeSizes(SimStruct *S)
{
ssSetNumSFcnParams(S, 0);
/* Number of expected parameters */
if (ssGetNumSFcnParams(S) != ssGetSFcnParamsCount(S)) {
/* Return if number of expected != number of actual parameters */
return;
}
if (!ssSetNumInputPorts(S, 1)) return;
ssSetInputPortWidth(S, 0, 2);
/*
* Set direct feedthrough flag (1=yes, 0=no).
* A port has direct feedthrough if the input is used in either
* the mdlOutputs or mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit functions.
*/
ssSetInputPortDirectFeedThrough(S, 0, 1);
if (!ssSetNumOutputPorts(S, 2)) return;
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 0, 1);
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 1, 1);
ssSetNumSampleTimes(S, 1);
/* Specify the operating point save/restore compliance to be same as a
* built-in block */
ssSetOperatingPointCompliance(S, USE_DEFAULT_OPERATING_POINT);
ssSetOptions(S,
SS_OPTION_WORKS_WITH_CODE_REUSE |
SS_OPTION_EXCEPTION_FREE_CODE |
SS_OPTION_USE_TLC_WITH_ACCELERATOR);
}
/* Function: mdlInitializeSampleTimes =========================================
* Abstract:
*
This function is used to specify the sample time(s) for your
*
S-function. You must register the same number of sample times as
*
specified in ssSetNumSampleTimes.
*/
static void mdlInitializeSampleTimes(SimStruct *S)
{
ssSetSampleTime(S, 0, INHERITED_SAMPLE_TIME);
ssSetOffsetTime(S, 0, 0.0);
ssSetModelReferenceSampleTimeDefaultInheritance(S);
}
#define MDL_INITIALIZE_CONDITIONS
/* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_INITIALIZE_CONDITIONS)
/* Function: mdlInitializeConditions ========================================
* Abstract:
*
In this function, you should initialize the continuous and discrete
*
states for your S-function block.
The initial states are placed
*
in the state vector, ssGetContStates(S) or ssGetRealDiscStates(S).
*
You can also perform any other initialization activities that your
*
S-function may require. Note, this routine will be called at the
*
start of simulation and if it is present in an enabled subsystem
*
configured to reset states, it will be call when the enabled subsystem
*
restarts execution to reset the states.
*/
static void mdlInitializeConditions(SimStruct *S)
{
}
#endif /* MDL_INITIALIZE_CONDITIONS */
#define MDL_START
/* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_START)
/* Function: mdlStart =======================================================
* Abstract:
*
This function is called once at start of model execution. If you
*
have states that should be initialized once, this is the place
*
to do it.
*/
static void mdlStart(SimStruct *S)
{
}
#endif /*
MDL_START */
/* Function: mdlOutputs =======================================================
* Abstract:
*
In this function, you compute the outputs of your S-function
*
block.
*/
static void mdlOutputs(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)
{
InputRealPtrsType u1 = ssGetInputPortRealSignalPtrs(S,0);
real_T
*y1 = ssGetOutputPortSignal(S,0); //获取第一个输出端口的指针
real_T
*y2 = ssGetOutputPortSignal(S,1); //获取第二个输出端口的指针
//
int_T
width = ssGetInputPortWidth(S,0);
y1[0] = (*u1[0]+*u1[1]);
//输入是二维,所以要用指针加数组的方式
y2[0] = (*u1[0]-*u1[1]);
}
#define MDL_UPDATE
/* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_UPDATE)
/* Function: mdlUpdate ======================================================
* Abstract:
*
This function is called once for every major integration time step.
*
Discrete states are typically updated here, but this function is useful
*
for performing any tasks that should only take place once per
*
integration step.
*/
static void mdlUpdate(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)
{
}
#endif /* MDL_UPDATE */
#define MDL_DERIVATIVES
/* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_DERIVATIVES)
/* Function: mdlDerivatives =================================================
* Abstract:
*
In this function, you compute the S-function block's derivatives.
*
The derivatives are placed in the derivative vector, ssGetdX(S).
*/
static void mdlDerivatives(SimStruct *S)
{
}
#endif /* MDL_DERIVATIVES */
/* Function: mdlTerminate =====================================================
* Abstract:
*
In this function, you should perform any actions that are necessary
*
at the termination of a simulation.
For example, if memory was
*
allocated in mdlStart, this is the place to free it.
*/
static void mdlTerminate(SimStruct *S)
{
}
/*=============================*
* Required S-function trailer *
*=============================*/
#ifdef
MATLAB_MEX_FILE
/* Is this file being compiled as a MEX-file? */
#include "simulink.c"
/* MEX-file interface mechanism */
#else
#include "cg_sfun.h"
/* Code generation registration function */
#endif
注意:这里非常奇怪的是,如果输入用两个,同样的编写方式,运行的时候Matlab会强退,所以输入尽量用一个,而且是多维的。
使用C Mex S函数编写一个简单的滤波器:
Y(t) = (U(t) - Y(t-1)) x Lc +Y(t-1)
U(t)表示当前采样时刻的输入,Y(t)表示当前采样时刻的输出,Y(t-1)表示上一个采样时刻的输出值,Lc表示一阶滤波器的滤波系数。
10.6 C Mex S函数的自动生成
10.6.1 S-Function Builder
详细介绍参照如下链接:
S-Function Builder用法及使用实例
10.6.2 Legacy Code Tool
Legacy Code Tool(代码继承工具)可以实现以下功能:
- 能够将既存的C/C++代码转换为Simulink模型中可以使用的C Mex S函数,同时也能生成TLC文件。
- 将用户既存的算法代码插入到C Mex S函数的Outputs子方法中,用户需要提供足够的信息,这些信息包括:为MATLAB安装一个C编译器,S函数名,既存算法的函数原型,及为了编译既存C文件所需要的其他头文件、源文件及其存放路径。
legacy_code命令可以完成以下几件事情:
- 根据既有C代码初始化Legacy Code Tool的数据结构;
- 生成可用于仿真的C Mex S函数;
- 将生成的S函数编译链接为动态可执行文件(mex文件);
- 生成一个封装起来的模块来调用S函数;
- Simulink Coder组件会生成S函数的模块级TLC文件。
LCT(Legacy Code Tool)的使用流程:
- 初始化LCT数据结构
- 构建LCT数据结构
- 生成S-Function源文件
- 编译S-Function源文件
- 编译S-Function封装模块
通常使用’initialize’作为legacy_code的参数初始化一个LCT对象:
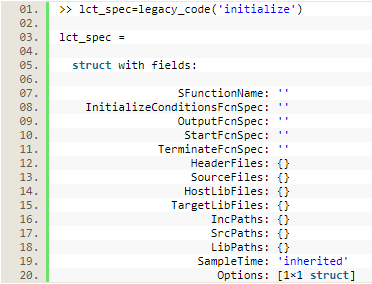
LCT对象的各个属性:
| 属性名 | 作用说明 |
|---|---|
| SFunctionName | 所生成S函数的名字 |
| InitializeConditionsFcnSpec | 应用于InitializeConditions子方法中的既存C代码函数原型 |
| OutputFcnSpec | 应用于OutputFcn子方法中的既存C代码函数原型 |
| StartFcnSpec | 应用于StartFcn子方法中的既存C代码函数原型 |
| TerminateFcnSpec | 应用于TerminateFcn子方法中的既存C代码函数原型 |
| HeaderFiles | 所生成S函数的名字 |
| SourceFiles | 定义既存C函数及其他需要编译的源文件 |
| HostLLibFiles/TargetLibFiles | 主机/目标端编译C文件所依赖的库文件 |
| IncPaths | LCT搜索路径寻找编译需要的头文件 |
| SrcPaths | LCT搜索路径寻找编译需要的源文件 |
| LibPaths | LCT搜索路径寻找编译需要的库和目标文件 |
| SampleTime | 采样时间 |
| Options | 控制S函数Options的选项 |
LCT动作执行:
- legacy_code(‘help’):打开LCT工具的详细使用说明的帮助文档;
- legacy_code(‘sfcn_cmex_generate’,lct_spec):根据lct_spec生成S函数源文件;
- legacy_code(‘compile’,lct_spec):对生成的S函数进行编译链接;
- legacy_code(‘slblock_generate’,lct_spec,modename):生成一个封装模块调用生成的S函数,并自动将此模块添加到名为modename的模型文件里;
- legacy_code(‘sfcn_tlc_generate’,lct_spec):生成S函数配套的TLC文件,用于加速仿真模型或通过Simulink模型生成代码;
- legacy_code(‘rtwmakecfg_generate’,lct_spec):生成rtwmakecfg.m文件,此文件是用于生成适用于当前lct_spec对象的makefile的M脚本。
示例1(将既有的正弦C代码使用LCT集成):
//EmMath.h
#ifndef __QM_MATH_H__
#define __QM_MATH_H__
#define PI
3.1415926
signed long Em_Sin(unsigned long Angle);
#endif
//EmMath.c
#include"EmMath.h"
const unsigned short SinTbl[] = {0x0000,
//0
0x0019, 0x0032, 0x004B, 0x0064, 0x007D, 0x0096, 0x00AF, 0x00C8, 0x00E2, 0x00FB,//10
0x0114, 0x012D, 0x0146, 0x015F, 0x0178, 0x0191, 0x01AA, 0x01C3, 0x01DC, 0x01F5,//20
0x020E, 0x0227, 0x0240, 0x0258, 0x0271, 0x028A, 0x02A3, 0x02BC, 0x02D4, 0x02ED,//30
0x0306, 0x031F, 0x0337, 0x0350, 0x0368, 0x0381, 0x0399, 0x03B2, 0x03CA, 0x03E3,//40
0x03FB, 0x0413, 0x042C, 0x0444, 0x045C, 0x0474, 0x048C, 0x04A4, 0x04BC, 0x04D4,//50
0x04EC, 0x0504, 0x051C, 0x0534, 0x054C, 0x0563, 0x057B, 0x0593, 0x05AA, 0x05C2,//60
0x05D9, 0x05F0, 0x0608, 0x061F, 0x0636, 0x064D, 0x0664, 0x067B, 0x0692, 0x06A9,//70
0x06C0, 0x06D7, 0x06ED, 0x0704, 0x071B, 0x0731, 0x0747, 0x075E, 0x0774, 0x078A,//80
0x07A0, 0x07B6, 0x07CC, 0x07E2, 0x07F8, 0x080E, 0x0824, 0x0839, 0x084F, 0x0864,//90
0x087A, 0x088F, 0x08A4, 0x08B9, 0x08CE, 0x08E3, 0x08F8, 0x090D, 0x0921, 0x0936,//100
0x094A, 0x095F, 0x0973, 0x0987, 0x099C, 0x09B0, 0x09C4, 0x09D7, 0x09EB, 0x09FF,//110
0x0A12, 0x0A26, 0x0A39, 0x0A4D, 0x0A60, 0x0A73, 0x0A86, 0x0A99, 0x0AAB, 0x0ABE,//120
0x0AD1, 0x0AE3, 0x0AF6, 0x0B08, 0x0B1A, 0x0B2C, 0x0B3E, 0x0B50, 0x0B61, 0x0B73,//130
0x0B85, 0x0B96, 0x0BA7, 0x0BB8, 0x0BC9, 0x0BDA, 0x0BEB, 0x0BFC, 0x0C0C, 0x0C1D,//140
0x0C2D, 0x0C3E, 0x0C4E, 0x0C5E, 0x0C6E, 0x0C7D, 0x0C8D, 0x0C9C, 0x0CAC, 0x0CBB,//150
0x0CCA, 0x0CD9, 0x0CE8, 0x0CF7, 0x0D06, 0x0D14, 0x0D23, 0x0D31, 0x0D3F, 0x0D4D,//160
0x0D5B, 0x0D69, 0x0D76, 0x0D84, 0x0D91, 0x0D9F, 0x0DAC, 0x0DB9, 0x0DC6, 0x0DD2,//170
0x0DDF, 0x0DEB, 0x0DF8, 0x0E04, 0x0E10, 0x0E1C, 0x0E28, 0x0E33, 0x0E3F, 0x0E4A,//180
0x0E55, 0x0E60, 0x0E6B, 0x0E76, 0x0E81, 0x0E8B, 0x0E96, 0x0EA0, 0x0EAA, 0x0EB4,//190
0x0EBE, 0x0EC8, 0x0ED1, 0x0EDB, 0x0EE4, 0x0EED, 0x0EF6, 0x0EFF, 0x0F07, 0x0F10,//200
0x0F18, 0x0F21, 0x0F29, 0x0F31, 0x0F39, 0x0F40, 0x0F48, 0x0F4F, 0x0F56, 0x0F5D,//210
0x0F64, 0x0F6B, 0x0F72, 0x0F78, 0x0F7F, 0x0F85, 0x0F8B, 0x0F91, 0x0F96, 0x0F9C,//220
0x0FA1, 0x0FA7, 0x0FAC, 0x0FB1, 0x0FB6, 0x0FBA, 0x0FBF, 0x0FC3, 0x0FC7, 0x0FCB,//230
0x0FCF, 0x0FD3, 0x0FD7, 0x0FDA, 0x0FDE, 0x0FE1, 0x0FE4, 0x0FE7, 0x0FE9, 0x0FEC,//240
0x0FEE, 0x0FF0, 0x0FF2, 0x0FF4, 0x0FF6, 0x0FF8, 0x0FF9, 0x0FFB, 0x0FFC, 0x0FFD,//250
0x0FFE, 0x0FFE, 0x0FFF, 0x0FFF, 0x0FFF, 0x0FFF};
//256
/****************************************************
Function name: Em_Sin
description:
calculate sin(theta)
input:
Angle(0x3FFFFF
equal
one Cycle
output:
****************************************************/
signed long Em_Sin(unsigned long Angle)
{
unsigned long AngleTemp;
signed long SineValue;
AngleTemp =
Angle >> 12;
AngleTemp &= 0x03FF;
//0~1024
if (AngleTemp <= 256)
{
SineValue = SinTbl[AngleTemp];
}
else if (AngleTemp <= 512)
{
AngleTemp = 512 - AngleTemp;
SineValue = SinTbl[AngleTemp];
}
else if (AngleTemp <= 768)
{
AngleTemp -= 512;
SineValue = -SinTbl[AngleTemp];
}
else if (AngleTemp <= 1024)
{
AngleTemp = 1024 - AngleTemp;
SineValue = -SinTbl[AngleTemp];
}
return (SineValue);
}
集成C代码的m脚本:
%% 结构体初始化
%%
def = legacy_code('initialize');
%% 涉及到的.c .h路径
%%
% def.IncPaths = '';
% def.SrcPaths = '';
%% 头文件和源文件
%%
def.SourceFiles
= {'EmMath.c'};
def.HeaderFiles
= {'EmMath.h'};
%% 生成的S-Function模块名称
%%
def.SFunctionName = 'sfun_Em_Math';
%% 输出函数名称,和C源码相同
%%
def.OutputFcnSpec
= 'int32 y1 = Em_Sin(uint32 u1)';
%% 创建C mex S函数文件
%%
legacy_code('sfcn_cmex_generate', def);
%% 生成MEXW64可执行文件,用于Simulink仿真
%%
legacy_code('compile', def);
%% 封装Sfunction
%%
%legacy_code('slblock_generate', def, '保存的模块名');
legacy_code('slblock_generate', def);
%Untitle
%% 生成TLC文件用于代码生成
%%
legacy_code('sfcn_tlc_generate', def);
运行脚本后,会生成以下文件:
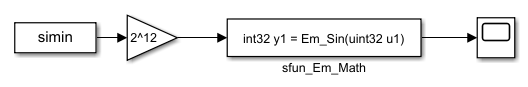
模型如下:
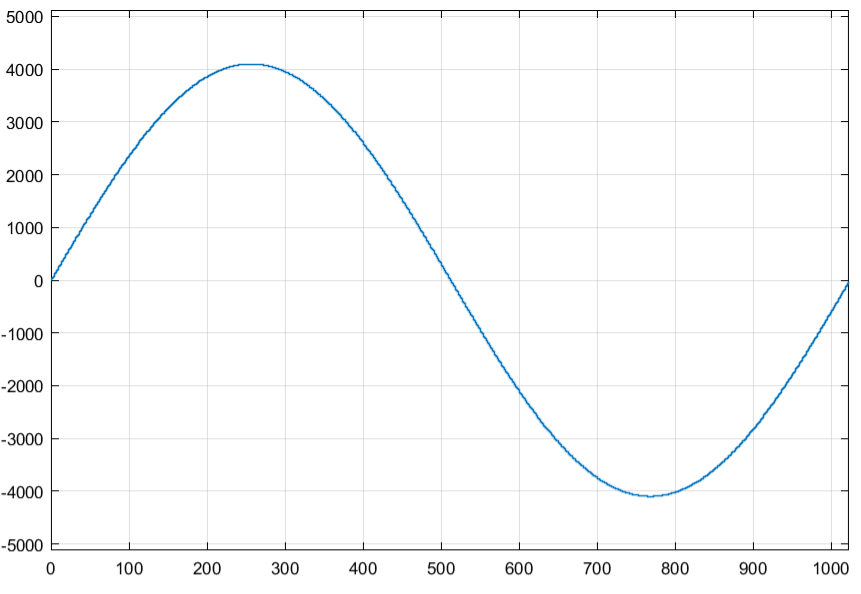
simin是Fromworkspace,StopTime设为1023,产生该数据的结构体如下:
stop_time = get_param(gcs, 'StopTime');
simin.time = [0:str2num(stop_time)]';
simin.signals.values = [0:length(simin.time) - 1]';
simin.signals.demensions = [length(simin.time) 1];
仿真结果入下:
示例2(用户驱动模型的创建):
一个DAC模块的.c和.h文件如下:
#include <DAC_TLC5615.h>
void Delay_us(unsigned char count)
{
while(count--);
}
/******************************************************************************
* Function: DacGpioInit
* Description: Dac gpio initialize function;
* Calls: none;
* Called By: main;
* Input: none;
* Output: none;
* Return: none;
* Others: none;
*****************************************************************************/
void DacGpioInit(void)
{
EALLOW;
/* CS pin */
GpioCtrlRegs.GPBMUX2.bit.GPIO57 = 0;
GpioCtrlRegs.GPBDIR.bit.GPIO57 = 1;
GpioDataRegs.GPBDAT.bit.GPIO57 = 1;
// Set CS pin;
/* SDA pin */
GpioCtrlRegs.GPBMUX2.bit.GPIO54 = 0;
GpioCtrlRegs.GPBDIR.bit.GPIO54 = 1;
// Direction = Output;
GpioDataRegs.GPBDAT.bit.GPIO54 = 1;
//
/* SCL pin */
GpioCtrlRegs.GPBMUX2.bit.GPIO56 = 0;
GpioCtrlRegs.GPBDIR.bit.GPIO56 = 1;
GpioDataRegs.GPBDAT.bit.GPIO56 = 1;
// Set SCL pin;
EDIS;
}
/**********************
end of DacGpioInit function
************************/
/******************************************************************************
* Function: DacDataOut
* Description: Dac data output function;
* Calls: Delay_us;
* Called By: main;
* Input: ui16_Input, Range: 0 ~ 1024, Step: 1;
* Output: none;
* Return: none;
* Others: TLC5615;
*****************************************************************************/
void DacDataOut(int ui16_Input,int Channel_Select)
{
Uint16 lui16_Input = 0;
Uint16 lui16_Daci = 0;
lui16_Input = ui16_Input;
lui16_Input = lui16_Input << 6;
// ֻ������ʮλ
if(Channel_Select==0)
{
DAC_CS_CLEAR;
// ƬѡDAC1оƬ
Delay_us(1);
DAC_SCL_CLEAR;
for (lui16_Daci = 0; lui16_Daci < 12; lui16_Daci ++)
// 12 data bits;
{
if ((lui16_Input & 0x8000) == 0x8000)
// ȡ���ݵ����λ
{
DAC_SDA_SET;
}
else
{
DAC_SDA_CLEAR;
}
Delay_us(1);
DAC_SCL_SET;
// ��SCL�������ش�������
lui16_Input = lui16_Input << 1;
// ����һλ
DAC_SCL_CLEAR;
Delay_us(1);
}
DAC_CS_SET;
Delay_us(1);
DAC_SCL_CLEAR;
}
}
/***********************
end of DacDataOut function
************************/
#ifndef DAC_TLC5615_H_
#define DAC_TLC5615_H_
#include "DSP2833x_Device.h"
#include "DSP2833x_Examples.h"
#define
DAC_CS_CLEAR
GpioDataRegs.GPBCLEAR.bit.GPIO57 = 1
#define
DAC_CS_SET
GpioDataRegs.GPBSET.bit.GPIO57= 1
#define
DAC_SDA_CLEAR
GpioDataRegs.GPBCLEAR.bit.GPIO54 = 1
#define
DAC_SDA_SET
GpioDataRegs.GPBSET.bit.GPIO54 = 1
#define
DAC_SCL_CLEAR
GpioDataRegs.GPBCLEAR.bit.GPIO56 = 1
#define
DAC_SCL_SET
GpioDataRegs.GPBSET.bit.GPIO56 = 1
extern void DacGpioInit(void);
extern void DacDataOut(Uint16 ui16_Input,Uint16 Channel_Select);
#endif
LCT的.m文件:
%结构体初始化
def= legacy_code('initialize')
%设计到的.c以及.h地址
%
def.IncPaths=""
%
def.SrcPaths=""
%驱动源码 以及头文件
%def.SourceFiles={''};
def.SourceFiles={'DAC_TLC5615.c'};
def.HeaderFiles={'DAC_TLC5615.h'};
%S-function 名称
def.SFunctionName='DAC_5615_Driver';
%初始化函数名称
和C源码相同
可选
def.InitializeConditionsFcnSpec='void DacGpioInit(void)';
%输出函数名称 和C源码内容相同
def.OutputFcnSpec='void DacDataOut(uint16 u1,uint16 u2)';
%创建.c文件 S funciton
c文件 LEVEL-2
legacy_code('sfcn_cmex_generate',def)
%生成MEXW64可执行文件名称 用于simulink仿真
legacy_code('compile',def)
%封装S-FUNCTION
legacy_code('slblock_generate',def)
%生成代码生成必要的TLC文件---模块TLC
legacy_code('sfcn_tlc_generate',def)
直接运行m文件编译会报错
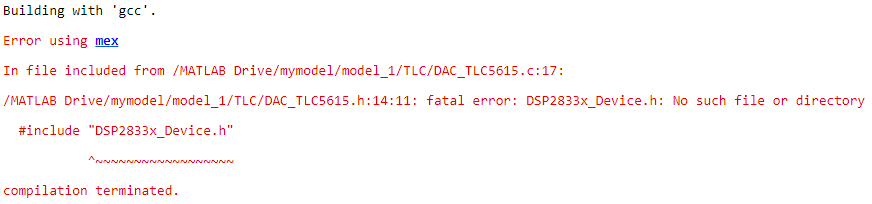
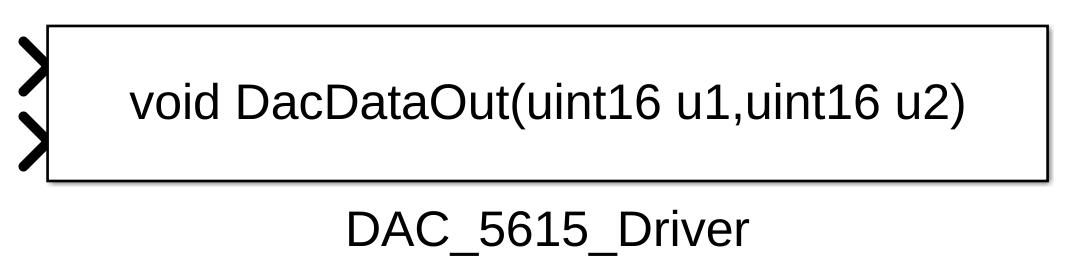
通过报错信息可以知道,是由于某些文件不存在造成的。由于.c和.h中存在处理器的硬件寄存器,会阻挠TLC代码的的编译,所以直接将函数内容屏蔽掉,只保留函数接口(因为编译不会对已存在代码做任何处理)。编译完成后会出现如下模块:
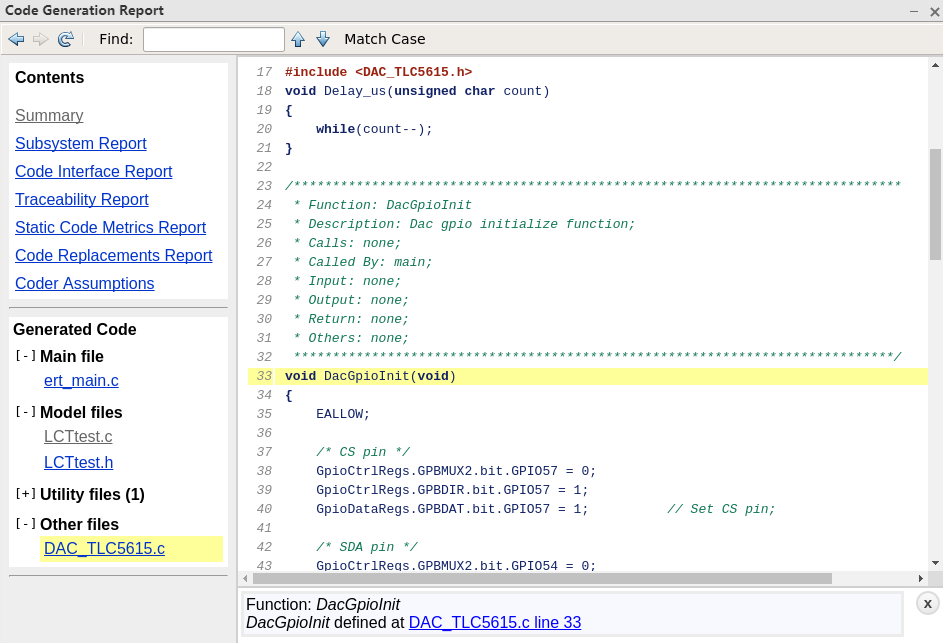
然后将注释的代码取消注释,加上输入后对模块进行代码生成,生成的报告如下:
在生成代码后,将屏蔽的部分注释符号去掉,该模块就可以正常使用。改方法需要进行一定的操作,属于非常规方法,一般的用法是通过CMex生成
最后
以上就是包容摩托最近收集整理的关于Simulink仿真入门到精通(十) S函数10.1. S函数的概述10.2 S函数的类型10.3 S函数的要素10.4 S函数的组成及执行顺序10.5 使用不同的语言编写S函数10.6 C Mex S函数的自动生成的全部内容,更多相关Simulink仿真入门到精通(十)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复