概述
蓝牙是一种工作在免费的ISM频段的短距离无线通信技术,在各种设备之间实现灵活、安全、低成本、低功耗的语音和数据通信。它采用自适应跳频技术,可以和多种无线通信共存于ISM频段,与同用于短距离无线通信的Zigbee和UWB相比,蓝牙协议和标准更加完善,设备间一致性和互连通性好,而且以Profile的形式定义了具体应用的实现方式,从而保证了兼容性。
蓝牙通讯原理
蓝牙通讯分为三个阶段:
- 1)设备发现和连接
- 2)鉴权
- 3)应用层信息服务
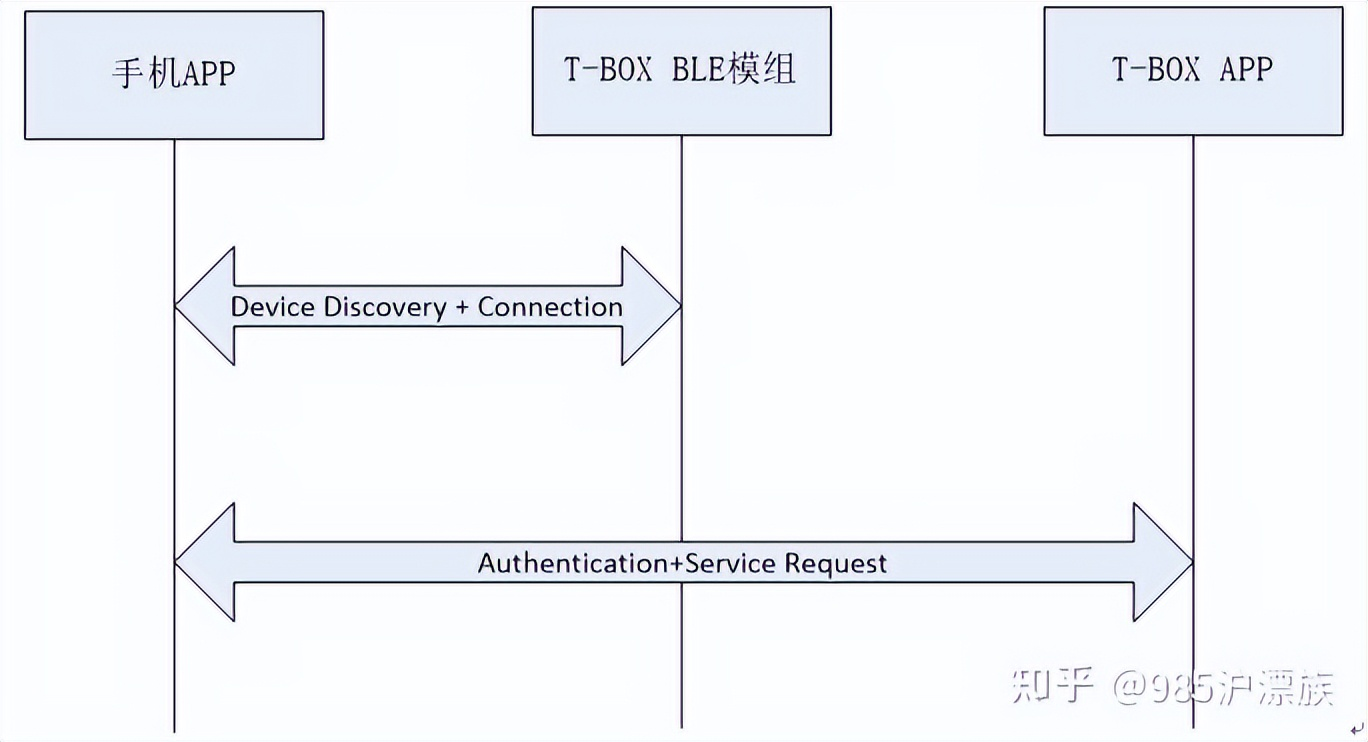
第一阶段,设备发现与连接。
在这个阶段,TBox定期广播蓝牙设备的地址。主设备搜索到此前用户通过TSP绑定的TBox蓝牙MAC地址列表中的其中一个后,主动请求蓝牙设备进行连接。蓝牙主设备根据信号TBox广播的信号强度,连接TBox并且建立数据通道。
第二阶段, 鉴权。
这个阶段,使主设备与TBox相互确认身份。
第三阶段,请求服务。
这个阶段,允许通过蓝牙通信请求服务。
TBOX有两路数据通道:通道1用于主设备与TBOX蓝牙模块的一级鉴权,通道2用于主设备与TBOX的MCU通讯。
Tbox的BLE模组和主设备交互流程图:
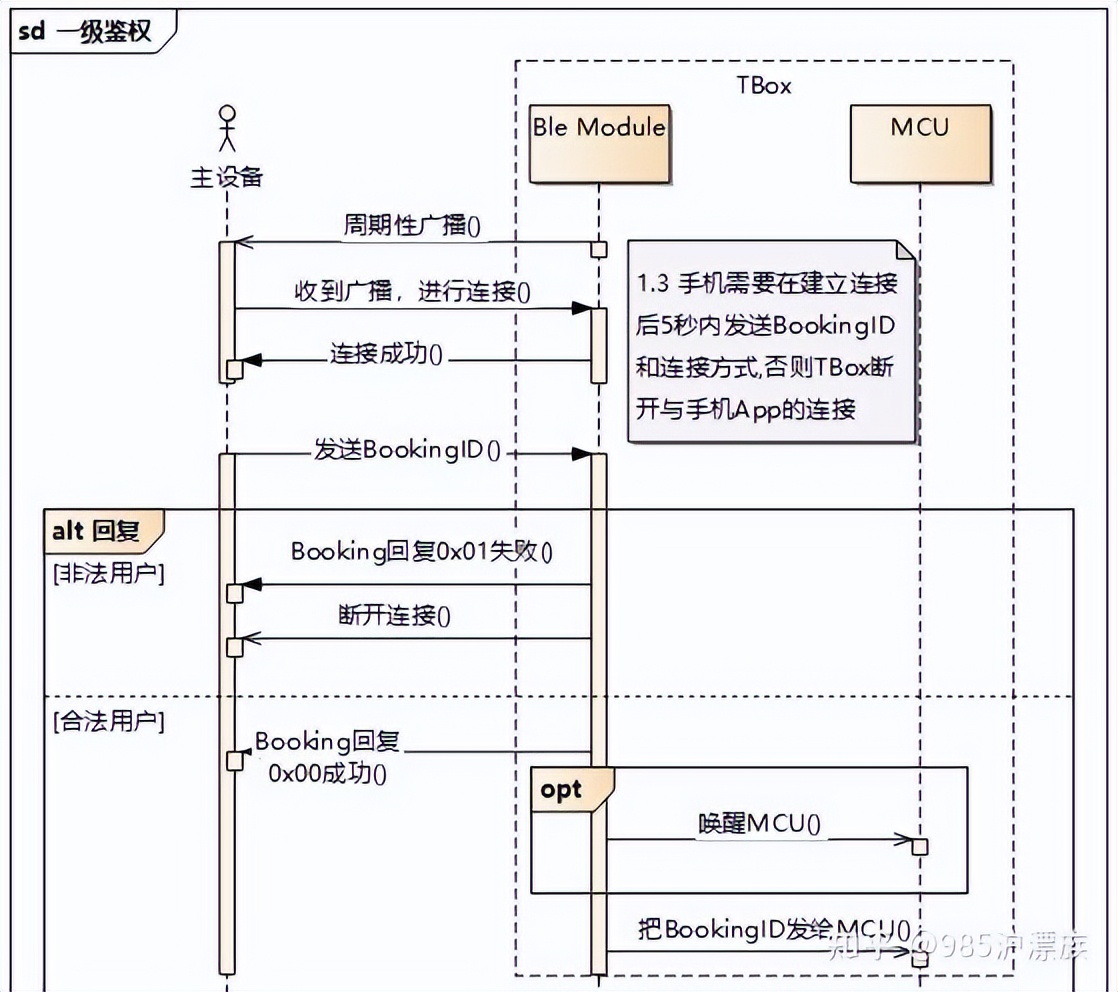
蓝牙广播的内容为蓝牙名称和服务的UUID,广播周期为2s。
主设备通过通道1发送Booking信息,TBox收到通道1主设备的BookingID后,如果ID号在白名单列表中,则认为通道一级鉴权,需要在通道1回复主设备信息并开始执行二级鉴权。
TBox收到通道1主设备的BookingID后,如果ID号在不在白名单中列表中,则认为一级鉴权失败,需要在通道1回复主设备信息,然后断开连接。
车载蓝牙通信实现
蓝牙电话
蓝牙电话主要用到BluetoothHeadsetClient这个类里面定义了很多广播意图,最有用的是这个action
/**
* Intent sent whenever state of a call changes.
*
*
It includes:
* {@link #EXTRA_CALL},
* with value of {@link BluetoothHeadsetClientCall} instance,
* representing actual call state.
*/
public static final String ACTION_CALL_CHANGED =
"android.bluetooth.headsetclient.profile.action.AG_CALL_CHANGED";
它监听来电,接听来电,去电,通话中等状态,要想在车载设备中操作电话需要知道这些状态。
private final BroadcastReceiver mReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
if (null != intent) {
String action = intent.getAction();
Log.i(TAG, "BTService receiver action == "+action);
//监听来电
if (BluetoothHeadsetClient.ACTION_CALL_CHANGED.equals(action)) {
BluetoothHeadsetClientCall mCall = (BluetoothHeadsetClientCall) intent.getExtra(BluetoothHeadsetClient.EXTRA_CALL, null);
if (mCall != null) {
int callState = mCall.getState();
Log.d(TAG, "when call status changes: mConnStat is " + mConnStat+" number == "+mCall.getNumber());
if (callState == BluetoothHeadsetClientCall.CALL_STATE_INCOMING) {
//来电
} else if (callState == BluetoothHeadsetClientCall.CALL_STATE_DIALING) {
//去电
} else if (callState == BluetoothHeadsetClientCall.CALL_STATE_ACTIVE) {
//接听中
} else if (callState == BluetoothHeadsetClientCall.CALL_STATE_TERMINATED) {
//结束
}
}
}
看下它的构造方法
BluetoothHeadsetClient(Context context, ServiceListener l) {
mContext = context;
mServiceListener = l;
mAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
IBluetoothManager mgr = mAdapter.getBluetoothManager();
if (mgr != null) {
try {
mgr.registerStateChangeCallback(mBluetoothStateChangeCallback);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG,"",e);
}
}
doBind();
}
mBluetoothStateChangeCallback监听蓝牙打开或关闭状态,重点看下doBind方法
boolean doBind() {
Intent intent = new Intent(IBluetoothHeadsetClient.class.getName());
ComponentName comp = intent.resolveSystemService(mContext.getPackageManager(), 0);
intent.setComponent(comp);
if (comp == null || !mContext.bindServiceAsUser(intent, mConnection, 0,
android.os.Process.myUserHandle())) {
Log.e(TAG, "Could not bind to Bluetooth Headset Client Service with " + intent);
return false;
}
return true;
}
其实就是去绑定一个service
private final ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "Proxy object connected");
mService = IBluetoothHeadsetClient.Stub.asInterface(Binder.allowBlocking(service));
if (mServiceListener != null) {
mServiceListener.onServiceConnected(BluetoothProfile.HEADSET_CLIENT,
BluetoothHeadsetClient.this);
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "Proxy object disconnected");
mService = null;
if (mServiceListener != null) {
mServiceListener.onServiceDisconnected(BluetoothProfile.HEADSET_CLIENT);
}
}
};
当服务连接时返回IBluetoothHeadsetClient并通知协议请求成功,这是aidl的客户端,不了解aidl的去查看一下android跨进程通信相关知识。
/**
* Connects to remote device.
*
* Currently, the system supports only 1 connection. So, in case of the
* second connection, this implementation will disconnect already connected
* device automatically and will process the new one.
*
* @param device a remote device we want connect to
* @return true if command has been issued successfully;
* false otherwise;
* upon completion HFP sends {@link #ACTION_CONNECTION_STATE_CHANGED}
* intent.
*/
public boolean connect(BluetoothDevice device) {
if (DBG) log("connect(" + device + ")");
final IBluetoothHeadsetClient service = mService;
if (service != null && isEnabled() && isValidDevice(device)) {
try {
return service.connect(device);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, Log.getStackTraceString(new Throwable()));
return false;
}
}
if (service == null) Log.w(TAG, "Proxy not attached to service");
return false;
}
连接设备就是调用服务端的connect方法。服务端的实现在packagesappsBluetoothsrccomandroidbluetoothhfpclientHeadsetClientService.java
接听电话
/**
* Accepts a call
*
* @param device remote device
* @param flag action policy while accepting a call. Possible values
* {@link #CALL_ACCEPT_NONE}, {@link #CALL_ACCEPT_HOLD},
* {@link #CALL_ACCEPT_TERMINATE}
* @return true if command has been issued successfully;
* false otherwise;
* upon completion HFP sends {@link #ACTION_CALL_CHANGED}
* intent.
*/
public boolean acceptCall(BluetoothDevice device, int flag)
拨打电话
/**
* Places a call with specified number.
*
* @param device remote device
* @param number valid phone number
* @return {@link BluetoothHeadsetClientCall} call if command has been
* issued successfully;
* {@link null} otherwise;
* upon completion HFP sends {@link #ACTION_CALL_CHANGED}
* intent in case of success; {@link #ACTION_RESULT} is sent
* otherwise;
*/
public BluetoothHeadsetClientCall dial(BluetoothDevice device, String number)
拒接接听
/**
* Rejects a call.
*
* @param device remote device
* @return true if command has been issued successfully;
* false otherwise;
* upon completion HFP sends {@link #ACTION_CALL_CHANGED}
* intent.
*
*
Feature required for successful execution is being reported by:
* {@link #EXTRA_AG_FEATURE_REJECT_CALL}.
* This method invocation will fail silently when feature is not supported.
*/
public boolean rejectCall(BluetoothDevice device)
挂断电话
/**
* Rejects a call.
*
* @param device remote device
* @return true if command has been issued successfully;
* false otherwise;
* upon completion HFP sends {@link #ACTION_CALL_CHANGED}
* intent.
*
*
Feature required for successful execution is being reported by:
* {@link #EXTRA_AG_FEATURE_REJECT_CALL}.
* This method invocation will fail silently when feature is not supported.
*/
public boolean rejectCall(BluetoothDevice device)
发送DTMF编码
/**
* Sends DTMF code.
*
* Possible code values : 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,*,#
*
* @param device remote device
* @param code ASCII code
* @return true if command has been issued successfully;
* false otherwise;
* upon completion HFP sends {@link #ACTION_RESULT} intent;
*/
public boolean sendDTMF(BluetoothDevice device, byte code)
根据自己的需求直接调用对应的方法,这里只列举了常用的.
本篇主要介绍车载开发中的基础,了解到车载开发基础的蓝牙通信原理以及举例蓝牙电话通信的示例实现。
Android车载的开发现在很吃香,想入行车载行业也是不错的选择。想学习更多的Android车载技术可以前往《Android车载技术手册》领取;由BYD高级车载开发整理制定的。我这里免费分享出来,能够刷到我这篇文章的可谓是赚到了一笔。
文末
现在的小轿车越来越多,几乎人人都拥有。以至于现在新能源的倡导;以后更换的车辆也会逐渐增多。现在入行车载系统开发来看;确实是很不错的前景。
最后
以上就是忐忑画板最近收集整理的关于Android车载开发基础学习——蓝牙通信是如何实现的?概述蓝牙通讯原理蓝牙通讯分为三个阶段:第一阶段,设备发现与连接。第二阶段, 鉴权。第三阶段,请求服务。车载蓝牙通信实现蓝牙电话文末的全部内容,更多相关Android车载开发基础学习——蓝牙通信是如何实现的?概述蓝牙通讯原理蓝牙通讯分为三个阶段:第一阶段,设备发现与连接。第二阶段,内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复