比赛已经告一段落,现在我们队兑现承诺,将比赛方案开源给大家,互勉互助,共同进步。
队伍介绍
我们的队伍名是Baseline,我们因分享Baseline结缘,所以就把队伍名叫Baseline。
队长: 方曦来自上海交通大学,研三。
队员 :吕晓欣来自网易,AI工程师
队员:王浩来自北京星河亮点,软件研发
队员:杨新达来自广州一家企业,AI工程师
方案
摘要
对于当前通信系统来说,物理层是通信服务得到保障的基础;而对于物理层来说,MIMO则是基本的支撑技术;对于MIMO来说,准确地确定信道质量并做有效反馈及利用又是必不可少的关键问题。
在国际标准化组织3GPP的讨论内,目前这部分工作是通过CSI 参考信号设计及CSI反馈机制完成。在当前的CSI反馈设计中,主要是依赖矢量量化、码本设计的方式来实现信道特征的提取与反馈,例如基于TYPE1、TYPE2的CSI反馈设计等。在目前的实践来看,这类反馈方式是有效的,但是由于其核心思想是基于信息抽取、码本反馈的方式,其所反馈的目标信息实际上是有损信道信息。
在本次大赛中,我们从计算机视觉角度建模,设计出一种基于CNN的自编码器结构。我们采用了带有SE结构的BCSP模块作为网络的基础组件,在计算效率和网络精度上都有较好的效果;采用带有误差恢复能力的量化模块,一方面能降低量化误差,同时也能提高编码器的训练效果;通过分析大赛数据,我们利用Fast-AutoAugment思路找到了4种数据增强方法,完美的解决了在384 附近bit数的网络过拟合问题;我们利用剪枝和降低量化精度的方式,大幅度加速了我们的训练过程。最终我们获得了第7名的好成绩。
关键词
无线通信, 信道反馈, 卷积神经网络, 注意力机制, 数据增强
1 注意力机制的使用
在我们采用的注意力机制是SE-Net: Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks,简称SE-Net[1],它赢得了最后一届ImageNet2017竞赛分类任务的冠军,其基本原理是对于每个输出channel,预测一个常数权重,对每个channel加权一下。结构如下图:
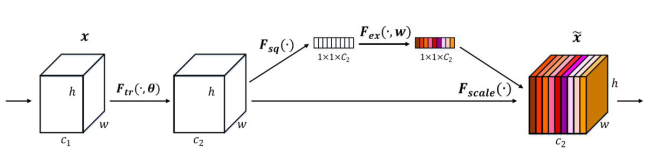
图1:SE 注意力机制
第一步每个通道H*W个数全局平均池化得到一个标量,称之为Squeeze,然后两个FC得到01之间的一个权重值,对原始的每个HxW的每个元素乘以对应通道的权重,得到新的feature map,称之为Excitation。任意的原始网络结构,都可以通过这个Squeeze-Excitation的方式进行feature recalibration,如下图。
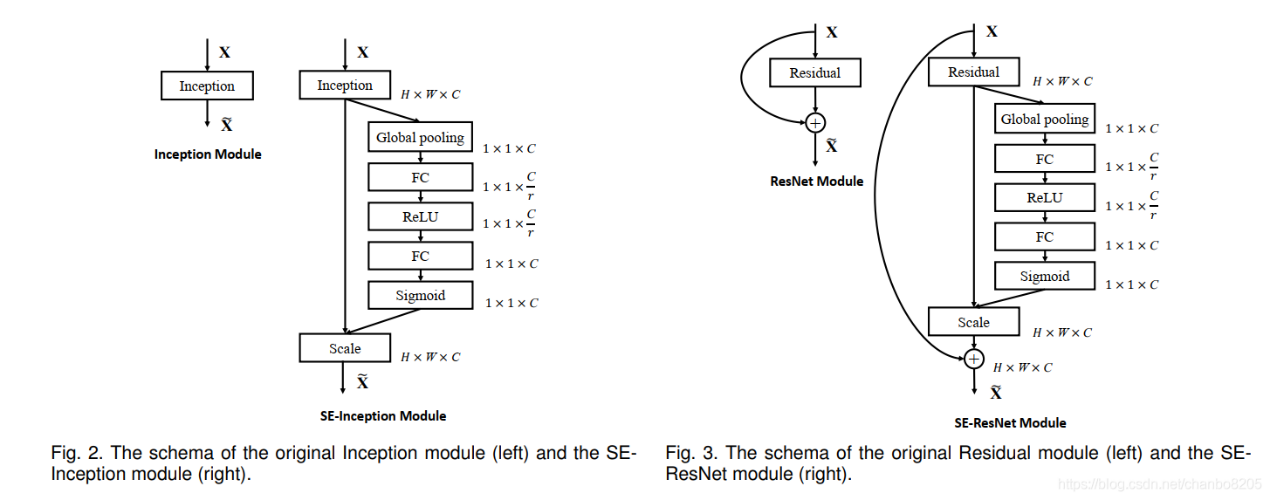
图2:SENet基础结构
具体实现上就是一个Global Average Pooling-FC-ReLU-FC-Sigmoid,第一层的FC会把通道降下来,然后第二层FC再把通道升上去,得到和通道数相同的C个权重,每个权重用于给对应的一个通道进行加权。上图中的r就是缩减系数,实验确定选取16,可以得到较好的性能并且计算量相对较小。SENet的核心思想在于通过网络根据loss去学习特征权重,使得有效的feature map权重大,无效或效果小的feature map权重小的方式训练模型达到更好的结果。
我们将SENet一个子结构,嵌入到C3和BottleneckCSP模块的最后一层。如图3所示。
在该赛题中SE结构或者说注意力机制能够大幅度提升模型的拟合能力,让我们的模型能够成功的完成432bit 达标,但随之而来的模型过拟合现象困扰了我们很长时间。
2 量化误差恢复模块
在量化编码过程中,经过量化-反量化操作,将会让原始编码丢失一部分信息,即量化误差,量化误差的存在不仅使得模型最终NMSE会比无量化操作的更高,还会减慢decoder的训练速度和效果。故我们提出量化误差恢复模块,即对反量化后的编码进行refine,使之更加接近无量化损失。
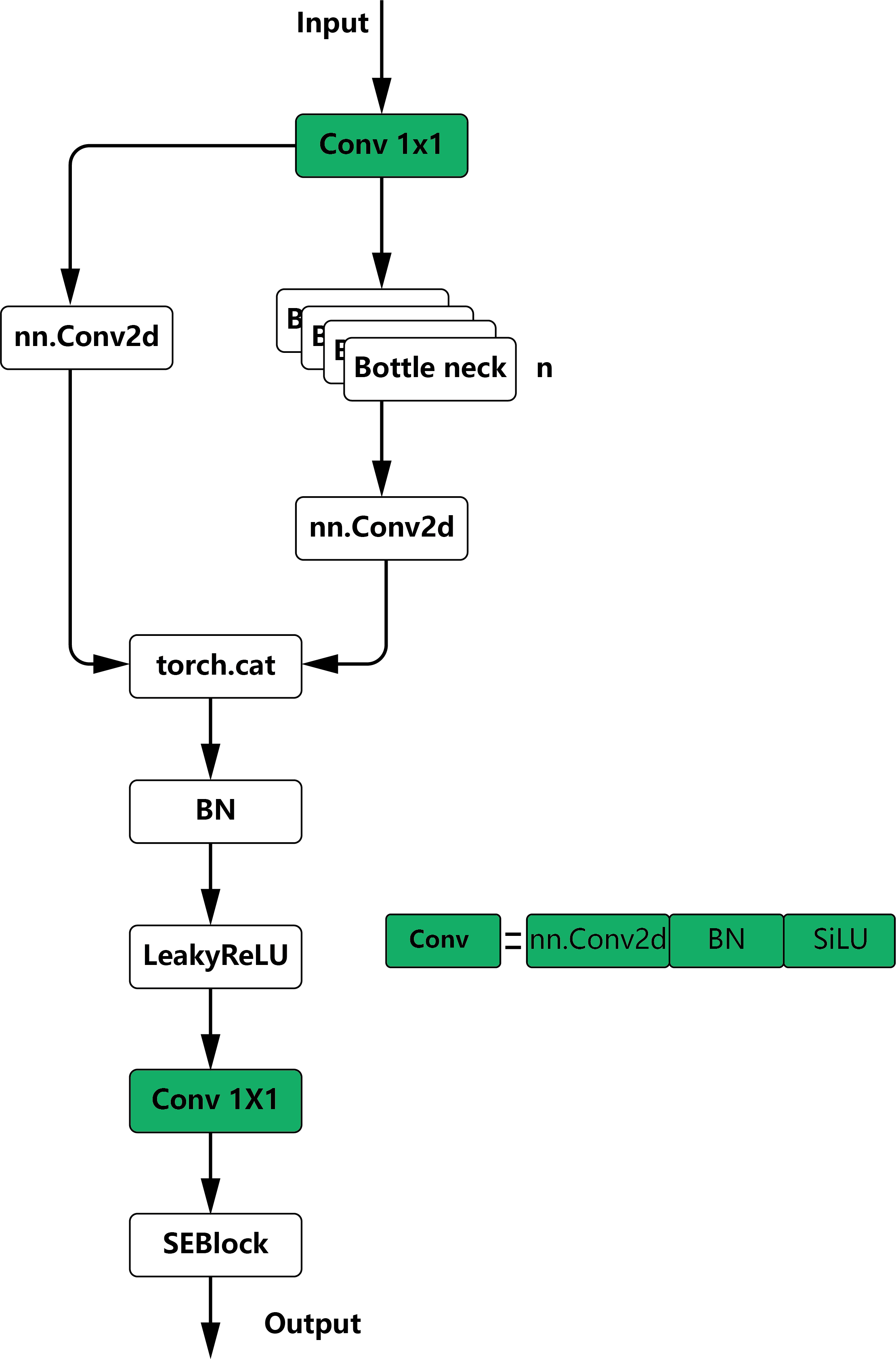
图3:基础模块图
具体操作是,我们对量化-反量化后的编码,通过两层全连接(带有bn和非线性层),并经过标准化处理,得到值域与量化误差值域相同的输出(通过sigmoid以及scale等操作调整值域为[-12B+1,12B+1]![]() )以残差的方式加到原始反量化编码之后,以起到恢复量化误差的效果。同时,为了使得这个模块能更好地按设想工作,我们对此模块的输出增加了一路损失函数,使得恢复后的编码与量化前的编码更加接近。
)以残差的方式加到原始反量化编码之后,以起到恢复量化误差的效果。同时,为了使得这个模块能更好地按设想工作,我们对此模块的输出增加了一路损失函数,使得恢复后的编码与量化前的编码更加接近。
设量化前编码为X,量化后编码为X’,我们的误差恢复模块为R,则额外监督表示为如下:L(X+R(X'), X)![]() 。
。
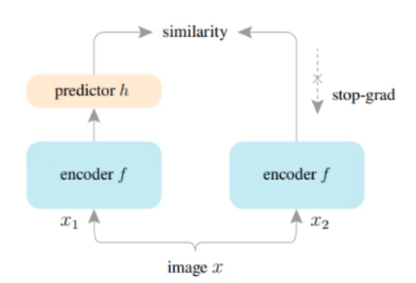
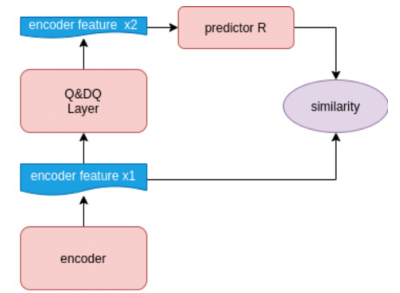
图4:误差恢复模块与Simsiam结构对比图
上图同对比了误差恢复模块和自监督算法中的SimSiam[2]结构对比图。如果我们把量化误差看座位一种数据增强,那么量化误差修复这一块刚好可以看作一种自监督学习网络,同时存在一条支路在反向传播过程中能够计算出准确的梯度,让我们能够获得更好的encoder层。
3 数据增强
赛方提供的数据200*3000是按序摆放的,通过分析,我们发现3000这个维度中各个数据似乎存在一些相似关系,在我们全部的数据增强过程中都不会去破坏这种模式。数据增强固然可以一定程度上缓解模型过拟合,但是如果设计的不得当,网络会学到很多没用的信息从而不能训到很低的nmse,为此我们借鉴了Fast-AutoAugment中的思想,对于每一种数据增强,我们利用原始数据训练的模型在验证集数据+该数据增强统计nmse,如果nmse过高,那么这种数据增强大概率改变了原始数据分布,不应该背采纳。通过这种方式我们选取了4中数据增强方法:
- 1-X
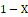
- 实部虚部shuffle
- MixUp
- CutMix
传统的MixUp和CutMix会破坏数据原有的模式,所以我们对其进行一些改造。在样本采样过程中,我们只会选择属于同一种patten的两个样本进行融合;我们不会去破坏16这个维度的数值关系,所以CutMix过程中随机选择24行中的一部分进行替换,这是因为24这个维度虽然有patten,但是似乎不存在特别明显的数值关系。通过这种方式我们能偶成功的训练出384bit的模型。
图5:数据增强效果图
5 剪枝与量化
量化层我们选择了简单的均匀量化操作。量化bit数目选取上,考虑到任务更加侧重更小传输bit而不是极致的精度(低NMSE),故可以选择使用更小的量化bit数目,而太小的量化bit数目会导致量化误差过大,使得decoder训练更加困难也更容易过拟合。权衡上述,我们选择了使用Bit=3的量化操作。
训练初始模型时,我们首先选择使用bit数为432的bitstream构建模型进行训练,训练完成之后对encoder最末层全连接和decoder最前层全连接进行裁剪,得到384bit的autoencoder模型,然后进行进一步finetune,得到384bit模型(3bit*128)。在比赛的最后阶段,我们选择对128个code中的6个,量化bit从3bit压缩到2bit量化,进一步finetune,得到最终提交的378bit模型。即最终提交的378bit模型中,有122个code采用3bit量化编码,6个code采用2bit量化。
致谢
感谢主办方提供数据,感谢DataFountain平台提供支持和及时的问题反馈!
Code
modelDesign.py
# =======================================================================================================================
# =======================================================================================================================
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from collections import OrderedDict
NUM_FEEDBACK_BITS_STARTS = 768
NUM_FEEDBACK_BITS = 384
# pytorch版本一定要有这个参数
channel_last = 1
CR_dim = 128
REFINEMENT = 1
class Mish(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x):
x = x * (torch.tanh(torch.nn.functional.softplus(x)))
return x
ACT = nn.SiLU()
# =======================================================================================================================
# =======================================================================================================================
# Number to Bit Defining Function Defining
def Num2Bit(Num, B):
Num_ = Num.type(torch.uint8)
def integer2bit(integer, num_bits=B * 2):
dtype = integer.type()
exponent_bits = -torch.arange(-(num_bits - 1), 1).type(dtype)
exponent_bits = exponent_bits.repeat(integer.shape + (1,))
out = integer.unsqueeze(-1) // 2 ** exponent_bits
return (out - (out % 1)) % 2
bit = integer2bit(Num_)
bit = (bit[:, :, B:]).reshape(-1, Num_.shape[1] * B)
return bit.type(torch.float32)
def Bit2Num(Bit, B):
Bit_ = Bit.type(torch.float32)
Bit_ = torch.reshape(Bit_, [-1, int(Bit_.shape[1] / B), B])
num = torch.zeros(Bit_[:, :, 1].shape).cuda()
for i in range(B):
num = num + Bit_[:, :, i] * 2 ** (B - 1 - i)
return num
# =======================================================================================================================
# =======================================================================================================================
# Quantization and Dequantization Layers Defining
class Quantization(torch.autograd.Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, x, B):
ctx.constant = B
step = 2 ** B
out = torch.round(x * step - 0.5)
out = Num2Bit(out, B)
return out
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
# return as many input gradients as there were arguments.
# Gradients of constant arguments to forward must be None.
# Gradient of a number is the sum of its B bits.
b, _ = grad_output.shape
grad_num = torch.sum(grad_output.reshape(b, -1, ctx.constant), dim=2) / ctx.constant
return grad_num, None
class Dequantization(torch.autograd.Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, x, B):
ctx.constant = B
step = 2 ** B
out = Bit2Num(x, B)
out = (out + 0.5) / step
return out
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
# return as many input gradients as there were arguments.
# Gradients of non-Tensor arguments to forward must be None.
# repeat the gradient of a Num for B time.
b, c = grad_output.shape
grad_output = grad_output.unsqueeze(2) / ctx.constant
grad_bit = grad_output.expand(b, c, ctx.constant)
return torch.reshape(grad_bit, (-1, c * ctx.constant)), None
class QuantizationLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, B):
super(QuantizationLayer, self).__init__()
self.B = B
def forward(self, x):
out = Quantization.apply(x, self.B)
return out
class DequantizationLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, B):
super(DequantizationLayer, self).__init__()
self.B = B
def forward(self, x):
out = Dequantization.apply(x, self.B)
return out
# =======================================================================================================================
# =======================================================================================================================
# Encoder and Decoder Class Defining
def autopad(k, p=None):
# kernel, padding
# Pad to 'same'
if p is None:
p = k // 2 if isinstance(k, int) else [x // 2 for x in k]
# auto-pad
return p
class SEBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_channels, internal_neurons):
super(SEBlock, self).__init__()
self.down = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=input_channels, out_channels=internal_neurons, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
bias=True, padding_mode='circular')
self.up = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=internal_neurons, out_channels=input_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
bias=True, padding_mode='circular')
def forward(self, inputs):
x = F.avg_pool2d(inputs, kernel_size=inputs.size(3))
x = self.down(x)
x = F.leaky_relu(x)
x = self.up(x)
x = torch.sigmoid(x)
x = x.repeat(1, 1, inputs.size(2), inputs.size(3))
return inputs * x
class Conv(nn.Module):
# Standard convolution
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True):
# ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super(Conv, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p), groups=g, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)
self.act = ACT
def forward(self, x):
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
# Standard bottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
# ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, expansion
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e)
# hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, 3, 1, g=g)
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
def forward(self, x):
return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
class BottleneckCSP(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck https://github.com/WongKinYiu/CrossStagePartialNetworks
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
# ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super(BottleneckCSP, self).__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e)
# hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = nn.Conv2d(c1, c_, 1, 1, bias=False)
self.cv3 = nn.Conv2d(c_, c_, 1, 1, bias=False)
self.cv4 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1, 1)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(2 * c_)
# applied to cat(cv2, cv3)
self.act = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*[Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)])
self.att = SEBlock(c2, c2 // 2)
def forward(self, x):
y1 = self.cv3(self.m(self.cv1(x)))
y2 = self.cv2(x)
return self.att(self.cv4(self.act(self.bn(torch.cat((y1, y2), dim=1)))))
class C3(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck with 3 convolutions
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
# ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super(C3, self).__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e)
# hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1)
# act=FReLU(c2)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*[Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)])
# self.m = nn.Sequential(*[CrossConv(c_, c_, 3, 1, g, 1.0, shortcut) for _ in range(n)])
self.att = SEBlock(c2, c2 // 2)
def forward(self, x):
return self.att(self.cv3(torch.cat((self.m(self.cv1(x)), self.cv2(x)), dim=1)))
class Focus(nn.Module):
# Focus wh information into c-space
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True):
# ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super(Focus, self).__init__()
self.conv = Conv(c1 * 4, c2, k, s, p, g, act)
# self.contract = Contract(gain=2)
def forward(self, x):
# x(b,c,w,h) -> y(b,4c,w/2,h/2)
return self.conv(torch.cat([x[..., ::2, ::2], x[..., 1::2, ::2], x[..., ::2, 1::2], x[..., 1::2, 1::2]], 1))
# return self.conv(self.contract(x))
class Contract(nn.Module):
# Contract width-height into channels, i.e. x(1,64,80,80) to x(1,256,40,40)
def __init__(self, gain=2):
super().__init__()
self.gain = gain
def forward(self, x):
N, C, H, W = x.size()
# assert (H / s == 0) and (W / s == 0), 'Indivisible gain'
s = self.gain
x = x.view(N, C, H // s, s, W // s, s)
# x(1,64,40,2,40,2)
x = x.permute(0, 3, 5, 1, 2, 4).contiguous()
# x(1,2,2,64,40,40)
return x.view(N, C * s * s, H // s, W // s)
# x(1,256,40,40)
class Expand(nn.Module):
# Expand channels into width-height, i.e. x(1,64,80,80) to x(1,16,160,160)
def __init__(self, c1, c2, gain=2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True):
super().__init__()
self.gain = gain
self.conv = Conv(c1 // 4, c2, k, s, p, g, act)
def forward(self, x):
N, C, H, W = x.size()
# assert C / s ** 2 == 0, 'Indivisible gain'
s = self.gain
x = x.view(N, s, s, C // s ** 2, H, W)
# x(1,2,2,16,80,80)
x = x.permute(0, 3, 4, 1, 5, 2).contiguous()
# x(1,16,80,2,80,2)
return self.conv(x.view(N, C // s ** 2, H * s, W * s))
# x(1,16,160,160)
def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
"""3x3 convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=1, bias=True)
class WLBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, paths, in_c, k=16, n=[1, 1], e=[1.0, 1.0], quantization=True):
super(WLBlock, self).__init__()
self.paths = paths
self.n = n
self.e = e
self.k = k
self.in_c = in_c
for i in range(self.paths):
self.__setattr__(str(i), nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("Conv0", Conv(self.in_c, self.k, 3)),
("BCSP_1", BottleneckCSP(self.k, self.k, n=self.n[i], e=self.e[i])),
("C3_1", C3(self.k, self.k, n=self.n[i], e=self.n[i])),
("Conv1", Conv(self.k, self.k, 3)),
])))
self.conv1 = conv3x3(self.k * self.paths, self.k)
def forward(self, x):
outs = []
for i in range(self.paths):
_ = self.__getattr__(str(i))(x)
outs.append(_)
out = torch.cat(tuple(outs), dim=1)
out = self.conv1(out)
out = out + x if self.in_c == self.k else out
return out
class Encoder(nn.Module):
B = 3
def __init__(self, feedback_bits, quantization=True):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.feedback_bits = feedback_bits
self.k = 256
self.encoder1 = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("Conv0", Conv(2, 16, 5)),
("BCSP_1", BottleneckCSP(16, 16, n=2, e=0.5)),
("C3_1", C3(16, 16, n=1, e=2.0)),
("Conv1", Conv(16, self.k, 3))
]))
self.encoder2 = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("Focus0", Focus(2, 16)),
("BCSP_1", BottleneckCSP(16, 16, n=1, e=1.0)),
("C3_1", C3(16, 16, n=2, e=2.0)),
("Expand0", Expand(16, 16)),
("Conv1", Conv(16, self.k, 3))
]))
self.encoder3 = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("Conv0", Conv(2, 32, 3)),
("WLBlock1", WLBlock(3, 32, 32, [1, 2, 3], [0.5, 1, 1.5])),
("WLBlock2", WLBlock(2, 32, 32, [2, 4], [1, 2])),
("Conv1", Conv(32, self.k, 3)),
]))
self.encoder_conv = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("conv1x1", Conv(self.k * 3, 2, 1)),
]))
self.fc = nn.Linear(768, int(NUM_FEEDBACK_BITS_STARTS / self.B))
self.dim_verify = nn.Linear(int(NUM_FEEDBACK_BITS_STARTS / self.B), int(self.feedback_bits / self.B))
self.sig = nn.Sigmoid()
self.quantize = QuantizationLayer(self.B)
self.quantization = quantization
def forward(self, x):
if channel_last:
x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous()
x0 = x.view(-1, 768)
encoder1 = self.encoder1(x)
encoder2 = self.encoder2(x)
encoder3 = self.encoder3(x)
out = torch.cat((encoder1, encoder2, encoder3), dim=1)
out = self.encoder_conv(out)
out = out.view(-1, 768) + x0
out = self.fc(out)
out = self.dim_verify(out)
out = self.sig(out)
enq_data = out
if self.quantization:
out = self.quantize(out)
elif self.quantization == 'check':
out = out
else:
out = self.fake_quantize(out)
return out, enq_data
class Decoder(nn.Module):
B = 3
def __init__(self, feedback_bits, quantization=True):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.k = 64
self.feedback_bits = feedback_bits
self.dequantize = DequantizationLayer(self.B)
self.dim_verify = nn.Linear(int(self.feedback_bits / self.B), int(NUM_FEEDBACK_BITS_STARTS / self.B))
self.fc = nn.Linear(int(NUM_FEEDBACK_BITS_STARTS / self.B), 768)
self.ende_refinement = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(int(self.feedback_bits / self.B), int(self.feedback_bits / self.B)),
nn.BatchNorm1d(int(self.feedback_bits / self.B)),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(int(self.feedback_bits / self.B), int(self.feedback_bits / self.B), bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid(),
)
self.decoder1 = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("Conv0", Conv(2, 16, 3)),
("BCSP_1", BottleneckCSP(16, 16, n=1, e=1.0)),
("Conv1", Conv(16, self.k, 1)),
]))
self.decoder2 = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("Conv0", Conv(2, 32, 5)),
("BCSP_1", BottleneckCSP(32, 32, n=4, e=2.0)),
("Conv1", Conv(32, self.k, 1)),
]))
self.decoder3 = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("Conv0", Conv(2, 32, (1, 3))),
("BCSP_1", BottleneckCSP(32, 32, n=4, e=2.0)),
("Conv1", Conv(32, self.k, 1)),
]))
self.decoder4 = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("Conv0", Conv(2, 32, (3, 1))),
("BCSP_1", BottleneckCSP(32, 32, n=4, e=2.0)),
("Conv1", Conv(32, self.k, 1)),
]))
self.decoder5 = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("Focus0", Focus(2, self.k)),
("WLBlock1", WLBlock(3, self.k, self.k, [1, 2, 3], [0.5, 1, 1.5])),
("WLBlock2", WLBlock(2, self.k, self.k, [2, 4], [1, 2])),
("Expand0", Expand(self.k, self.k)),
("Conv1", Conv(self.k, self.k, 1)),
]))
self.decoder6 = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("Conv0", Conv(2, 32, (3, 5))),
("BCSP_1", BottleneckCSP(32, 32, n=4, e=2.0)),
("Conv1", Conv(32, self.k, 5)),
]))
self.decoder7 = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("Conv0", Conv(2, 32, (5, 3))),
("BCSP_1", BottleneckCSP(32, 32, n=4, e=2.0)),
("Conv1", Conv(32, self.k, 3)),
]))
self.decoder8 = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("Focus0", Focus(2, self.k, 5)),
("WLBlock1", WLBlock(2, self.k, self.k, [1, 2], [0.5, 1])),
("WLBlock2", WLBlock(2, self.k, self.k, [1, 2], [1, 0.5])),
("Expand0", Expand(self.k, self.k)),
("Conv1", Conv(self.k, self.k, 5)),
]))
if REFINEMENT:
self.refinemodel = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("Conv0", Conv(2, 64, 3)),
("WLBlock1", WLBlock(3, 64, 64, [1, 2, 3], [0.5, 1, 1.5])),
("WLBlock2", WLBlock(2, 64, 64, [2, 4], [1, 2])),
("WLBlock3", WLBlock(2, 64, 64, [2, 4], [1, 2])),
("WLBlock4", WLBlock(2, 64, 64, [1, 3], [1, 2])),
("Conv1", Conv(64, 2, 3)),
]))
self.decoder_conv = conv3x3(self.k * 8, 2)
self.sig = nn.Sigmoid()
self.quantization = quantization
def forward(self, x):
if self.quantization:
out = self.dequantize(x)
else:
out = x
out = out.view(-1, int(self.feedback_bits / self.B))
out_error = self.ende_refinement(out)
out = out + out_error - 0.5
deq_data = out
out = self.dim_verify(out)
out = self.sig(self.fc(out))
out = out.view(-1, 2, 24, 16)
out0 = out
out1 = self.decoder1(out)
out2 = self.decoder2(out)
out3 = self.decoder3(out)
out4 = self.decoder4(out)
out5 = self.decoder5(out)
out6 = self.decoder6(out)
out7 = self.decoder7(out)
out8 = self.decoder8(out)
out = torch.cat((out1, out2, out3, out4, out5, out6, out7, out8), dim=1)
out = self.decoder_conv(out) + out0
out = self.sig(out)
if REFINEMENT:
out = self.sig(self.refinemodel(out)) - 0.5 + out
if channel_last:
out = out.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
return out, deq_data
class AutoEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, feedback_bits):
super(AutoEncoder, self).__init__()
self.encoder = Encoder(feedback_bits)
self.decoder = Decoder(feedback_bits)
def forward(self, x):
feature, enq_data = self.encoder(x)
out, deq_data = self.decoder(feature)
return out, feature, enq_data, deq_data
# =======================================================================================================================
# =======================================================================================================================
# NMSE Function Defining
def NMSE(x, x_hat):
x_real = np.reshape(x[:, :, :, 0], (len(x), -1))
x_imag = np.reshape(x[:, :, :, 1], (len(x), -1))
x_hat_real = np.reshape(x_hat[:, :, :, 0], (len(x_hat), -1))
x_hat_imag = np.reshape(x_hat[:, :, :, 1], (len(x_hat), -1))
x_C = x_real - 0.5 + 1j * (x_imag - 0.5)
x_hat_C = x_hat_real - 0.5 + 1j * (x_hat_imag - 0.5)
power = np.sum(abs(x_C) ** 2, axis=1)
mse = np.sum(abs(x_C - x_hat_C) ** 2, axis=1)
nmse = np.mean(mse / power)
return nmse
def Score(NMSE):
score = 1 - NMSE
return score
def NMSE_cuda(x, x_hat):
x_real = x[:, 0, :, :].view(len(x), -1) - 0.5
x_imag = x[:, 1, :, :].view(len(x), -1) - 0.5
x_hat_real = x_hat[:, 0, :, :].view(len(x_hat), -1) - 0.5
x_hat_imag = x_hat[:, 1, :, :].view(len(x_hat), -1) - 0.5
power = torch.sum(x_real ** 2 + x_imag ** 2, axis=1)
mse = torch.sum((x_real - x_hat_real) ** 2 + (x_imag - x_hat_imag) ** 2, axis=1)
nmse = mse / power
return nmse
class NMSELoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, reduction='sum'):
super(NMSELoss, self).__init__()
self.reduction = reduction
def forward(self, x_hat, x):
nmse = NMSE_cuda(x, x_hat)
if self.reduction == 'mean':
nmse = torch.mean(nmse)
else:
nmse = torch.sum(nmse)
return nmse
# =======================================================================================================================
# =======================================================================================================================
import random
# Data Loader Class Defining
class DatasetFolder(Dataset):
def __init__(self, matData, phase='val'):
self.matdata = matData
self.phase = phase
def __getitem__(self, index):
y = self.matdata[index]
if self.phase == 'train' and random.random() < -0.5:
y = y[::-1, :, :].copy()
if self.phase == 'train' and random.random() < 0.5:
y = y[:, ::-1, :].copy()
if self.phase == 'train' and random.random() < 0.5:
y = 1 - self.matdata[index]
# 数据中存在类似正交的关系
if self.phase == 'train' and random.random() < 0.5:
_ = y
_[:, :, 0] = y[:, :, 1]
_[:, :, 1] = y[:, :, 0]
y = _
# 不同时刻数据实虚存在部分相等的情况
if self.phase == 'train' and random.random() < 0.5:
index_ = random.randint(0, self.matdata.shape[0] // 3000 - 1) * 3000 + index % 3000
p = random.random()
rows = max(int(24 * p), 1)
_rows = [i for i in range(24)]
random.shuffle(_rows)
_rows = _rows[:rows]
if random.random() < 0.7:
y[_rows] = self.matdata[index_][_rows]
# 不同采样点按行合并,保持采样点独有特性,减轻模型对24那个维度的依赖
else:
y = (1 - p * 0.2) * y + (p * 0.2) * self.matdata[index_]
# 增加数值扰动,保持采样点独有特性
return y
def __len__(self):
return self.matdata.shape[0]
modelTrain.py
#=======================================================================================================================
#=======================================================================================================================
import numpy as np
import torch
from modelDesign import AutoEncoder,DatasetFolder,NUM_FEEDBACK_BITS,NUM_FEEDBACK_BITS_STARTS,NMSELoss,channel_last #*
import os
import torch.nn as nn
import scipy.io as sio
import random
from torch.cuda.amp import autocast, GradScaler
def NMSE_cuda1(x, x_hat):
x_real = x[:, :, :, 0].view(len(x),-1) - 0.5
x_imag = x[:, :, :, 1].view(len(x),-1) - 0.5
x_hat_real = x_hat[:, :, :, 0].view(len(x_hat), -1) - 0.5
x_hat_imag = x_hat[:, :, :, 1].view(len(x_hat), -1) - 0.5
power = torch.sum(x_real**2 + x_imag**2, axis=1)
mse = torch.sum((x_real-x_hat_real)**2 + (x_imag-x_hat_imag)**2, axis=1)
nmse = mse/power
return nmse
class NMSELoss1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, reduction='sum'):
super(NMSELoss1, self).__init__()
self.reduction = reduction
def forward(self, x_hat, x):
nmse = NMSE_cuda1(x, x_hat)
if self.reduction == 'mean':
nmse = torch.mean(nmse)
else:
nmse = torch.sum(nmse)
return nmse
#=======================================================================================================================
#=======================================================================================================================
# Parameters Setting for Data
CHANNEL_SHAPE_DIM1 = 24
CHANNEL_SHAPE_DIM2 = 16
CHANNEL_SHAPE_DIM3 = 2
# Parameters Setting for Training
BATCH_SIZE = 64
EPOCHS = 1000
LEARNING_RATE = 1e-5
PRINT_RREQ = 100
#NUM_FEEDBACK_BITS =NUM_FEEDBACK_BITS_3
torch.manual_seed(42)
random.seed(42)
#=======================================================================================================================
#=======================================================================================================================
def load_pretrained_weights(model,model_path):
encoder_pretrained = torch.load(model_path)['state_dict']
model_dict = model.state_dict()
#pretrained_weights ={k:v for k,v in encoder_pretrained.items() if (k in model_dict and 'dim_verify' not in k and 'ende_refinement' not in k and 'fc' not in k)}
pretrained_weights ={k:v for k,v in encoder_pretrained.items() if (k in model_dict )}
# prune dim_verify layer
if 0 and NUM_FEEDBACK_BITS != NUM_FEEDBACK_BITS_STARTS:
w = encoder_pretrained['dim_verify.weight']
b = encoder_pretrained['dim_verify.bias']
if
model_dict['dim_verify.weight'].shape[0] != encoder_pretrained['dim_verify.weight'].shape[0]:
dim = -1
bits_num =model_dict['dim_verify.weight'].shape[0]
long = encoder_pretrained['dim_verify.weight'].shape[0]
else:
dim = 0
bits_num =model_dict['dim_verify.weight'].shape[1]
long = encoder_pretrained['dim_verify.weight'].shape[1]
#importance = abs(w).sum(dim)
#sorted_index = torch.argsort(-1*importance) # descend
start = (long -bits_num)//2
end = bits_num + (long - bits_num)//2
if dim == -1:
pretrained_weights['dim_verify.weight'] = w[start:end,:]
else:
pretrained_weights['dim_verify.weight'] = w[:,start:end]
model_dict.update(pretrained_weights)
model.load_state_dict(model_dict)
return model
# Model Constructing
autoencoderModel = AutoEncoder(NUM_FEEDBACK_BITS)
# model_path = './modelSubmit/encoder.pth.tar'
# autoencoderModel.encoder =load_pretrained_weights(autoencoderModel.encoder,model_path)
# model_path = './modelSubmitTeacher/decoder.pth.tar'
# autoencoderModel.decoder =load_pretrained_weights(autoencoderModel.decoder,model_path)
model_path = './modelSubmit/encoder.pth.tar'
autoencoderModel.encoder.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path)['state_dict'])
model_path = './modelSubmit/decoder.pth.tar'
autoencoderModel.decoder.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path)['state_dict'])
#=======================================================================================================================
#=======================================================================================================================
# Data Loading
mat = sio.loadmat('channelData/H_4T4R.mat')
data = mat['H_4T4R']
data = data.astype('float32')
data = np.reshape(data, (-1, CHANNEL_SHAPE_DIM1, CHANNEL_SHAPE_DIM2, CHANNEL_SHAPE_DIM3))
if not channel_last:
data = np.transpose(data, (0, 3, 1, 2))
#random.shuffle(data)
split = int(data.shape[0] * 0.95)
data_train0, data_test = data[:split], data[split:]
random.shuffle(data_train0)
split = int(data_train0.shape[0]*0.95)
data_train, data_val = data_train0[:split],data_train0[split:]
train_dataset = DatasetFolder(data_train0,'train')
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True, num_workers=0, pin_memory=True)
val_dataset = DatasetFolder(data_val,'val')
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False, num_workers=0, pin_memory=True)
test_dataset = DatasetFolder(data_test,'val')
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False, num_workers=0, pin_memory=True)
#=======================================================================================================================
#=======================================================================================================================
#autoencoderModel = autoencoderModel.cuda()
autoencoderModel = torch.nn.DataParallel(autoencoderModel.cuda())
ctl = NMSELoss1(reduction='mean') if channel_last else NMSELoss(reduction='mean')
criterion = ctl #nn.MSELoss()
criterion_test = ctl
feature_criterion = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(autoencoderModel.parameters(), lr=LEARNING_RATE)
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingWarmRestarts(optimizer, T_0=20, T_mult=1, eta_min=1e-9, last_epoch=-1)
#=======================================================================================================================
#=======================================================================================================================
# Model Training and Saving
bestLoss = 0.105
valLoss = 1e-5
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
scaler = GradScaler()
print('lr:',optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr'])
autoencoderModel.train()
for i, autoencoderInput in enumerate(train_loader):
autoencoderInput = autoencoderInput.cuda()
with autocast():
autoencoderOutput,_, enq, deq = autoencoderModel(autoencoderInput)
loss1 = criterion(autoencoderOutput, autoencoderInput)
loss2 = feature_criterion(enq, deq)
loss = loss1+0*loss2
scaler.scale(loss).backward()
scaler.step(optimizer)
scaler.update()
optimizer.zero_grad()
if i % PRINT_RREQ == 0:
print('Epoch: [{0}][{1}/{2}]t' 'Loss {loss:.4f}t,Loss_nmse {loss_nmse:.4f}t,Loss ende {loss_q:.4f}t'.format(epoch,
i, len(train_loader), loss=loss.item(),loss_nmse=loss1.item(),loss_q=loss2.item()))
# if (i+1) % (4*PRINT_RREQ) == 0:
#
break
# Model Evaluating
autoencoderModel.eval()
totalLoss = 0
hist =0
with torch.no_grad():
for i, autoencoderInput in enumerate(val_loader):
autoencoderInput = autoencoderInput.cuda()
autoencoderOutput, feature, enq, deq
= autoencoderModel(autoencoderInput)
hist = hist+feature.sum(0)/autoencoderInput.shape[0]
totalLoss += criterion_test(autoencoderOutput, autoencoderInput).item()*autoencoderInput.shape[0]
averageLoss = totalLoss / len(test_dataset)
loss2 = feature_criterion(enq, deq)
print('==random split test step==')
print(np.std(hist.cpu().numpy()))
print(averageLoss,loss2.item())
valavgloss = averageLoss
totalLoss = 0
hist =0
with torch.no_grad():
for i, autoencoderInput in enumerate(test_loader):
autoencoderInput = autoencoderInput.cuda()
autoencoderOutput, feature, enq, deq
= autoencoderModel(autoencoderInput)
hist = hist+feature.sum(0)/autoencoderInput.shape[0]
totalLoss += criterion_test(autoencoderOutput, autoencoderInput).item()*autoencoderInput.shape[0]
averageLoss = totalLoss / len(test_dataset)
loss2 = feature_criterion(enq, deq)
print('==last split test step==')
print(np.std(hist.cpu().numpy()))
print(averageLoss,loss2.item())
if averageLoss < bestLoss:
# Model saving
# Encoder Saving
torch.save({'state_dict': autoencoderModel.module.encoder.state_dict(), }, './modelSubmit/encoder.pth.tar')
# Decoder Saving
torch.save({'state_dict': autoencoderModel.module.decoder.state_dict(), }, './modelSubmit/decoder.pth.tar')
print("Model saved,avgloss:",averageLoss)
bestLoss = averageLoss
valLoss = valavgloss
print('==show best==')
print('valloss:', valLoss, 'testloss:',bestLoss)
if epoch>0*50:
scheduler.step()
#break
#=======================================================================================================================
#=======================================================================================================================
最后
以上就是昏睡羊最近收集整理的关于AI+无线通信——Top7 (Baseline)总结队伍介绍方案Code的全部内容,更多相关AI+无线通信——Top7内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复