介绍
MyBatis 是支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射,它避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集,它可以使用简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原生信息,将接口和 Java 的 POJOs(Plain Old Java Objects,普通的 Java对象)映射成数据库中的记录。
架构
构造由数据源配置文件、SQL映射配置文件、会话工厂、会话、执行器、底层封装对象组成!
数据源:
负责连接数据库,并对数据进行操作的一套框架,连接数据库是最重要的一步!!!
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2 <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
3 <configuration>
4
5 <!-- 引用db.properties配置文件 -->
6 <properties resource="db.properties"/>
7 <!--
8 development : 开发模式
9 work : 工作模式
10 -->
11 <environments default="development">
12 <environment id="development">
13 <transactionManager type="JDBC" />
14 <!-- 配置数据库连接信息 -->
15 <dataSource type="POOLED">
16 <!-- value属性值引用db.properties配置文件中配置的值 -->
17 <property name="driver" value="${driver}" />
18 <property name="url" value="${url}" />
19 <property name="username" value="${name}" />
20 <property name="password" value="${password}" />
21 </dataSource>
22 </environment>
23 </environments>
24
25 </configuration>SQL映射配置文件:
Mapper配置文件,可以配置任何类型的SQL语句,包括select、update、delete、insert。
INSERT
我们在Mapper XML的文件中使用<insert>来配置INSERT的语言。如下:
<insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="Student">
INSERT INTO STUDENTS(STUD_ID,NAME,EMAIL, PHONE)
VALUES(#{studId},#{name},#{email},#{phone})
</insert>
在这儿,我们给出了inSertStudent作为ID,这个可以关联的独有的命名空间是:com.owen.mybatis.mappers.StuentMapper.insertStudent.我们定义的parameterType的属性值必须是完整的限定名,或是别名。我们可以执行上面的代码如下:
int count =
sqlSession.insert("com.owen.mybatis.mappers.StudentMapper.insertStuden
t", student);
这个sqlSession.insert()方法返回的数值就是插入的行数。取代上面通过命名空间和声明的ID,你可以创建一个Mapper的接口和调用的方式如下:
package com.owen.mybatis.mappers;
public interface StudentMapper
{
int insertStudent(Student student);
}
你可以调用的insertStudent映射声明如下:
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
int count = mapper.insertStudent(student);
这样的方式比Hibernate好用了,不是使用固定的格式,而是通过自己的想法至尊命名,然后去调用。自动生成Key
在前面的INSERT声明中,我们插入STUDENT的表时,使用了自己手动的STUD_ID作为主键的列值。其实我们可以应用一个useGeneratedKeys和keyProperty属性来生成auto_increment列的值,而将生成的值赋予给STUD_ID.
<insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="Student"
useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="studId">
INSERT INTO STUDENTS(NAME, EMAIL, PHONE)
VALUES(#{name},#{email},#{phone})
</insert>
这里的STUD_ID值将会由MySQL数据库自动生成,而且生成的值将会给student对象的参数studId。
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
mapper.insertStudent(student);
现在你可以获取STUD_ID的值:
int studentId = student.getStudId();
一些数据库,如Oracle不能够提供AUTO_INCREMENT列和运用SEQUENCE去创建主键的值。现在,我们拥有一个SEQUENCE名称为STUD_ID_SEQ去生成STUD_ID的主键值。运用的代码如下:
<insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="Student">
<selectKey keyProperty="studId" resultType="int" order="BEFORE">
SELECT ELEARNING.STUD_ID_SEQ.NEXTVAL FROM DUAL
</selectKey>
INSERT INTO STUDENTS(STUD_ID,NAME,EMAIL, PHONE)
VALUES(#{studId},#{name},#{email},#{phone})
</insert>
这里我们运用了<selectKey>的子元素去生成一个主键的值,并且储蓄它在Student对象的studId的属性中。我们设置属性order=”BEFORE”,这个说明MyBatis在执行INSERT之前,会先对已有的主键进行排序,然后将主键储蓄到studId中。
当然, 我们也可以用触发器来设置主键值,可以从序列中获得一个主键值,并将其设置为主键的列值插入到查询中。如果你使用这个方法,你可以用下面的代码:
<insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="Student">
INSERT INTO STUDENTS(NAME,EMAIL, PHONE)
VALUES(#{name},#{email},#{phone})
<selectKey keyProperty="studId" resultType="int" order="AFTER">
SELECT ELEARNING.STUD_ID_SEQ.CURRVAL FROM DUAL
</selectKey>
</insert> 声明UPDATE
UPDATE的声明可以使用<update>的元素配置在MapperXML文件中。
<update id="updateStudent" parameterType="Student">
UPDATE STUDENTS SET NAME=#{name}, EMAIL=#{email}, PHONE=#{phone}
WHERE STUD_ID=#{studId}
</update>
我们可以使用如下的代码来调用声明:
int noOfRowsUpdated =
sqlSession.update("com.owen.mybatis.mappers.StudentMapper.updateStudent",
student);
通过UPDATE的声明,sqlSession().update()方法将会返回受影响的行。
这里我们就不使用声明的命名空间和声明的id来执行,我们使用Mapper的接口和调用 方法如下:
package com.owen.mybatis.mappers;
public interface StudentMapper
{
int updateStudent(Student student);
}
你可发调用updateStudent声明使用Mapper接口。
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
int noOfRowsUpdated = mapper.updateStudent(student); 会话工厂、会话:
SqlSessionFactory类会根据Resource资源信息加载对象,获取开发人员在项目中配置的数据库连接池配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml信息,从而产生一种可与数据库交互的会话实例SqlSession.
//MyBatis的配置文件
Stringresource= "SqlMapConfig.xml";
InputStreaminputStream= Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//创建会话工厂
SqlSessionFactorysqlSessionFactory= newSqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//从会话工厂中得到会话
SqlSessionsqlSession= sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
Useruser= sqlSession.selectOne("test.findUserByName","jasber");
System.out.println("-------------------------------------result-----------------------------------");
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
//关闭session
sqlSession.close(); 执行器:
SimpleExecutor继承BaseExecutor
主要实现:doUpdate、doQuery、doFlushStatements
可以看代码主要是:
1、获取声明处理类:StatementHandler handler
2、获取声明类:stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
3、处理声明,执行SQL处理底层封装对象:
<resultMap id="SmsHouseholdOrderDto" type="com.dzmsoft.sms.base.dto.SmsHouseholdOrderDto">
<id column="id_smsOrder" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="id" />
<association column="id_smsHouseholdOrder" javaType="com.dzmsoft.sms.base.pojo.SmsHouseholdOrder" property="smsHouseholdOrder" resultMap="com.dzmsoft.sms.base.dao.SmsHouseholdOrderMapper.BaseResultUdfMap">
</association>
<association column="id_smsOrder" javaType="com.dzmsoft.sms.base.pojo.SmsOrder" property="smsOrder" resultMap="com.dzmsoft.sms.base.dao.SmsOrderMapper.BaseResultUdfMap">
</association>
</resultMap>public class SmsHouseholdOrderDto {
private String id;
private SmsHouseholdOrder smsHouseholdOrder;
private SmsOrder smsOrder;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public SmsHouseholdOrder getSmsHouseholdOrder() {
return smsHouseholdOrder;
}
public void setSmsHouseholdOrder(SmsHouseholdOrder smsHouseholdOrder) {
this.smsHouseholdOrder = smsHouseholdOrder;
}
public SmsOrder getSmsOrder() {
return smsOrder;
}
public void setSmsOrder(SmsOrder smsOrder) {
this.smsOrder = smsOrder;
}
}自定义字段
<sql id="Base_Column_List_Udf">
smsOrder.id id_smsOrder, smsOrder.order_time order_time_smsOrder, smsOrder.appointment_time appointment_time_smsOrder, smsOrder.director director_smsOrder, smsOrder.status status_smsOrder, smsOrder.member member_smsOrder
, smsOrder.address address_smsOrder, smsOrder.individual_needs individual_needs_smsOrder,
smsOrder.order_type order_type_smsOrder, smsOrder.member_phone member_phone_smsOrder,smsOrder.member_name member_name_smsOrder
</sql><sql id="Base_Column_List_Udf">
smsHouseholdOrder.id id_smsHouseholdOrder, smsHouseholdOrder.order_id order_id_smsHouseholdOrder, smsHouseholdOrder.times times_smsHouseholdOrder, smsHouseholdOrder.price price_smsHouseholdOrder
, smsHouseholdOrder.discount discount_smsHouseholdOrder, smsHouseholdOrder.amount amount_smsHouseholdOrder
</sql>层次架构
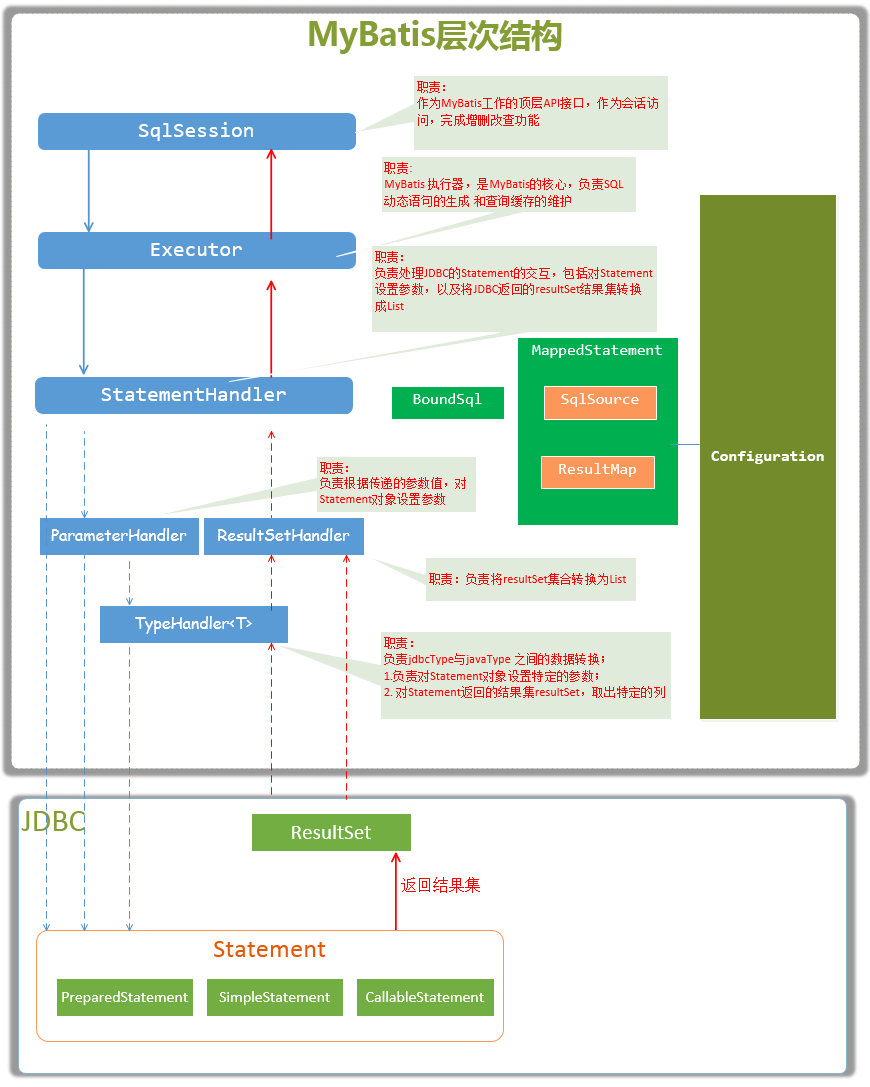
MyBatis的主要成员
Configuration MyBatis所有的配置信息都保存在Configuration对象之中,配置文件中的大部分配置都会存储到该类中SqlSession 作为MyBatis工作的主要顶层API,表示和数据库交互时的会话,完成必要数据库增删改查功能
Executor MyBatis执行器,是MyBatis 调度的核心,负责SQL语句的生成和查询缓存的维护
StatementHandler 封装了JDBC Statement操作,负责对JDBC statement 的操作,如设置参数等
ParameterHandler 负责对用户传递的参数转换成JDBC Statement 所对应的数据类型
ResultSetHandler 负责将JDBC返回的ResultSet结果集对象转换成List类型的集合
TypeHandler 负责java数据类型和jdbc数据类型(也可以说是数据表列类型)之间的映射和转换
MappedStatement MappedStatement维护一条<select|update|delete|insert>节点的封装
SqlSource 负责根据用户传递的parameterObject,动态地生成SQL语句,将信息封装到BoundSql对象中,并返回
BoundSql 表示动态生成的SQL语句以及相应的参数信息
以上主要成员在一次数据库操作中基本都会涉及,在SQL操作中重点需要关注的是SQL参数什么时候被设置和结果集怎么转换为JavaBean对象的,这两个过程正好对应StatementHandler和ResultSetHandler类中的处理逻辑。
运行流程
1 使用连接池
2 统一sql 存取xml
3 参数封装和结果映射
4 sql语句的复用封装
(1)加载配置并初始化:触发条件:加载配置文件.配置来源于两个地方,一处是配置文件,一处是Java代码的注解,将SQL的配置信息加载成为一个个MappedStatement对象(包括了传入参数映射配置、执行的SQL语句、结果映射配置),存储在内存中。
(2)接收调用请求:触发条件:调用Mybatis提供的API。传入参数:为SQL的ID和传入参数对象。处理过程:将请求传递给下层的请求处理层进行处理。
(3)处理操作请求 触发条件:API接口层传递请求过来。传入参数:为SQL的ID和传入参数对象。
(4)返回处理结果将最终的处理结果返回。配置文件详解
| 名称 | 含义 | 简介 |
| configuration | 顶级配置 | 顶级配置 |
| properties | 属性 | 这些属性都是可外部配置且可动态替换的,既可以在典型的 Java 属性文件中配置,亦可通过 properties 元素的子元素来传递。 |
| settings | 设置 | 这是 MyBatis 中极为重要的调整设置,它们会改变 MyBatis 的运行时行为。下表描述了设置中各项的意图、默认值等。 |
| typeAliases | 类型别名 | 类型别名是为 Java 类型设置一个短的名字。它只和 XML 配置有关,存在的意义仅在于用来减少类完全限定名的冗余。 |
| typeHandlers | 类型处理器 | 无论是 MyBatis 在预处理语句(PreparedStatement)中设置一个参数时,还是从结果集中取出一个值时, 都会用类型处理器将获取的值以合适的方式转换成 Java 类型。下表描述了一些默认的类型处理器。 |
| objectFactory | 对象工厂 | MyBatis 每次创建结果对象的新实例时,它都会使用一个对象工厂(ObjectFactory)实例来完成。 默认的对象工厂需要做的仅仅是实例化目标类,要么通过默认构造方法,要么在参数映射存在的时候通过参数构造方法来实例化。 如果想覆盖对象工厂的默认行为,则可以通过创建自己的对象工厂来实现。 |
| plugins | 插件 | MyBatis 允许你在已映射语句执行过程中的某一点进行拦截调用。 |
| environments | 环境 | MyBatis 可以配置成适应多种环境,这种机制有助于将 SQL 映射应用于多种数据库之中, 现实情况下有多种理由需要这么做。 |
| environment | 环境变量 | 同上 |
| transactionManager | 事务管理器 | 这个配置就是直接使用了 JDBC 的提交和回滚设置,它依赖于从数据源得到的连接来管理事务作用域。 |
| dataSource | 数据源 | dataSource 元素使用标准的 JDBC 数据源接口来配置 JDBC 连接对象的资源。 |
| databaseIdProvider | 数据库厂商标识 | MyBatis 可以根据不同的数据库厂商执行不同的语句,这种多厂商的支持是基于映射语句中的 databaseId 属性。 |
| mappers | 映射器 | 既然 MyBatis 的行为已经由上述元素配置完了,我们现在就要定义 SQL 映射语句了。 |
Setting
设置参数 描述 有效值 默认值
cacheEnabled 全局地开启或关闭配置文件中的所有映射器已经配置的任何缓存。 true | false true
lazyLoadingEnabled 延迟加载的全局开关。当开启时,所有关联对象都会延迟加载。 特定关联关系中可通过设置fetchType属性来覆盖该项的开关状态。 true | false false
aggressiveLazyLoading 当开启时,任何方法的调用都会加载该对象的所有属性。否则,每个属性会按需加载(参考lazyLoadTriggerMethods). true | false false (true in ≤3.4.1)
multipleResultSetsEnabled 是否允许单一语句返回多结果集(需要兼容驱动)。 true | false true
useColumnLabel 使用列标签代替列名。不同的驱动在这方面会有不同的表现, 具体可参考相关驱动文档或通过测试这两种不同的模式来观察所用驱动的结果。 true | false true
useGeneratedKeys 允许 JDBC 支持自动生成主键,需要驱动兼容。 如果设置为 true 则这个设置强制使用自动生成主键,尽管一些驱动不能兼容但仍可正常工作(比如 Derby)。 true | false False
autoMappingBehavior 指定 MyBatis 应如何自动映射列到字段或属性。 NONE 表示取消自动映射;PARTIAL 只会自动映射没有定义嵌套结果集映射的结果集。 FULL 会自动映射任意复杂的结果集(无论是否嵌套)。 NONE, PARTIAL, FULL PARTIAL
autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior 指定发现自动映射目标未知列(或者未知属性类型)的行为。
NONE: 不做任何反应
WARNING: 输出提醒日志 ('org.apache.ibatis.session.AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior' 的日志等级必须设置为 WARN)
FAILING: 映射失败 (抛出 SqlSessionException)
NONE, WARNING, FAILING NONE
defaultExecutorType 配置默认的执行器。SIMPLE 就是普通的执行器;REUSE 执行器会重用预处理语句(prepared statements); BATCH 执行器将重用语句并执行批量更新。 SIMPLE REUSE BATCH SIMPLE
defaultStatementTimeout 设置超时时间,它决定驱动等待数据库响应的秒数。 任意正整数 Not Set (null)
defaultFetchSize 为驱动的结果集获取数量(fetchSize)设置一个提示值。此参数只可以在查询设置中被覆盖。 任意正整数 Not Set (null)
safeRowBoundsEnabled 允许在嵌套语句中使用分页(RowBounds)。如果允许使用则设置为false。 true | false False
safeResultHandlerEnabled 允许在嵌套语句中使用分页(ResultHandler)。如果允许使用则设置为false。 true | false True
mapUnderscoreToCamelCase 是否开启自动驼峰命名规则(camel case)映射,即从经典数据库列名 A_COLUMN 到经典 Java 属性名 aColumn 的类似映射。 true | false False
localCacheScope MyBatis 利用本地缓存机制(Local Cache)防止循环引用(circular references)和加速重复嵌套查询。 默认值为 SESSION,这种情况下会缓存一个会话中执行的所有查询。 若设置值为 STATEMENT,本地会话仅用在语句执行上,对相同 SqlSession 的不同调用将不会共享数据。 SESSION | STATEMENT SESSION
jdbcTypeForNull 当没有为参数提供特定的 JDBC 类型时,为空值指定 JDBC 类型。 某些驱动需要指定列的 JDBC 类型,多数情况直接用一般类型即可,比如 NULL、VARCHAR 或 OTHER。 JdbcType 常量. 大多都为: NULL, VARCHAR and OTHER OTHER
lazyLoadTriggerMethods 指定哪个对象的方法触发一次延迟加载。 用逗号分隔的方法列表。 equals,clone,hashCode,toString
defaultScriptingLanguage 指定动态 SQL 生成的默认语言。 一个类型别名或完全限定类名。 org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.XMLLanguageDriver
defaultEnumTypeHandler 指定 Enum 使用的默认 TypeHandler 。 (从3.4.5开始) 一个类型别名或完全限定类名。 org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumTypeHandler
callSettersOnNulls 指定当结果集中值为 null 的时候是否调用映射对象的 setter(map 对象时为 put)方法,这对于有 Map.keySet() 依赖或 null 值初始化的时候是有用的。注意基本类型(int、boolean等)是不能设置成 null 的。 true | false false
returnInstanceForEmptyRow 当返回行的所有列都是空时,MyBatis默认返回null。 当开启这个设置时,MyBatis会返回一个空实例。 请注意,它也适用于嵌套的结果集 (i.e. collectioin and association)。(从3.4.2开始) true | false false
logPrefix 指定 MyBatis 增加到日志名称的前缀。 任何字符串 Not set
logImpl 指定 MyBatis 所用日志的具体实现,未指定时将自动查找。 SLF4J | LOG4J | LOG4J2 | JDK_LOGGING | COMMONS_LOGGING | STDOUT_LOGGING | NO_LOGGING Not set
proxyFactory 指定 Mybatis 创建具有延迟加载能力的对象所用到的代理工具。 CGLIB | JAVASSIST JAVASSIST (MyBatis 3.3 or above)
vfsImpl 指定VFS的实现 自定义VFS的实现的类全限定名,以逗号分隔。 Not set
useActualParamName 允许使用方法签名中的名称作为语句参数名称。 为了使用该特性,你的工程必须采用Java 8编译,并且加上-parameters选项。(从3.4.1开始) true | false true
configurationFactory 指定一个提供Configuration实例的类。 这个被返回的Configuration实例用来加载被反序列化对象的懒加载属性值。 这个类必须包含一个签名方法static Configuration getConfiguration(). (从 3.2.3 版本开始) 类型别名或者全类名. Not set<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="multipleResultSetsEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="useColumnLabel" value="true"/>
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="false"/>
<setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="PARTIAL"/>
<setting name="autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior" value="WARNING"/>
<setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="SIMPLE"/>
<setting name="defaultStatementTimeout" value="25"/>
<setting name="defaultFetchSize" value="100"/>
<setting name="safeRowBoundsEnabled" value="false"/>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="false"/>
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="SESSION"/>
<setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="OTHER"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value="equals,clone,hashCode,toString"/>
</settings>typeAliases
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="Author" type="domain.blog.Author"/>
<typeAlias alias="Blog" type="domain.blog.Blog"/>
<typeAlias alias="Comment" type="domain.blog.Comment"/>
<typeAlias alias="Post" type="domain.blog.Post"/>
<typeAlias alias="Section" type="domain.blog.Section"/>
<typeAlias alias="Tag" type="domain.blog.Tag"/>
</typeAliases>
当这样配置时,Blog可以用在任何使用domain.blog.Blog的地方。
也可以指定一个包名,MyBatis 会在包名下面搜索需要的 Java Bean,比如:
<typeAliases>
<package name="domain.blog"/>
</typeAliases>
每一个在包 domain.blog 中的 Java Bean,在没有注解的情况下,会使用 Bean 的首字母小写的非限定类名来作为它的别名。 比如 domain.blog.Author 的别名为 author;若有注解,则别名为其注解值。看下面的例子:
@Alias("author")
public class Author {
...
}typeHandlers:
// ExampleTypeHandler.java
@MappedJdbcTypes(JdbcType.VARCHAR)
public class ExampleTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<String> {
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, String parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
ps.setString(i, parameter);
}
@Override
public String getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException {
return rs.getString(columnName);
}
@Override
public String getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
return rs.getString(columnIndex);
}
@Override
public String getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
return cs.getString(columnIndex);
}
}
<!-- mybatis-config.xml -->
<typeHandlers>
<typeHandler handler="org.mybatis.example.ExampleTypeHandler"/>
</typeHandlers>通过类型处理器的泛型,MyBatis 可以得知该类型处理器处理的 Java 类型,不过这种行为可以通过两种方法改变:
在类型处理器的配置元素(typeHandler element)上增加一个 javaType 属性(比如:javaType="String");
在类型处理器的类上(TypeHandler class)增加一个 @MappedTypes 注解来指定与其关联的 Java 类型列表。 如果在 javaType 属性中也同时指定,则注解方式将被忽略。
可以通过两种方式来指定被关联的 JDBC 类型:
<!-- mybatis-config.xml -->
<typeHandlers>
<package name="org.mybatis.example"/>
</typeHandlers>// ExampleObjectFactory.java
public class ExampleObjectFactory extends DefaultObjectFactory {
public Object create(Class type) {
return super.create(type);
}
public Object create(Class type, List<Class> constructorArgTypes, List<Object> constructorArgs) {
return super.create(type, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs);
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
super.setProperties(properties);
}
public <T> boolean isCollection(Class<T> type) {
return Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(type);
}}
<!-- mybatis-config.xml -->
<objectFactory type="org.mybatis.example.ExampleObjectFactory">
<property name="someProperty" value="100"/>
</objectFactory>插件(plugins)
// ExamplePlugin.java
@Intercepts({@Signature(
type= Executor.class,
method = "update",
args = {MappedStatement.class,Object.class})})
public class ExamplePlugin implements Interceptor {
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
return invocation.proceed();
}
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
}
<!-- mybatis-config.xml -->
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="org.mybatis.example.ExamplePlugin">
<property name="someProperty" value="100"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>配置环境(environments)
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">
<property name="..." value="..."/>
</transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>JDBC – 这个配置就是直接使用了 JDBC 的提交和回滚设置,它依赖于从数据源得到的连接来管理事务作用域。
MANAGED – 这个配置几乎没做什么。它从来不提交或回滚一个连接,而是让容器来管理事务的整个生命周期(比如 JEE 应用服务器的上下文)。 默认情况下它会关闭连接,然而一些容器并不希望这样,因此需要将 closeConnection 属性设置为 false 来阻止它默认的关闭行为。例如:
<transactionManager type="MANAGED">
<property name="closeConnection" value="false"/>
</transactionManager>
提示如果你正在使用 Spring + MyBatis,则没有必要配置事务管理器, 因为 Spring 模块会使用自带的管理器来覆盖前面的配置。
这两种事务管理器类型都不需要任何属性。它们不过是类型别名,换句话说,你可以使用 TransactionFactory 接口的实现类的完全限定名或类型别名代替它们。
public interface TransactionFactory {
void setProperties(Properties props);
Transaction newTransaction(Connection conn);
Transaction newTransaction(DataSource dataSource, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit);
}
任何在 XML 中配置的属性在实例化之后将会被传递给 setProperties() 方法。你也需要创建一个 Transaction 接口的实现类,这个接口也很简单:
public interface Transaction {
Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;
void commit() throws SQLException;
void rollback() throws SQLException;
void close() throws SQLException;
Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException;
}一对一查询
public interface UserMapper {
User getUser(int userId);
}
public interface ArticleMapper {
List<Article> getArticleByUserId(int userId);
}<resultMap id="article" type="com.mybatis.model.Article">
<id property="articleId" column="article_id" ></id>
<result property="title" column="title"></result>
<result property="content" column="content"></result>
<result property="createDate" column="create_date" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP"></result>
<association property="user" column="user_id" select="com.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper.getUser"></association>
</resultMap>
<select id="getArticleByUserId" parameterType="int" resultMap="article">
SELECT
a.article_id,
a.user_id,
a.title,
a.content,
a.create_date
FROM
t_artile a
where a.user_id = #{id}
</select> <select id="getUser" parameterType="int" resultType="com.mybatis.model.User">
select user_id as userId,
username,
password,
age
from t_user where user_id=#{id}
</select>这种方式很简单, 但是对于大型数据集合和列表将不会表现很好。 问题就是我们熟知的 “N+1 查询问题”。概括地讲,N+1 查询问题可以是这样引起的:
你执行了一个单独的 SQL 语句来获取结果列表(就是“+1”)。对返回的每条记录,你执行了一个查询语句来为每个加载细节(就是“N”)。这个问题会导致成百上千的 SQL 语句被执行。这通常不是期望的。
MyBatis 能延迟加载这样的查询就是一个好处,因此你可以分散这些语句同时运行的消 耗。然而,如果你加载一个列表,之后迅速迭代来访问嵌套的数据,你会调用所有的延迟加 载,这样的行为可能是很糟糕的。
或
<resultMap id="article" type="com.mybatis.model.Article">
<id property="articleId" column="article_id" ></id>
<result property="title" column="title"></result>
<result property="content" column="content"></result>
<result property="createDate" column="create_date" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP"></result>
<association property="user" column="user_id" resultMap="user"></association>
</resultMap>
<resultMap id="user" type="com.mybatis.model.User">
<id property="userId" column="user_id"></id>
<result property="username" column="username"></result>
<result property="password" column="password"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
</resultMap>
--------------OR-------------------------
<resultMap id="article" type="com.mybatis.model.Article">
<id property="articleId" column="article_id" ></id>
<result property="title" column="title"></result>
<result property="content" column="content"></result>
<result property="createDate" column="create_date" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP"></result>
<association property="user" javaType="com.mybatis.model.User" >
<id property="userId" column="user_id"></id>
<result property="username" column="username"></result>
<result property="password" column="password"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="getArticleByUserId" parameterType="int" resultMap="article">
SELECT
a.article_id,
a.user_id,
a.title,
a.content,
a.create_date,
b.username,
b.password,
b.age
FROM
t_artile a
INNER JOIN t_user b ON a.user_id = b.user_id
where a.user_id = #{id}
</select>一对多查询
一对多关联和多对一关联的区别:是从一的一端取多的一端,还是从多的一端取一的一端。
-- 用户表
CREATE TABLE `user1`(
`id` INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_name` VARCHAR(20),-- 用户姓名
`address` VARCHAR(60)-- 联系地址
) ENGINE INNODB CHARSET utf8;
INSERT INTO `user1` VALUES(1,'陈大','深圳市南山区');
INSERT INTO `user1` VALUES(2,'王二','深圳市福田区');
INSERT INTO `user1` VALUES(3,'张三','深圳市龙华新区');
INSERT INTO `user1` VALUES(4,'李四','深圳市龙岗区');
-- 卡表
CREATE TABLE `card1`(
`id` INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
`card_no` VARCHAR(18),
`remark` VARCHAR(100),
`user_id` INT-- 用于关联user1的主键id(不设置外键,避免级联问题)
) ENGINE=INNODB CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `card1` VALUES(1,'420001','工资卡',1);
INSERT INTO `card1` VALUES(2,'420002','工资卡',2);
INSERT INTO `card1` VALUES(3,'420003','工资卡',3);
INSERT INTO `card1` VALUES(4,'420004','工资卡',3);
-- SELECT * FROM `user1`;
-- SELECT * FROM `card1`; package com.chensan.o2m.entity;
public class Card1 {
private int id;
private String cardNo;
private String remark;
//...省略setter、getter方法
} package com.chensan.o2m.entity;
import java.util.List;
public class User1 {
private int id;
private String userName;
private String address;
private List<Card1> cards;
public String toString(){
return "[ id = " + id + ", userName = "
+ userName + ", address = " + address + "]";
}
//...省略setter、getter方法
} <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.chensan.o2m.entity.User1Mapper">
<resultMap id="user1" type="com.chensan.o2m.entity.User1">
<id property="id" column="user_id"/>
<result property="userName" column="user_name"/>
<result property="address" column="address"/>
<collection property="cards" column="user_id" ofType="com.chensan.o2m.entity.Card1">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="cardNo" column="card_no"/>
<result property="remark" column="remark"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="query" parameterType="int" resultMap="user1">
SELECT t1.`id` `user_id`,t1.`user_name`,t1.`address`,t2.`id`,t2.`card_no`,t2.`remark`
FROM `user1` t1,`card1` t2
WHERE t1.`id`=t2.`user_id` AND t1.`id`=#{id}
</select>
</mapper> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 和spring整合后 environments配置将废除-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<!-- 使用jdbc事务管理 或者JTA事务管理-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<!-- 数据库连接池 第三方组件:c3p0-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis01"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 加载实体类的映射文件 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/chensan/o2m/mapper/User1Mapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration> public class TestO2M {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
private static Reader resource;
//创建会话工厂
static{
try{
resource = Resources.getResourceAsReader("myBatisConfig.xml");
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resource);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static SqlSessionFactory getSession(){
return sqlSessionFactory;
}
//一对多:查询用户对应卡(银行卡)
public void getUserCard(){
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
User1 user = sqlSession.selectOne("com.chensan.o2m.entity.User1Mapper.query", 3);
System.out.println(user);
for(Card1 card : user.getCards()){
System.out.println(
"[ " +
"userId = " + user.getId() + ", " +
"userName = " + user.getUserName() + ", " +
"address = " + user.getAddress() + ", " +
"cardId = " + card.getId() + ", " +
"cardNo = " + card.getCardNo() + ", " +
"remark = " + card.getRemark() +
" ]"
);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestO2M testMyBatisOneToMany = new TestO2M();
testMyBatisOneToMany.getUserCard();
}
} 多对多查询
SELECT
orders.*,
user.username,
user.sex,
user.address,
orderdetail.id orderdetail_id,
orderdetail.items_id,
orderdetail.items_num,
orderdetail.orders_id,
items.name items_name,
items.detail items_detail,
items.price items_price
FROM
orders,
user,
orderdetail,
items
WHERE orders.user_id = user.id AND orderdetail.orders_id=orders.id AND orderdetail.items_id = items.id<!-- 查询用户及购买的商品信息,使用resultmap -->
<select id="findUserAndItemsResultMap" resultMap="UserAndItemsResultMap">
SELECT
orders.*,
user.username,
user.sex,
user.address,
orderdetail.id orderdetail_id,
orderdetail.items_id,
orderdetail.items_num,
orderdetail.orders_id,
items.name items_name,
items.detail items_detail,
items.price items_price
FROM
orders,
user,
orderdetail,
items
WHERE orders.user_id = user.id AND orderdetail.orders_id=orders.id AND orderdetail.items_id = items.id
</select><!-- 查询用户及购买的商品 -->
<resultMap type="com.iot.mybatis.po.User" id="UserAndItemsResultMap">
<!-- 用户信息 -->
<id column="user_id" property="id"/>
<result column="username" property="username"/>
<result column="sex" property="sex"/>
<result column="address" property="address"/>
<!-- 订单信息
一个用户对应多个订单,使用collection映射
-->
<collection property="ordersList" ofType="com.iot.mybatis.po.Orders">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="user_id" property="userId"/>
<result column="number" property="number"/>
<result column="createtime" property="createtime"/>
<result column="note" property="note"/>
<!-- 订单明细
一个订单包括 多个明细
-->
<collection property="orderdetails" ofType="com.iot.mybatis.po.Orderdetail">
<id column="orderdetail_id" property="id"/>
<result column="items_id" property="itemsId"/>
<result column="items_num" property="itemsNum"/>
<result column="orders_id" property="ordersId"/>
<!-- 商品信息
一个订单明细对应一个商品
-->
<association property="items" javaType="com.iot.mybatis.po.Items">
<id column="items_id" property="id"/>
<result column="items_name" property="name"/>
<result column="items_detail" property="detail"/>
<result column="items_price" property="price"/>
</association>
</collection>
</collection>
</resultMap>//查询用户购买商品信息
public List<User> findUserAndItemsResultMap()throws Exception;resultType
作用:将查询结果按照sql列名pojo属性名一致性映射到pojo中。
场合:常见一些明细记录的展示,比如用户购买商品明细,将关联查询信息全部展示在页面时,此时可直接使用resultType将每一条记录映射到pojo中,在前端页面遍历list(list中是pojo)即可。
resultMap
使用association和collection完成一对一和一对多高级映射(对结果有特殊的映射要求)。
association:
作用:将关联查询信息映射到一个pojo对象中。
场合:为了方便查询关联信息可以使用association将关联订单信息映射为用户对象的pojo属性中,比如:查询订单及关联用户信息。
使用resultType无法将查询结果映射到pojo对象的pojo属性中,根据对结果集查询遍历的需要选择使用resultType还是resultMap。
collection:
作用:将关联查询信息映射到一个list集合中。
场合:为了方便查询遍历关联信息可以使用collection将关联信息映射到list集合中,比如:查询用户权限范围模块及模块下的菜单,可使用collection将模块映射到模块list中,将菜单列表映射到模块对象的菜单list属性中,这样的作的目的也是方便对查询结果集进行遍历查询。如果使用resultType无法将查询结果映射到list集合中。延迟加载
延迟加载的条件:resultMap可以实现高级映射(使用association、collection实现一对一及一对多映射),association、collection具备延迟加载功能。
延迟加载的好处:
先从单表查询、需要时再从关联表去关联查询,大大提高 数据库性能,因为查询单表要比关联查询多张表速度要快。
延迟加载的实例:
如果查询订单并且关联查询用户信息。如果先查询订单信息即可满足要求,当我们需要查询用户信息时再查询用户信息。把对用户信息的按需去查询就是延迟加载。
<settings>
<!--开启延迟加载-->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--关闭积极加载-->
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
</settings>aggressiveLazyLoading:当设置为‘true’的时候,懒加载的对象可能被任何懒属性全部加载。否则,每个属性都按需加载。默认为true
延迟加载的resultMap
在resultMap中使用association或者collection,即可使用延迟加载。
延迟加载需要两个statement语句来完成在resultMap中使用association或者collection来配置两个statement直接的管理。
延迟加载的mapper文件
必须要有两个statement
两个statement直接必须存在关联的数据列
<select id="findOrdersByLazyLoad" resultMap="OrderAndUserLazyLoad">
SELECT * FROM orders
</select>
<select id="findUser" parameterType="int" resultType="User">
SELECT * FROM User WHERE id = #{value}
</select>Mapper动态代理
Mapper接口开发方法只需要程序员编写Mapper接口(相当于Dao接口),由Mybatis框架根据接口定义创建接口的动态代理对象,代理对象的方法体同上边Dao接口实现类方法。
Mapper接口开发需要遵循以下规范:
1、 Mapper.xml文件中的namespace与mapper接口的类路径相同
2、 Mapper接口方法名和Mapper.xml中定义的每个statement的id相同
3、 Mapper接口方法的输入参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql 的parameterType的类型相同
4、 Mapper接口方法的输出参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的resultType的类型相同
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="cn.itcast.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper">
<!-- 根据id获取用户信息 -->
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User">
select * from user where id = #{id}
</select>
<!-- 自定义条件查询用户列表 -->
<select id="findUserByUsername" parameterType="java.lang.String"
resultType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User">
select * from user where username like '%${value}%'
</select>
<!-- 添加用户 -->
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" order="AFTER" resultType="java.lang.Integer">
select LAST_INSERT_ID()
</selectKey>
insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address)
values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
</insert>
</mapper> /**
* 用户管理mapper
*/
Public interface UserMapper {
//根据用户id查询用户信息
public User findUserById(int id) throws Exception;
//查询用户列表
public List<User> findUserByUsername(String username) throws Exception;
//添加用户信息
public void insertUser(User user)throws Exception;
} <!-- 加载映射文件 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers> Public class UserMapperTest extends TestCase {
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
protected void setUp() throws Exception {
//mybatis配置文件
String resource = "sqlMapConfig.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//使用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建sessionFactory
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
}
Public void testFindUserById() throws Exception {
//获取session
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//获取mapper接口的代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//调用代理对象方法
User user = userMapper.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
//关闭session
session.close();
}
@Test
public void testFindUserByUsername() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> list = userMapper.findUserByUsername("张");
System.out.println(list.size());
}
Public void testInsertUser() throws Exception {
//获取session
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//获取mapper接口的代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//要添加的数据
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("张三");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
user.setSex("1");
user.setAddress("北京市");
//通过mapper接口添加用户
userMapper.insertUser(user);
//提交
session.commit();
//关闭session
session.close();
}
} 一级查询缓存
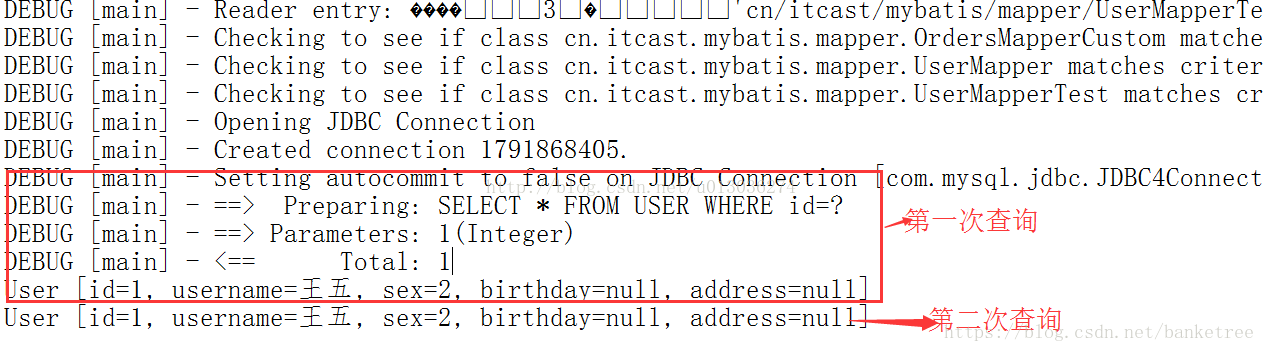
是SQlSession级别的缓存。在操作数据库时需要构造SqlSession对象,在对象中有一个数据结构(HashMap)用于存储缓存数据。不同的SqlSession之间的缓存数据区域(HashMap)是互相不影响的。其默认是开启的,无法关闭,作用范围为namespace,生命周期同整个SqlSession相同。
public class UserMapperTest {
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
// 此方法是在执行testFindUserById之前执行
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
// 创建sqlSessionFactory
// mybatis配置文件
String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
// 得到配置文件流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 创建会话工厂,传入mybatis的配置文件信息
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
}
@Test
public void testFindUserById() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 创建UserMapper对象,mybatis自动生成mapper代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 调用userMapper的方法
// 第一次查询(先去缓存中查找,有则直接获取,没有则执行SQL语句查询)
User user = userMapper.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
// 第二次查询(先去缓存中查找,有则直接获取,没有则执行SQL语句查询)
User user2 = userMapper.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user1);
}
}
public class UserMapperTest {
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
// 此方法是在执行testFindUserById之前执行
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
// 创建sqlSessionFactory
// mybatis配置文件
String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
// 得到配置文件流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 创建会话工厂,传入mybatis的配置文件信息
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
}
@Test
public void testFindUserById() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 创建UserMapper对象,mybatis自动生成mapper代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 调用userMapper的方法
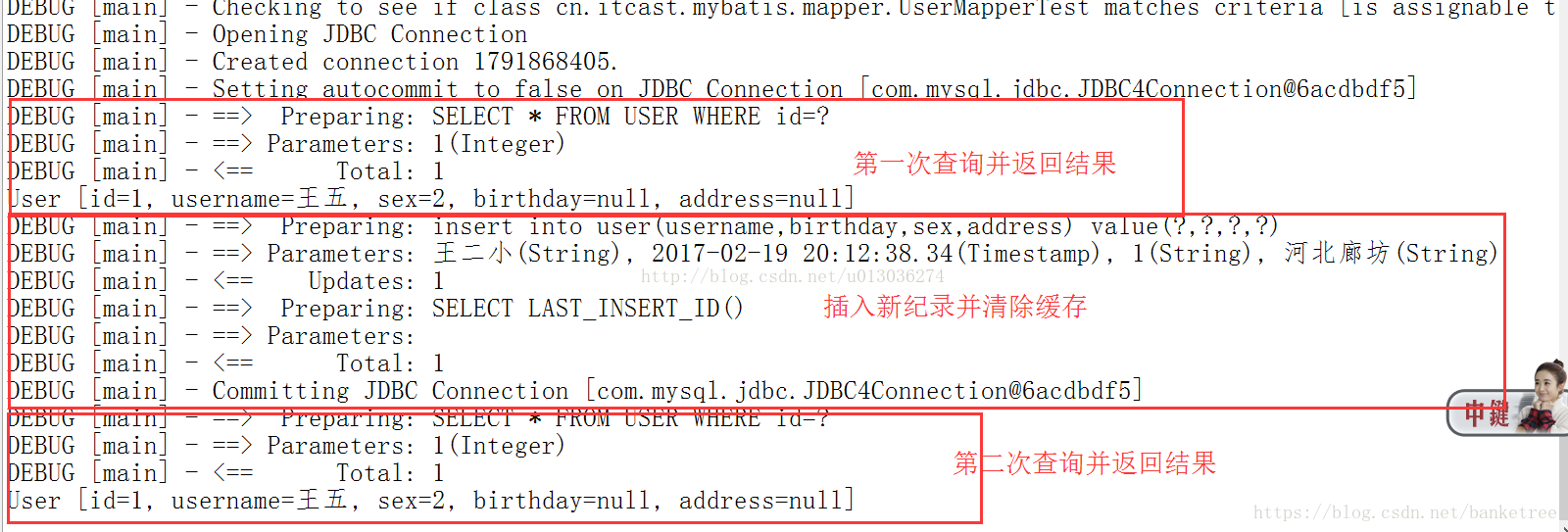
// ①第一次查询(先去缓存中查找,有则直接获取,没有则执行SQL语句查询)
User user1 = userMapper.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user1);
// ②插入用户对象
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("王二小");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
user.setSex("1");
user.setAddress("河北廊坊");
sqlSession.insert("test.insertUser", user);
// 提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
// ③第二次查询(先去缓存中查找,有则直接获取,没有则执行SQL语句查询)
User user2 = userMapper.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user2);
}
}
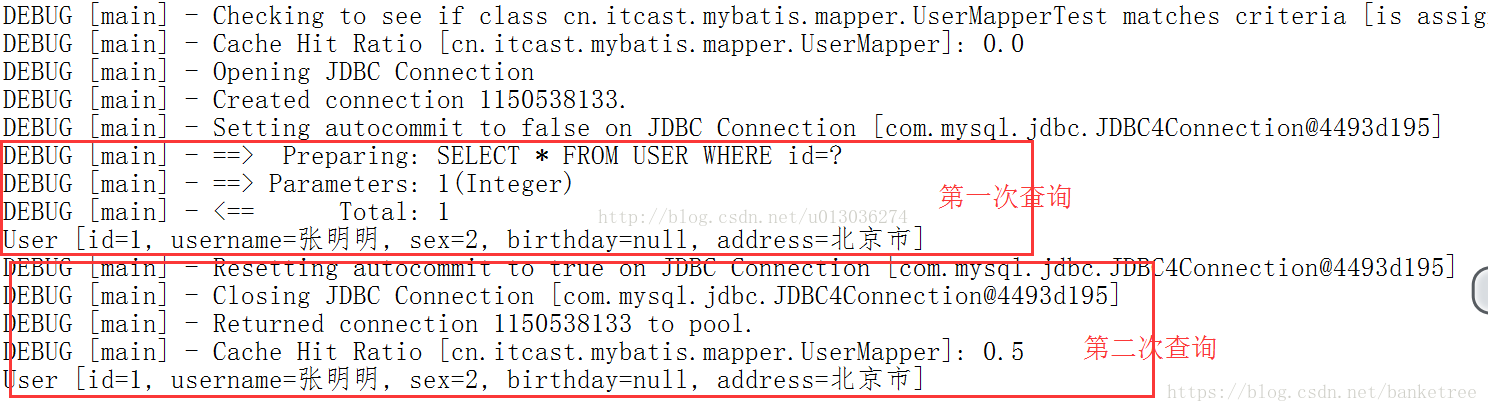
二级查询缓存
是mapper级别的缓存,多个SqlSession去操作同一个mapper的sql语句,多个SqlSession可以共用二级缓存,二级缓存是跨SqlSession的。其默认是开启的,无法关闭,作用范围为namespace,生命周期同整个SqlSession相同。

在核心配置文件SQLMapConfig.xml中的全局设置中开启二级缓存,将value设为true。如下:
<span style="font-family:'Comic Sans MS';"><settings>
<!-- 开启二级缓存 -->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings></span><span style="font-family:'Comic Sans MS';"><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- namespace命名空间,作用就是对sql进行分类化管理,理解sql隔离
注意:使用mapper代理方法开发,namespace有特殊重要的作用,namespace等于mapper接口地址
-->
<mapper namespace="cn.itcast.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper">
<!-- 开启本mapper的namespace下的二缓存
type:指定cache接口的实现类的类型,mybatis默认使用PerpetualCache
要和ehcache整合,需要配置type为ehcache实现cache接口的类型
-->
<cache />
<!-- 下面的一些SQL语句暂时略 -->
</mapper></span> public class UserMapperTest {
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
// 此方法是在执行testFindUserById之前执行
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
// 创建sqlSessionFactory
// mybatis配置文件
String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
// 得到配置文件流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 创建会话工厂,传入mybatis的配置文件信息
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
}
@Test
public void testFindUserById() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
SqlSession sqlSession3 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 创建代理对象
UserMapper userMapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 第一次发起请求,查询id为1的用户
User user1 = userMapper1.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user1);
//这里执行关闭操作,将sqlsession中的数据写到二级缓存区域
sqlSession1.close();
UserMapper userMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 第二次发起请求,查询id为1的用户
User user2 = userMapper2.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user2);
sqlSession2.close();
}
}
逆向工程
MyBatis的一个主要的特点就是需要程序员自己编写sql,那么如果表太多的话,难免会很麻烦,所以mybatis官方提供了一个逆向工程,可以针对单表自动生成mybatis执行所需要的代码(包括mapper.xml、mapper.java、po..)。一般在开发中,常用的逆向工程方式是通过数据库的表生成代码。
使用MyBatis的逆向工程,需要导入逆向工程的jar包 mybatis-generator-core-1.3.2.jar。
配置逆向工程的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd">
<generatorConfiguration>
<context id="testTables" targetRuntime="MyBatis3">
<commentGenerator>
<!-- 是否去除自动生成的注释 true:是 : false:否 -->
<property name="suppressAllComments" value="true" />
</commentGenerator>
<!--数据库连接的信息:驱动类、连接地址、用户名、密码 -->
<jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis" userId="root"
password="yezi">
</jdbcConnection>
<!-- <jdbcConnection driverClass="oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver"
connectionURL="jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:yycg"
userId="yycg"
password="yycg">
</jdbcConnection> -->
<!-- 默认false,把JDBC DECIMAL 和 NUMERIC 类型解析为 Integer,为 true时把JDBC DECIMAL 和
NUMERIC 类型解析为java.math.BigDecimal -->
<javaTypeResolver>
<property name="forceBigDecimals" value="false" />
</javaTypeResolver>
<!-- targetProject:生成PO类的位置 -->
<javaModelGenerator targetPackage="com.itheima.mybatis.po"
targetProject=".src">
<!-- enableSubPackages:是否让schema作为包的后缀 -->
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" />
<!-- 从数据库返回的值被清理前后的空格 -->
<property name="trimStrings" value="true" />
</javaModelGenerator>
<!-- targetProject:mapper映射文件生成的位置 -->
<sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="com.itheima.mybatis.mapper"
targetProject=".src">
<!-- enableSubPackages:是否让schema作为包的后缀 -->
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" />
</sqlMapGenerator>
<!-- targetPackage:mapper接口生成的位置 -->
<javaClientGenerator type="XMLMAPPER"
targetPackage="com.itheima.mybatis.mapper"
targetProject=".src">
<!-- enableSubPackages:是否让schema作为包的后缀 -->
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" />
</javaClientGenerator>
<!-- 指定数据库表 -->
<table schema="" tableName="user"></table>
<table schema="" tableName="orders"></table>
<!-- 有些表的字段需要指定java类型
<table schema="" tableName="">
<columnOverride column="" javaType="" />
</table> -->
</context>
</generatorConfiguration>public class GeneratorSqlmap {
public void generator() throws Exception{
List<String> warnings = new ArrayList<String>();
boolean overwrite = true;
//指定 逆向工程配置文件
File configFile = new File("generatorConfig.xml");
ConfigurationParser cp = new ConfigurationParser(warnings);
Configuration config = cp.parseConfiguration(configFile);
DefaultShellCallback callback = new DefaultShellCallback(overwrite);
MyBatisGenerator myBatisGenerator = new MyBatisGenerator(config,
callback, warnings);
myBatisGenerator.generate(null);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try {
GeneratorSqlmap generatorSqlmap = new GeneratorSqlmap();
generatorSqlmap.generator();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<!-- 配置要扫描的包,如果扫描多个包使用半角逗号分隔 -->
<!-- <property name="basePackage" value="cn.itheima.mybatis.mapper,com.itheima.mybatis.mapper" /> -->
<property name="basePackage" value="com.itheima.mybatis.mapper" />
</bean>public class UserMapperTest {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Before
public void init() {
// 初始化Spring容器
applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring/application-context.xml");
}
@Test
public void testDeleteByPrimaryKey() {
// 请读者自行测试...
}
@Test
public void testInsert() {
UserMapper userMapper = applicationContext.getBean(UserMapper.class);
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("武大郎");
user.setSex("1");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
user.setAddress("河北清河县");
userMapper.insert(user);
}
@Test
public void testSelectByExample() {
UserMapper userMapper = applicationContext.getBean(UserMapper.class);
UserExample example = new UserExample();
// Criteria类是UserExample类里面的内部类,Criteria类是干什么用的呢?它专门用于封装自定义查询条件的
// Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();
// criteria.andUsernameLike("%张%");
// 执行查询
List<User> list = userMapper.selectByExample(example);
for (User user : list) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
@Test
public void testSelectByPrimaryKey() {
UserMapper userMapper = applicationContext.getBean(UserMapper.class);
User user = userMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(10);
System.out.println(user);
}
@Test
public void testUpdateByPrimaryKey() {
// 请读者自行测试...
}
}……
最后
以上就是机灵未来最近收集整理的关于Spring Mybatis详解的全部内容,更多相关Spring内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。

![8.MYSQL:触发器的使用[TRIGGER]](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg5.png)






发表评论 取消回复