模糊控制器设计实验
- 模糊控制
- 代码
- 输入
- 输出
- 输出说明
- 运行结果
- 实验小结
模糊控制
模糊控制是指,要根据几个变量的输入以及一组模糊表述的规则,来决定输出。
模糊控制器包括四部分:
(1)模糊化。主要作用是选定模糊控制器的输入量,并将其转换为系统可识别的模糊量,具体包含以下三步:
第一,对输入量进行满足模糊控制需求的处理;
第二,对输入量进行尺度变换;
第三,确定各输入量的模糊语言取值和相应的隶属度函数。
(2)规则库。根据人类专家的经验建立模糊规则库。模糊规则库包含众多控制规则,是从实际控制经验过渡到模糊控制器的关键步骤。
(3)模糊推理。主要实现基于知识的推理决策。
(4)解模糊。主要作用是将推理得到的控制量转化为控制输出。
代码
该模糊控制器实现了车辆跟驰情景。
根据生活经验,当两车距离比较长,两车的相对速度比较小时,后车可以加快速度;当两车距离比较短,两车相对速度比较大时,后车应该减慢速度,等等。
%模糊控制器设计
a=newfis('fuzzf');
%创建新的模糊推理系统
%输入1
f1=1;
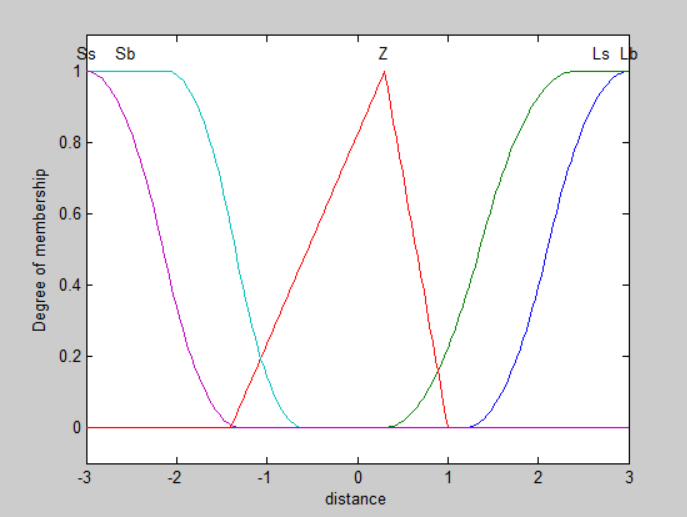
a=addvar(a,'input','distance',[-3*f1,3*f1]);
%添加 e 的模糊语言变量
a=addmf(a,'input',1,'Lb','smf',[1.2*f1,3*f1]);
%添加 e 的模糊语言变量的隶属度函数(s型)
a=addmf(a,'input',1,'Ls','smf',[0.3*f1,2.4*f1]);
%隶属度函数为三角形
a=addmf(a,'input',1,'Z','trimf',[-1.4*f1,0.3*f1,1*f1]);
a=addmf(a,'input',1,'Sb','zmf',[-2.1*f1,-0.6*f1]);
a=addmf(a,'input',1,'Ss','zmf',[-3*f1,-1.3*f1]);
%输入2
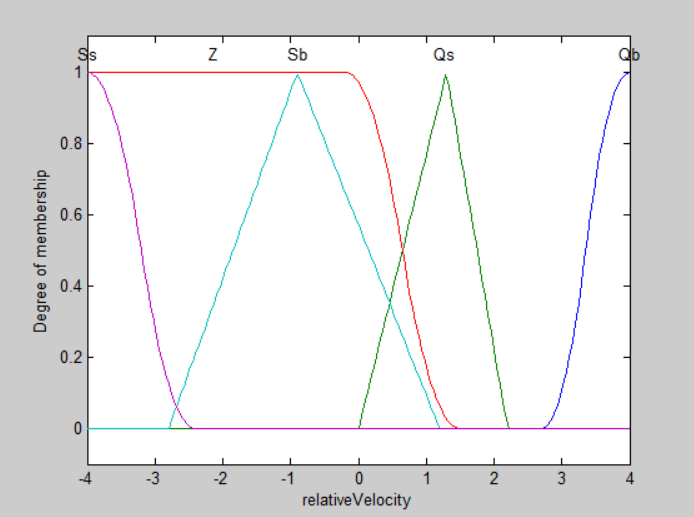
f2=1;
a=addvar(a,'input','relativeVelocity',[-4*f2,4*f2]);
%添加 ec 的模糊语言变量
a=addmf(a,'input',2,'Qb','smf',[2.7*f2,4*f2]);
a=addmf(a,'input',2,'Qs','trimf',[0,1.3*f2,2.2*f2]);
a=addmf(a,'input',2,'Z','zmf',[-0.2*f2,1.5*f2]);
a=addmf(a,'input',2,'Sb','trimf',[-2.8*f2,-0.9*f2,1.2*f2]);
a=addmf(a,'input',2,'Ss','zmf',[-4*f2,-2.4*f2]);
%输出
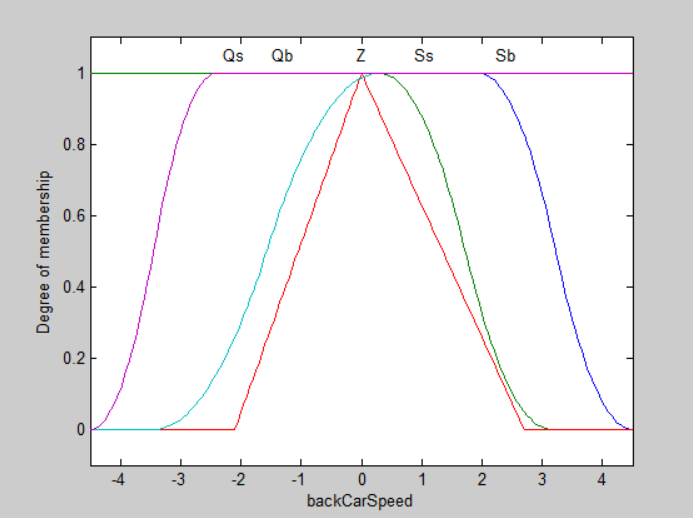
f3=1.5;
a=addvar(a,'output','backCarSpeed',[-3*f3,3*f3]);
%添加 u 的模糊语言变量
a=addmf(a,'output',1,'Qb','zmf',[1.3*f3,3*f3]);
a=addmf(a,'output',1,'Qs','zmf',[0.2*f3,2.1*f3]);
a=addmf(a,'output',1,'Z','trimf',[-1.4*f3,0,1.8*f3]);
a=addmf(a,'output',1,'Sb','smf',[-2.3*f3,0.2*f3]);
a=addmf(a,'output',1,'Ss','smf',[-3*f3,-1.6*f3]);
%规则库
rulelist=[1 1 3 1 1;
%编辑模糊规则,后俩个数分别是规则权重和AND OR选项
1 2 2 1 1;
1 3 2 1 1;
1 4 1 1 1;
1 5 1 1 1;
2 1 3 1 1;
2 2 3 1 1;
2 3 2 1 1;
2 4 2 1 1;
2 5 1 1 1;
3 1 5 1 1;
3 2 4 1 1;
3 3 3 1 1;
3 4 2 1 1;
3 5 2 1 1;
4 1 5 1 1;
4 2 5 1 1;
4 3 4 1 1;
4 4 4 1 1;
4 5 3 1 1;
5 1 5 1 1;
5 2 5 1 1;
5 3 4 1 1;
5 4 4 1 1;
5 5 4 1 1;
];
a=addrule(a,rulelist);
%添加模糊规则函数
showrule(a)
%显示模糊规则函数
a1=setfis(a,'DefuzzMethod','centroid');
%设置解模糊方法
writefis(a1,'fuzzf');
%保存模糊系统
a2=readfis('fuzzf');
%从磁盘读出保存的模糊系统
disp('fuzzy Controller table:distance=[-3,+3],relativeVelocity=[-4,+4]');%显示矩阵和数组内容
%推理
Ulist=zeros(5,5);
%全零矩阵
for i=1:5
for j=1:5
e(i)=-1+i;
ec(j)=-1+j;
Ulist(i,j)=evalfis([e(i),ec(j)],a1);
%完成模糊推理计算
end
end
%
Ulist=ceil(Ulist)
%朝正无穷方向取整
Ulist
%朝正无穷方向取整
%画出模糊系统
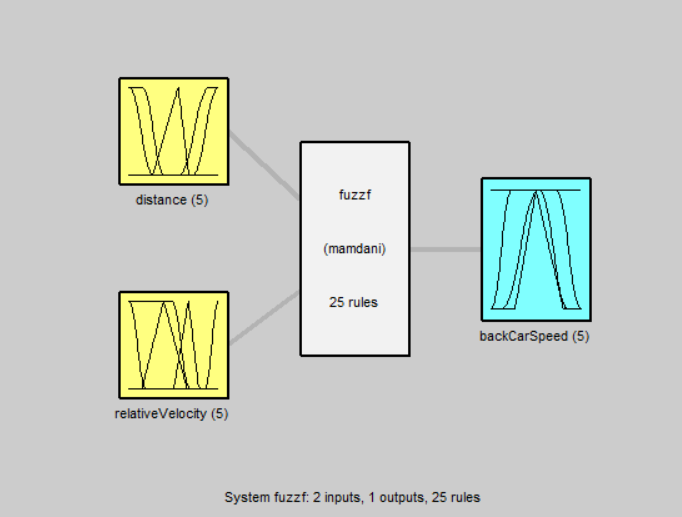
figure(1); plotfis(a1);
figure(2);plotmf(a,'input',1);
figure(3);plotmf(a,'input',2);
figure(4);plotmf(a,'output',1);
输入
该模糊控制器有两个输入,分别是两车的距离和两车的相对速度。
输出
该模糊控制器有一个输出,就是后车的加速状态。
输出说明
因为两种输入分别有5种选择,所以模糊规则函数定义了25条。
- If (distance is Lb) and (relativeVelocity is Qb) then (backCarSpeed is Z) (1)
- If (distance is Lb) and (relativeVelocity is Qs) then (backCarSpeed is Qs) (1)
- If (distance is Lb) and (relativeVelocity is Z) then (backCarSpeed is Qs) (1)
- If (distance is Lb) and (relativeVelocity is Sb) then (backCarSpeed is Qb) (1)
- If (distance is Lb) and (relativeVelocity is Ss) then (backCarSpeed is Qb) (1)
- If (distance is Ls) and (relativeVelocity is Qb) then (backCarSpeed is Z) (1)
- If (distance is Ls) and (relativeVelocity is Qs) then (backCarSpeed is Z) (1)
- If (distance is Ls) and (relativeVelocity is Z) then (backCarSpeed is Qs) (1)
- If (distance is Ls) and (relativeVelocity is Sb) then (backCarSpeed is Qs) (1)
- If (distance is Ls) and (relativeVelocity is Ss) then (backCarSpeed is Qb) (1)
- If (distance is Z) and (relativeVelocity is Qb) then (backCarSpeed is Ss) (1)
- If (distance is Z) and (relativeVelocity is Qs) then (backCarSpeed is Sb) (1)
- If (distance is Z) and (relativeVelocity is Z) then (backCarSpeed is Z) (1)
- If (distance is Z) and (relativeVelocity is Sb) then (backCarSpeed is Qs) (1)
- If (distance is Z) and (relativeVelocity is Ss) then (backCarSpeed is Qs) (1)
- If (distance is Sb) and (relativeVelocity is Qb) then (backCarSpeed is Ss) (1)
- If (distance is Sb) and (relativeVelocity is Qs) then (backCarSpeed is Ss) (1)
- If (distance is Sb) and (relativeVelocity is Z) then (backCarSpeed is Sb) (1)
- If (distance is Sb) and (relativeVelocity is Sb) then (backCarSpeed is Sb) (1)
- If (distance is Sb) and (relativeVelocity is Ss) then (backCarSpeed is Z) (1)
- If (distance is Ss) and (relativeVelocity is Qb) then (backCarSpeed is Ss) (1)
- If (distance is Ss) and (relativeVelocity is Qs) then (backCarSpeed is Ss) (1)
- If (distance is Ss) and (relativeVelocity is Z) then (backCarSpeed is Sb) (1)
- If (distance is Ss) and (relativeVelocity is Sb) then (backCarSpeed is Sb) (1)
- If (distance is Ss) and (relativeVelocity is Ss) then (backCarSpeed is Sb) (1)
显示矩阵和数组内容:(两个输入的范围)
fuzzy Controller table:distance=[-3,+3],relativeVelocity=[-4,+4]
模糊推理结果:
Ulist =
-1.0824 1.1521 0.9583 0.1838 0.4726
-1.0109 -0.8129 0.2668 0.2823 0.2668
-0.9634 -0.6843 -1.0109 0.2823 0.2006
-0.8638 -1.1569 -1.0109 0.2823 0.1996
-0.8638 -1.1569 -1.0109 0.2823 0.1996
运行结果
实验小结
实验中的模糊控制的输入是自己定义输入范围和输入的隶属度函数,在这边要注意的是隶属度函数的范围不可以超过自己设定的输入范围,因为超出输入范围的隶属度函数没有意义。并且,不同输入的左右区间也不能重合,否则在进行规则判断的时候无法判断到底应该用哪个输入。
最后
以上就是发嗲牛排最近收集整理的关于计算智能——模糊控制器设计实验模糊控制代码输入输出输出说明运行结果实验小结的全部内容,更多相关计算智能——模糊控制器设计实验模糊控制代码输入输出输出说明运行结果实验小结内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。



![MATLAB交通信号灯识别[完美运行,详细解释,GUI界面,万字文稿]](https://file2.kaopuke.com:8081/files_image/reation/bcimg6.png)




发表评论 取消回复