最近涉足MEMS激光相关的机器 视觉行业中,设计AGV的部分还是很多,这里网上收集了一些AGV的资料,补充一下基础知识:
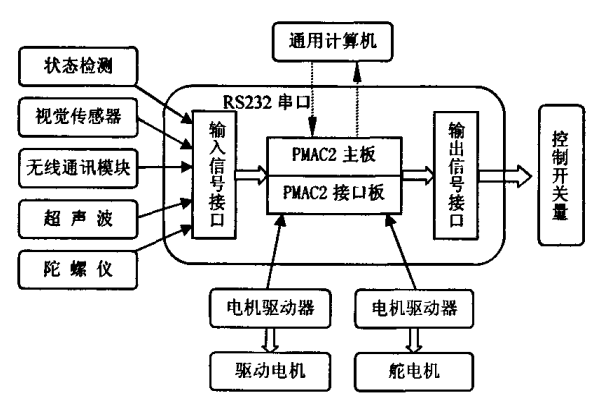
Wired(有线-地板槽方式)又叫感应式Inductive Guidance Technology
A slot is cut in to the floor and a wire is placed approximately 1 inch below the surface. This slot is cut along the path the AGV is to follow. This wire is used to transmit a radio signal. A sensor is installed on the bottom of the AGV close to the ground. The sensor detects the relative position of the radio signal being transmitted from the wire. This information is used to regulate the steering circuit, making the AGV follow the wire.
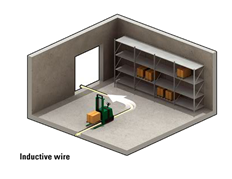
- Floor is cut and a wire is imbedded to represent the guide path
- Guide path sensor is mounted on the vehicle
- Paths are well marked on the floor
- Paths are continuous
- Paths are fixed, the systems guide path is not easily changed
- Expansion of the facility is not as flexible as some other navigation technologies and may be limited due to constraints
Guide tape or Spot(导引点,带方式)
AGVs (some known as automated guided carts or AGCs) use tape for the guide path. The tapes can be one of two styles: magnetic or colored. The AGV is fitted with the appropriate guide sensor to follow the path of the tape. One major advantage of tape over wired guidance is that it can be easily removed and relocated if the course needs to change. Colored tape is initially less expensive, but lacks the advantage of being embedded in high traffic areas where the tape may become damaged or dirty. A flexible magnetic bar can also be embedded in the floor like wire but works under the same provision as magnetic tape and so remains unpowered or passive. Another advantage of magnetic guide tape is the dual polarity. small pieces of magnetic tape may be placed to change states of the AGC based on polarity and sequence of the tags.
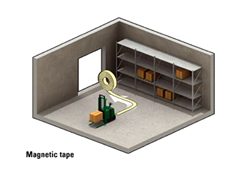
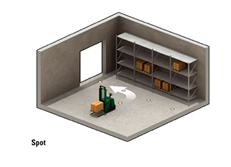
- Guide path is marked with a magnetic tape that is placed on the floor surface
- Guide path sensor is mounted on the vehicle
- Paths are continuous
- Paths are fixed, the systems guide path can be changed easily and quickly(对比第一种方式贴带较容易定制)
- Tape may have to be epoxy coated to floor
- Recommended for Automatic Guided Carts (AGC)
Laser target navigation[激光目标导航]
此项技术最大的优点是,AGV定位精确;地面无需其他定位设施;行驶路径可灵活多变,能够适合多种现场环境,它是目前国外许多AGV生产厂家优先采用的先进导引方式;缺点是制造成本高,对环境要求较相对苛刻(外界光线,地面要求,能见度要求等),不适合室外(尤其是易受雨、雪、雾的影响)。
The navigation is done by mounting reflective tape on walls, poles(柱子) or fixed machines. The AGV carries a laser transmitter and receiver on a rotating turret(旋转的接受角). The laser is transmitted and received by the same sensor. The angle and (sometimes) distance to any reflectors (反射器)that in line of sight and in range are automatically calculated. This information is compared to the map of the reflector layout stored in the AGV's memory. This allows the navigation system to triangulate(三角计算) the current position of the AGV. The current position is compared to the path programmed in to the reflector layout map. The steering is adjusted accordingly to keep the AGV on track. It can then navigate to a desired target using the constantly updating position.
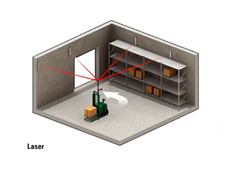
- Modulated Lasers(调制激光) The use of modulated laser light gives greater range and accuracy over pulsed laser systems. By emitting(发射) a continuous fan of modulated laser light a system can obtain an uninterrupted reflection as soon as the scanner achieves line of sight with a reflector. The reflection ceases at the trailing edge of the reflector which ensures an accurate and consistent measurement from every reflector on every scan. By using a modulated laser a system can achieve an angular resolution of ~ 0.1 mrad毫拉德 (0.006°) at 8 scanner revolutions per second.
- Pulsed Lasers A typical pulsed laser scanner emits pulsed laser light at a rate of 14,400 Hz which gives a maximum possible resolution of ~ 3.5 mrad (0.2°) at 8 scanner revolutions per second. To achieve a workable navigation, the
- readings must be interpolated based on the intensity of the reflected laser light, to identify the centre of the reflector.
- 特性分析:
- Area is mapped and stored in the vehicle’s computer memory
- Multiple, fixed reference points, reflective strips, located within the operating area that can be detected by a laser head that is mounted on the vehicle
- Guide path is easily changed and expanded
- Most flexible for vehicle movement
- Most reliable and secure form of navigation
- Most accurate form of guidance
- System can be expanded without alteration to the facility
- Most dynamic control of blocking and traffic management
- Recommended by TRANSBOTICS
Inertial (Gyroscopic) navigation[惯性导航]
Another form of an AGV guidance is inertial navigation. With inertial guidance, a computer control system directs and assigns tasks to the vehicles. Transponders are embedded in the floor of the work place. The AGV uses these transponders to verify that the vehicle is on course. A gyroscope(陀螺仪,回转仪) is able to detect the slightest change in the direction of the vehicle and corrects it in order to keep the AGV on its path. The margin of error for the inertial method is ±1 inch.[1]
Inertial can operate in nearly any environment including tight aisles or extreme temperatures.[2] Inertial navigation can include use of magnets embedded in the floor of the facility that the vehicle can read and follow.[3]
Natural features (Natural Targeting) navigatin(无 部件导航)
Navigation without retrofitting(新部件) of the workspace is called Natural Features or Natural Targeting Navigation. One method uses one or more range-finding sensors, such as a laser range-finder, as well as gyroscopes or inertial measurement units with Monte-Carlo蒙特卡罗方法/Markov马尔可夫; localization techniques to understand where it is as it dynamically plans the shortest permitted path to its goal. The advantage of such systems is that they are highly flexible for on-demand delivery to any location. They can handle failure without bringing down the entire manufacturing operation, since AGVs can plan paths around the failed device. They also are quick to install, with less down-time for the factory.[4]

- Area is mapped and stored in the vehicle's computer memory
- Use of existing environment scanned by laser bumpers, with the aid of a few fixed reference points
- Guide path is easily changed and expanded
- Most flexible for vehicle movement
- System can be expanded without alteration to the facility
- Dynamic control of blocking and traffic management
- Ideal for environments that can change frequently, but not significantly
- Short installation times, reducing costs and minimizing the effect on operations
Vision guidance[视觉导航]
Vision-Guided AGVs can be installed with no modifications to the environment or infrastructure. They operate by using cameras to record features along the route, allowing the AGV to replay the route by using the recorded features to navigate. Vision-Guided AGVs use Evidence Grid technology, an application of probabilistic 盖然论的,或然说的;volumetric sensing, and was invented and initially developed by Dr. Hans Moravec at Carnegie Mellon University. The Evidence Grid technology uses probabilities of occupancy for each point in space to compensate补偿 for the uncertainty in the performance of sensors and in the environment. The primary navigation sensors are specially designed stereo cameras. The vision-guided AGV uses 360-degree images and build a 3D map, which allows the vision-guided AGVs to follow a trained route without human assistance or the addition of special features, landmarks or positioning systems.
Geoguidance[edit]
A geoguided AGV recognizes its environment to establish its location. Without any infrastructure基础设施; 基础建设;, the forklift(铲车) equipped with geoguidance technology detects and identifies columns, racks and walls within the warehouse. Using these fixed references, it can position itself, in real time and determine its route. There are no limitations on distances to cover number of pick-up or drop-off locations. Routes are infinitely modifiable.
参考:
1 Guidance / Navigation Technology
https://www.transbotics.com/learning-center/guidance-navigation
2 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Automated_guided_vehicle#Navigation
3 https://blog.csdn.net/wh9602/article/details/4699988
最后
以上就是美丽哈密瓜最近收集整理的关于AGV (Automated guided vehicle)基础(一) - AGV的导航种类的全部内容,更多相关AGV内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复