一、理论
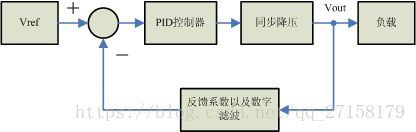
下图是采用了PID控制器的闭环控制策略。
PID控制器的传递函数:
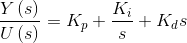
上式中,Y是控制器的输出,U是控制器的输入。
有时候,在Matlab仿真中已经调好了Kp和Ki、Kd参数,但是离散化后,系数和离散时间有关。因此需要重新计算系数。
方法一、用公式替代s算子
用Trapezoid(Tustin)方法离散化PID控制器。另外更多的传递函数离散化方法请浏览:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27158179/article/details/82739641#2%E3%80%81%E7%A6%BB%E6%95%A3%E5%8C%96%E9%A2%84%E5%A4%87%E7%9F%A5%E8%AF%86
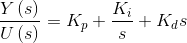
把
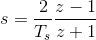 代入上式,得到
代入上式,得到
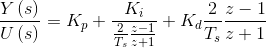
化简过程略,得到:
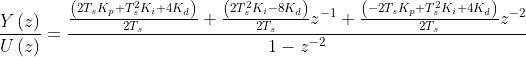
故离散化公式为:
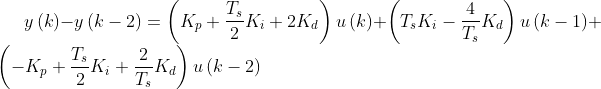
方法二、传统计算方法
PID控制器分为比例环节、积分环节、微分环节。如下:
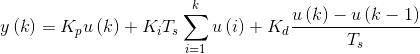
上式也是位置式PID。
如果要转换为增量式,过程如下:
我们把PID控制器分为比例环节、积分环节、微分环节。由于控制器的输出就是三个环节的叠加,因此可以分别计算每个环节:
比例部分:
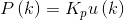
积分部分:
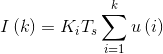
由于
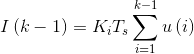
因此,可以用I(k-1)替代冗长的u(i),i=1,2,...,k的累加。
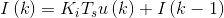
微分部分:
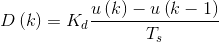
把比例、积分、微分三部分叠加,可以得到公式:
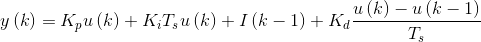
化简:
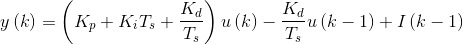
至此,只要需要了解离散时间,也就是执行本控制器算法的间隔Ts,即可把已经在上位机仿真模型中调好的Kp、Ki、Kd、通过计算转换成u(k)和u(k-1)的系数。
二、实践
上机,以下代码主要来自XMC™ Control Library。Infineon提供的library中有PI控制器,我在这个基础上增加了微分环节。
1、PID.c
/*
* PID.c
*
* Created on: 2018年10月1日
* Author: xxJian
*/
#include "PID.h"
/* Initializes a PID controller with anti-windup scheme and programmable output limit saturation. */
void XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PIDFloatInit(XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PID_DATA_FLOAT_t* handle_ptr,
volatile float* ref_ptr, volatile float* fdbk_ptr,
float kp, float ki, float kd,
float limit_min, float limit_max,
volatile uint32_t* out)
{
//memset((void *)handle_ptr, 0, sizeof(*handle_ptr));
handle_ptr->fdbk_ptr = fdbk_ptr; /**< pointer to ADC register which is used for feedback */
handle_ptr->ref_ptr = ref_ptr; /**< ADC ref */
handle_ptr->kp = kp; /*coefficient filter current input*/
handle_ptr->ki = ki; /*coefficient filter input one previous*/
handle_ptr->kd = kd;
handle_ptr->out_limit_max = limit_max; /*maximum output saturation*/
handle_ptr->out_limit_min = limit_min; /*output saturation min for filter implementation*/
handle_ptr->out = out;
}
void XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PIDFloat(XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PID_DATA_FLOAT_t* handle_ptr)
{
/*
* I(k) = Ki * error + I(k-1)
* U(k) = Kp * error + I(k) + Kd * (error - error_1)
* if(min < U(k) < max){I(k-1) = I(k);}//Anti wind-up
*/
handle_ptr->error = *(handle_ptr->ref_ptr) - *(handle_ptr->fdbk_ptr);
handle_ptr->ik = (handle_ptr->error * handle_ptr->ki) + handle_ptr->ik_1;
handle_ptr->uk = (handle_ptr->error * handle_ptr->kp) + handle_ptr->ik + handle_ptr->kd*(handle_ptr->error - handle_ptr->error_1);
if (handle_ptr->uk > handle_ptr->out_limit_max)
{
handle_ptr->uk = handle_ptr->out_limit_max; /*Disable anti wind up filter*/
}
else if (handle_ptr->uk < handle_ptr->out_limit_min)
{
handle_ptr->uk = handle_ptr->out_limit_min; /*Disable anti wind up filter*/
}
else
{
handle_ptr->ik_1 = handle_ptr->ik; /*Enable anti wind up filter*/
}
handle_ptr->error_1 = handle_ptr->error;
*(handle_ptr->out) = (uint32_t)handle_ptr->uk;
}
2、PID.h
/*
* PID.h
*
* Created on: 2018年10月1日
* Author: xxJian
*/
#ifndef PID_H_
#define PID_H_
#include "main.h"
#include "stm32f4xx_hal.h"
/**
* @brief PI floating point data & coefficients structure
*/
typedef struct XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PID_DATA_FLOAT
{
volatile float* fdbk_ptr; /**< Pointer to feedback, generally ADC result register*/
volatile float* ref_ptr; /**< Pointer to reference */
float error; /*!< PID error signal (reference value - feedback value), error[k] */
float error_1; /*!< PID error signal (reference value - feedback value), error[k-1] */
float kp; /*!< Proportional gain Kp constant */
float ki; /*!< Integral gain Ki constant*/
float kd; /*!< Differential gain Ki constant*/
float out_limit_max; /*!< Maximum value of the PI output */
float out_limit_min; /*!< Minimum value of the PI output */
float uk; /*!< PI output U[k] */
float ik; /*!< Integral result I[k] */
float ik_1; /*!< Integral result I[k-1] */
volatile uint32_t* out; /*!< PI Output after anti-windup scheme */
} XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PID_DATA_FLOAT_t;
/*******************************************************************************************************************/
/**
* @brief Initializes the data structure of XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PIFloat() API.
* @param handle_ptr pointer to XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PI_DATA_FLOAT_t structure
* @param ref_ptr Pointer to reference voltage variable
* @param fdbk_ptr pointer to feedback variable
* @param kp Proportional gain constant
* @param ki Integral gain constant
* @param ki Differential gain constant
* @param limit_max maximum output limit for anti-windup scheme
* @param limit_min minimum output limit for anti-windup scheme
* @param out Pointer to PI output variable
*
* parDescription:
* The function can be used to initialize the data structure XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PI_DATA_FLOAT_t used by
* XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PIFloat() API.
*
* Example Usage:
* @code
#include int main(void)
{
uint32_t ref = 3247.1304f; //reference voltage 3.3 volts in steps of ADC
uint32_t vout = 2702.5139f; //measured feedback voltage 3 volts in steps of ADC
uint32_t compare_value; //CCU4/8 compare value for PWM generation
float kp = 0.001f; //Proportional gain constant
float ki = 0.01f; //Integral gain constant
float kd = 0.0f; //Integral gain constant
float limit_max = 1023.0f; //maximum output for anti-windup scheme
float limit_min = 155.0f; //minimum output for anti-windup scheme
XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PID_DATA_FLOAT_t handle; //control data structure
XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PIDFloatInit(&handle,
&ref, &vout,
kp, ki, kd,
limit_min, limit_max,
&compare_value
);
XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PIDFloat(&handle);
//compare_value will holds the output
while(1)
{
}
return 0;
}
* @endcode
*
*/
void XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PIDFloatInit(XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PID_DATA_FLOAT_t* handle_ptr,
volatile float* ref_ptr, volatile float* fdbk_ptr,
float kp, float ki, float kd,
float limit_min, float limit_max,
volatile uint32_t* out);
/**
* @brief Calculates a proportional integral controller output with programmable output limits for anti-windup scheme.
* @param handle_ptr XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PI_DATA_FLOAT_t structure with proper input values.
*
* parDescription:
* The function can be used to implement control loop feedback mechanism which commonly used in industrial applications.
* A PI controller continuously calculates an error value as the difference between a reference and a feedback.
*
* I[k] = Ki * error + I[k-1]
* U[k] = Kp * error + I[k] + Kd* (error[k]-error[k-1])
* if(min < U[k] < max){I[k-1] = I[k];}//Anti wind-up
*
* Example Usage:
* @code
#include int main(void)
{
uint32_t ref = 3247.1304f; //reference voltage 3.3 volts in steps of ADC
uint32_t vout = 2702.5139f; //measured feedback voltage 3 volts in steps of ADC
uint32_t compare_value; //CCU4/8 compare value for PWM generation
float kp = 0.001f; //Proportional gain constant
float ki = 0.01f; //Integral gain constant
float kd = 0.0f; //Integral gain constant
float limit_max = 1023.0f; //maximum output for anti-windup scheme
float limit_min = 155.0f; //minimum output for anti-windup scheme
XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PI_DATA_FLOAT_t handle; //control data structure
XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PIDFloatInit(&handle,
&ref, &vout,
kp, ki, kd,
limit_min, limit_max,
&compare_value
);
XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PIDFloat(&handle);
//compare_value will holds the output
while(1)
{
}
return 0;
}
* @endcode
*
*/
void XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PIDFloat(XMC_CONTROL_LIB_PID_DATA_FLOAT_t* handle_ptr);
#endif /* PID_H_ */
在STM32开发板上和直流有刷电机连接,电机上的霍尔编码器和单片机的TIM3连接。对电机进行PID闭环控制。由于我不喜欢微分环节(某些地方不喜欢振荡,微分环节会引入振荡,即闭环控制的输出参数会围绕着参考值上下波动),因此把Kd整为0.把Kp和Ki调节到合适的参数,可以让电机稳定在一个转速。我想把电机控制到1.6转每秒。把实时的转速通过USB转UART上传到电脑,使用STLINK可以直接改变Kp和Ki的值。Kp=100,Ki=0.5,可以让系统有微微的超调量。让电机运动有较好的快速性和稳定性。
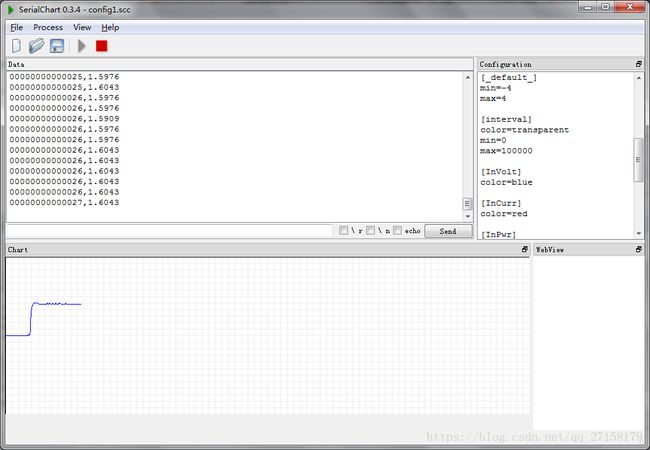
现在TI的资料,controlSuite里面的软件,都用上汇编语言了,十分不方便移植到别的单片机中。看来围绕着Arduino、树莓派等开源活动,已经动摇电子界了。工程师们的知识产权有了提高,在开源所带来的声誉,和闭源所带来的安全,有了一个更好的平衡点。
特别鸣谢:www.infineon.com/xmc。
最后
以上就是大胆老虎最近收集整理的关于c语言中离散化,PID控制器的离散化推导及其C语言实现的全部内容,更多相关c语言中离散化,PID控制器内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复