某一问题有很多重叠子问题
每一状态一定由上一状态推导出来
而贪心没有状态推导,而是直接选局部最优
解决方式:
- 确定dp数组(dp table)以及下标的含义
- 确定递推公式
- dp数组如何初始化
- 确定遍历顺序
- 举例推导dp数组
模拟:举例推导dp数组
检查:打印dp数组
1.Leetcode509. 斐波那契数
class Solution {
public:
int fib(int n) {
//第i个数的值
vector<int>num(n+2,0);
//初始化
num[0]=0;
num[1]=1;
//确定遍历顺序
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
num[i]=num[i-1]+num[i-2];
}
return num[n];
}
};递归写法
class Solution {
public:
int fib(int n) {
if(n<2)return n;
return fib(n-1)+fib(n-2);
}
};2.Leetcode70. 爬楼梯
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
vector<int>dp(n+2,0);
//不用考虑dp[0]的初始化,n>0
dp[1]=1;
dp[2]=2;
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++){
dp[i]=dp[i-1]+dp[i-2];
}
return dp[n];
}
};优化空间复杂度O(n)->O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n<=2)return n;
int dp[3];
dp[1]=1;
dp[2]=2;
int sum;
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++){
sum=dp[1]+dp[2];
dp[1]=dp[2];
dp[2]=sum;
}
return sum;
}
};升级:一步一个台阶,两个台阶,...直到m个台阶,有多少种方法爬到n阶
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n,int m) {
vector<int>dp(n+1,0);
dp[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m&&j<=i;j++){
dp[i]+=dp[i-j];
}
}
return dp[n];
}
};3.Leetcode746. 使用最小花费爬楼梯
class Solution {
public:
int minCostClimbingStairs(vector<int>& cost) {
//从第i个楼梯向上爬的最小花费
int len=cost.size();
vector<int>dp(len,0);
dp[0]=cost[0];
dp[1]=cost[1];
for(int i=2;i<len;i++){
dp[i]=min(dp[i-1],dp[i-2])+cost[i];
}
return min(dp[len-1],dp[len-2]);
}
};class Solution {
public:
int minCostClimbingStairs(vector<int>& cost) {
int len=cost.size();
int dp0=cost[0];
int dp1=cost[1];
int t;
for(int i=2;i<len;i++){
t=min(dp0,dp1)+cost[i];
dp0=dp1;
dp1=t;
}
return min(dp0,dp1);
}
};4.Leetcode62. 不同路径
dfs
class Solution {
public:
int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
vector<vector<int>>dp(m+1,vector<int>(n+1,0));
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)dp[i][1]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)dp[1][i]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=m;i++){
for(int j=2;j<=n;j++){
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j-1];
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
};滚动数组优化
数论
5.Leetcode63. 不同路径 II
class Solution {
public:
int uniquePathsWithObstacles(vector<vector<int>>& obstacleGrid) {
int m=obstacleGrid.size(),n=obstacleGrid[0].size();
vector<vector<int>>dp(m,vector<int>(n,0));
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
if(obstacleGrid[i][0])break;
dp[i][0]=1;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(obstacleGrid[0][i])break;
dp[0][i]=1;
}
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
for(int j=1;j<n;j++){
if(!obstacleGrid[i][j]){
if(!obstacleGrid[i-1][j])dp[i][j]+=dp[i-1][j];
if(!obstacleGrid[i][j-1])dp[i][j]+=dp[i][j-1];
}
//printf("i==%d j==%d dp=%dn",i,j,dp[i][j]);
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
};6.Leetcode343. 整数拆分
- 自己的傻瓜推导法
class Solution {
public:
int integerBreak(int n) {
//正整数i的最大乘积
vector<int>dp(n+11);
dp[2]=1;//1
dp[3]=2;//2
dp[4]=4;//2*2
dp[5]=6;//2*3
dp[6]=9;//3*3
dp[7]=12;//2*2*3
dp[8]=18;//2*3*3
dp[9]=27;//3*3*3
for(int i=10;i<=n;i++){
for(int k=3;k<i-1;k++){
dp[i]=max(dp[i],dp[i-k]*dp[k]);
}
}
return dp[n];
// dp[2]=1;
// dp[3]=1*2;
// dp[4]=2*2;
// dp[5]=2*3=6;
// dp[6]=3*3;
// dp[7]=3*4;
// dp[8]=3*3*2;
// dp[9]=3*3*3;
// dp[10]=3*3*4=dp[6]*dp[4]=dp[5]*dp[5];
// dp[11]=3*3*3*2=dp[5]*dp[6];
}
};2. 从1遍历j,有两种渠道得到dp[i]
一个是j * (i - j) 直接相乘。
一个是j * dp[i - j],相当于是拆分(i - j)
class Solution {
public:
int integerBreak(int n) {
vector<int>dp(n+3);
dp[2]=1;
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=4&&j<i;j++){
dp[i]=max(dp[i],max((i-j)*j,dp[i-j]*j));
}
}
return dp[n];
}
};3. 贪心解法
每次拆成n个3,如果剩下是4,则保留4,然后相乘,但是这个结论需要数学证明其合理性
class Solution {
public:
int integerBreak(int n) {
if(n==2)return 1;
if(n==3)return 2;
if(n==4)return 4;
int ans=1;
while(n>=3){
ans*=3;
n-=3;
}
if(n==1)ans=ans*4/3;
if(n==2)ans*=2;
return ans;
}
};7.Leetcode96. 不同的二叉搜索树
class Solution {
public:
int numTrees(int n) {
vector<int>dp(n+1,0);
dp[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){
//对于第i个节点,需要考虑1作为根节点直到i作为根节点的情况,所以需要累加
//一共i个节点,对于根节点j时,左子树的节点个数为j-1,右子树的节点个数为i-j
dp[i]+=dp[j-1]*dp[i-j];
}
}
return dp[n];
}
};dp[3],就是 元素1为头结点搜索树的数量 + 元素2为头结点搜索树的数量 + 元素3为头结点搜索树的数量
元素1为头结点搜索树的数量 = 右子树有2个元素的搜索树数量 * 左子树有0个元素的搜索树数量
元素2为头结点搜索树的数量 = 右子树有1个元素的搜索树数量 * 左子树有1个元素的搜索树数量
元素3为头结点搜索树的数量 = 右子树有0个元素的搜索树数量 * 左子树有2个元素的搜索树数量
01背包
暴力解法:回溯,每个物品取或不取,时间复杂度O(2^n)
暴力解法指的是时间复杂度是指数级别的
滚动数组优化->二维变一维
第二维为什么要反向遍历?
防止物品重复放入
8.Leetcode416. 分割等和子集
初步可以想用回溯法,但是N可以到100,会超时
原本设置dp[][]为int类型,但值会超int大小,设置为bool
class Solution {
public:
bool canPartition(vector<int>& nums) {
int sum=0;
int len=nums.size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)sum+=nums[i];
if(sum%2==1)return false;
vector<vector<bool>>dp(len,vector<bool>(sum/2+1,0));
if(nums[0]<=sum/2)dp[0][nums[0]]=true;
else return false;
//在前i个数中选
for(int i=1;i<len;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=sum/2;j++){
if(dp[i-1][j])dp[i][j]=true;
if(j>=nums[i]&&dp[i-1][j-nums[i]])dp[i][j]=true;
//printf("i==%d j==%d dp=%dn",i,j,dp[i][j]);
}
}
return dp[len-1][sum/2];
return false;
}
};优化为一维
class Solution {
public:
bool canPartition(vector<int>& nums) {
int sum=0;
int len=nums.size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)sum+=nums[i];
if(sum%2==1)return false;
vector<bool>dp(sum/2+1,0);
if(nums[0]<=sum/2)dp[nums[0]]=true;
else return false;
//在前i个数中选
for(int i=1;i<len;i++){
for(int j=sum/2;j>=0;j--){
if(j>=nums[i]&&dp[j-nums[i]])dp[j]=true;
//printf("i==%d j==%d dp=%dn",i,j,dp[i][j]);
}
}
return dp[sum/2];
return false;
}
};9.Leetcode1049. 最后一块石头的重量 II
尽量让石头分成重量相同的两堆,相撞之后剩下的石头最小
class Solution {
public:
int lastStoneWeightII(vector<int>& stones) {
int len=stones.size();
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
sum+=stones[i];
}
int target=sum/2;
//容量为i的背包能放下的最大容量
vector<int>dp(target+1,0);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
for(int j=target;j>=stones[i];j--){
dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j-stones[i]]+stones[i]);
}
}
return sum-dp[target]-dp[target];
}
};10.Leetcode494. 目标和
本题要如何使表达式结果为target,
既然为target,那么就一定有 left组合 - right组合 = target。
left + right等于sum,而sum是固定的。
公式来了, left - (sum - left) = target -> left = (target + sum)/2 。
target是固定的,sum是固定的,left就可以求出来。
此时问题就是在集合nums中找出和为left的组合。
class Solution {
public:
int findTargetSumWays(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int len=nums.size();
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)sum+=nums[i];
if(abs(target)>sum)return false;
if((target+sum)%2==1)return false;
int s=(target+sum)/2;
vector<int>dp(s+1,0);
dp[0]=1;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
for(int j=s;j>=nums[i];j--){
dp[j]+=dp[j-nums[i]];
}
}
return dp[s];
}
};11.Leetcode474. 一和零
是典型的01背包,但是物品重量有两个维度
typedef pair<int,int>PII;
#define x first
#define y second
class Solution {
public:
int findMaxForm(vector<string>& strs, int m, int n) {
//前0后1
vector<vector<int>>dp(m+1,vector<int>(n+1,0));
for(int i=0;i<strs.size();i++){
int x=0,y=0;
for(int j=0;j<strs[i].size();j++){
if(strs[i][j]=='0')x++;
if(strs[i][j]=='1')y++;
}
//printf("x==%d y==%dn",x,y);
for(int j=m;j>=x;j--){
for(int k=n;k>=y;k--){
dp[j][k]=max(dp[j][k],dp[j-x][k-y]+1);
//printf("j==%d k==%d dp=%dn",j,k,dp[j][k]);
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
};完全背包:
12.Leetcode518. 零钱兑换 II
class Solution {
public:
int change(int amount, vector<int>& coins) {
int len=coins.size();
//前i个面额的硬币,可以组成总金额为j的最大组合数
vector<int>dp(amount+1,0);
dp[0]=1;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
printf("i==%dn",i);
for(int j=coins[i];j<=amount;j++){
dp[j]+=dp[j-coins[i]];
//printf("j==%d,dp==%dn",j,dp[j]);
}
}
return dp[amount];
}
};13.Leetcode377. 组合总和 Ⅳ
class Solution {
public:
int combinationSum4(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int len=nums.size();
vector<int>dp(target+1,0);
dp[0]=1;
//求排列数
for(int j=0;j<=target;j++){
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
//C++测试用例有超过两个树相加超过int的数据,所以需要在if里加上dp[i] < INT_MAX - dp[i - num]。
if(j>=nums[i]&&dp[j]<INT_MAX-dp[j-nums[i]])dp[j]+=dp[j-nums[i]];
}
}
return dp[target];
}
};如果求组合数就是外层for循环遍历物品,内层for遍历背包。
如果求排列数就是外层for遍历背包,内层for循环遍历物品。
14.Leetcode70. 爬楼梯
完全背包求排列问题->遍历背包放在外面,遍历物品放在里面
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
vector<int>dp(n+2,0);
dp[1]=1;
dp[2]=2;
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=2&&j<=i;j++){
dp[i]+=dp[i-j];
}
}
return dp[n];
}
};15.Leetcode322. 零钱兑换
class Solution {
public:
int coinChange(vector<int>& coins, int amount) {
int len=coins.size();
//凑成总金额所需的最小硬币个数
vector<int>dp(amount+1,0x3f3f3f3f);
dp[0]=0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
for(int j=coins[i];j<=amount;j++){
dp[j]=min(dp[j],dp[j-coins[i]]+1);
}
}
if(dp[amount]==0x3f3f3f3f)return -1;
return dp[amount];
}
};16.Leetcode279. 完全平方数
class Solution {
public:
int numSquares(int n) {
vector<int>dp(n+1,0x3f3f3f3f);
dp[0]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n/i;i++){
//printf("i==%dn",i);
for(int j=i*i;j<=n;j++){
dp[j]=min(dp[j],dp[j-i*i]+1);
//printf("j==%d dp==%dn",j,dp[j]);
}
}
return dp[n];
}
};17.Leetcode139. 单词拆分
- 回溯法
切割问题类似组合问题
时间复杂度O(2^n)每个单词都有两种状态-切割和不切割
class Solution {
public:
bool dfs(int st,const string&s,const unordered_set<string>&wordSet){
if(st>=s.size())return true;
for(int i=st;i<s.size();i++){
string word=s.substr(st,i-st+1);//start len
if(wordSet.find(word)!=wordSet.end()&&dfs(i+1,s,wordSet)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) {
unordered_set<string>wordSet(wordDict.begin(),wordDict.end());
return dfs(0,s,wordSet);
}
};利用记忆数组存储递归过程中计算的结果--记忆化递归
时间复杂度O(2^n)
class Solution {
public:
bool dfs(int st,const string&s,const unordered_set<string>&wordSet,vector<int>&memory){
if(st>=s.size()){
return true;
}
if(memory[st]!=-1)return memory[st];
for(int i=st;i<s.size();i++){
string word=s.substr(st,i-st+1);
if(wordSet.find(word)!=wordSet.end()&&dfs(i+1,s,wordSet,memory)){
memory[st]=1;//记录以st开始的字符串是可以被拆分的
return true;
}
}
memory[st]=0;
return false;
}
bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) {
unordered_set<string>wordSet(wordDict.begin(),wordDict.end());
vector<int>memory(s.size(),-1);
return dfs(0,s,wordSet,memory);
}
};- 动态规划
组合(先遍历物品再遍历背包)---->这道题用组合只能过39/45
class Solution {
public:
bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) {
unordered_set<string>wordSet(wordDict.begin(),wordDict.end());
//是否可以用字典中的单词拼出s0~i
//背包问题
//完全背包
//组合、排列都ok????
//如果将word作为物品其实只能用排列,用过的word不能再用
//无法通过的样例
//"applepenapple"
//["apple","pen"]
//组合写法 常常是-x-x-x-y-y-y-y-z-z
//排列可能涉及,x-y-z-z-x-y,所以这题不能用
vector<int>dp(s.size()+1,0);
dp[0]=true;
for(int i=0;i<wordSet.size();i++){
cout<<"i=="<<i<<endl;
int len=wordDict[i].size();
cout<<wordDict[i]<<endl;
for(int j=len;j<=s.size();j++){
cout<<"j=="<<j<<endl;
string word=s.substr(j-len,len);
cout<<word<<endl;
if(wordSet.find(word)!=wordSet.end()&&dp[j-len]){
dp[j]=true;
}
cout<<"dp "<<j<<"=="<<dp[j]<<endl;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<=s.size();i++){
if(dp[i])printf("%dn",i);
}
return dp[s.size()];
}
};正解:
class Solution {
public:
bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) {
unordered_set<string>wordSet(wordDict.begin(),wordDict.end());
vector<int>dp(s.size()+1,0);
//排列
dp[0]=true;
for(int i=1;i<=s.size();i++){
for(int j=0;j<wordDict.size();j++){
if(i+wordDict[j].size()-1>s.size())continue;
string word=s.substr(i-1,wordDict[j].size());
//cout<<word<<endl;
if(wordSet.find(word)!=wordSet.end()&&dp[i-1]){
dp[i+wordDict[j].size()-1]=true;
//cout<<"i=="<<i<<endl;
//cout<<"???"<<i+wordDict[j].size()-1<<endl;
}
}
}
//for(int i=0;i<=s.size();i++)if(dp[i])cout<<i<<endl;
return dp[s.size()];
}
};代码随想录解法:
对区间i-j上字符进行判断
class Solution {
public:
bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) {
unordered_set<string> wordSet(wordDict.begin(), wordDict.end());
vector<bool> dp(s.size() + 1, false);
dp[0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= s.size(); i++) { // 遍历背包
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { // 遍历物品
string word = s.substr(j, i - j); //substr(起始位置,截取的个数)
if (wordSet.find(word) != wordSet.end() && dp[j]) {
dp[i] = true;
}
}
}
return dp[s.size()];
}
};多重背包和01背包最为相似
将多重背包转换为01背包的方法
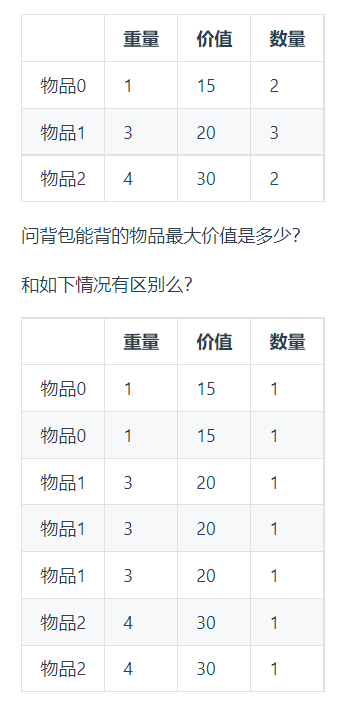
vector<int> weight = {1, 3, 4};
vector<int> value = {15, 20, 30};
vector<int> nums = {2, 3, 2};
int bagWeight = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
while (nums[i] > 1) { // nums[i]保留到1,把其他物品都展开
weight.push_back(weight[i]);
value.push_back(value[i]);
nums[i]--;
}
}- 时间复杂度:$O(m × n × k)$,m:物品种类个数,n背包容量,k单类物品数量
18.Leetcode198. 打家劫舍
class Solution {
public:
int rob(vector<int>& nums) {
//打劫到第i家得到的最高金额
vector<int>dp(1+nums.size(),0);
dp[0]=0;
dp[1]=nums[0];
for(int i=2;i<=nums.size();i++)dp[i]=max(dp[i-2]+nums[i-1],dp[i-1]);
return dp[nums.size()];
}
};19.Leetcode213. 打家劫舍 II
注意打劫可以隔2个房间,跟奇偶无关
注意边界
class Solution {
public:
int robnum(int st,int ed,vector<int>& nums){
//!!!
if(st==ed)return nums[st];
int len=ed-st+1;
vector<int>dp(ed+1,0);
dp[st]=nums[st];
dp[st+1]=max(dp[st],nums[st+1]);
for(int i=st+2;i<=ed;i++)dp[i]=max(dp[i-2]+nums[i],dp[i-1]);
return dp[ed];
}
int rob(vector<int>& nums) {
int len=nums.size();
//!!!!
if(len==0)return 0;
if(len==1)return nums[0];
//有2种情况 1.头+中 2.中+尾
return max(robnum(0,len-2,nums),robnum(1,len-1,nums));
}
};20.Leetcode337. 打家劫舍 III(树形DP)
法一:暴力递归超时
空间复杂度O(logn)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int rob(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL)return 0;
if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL)return root->val;
int res0=0,res1=root->val;
//偷父节点
if(root->left)res1+=rob(root->left->left)+rob(root->left->right);
if(root->right)res1+=rob(root->right->left)+rob(root->right->right);
//不偷
if(root->right)res0+=rob(root->right);
if(root->left)res0+=rob(root->left);
return max(res0,res1);
}
};法二:记忆化递推
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(logn)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<TreeNode*,int>umap;
int rob(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL)return 0;
if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL)return root->val;
if(umap[root])return umap[root];
int res0=0,res1=root->val;
//偷父节点
if(root->left)res1+=rob(root->left->left)+rob(root->left->right);
if(root->right)res1+=rob(root->right->left)+rob(root->right->right);
//不偷
if(root->right)res0+=rob(root->right);
if(root->left)res0+=rob(root->left);
umap[root]=max(res1,res0);
return umap[root];
}
};法三:动态规划
用长度为2的数组记录每个节点偷与不偷
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> robTree(TreeNode *root){
if(root==NULL)return {0,0};
vector<int> left=robTree(root->left);
vector<int> right=robTree(root->right);
//偷
int val1=root->val+left[0]+right[0];
//不偷
int val0=max(left[0],left[1])+max(right[0],right[1]);
return {val0,val1};
}
int rob(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int>ans=robTree(root);
return max(ans[0],ans[1]);
}
};21.Leetcode121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
只能交易一次
法一:暴力解法 O(n^2)超时
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int len=prices.size();
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<len;j++){
ans=max(prices[j]-prices[i],ans);
}
}
return ans;
}
};法二:贪心,取左最小值,右最大值
时间复杂度O(n)
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int len=prices.size();
int ans=0;
vector<int>low(len,0);
low[0]=prices[0];
for(int i=1;i<len;i++){
low[i]=min(low[i-1],prices[i]);
ans=max(prices[i]-low[i],ans);
}
return ans;
}
};法三:动态规划
- 确定dp数组(dp table)以及下标的含义
dp[i][0]表示第i天时持有股票所得最多的现金
dp[i][1]表示第i天时不持有股票所得最多现金
注意:第i天时持有不是第i天买入
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int len=prices.size();
vector<vector<int>>dp(len,vector<int>(2,0));
//第i天持有股票所得最多的现金dp[i][0]
//第i天不持有股票所得的最多现金
dp[0][0]=-prices[0];
dp[0][1]=0;
for(int i=1;i<len;i++){
//上一天持有,今天买入
dp[i][0]=max(dp[i-1][0],-prices[i]);
//上一天也不持有/今天卖出
dp[i][1]=max(dp[i-1][1],dp[i-1][0]+prices[i]);
}
return dp[len-1][1];
}
};优化空间复杂度
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int len=prices.size();
vector<vector<int>>dp(2,vector<int>(2,0));
dp[0][0]=-prices[0];
dp[0][1]=0;
for(int i=1;i<len;i++){
dp[i%2][0]=max(dp[(i-1)%2][0],-prices[i]);
dp[i%2][1]=max(dp[(i-1)%2][1],dp[(i-1)%2][0]+prices[i]);
}
return dp[(len-1)%2][1];
}
};22.Leetcode122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II
可以无限次交易
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int len=prices.size();
vector<vector<int>>dp(len,vector<int>(2,0));
dp[0][0]=-prices[0];
dp[0][1]=0;
for(int i=1;i<len;i++){
dp[i][0]=max(dp[i-1][1]-prices[i],dp[i-1][0]);
dp[i][1]=max(dp[i-1][0]+prices[i],dp[i-1][1]);
}
return dp[len-1][1];
}
};23.Leetcode123. 买卖股票的最佳时机 III
最多交易两次
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int len=prices.size();
//第i天所对应的状态
//最多可以完成两笔交易
//1.无交易
//2.买入第一次
//3.卖出第一次
//4.买入第二次
//5.卖出第二次
vector<vector<int>>dp(len+2,vector<int>(5,0));
dp[0][0]=0;
dp[0][1]=-prices[0];
//一定要初始化dp[0][3],循环里的逻辑也是可以一天买两次
dp[0][3]=-prices[0];
for(int i=1;i<len;i++){
dp[i][0]=dp[i-1][0];
dp[i][1]=max(dp[i-1][1],dp[i-1][0]-prices[i]);
dp[i][2]=max(dp[i-1][2],dp[i-1][1]+prices[i]);
dp[i][3]=max(dp[i-1][3],dp[i-1][2]-prices[i]);
dp[i][4]=max(dp[i-1][4],dp[i-1][3]+prices[i]);
}
return dp[len-1][4];
}
};24.Leetcode188. 买卖股票的最佳时机 IV
最多交易k次
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(int k, vector<int>& prices) {
int len=prices.size();
if(len==0||len==1)return 0;
vector<vector<int>>dp(len+1,vector<int>(2*k+1,0));
for(int i=0;i<=2*k;i++){
if(i%2)dp[0][i]=-prices[0];
}
for(int i=1;i<len;i++){
dp[i][0]=dp[i-1][0];
for(int j=1;j<=2*k;j++){
if(j%2)dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i-1][j-1]-prices[i]);
else dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i-1][j-1]+prices[i]);
}
}
return dp[len-1][k*2];
}
};25.Leetcode309. 最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int len=prices.size();
vector<vector<int>>dp(len+1,vector<int>(5,0));
//1.买入状态
//卖出状态:
//2.度过冷冻期保持卖出
//3.今天卖出
//4.冷冻期
dp[0][1]=-prices[0];
for(int i=1;i<len;i++){
dp[i][0]=dp[i-1][0];
//买入状态
//前一天持有,今天买(前一天是冷冻期,前一天非冷冻期)
dp[i][1]=max(dp[i-1][1],max(dp[i-1][4],dp[i-1][2])-prices[i]);
//卖出
//今天卖出,前一天卖出
dp[i][2]=max(dp[i-1][2],dp[i-1][4]);
dp[i][3]=dp[i-1][1]+prices[i];
dp[i][4]=dp[i-1][3];
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<=4;i++){
ans=max(ans,dp[len-1][i]);
}
return ans;
}
};26.Leetcode714. 买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices, int fee) {
int len=prices.size();
vector<vector<int>>dp(len+1,vector<int>(2,0));
dp[0][1]=-prices[0];
for(int i=1;i<len;i++){
dp[i][0]=max(dp[i-1][0],dp[i-1][1]+prices[i]-fee);
dp[i][1]=max(dp[i-1][1],dp[i-1][0]-prices[i]);
}
return dp[len-1][0];
}
};27.Leetcode300. 最长递增子序列
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLIS(vector<int>& nums) {
int len=nums.size();
//以nums[i]为结尾的递增子序列长度
vector<int>dp(len+1,1);
int ans=1;
for(int i=1;i<len;i++){
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
if(nums[i]>nums[j])dp[i]=max(dp[j]+1,dp[i]);
}
ans=max(ans,dp[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};28.Leetcode674. 最长连续递增序列
class Solution {
public:
int findLengthOfLCIS(vector<int>& nums) {
int len=nums.size();
//以nums[i]结尾的最长连续递增子序列
vector<int>dp(len+1,1);
int ans=1;
for(int i=1;i<len;i++){
if(nums[i]>nums[i-1])dp[i]=dp[i-1]+1;
ans=max(ans,dp[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};29.Leetcode718. 最长重复子数组
注意是连续的
class Solution {
public:
int findLength(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
int len1=nums1.size(),len2=nums2.size();
//nums1的前i个和nums2的前j个中有多少个重复的
vector<vector<int>>dp(len1+1,vector<int>(len2+1,0));
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=len1;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=len2;j++){
if(nums1[i-1]==nums2[j-1])dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
ans=max(ans,dp[i][j]);
}
}
return ans;
}
};30.Leetcode1143. 最长公共子序列
class Solution {
public:
int longestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) {
int len1=text1.size(),len2=text2.size();
//nums1的前i个和nums2的前j个中有多少个重复的
vector<vector<int>>dp(len1+1,vector<int>(len2+1));
for(int i=1;i<=len1;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=len2;j++){
if(text1[i-1]==text2[j-1])dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
else dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
return dp[len1][len2];
}
};31.Leetcode1035. 不相交的线
class Solution {
public:
int maxUncrossedLines(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
int len1=nums1.size(),len2=nums2.size();
vector<vector<int>>dp(len1+1,vector<int>(len2+1,0));
for(int i=1;i<=len1;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=len2;j++){
if(nums1[i-1]==nums2[j-1])dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
else dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
return dp[len1][len2];
}
};32.Leetcode53. 最大子数组和
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int len=nums.size();
//j~i连续数组总和
vector<vector<int>>dp(len+1,vector<int>(len+1,0));
int ans=nums[0];
for(int i=1;i<=len;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){
dp[j][i]=dp[j][i-1]+nums[i-1];
ans=max(ans,dp[j][i]);
}
}
return ans;
}
};class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int len=nums.size();
//以i结尾的具有最大和的连续数组
vector<int>dp(len+1,0);
int ans=nums[0];
for(int i=1;i<=len;i++){
dp[i]=max(dp[i-1]+nums[i-1],nums[i-1]);
ans=max(ans,dp[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};33.Leetcode392. 判断子序列
法一:最长公共子序列值大于等于子串长度,时间复杂度O(n*m)
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubsequence(string s, string t) {
int len1=s.size(),len2=t.size();
//s到i,t到j的最长公共子序列长度
vector<vector<int>>dp(len1+1,vector<int>(len2+1,0));
for(int i=1;i<=len1;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=len2;j++){
if(s[i-1]==t[j-1])dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
else dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
return dp[len1][len2]>=len1;
}
};法二:双指针O(n)
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubsequence(string s, string t) {
int len1=s.size(),len2=t.size();
bool flag=true;
for(int i=0,j=-1;i<len1;i++){
j++;
while(j<len2&&s[i]!=t[j])j++;
if(j==len2)flag=false;
}
return flag;
}
};34.Leetcode115. 不同的子序列
如果不是子序列,而是要求连续序列的,那就可以考虑用KMP
本题相当于编辑距离只有删除操作,不用考虑替换增加
class Solution {
public:
int numDistinct(string s, string t) {
int len1=s.size(),len2=t.size();
vector<vector<uint64_t>>dp(len1+1,vector<uint64_t>(len2+1,0));
//dp[i][j]是s[0~i-1]的子序列中t[0~t-1]的出现个数
//以i-1为结尾的s可以随便删除元素,出现空字符串的个数。
for(int i=0;i<=len1;i++)dp[i][0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=len2;i++)dp[0][i]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=len1;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=len2;j++){
//s[i-1]==t[i-1]时不用进行编辑
//dp[i-1][j]相当于删除s[i-1]
//相同时可以用s[i-1]进行匹配,也可以不用s[i-1]进行匹配
//bagg bag
//不相同时要进行编辑
if(s[i-1]==t[j-1])dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]+dp[i-1][j];
else dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j];
}
}
return dp[len1][len2];
}
};35.Leetcode583. 两个字符串的删除操作
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
int len1=word1.size(),len2=word2.size();
vector<vector<int>>dp(len1+1,vector<int>(len2+1,0));
for(int i=0;i<=len1;i++)dp[i][0]=i;
for(int i=0;i<=len2;i++)dp[0][i]=i;
for(int i=1;i<=len1;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=len2;j++){
if(word1[i-1]==word2[j-1]){
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1];
}else{
dp[i][j]=min({dp[i-1][j-1]+2,dp[i][j-1]+1,dp[i-1][j]+1});
}
}
}
return dp[len1][len2];
}
};36.Leetcode72. 编辑距离
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
int len1=word1.size(),len2=word2.size();
vector<vector<int>>dp(len1+1,vector<int>(len2+1,0));
for(int i=0;i<=len1;i++)dp[i][0]=i;
for(int i=0;i<=len2;i++)dp[0][i]=i;
for(int i=1;i<=len1;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=len2;j++){
if(word1[i-1]==word2[j-1])dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1];
else dp[i][j]=min(min(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]),dp[i-1][j-1])+1;
}
}
return dp[len1][len2];
}
};37.Leetcode647. 回文子串
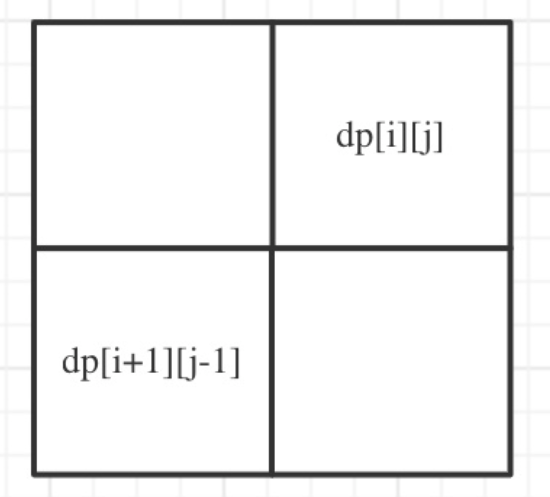
遍历顺序一定从下到上,从左到右
class Solution {
public:
int countSubstrings(string s) {
int len=s.size();
vector<vector<bool>>dp(len+1,vector<bool>(len+1,false));
int res=0;
for(int i=len;i>=1;i--){
for(int j=i;j<=len;j++){
if(s[i-1]==s[j-1]){
if(i==j)dp[i][j]=true;
else if(j-i==1)dp[i][j]=true;
else if(dp[i+1][j-1])dp[i][j]=true;
if(dp[i][j]){
res++;
}
}else{
dp[i][j]=false;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};38.Leetcode516. 最长回文子序列
class Solution {
public:
int longestPalindromeSubseq(string s) {
int len=s.size();
vector<vector<int>>dp(len+1,vector<int>(len+1,1));
int ans=1;
for(int i=len;i>=1;i--){
for(int j=i+1;j<=len;j++){
if(s[i-1]==s[j-1]){
if(j-i==1)dp[i][j]=2;
if(j-i>1)dp[i][j]=dp[i+1][j-1]+2;
}else{
dp[i][j]=max(dp[i+1][j],dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
}
return dp[1][len];
}
};最后
以上就是孝顺大碗最近收集整理的关于Leetcode动态规划专题(共38道)1.Leetcode509. 斐波那契数2.Leetcode70. 爬楼梯3.Leetcode746. 使用最小花费爬楼梯4.Leetcode62. 不同路径5.Leetcode63. 不同路径 II6.Leetcode343. 整数拆分7.Leetcode96. 不同的二叉搜索树8.Leetcode416. 分割等和子集9.Leetcode1049. 最后一块石头的重量 II10.Leetcode494. 目标和11.Leetcode474. 一和零12的全部内容,更多相关Leetcode动态规划专题(共38道)1.Leetcode509.内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复