文章目录
- 总结
- 2021.08.11 第1 天 求和问题
- [1 1 两数之和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/)
- [2 167. 两数之和 II - 输入有序数组](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum-ii-input-array-is-sorted/)
- 2021.08.12 第2天 求和问题
- [3 15. 三数之和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum/)
- [4 18. 四数之和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/4sum/)
- 2021.08.13 第3天 斐波拉契数列
- [5 509. 斐波那契数](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/fibonacci-number/)
- [6 70. 爬楼梯](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/)
- 2021.08.14 第4天 动态规划法
- [7 53. 最大子序和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-subarray/)
- [8 416. 分割等和子集](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/partition-equal-subset-sum/)
- [9 322. 零钱兑换](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/coin-change/submissions/)
- 2021.08.15 第5 天 堆栈
- [10 20. 有效的括号](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-parentheses/)
- [11 496. 下一个更大元素 I](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/next-greater-element-i/)
- [503. 下一个更大元素 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/next-greater-element-ii/)
- [12 456. 132 模式](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/132-pattern/)
- 2021.08.16 第6天 数字
- [13 119. 杨辉三角 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pascals-triangle-ii/)
- [14 279. 完全平方数](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/perfect-squares/)
- [15 483. 最小好进制](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/smallest-good-base/)
- 2021.08.17 第7天 树
- [16 112. 路径总和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum/)
- [17 230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/)
- [18 968. 监控二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-cameras/)
- 2021.08.18 第8天 字符串
- [()19 720. 词典中最长的单词](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-word-in-dictionary/)
- [20 3. 无重复字符的最长子串](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/)
- [21 97. 交错字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/interleaving-string/)
- 2021.08.19 第9天
- [()22 28. 实现 strStr()](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-strstr/)
- [23 524. 通过删除字母匹配到字典里最长单词](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-word-in-dictionary-through-deleting/)
- [()24 1392. 最长快乐前缀](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-happy-prefix/)
- 2021.08.20 第10天
- [25 1042. 不邻接植花](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flower-planting-with-no-adjacent/)
- [26 787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/cheapest-flights-within-k-stops/)
- 2021.08.21 第11天 图
- [27 79. 单词搜索](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-search/)
- [28 329. 矩阵中的最长递增路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-increasing-path-in-a-matrix/)
- 2021.08.22 第12天 生活趣题
- [29 121. 买卖股票的最佳时机](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/)
- [30 122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/)
总结
由给出的矩阵构建邻接矩阵
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) graph.add(new ArrayList<>(3));
for (int[] path : paths) {
graph.get(path[0] - 1).add(path[1] - 1);
graph.get(path[1] - 1).add(path[0] - 1);
}
在可以四个方向走的矩阵中,一般用memo[][是会出错的,因为memo[][]只能代表当前点走3个方向得到的结果,它不能往回走,所以例如第79题,单词搜索中,我们可以预先判断有没有可能搜索到目标字符串,这也是一种剪枝。
2021.08.11 第1 天 求和问题
1 1 两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
思路:遍历数组,将遍历过的元素入Map,然后比那里的过程中看map中是否有target-nums[i]
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer,Integer>map=new HashMap();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(map.containsKey(target-nums[i]))
return new int[]{i,map.get(target-nums[i])};
map.put(nums[i],i);
}
return null;
}
}
2 167. 两数之和 II - 输入有序数组
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
int i=0;int j=numbers.length-1;
while(i<j){
if(numbers[i]+numbers[j]<target) i++;
else if(numbers[i]+numbers[j]>target) j--;
else return new int[]{i+1,j+1};
}
return null;
}
}
2021.08.12 第2天 求和问题
3 15. 三数之和
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
解题思路,固定第一个数,然后利用双指针找剩下的两个数,每次找到之后记得去重,为了避免重复,先把数组排序,好降重
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>>list=new ArrayList();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(i>0&&nums[i]==nums[i-1])
continue;//去重
int L=i+1;int R=nums.length-1;
while(L<R){
if(nums[L]+nums[R]>0-nums[i])
R--;
else if(nums[L]+nums[R]<0-nums[i])
L++;
else {
list.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[L],nums[R]));
int temp=nums[L];
int temp2=nums[R];
while(L<R&&nums[++L]==temp);//L去重,且要注意避免越界
while(L<R&&nums[--R]==temp2);//R去重,且要注意避免越界
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
4 18. 四数之和

先看暴力解法,四重for循环枚举,然后利用 Collections.sort(ans);排序,再降重
class Solution {
public static List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> resp = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<nums.length;j++){
for(int k=j+1;k<nums.length;k++){
for(int l=k+1;l<nums.length;l++){
if(nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[k]+nums[l] == target){
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
ans.add(nums[i]);
ans.add(nums[j]);
ans.add(nums[k]);
ans.add(nums[l]);
Collections.sort(ans);
if(!resp.contains(ans)){
resp.add(ans);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return resp;
}
}
然后就是在三数之和的基础上加上一层for循环
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>>list=new ArrayList();
for(int k=0;k<nums.length;k++){
if(k>0&&nums[k]==nums[k-1])
continue;//去重
for(int i=k+1;i<nums.length;i++){
if(i>k+1&&nums[i]==nums[i-1])
continue;//去重
int L=i+1;int R=nums.length-1;
while(L<R){
if(nums[L]+nums[R]>target-nums[k]-nums[i])
R--;
else if(nums[L]+nums[R]<target-nums[k]-nums[i])
L++;
else {
list.add(Arrays.asList(nums[k],nums[i],nums[L],nums[R]));
int temp=nums[L];
int temp2=nums[R];
while(L<R&&nums[++L]==temp);//L去重,且要注意避免越界
while(L<R&&nums[--R]==temp2);//R去重,且要注意避免越界
}
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
剪枝的效果还是立竿见影的
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null || nums.length < 4) {
return result;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
int length = nums.length;
// 遍历
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 3; i++) {
// 剪枝
if (nums[i] + nums[i + 1] + nums[i + 2] + nums[i + 3] > target) break;
if (nums[i] + nums[length - 3] + nums[length - 2] + nums[length - 1] < target) continue;
// 去重
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) continue;
// 对第二个数进行循环
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length - 2; j++) {
// 剪枝
if (nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[j + 1] + nums[j + 2] > target) break;
if (nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[length - 2] + nums[length - 1] < target) continue;
// 去重
if (j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) continue;
// 定义指针
int left = j + 1, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if (sum > target) {
right--;
} else if (sum < target) {
left++;
} else if (sum == target) {
result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], nums[left], nums[right]));
// 在找到一个数组后进行去重
while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--;
while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++;
// 移动指针
right--;
left++;
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
2021.08.13 第3天 斐波拉契数列
5 509. 斐波那契数

class Solution {
public int fib(int n) {
if(n<=1)
return n;
int a=0,b=1,c=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
c=a+b;
a=b;
b=c;
}
return c;
}
}
6 70. 爬楼梯
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
注意:给定 n 是一个正整数。
解题思路,第n几楼梯可以由第n-1级楼梯跳1步得到,也可以由第n-2级楼梯跳2步得到,所以,f(n)=f(n-1+f(n-2)
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n<3)
return n;
int a=1,b=2,c=0;
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++){
c=a+b;
a=b;
b=c;
}
return c;
}
}
2021.08.14 第4天 动态规划法
7 53. 最大子序和
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
思路:dp[i]表示以每个元素结尾的最大子序和,
如果以前一个元素结尾的最大子序和大于0,那么当前元素结尾的最大子序和就是当前元素加上以前一个元素结尾的最大子序和
否则当前元素结尾的最大子序和就是当前元素
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int dp[]=new int [nums.length];
dp[0]=nums[0];
int max=dp[0];
for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){
dp[i]=dp[i-1]>0?nums[i]+dp[i-1]:nums[i];
max=Math.max(dp[i],max);
}
return max;
}
}
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
//解题思路,当前指针之前的序列和小于0就丢弃,就是已经小于0的连续数列就不要参与后面的计算了,大于0就加到nums[i]上面
int curSum=nums[0];
int max=nums[0];
for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++)
{
if(nums[i-1]>0) nums[i]=nums[i-1]+nums[i];
max=Math.max(nums[i],max);
}
return max;
}
}
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int result=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++)
{
sum+=nums[i];
if(sum>result) result=sum;
if(sum<0) sum=0;
}
return result;
}
}
8 416. 分割等和子集
给你一个 只包含正整数 的 非空 数组 nums 。请你判断是否可以将这个数组分割成两个子集,使得两个子集的元素和相等。
思路1 记忆化归搜索,
最后那个
return memo[i][target] = dfs(nums, target - nums[i], i + 1, memo) || dfs(nums, target, i + 1, memo);
意思是 nums[i]可以取或者不取,如果不取的话,就要在接下来的元素中搜索target,取了的话,就要在接下来的元素中搜索target - nums[i]。
class Solution {
public boolean canPartition(int[] nums) {
int sum = Arrays.stream(nums).sum();
if (sum % 2 != 0) return false;
Arrays.sort(nums);
return dfs(nums, sum / 2, 0, new Boolean[nums.length][sum / 2 + 1]);
}
private boolean dfs(int[] nums, int target, int i, Boolean[][] memo) {
if (i >= nums.length || nums[i] > target)
return false;
if (nums[i] == target)
return true;
if (memo[i][target] != null)
return memo[i][target];
return memo[i][target] = dfs(nums, target - nums[i], i + 1, memo) || dfs(nums, target, i + 1, memo);
}
}

思路2:动态规划

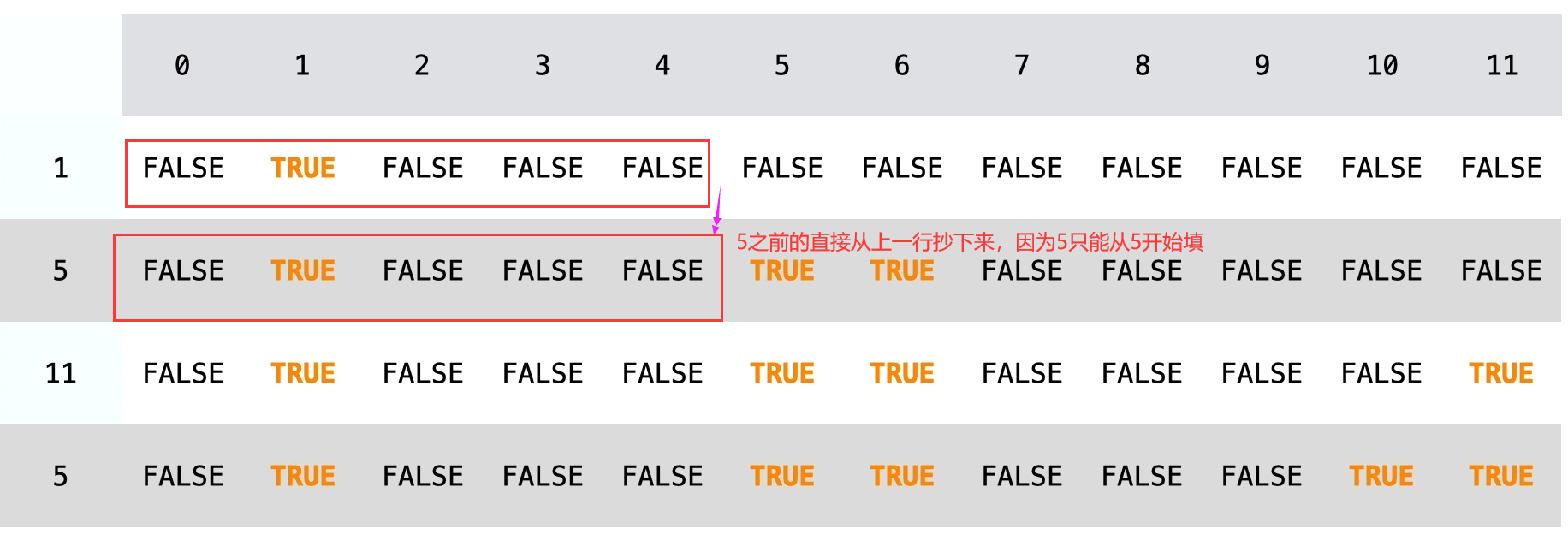
考虑当前元素,那么dp就由上一行左边的某一个数转移过来,比如当前nums[i]等于5,而target=9,我们去了5就要考虑之前的nums元素能不能凑成4
不考虑当前元素,状态直接从上一格抄下来,原来能组成哪些,现在就能组成哪些
class Solution {
public boolean canPartition(int[] nums) {
//实质上是求数组中有没有几个数相加能够达到数组所有元素和的一半,且每个元素只能用1次,是一个0,1背包问题
int sum=0;
int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
sum+=nums[i];
max=Math.max(nums[i],max);
}
if(sum%2!=0||max>sum/2)
return false;
int target=sum/2;
boolean dp[][]=new boolean[nums.length+1][target+1];
for(int i=1;i<=nums.length;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<=target;j++){
if(nums[i-1]>j)//肯定不能用nums[i-1]来组成j,只能用上一行的结果
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j];//直接抄上一行的结果
else if(nums[i-1]<j)//可以用当前nums[i-1]来组成j,那么还要看前面的元素能不能组成j-nums[i-1],也可以不用当前nums[i-1],直接抄前面的结果,两者相或就行了
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j]||dp[i-1][j-nums[i-1]];
else
dp[i][j]=true;//可以组成j,因为nums[i-1]=j
}
}
return dp[nums.length][target];
}
}
???
9 322. 零钱兑换
public class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int max = amount + 1;
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp, max);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < coins.length; j++) {
if (coins[j] <= i) {
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coins[j]] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
}
我之前用hashSet写的超时
public class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
if(amount==0) return 0;
int dp[]=new int [amount+1];
dp[0]=0;
Set<Integer>set=new HashSet();
for(int i=0;i<coins.length;i++) set.add(coins[i]);
for(int i=1;i<=amount;i++)
{
dp[i]=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(set.contains(i)) dp[i]=1;
else {
for(int j=1;j<=i/2;j++)
{
if(dp[j]!=-1&&dp[i-j]!=-1)
dp[i]=Math.min(dp[i],dp[j]+dp[i-j]);
}
if(dp[i]==Integer.MAX_VALUE) dp[i]=-1;
}
}
return dp[amount];
}
}
2021.08.15 第5 天 堆栈
10 20. 有效的括号
给定一个只包括 ‘(’,’)’,’{’,’}’,’[’,’]’ 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character>stack=new Stack();
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(s.charAt(i)==')'){
if(!stack.isEmpty()&&stack.peek()=='(') stack.pop();
else return false;
}
else if(s.charAt(i)=='}'){
if(!stack.isEmpty()&&stack.peek()=='{') stack.pop();
else return false;
}
else if(s.charAt(i)==']'){
if(!stack.isEmpty()&&stack.peek()=='[') stack.pop();
else return false;
}
else
stack.push(s.charAt(i));
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
11 496. 下一个更大元素 I
给你两个 没有重复元素 的数组 nums1 和 nums2 ,其中nums1 是 nums2 的子集。
请你找出 nums1 中每个元素在 nums2 中的下一个比其大的值。
nums1 中数字 x 的下一个更大元素是指 x 在 nums2 中对应位置的右边的第一个比 x 大的元素。如果不存在,对应位置输出 -1 。
思路1:暴力比那里,现在数组2中找到数组1中对应的元素,然后从该位置开始找下一个大于该元素的元素
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int arr[]=new int [nums1.length];
for(int i=0;i<nums1.length;i++){
int j=0;
while(j<nums2.length&&nums2[j]!=nums1[i])
j++;
j++;//后移一位
while(j<nums2.length&&nums2[j]<nums1[i])
j++;
arr[i]=j>=nums2.length?-1:nums2[j];
}
return arr;
}
}
我也是傻了,可以就在原来的数组nums1上修改,不用额外的空间
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
for(int i=0;i<nums1.length;i++){
int j=0;
while(j<nums2.length&&nums2[j++]!=nums1[i]);
while(j<nums2.length&&nums2[j]<nums1[i])
j++;
nums1[i]=j>=nums2.length?-1:nums2[j];
}
return nums1;
}
}
事实上,找右边第 1 个大于比自己大的数,这是一个典型的「栈」的应用(也叫「单调栈」),将每一个元素进栈一次、出栈一次,这样的过程中就可以找到找右边第 1 个大于比自己大的数。
思路2:单调栈
遍历nums2,从前往后,没有找到比该元素小的,就把该元素入栈,然后找到比栈顶大的,就把栈顶元素和对应比它的大的那个元素存入map同时弹出栈顶,注意循环比较栈顶
最后在map里面找不到的元素,对应就置为-1;
public class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int len1 = nums1.length;
int len2 = nums2.length;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// 先处理 nums2,把对应关系存入哈希表
for (int i = 0; i < len2; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() < nums2[i]) {
map.put(stack.pop(), nums2[i]);
}
stack.add(nums2[i]);
}
// 遍历 nums1 得到结果集
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++) {
nums1[i] = map.getOrDefault(nums1[i], -1);
}
return nums1;
}
}
503. 下一个更大元素 II
给定一个循环数组(最后一个元素的下一个元素是数组的第一个元素),输出每个元素的下一个更大元素。数字 x 的下一个更大的元素是按数组遍历顺序,这个数字之后的第一个比它更大的数,这意味着你应该循环地搜索它的下一个更大的数。如果不存在,则输出 -1。
解题思路,把循环数组拉直
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
int ret[]=new int[n];
Arrays.fill(ret, -1);
Stack<Integer>stack=new Stack();
// Map<Integer,Integer>map=new HashMap();//数组中有重复元素,不好用map了
for(int i=0;i<n*2-1;i++){
while(!stack.isEmpty()&&nums[stack.peek()]<nums[i%n]){
ret[stack.pop()]=nums[i%n];
}
//stack.push(nums[i%n]);
stack.push(i%n);//存索引,绝了
}
return ret;
}
}
改进版,不然有重复判断
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
int ret[]=new int[n];
Arrays.fill(ret, -1);
Stack<Integer>stack=new Stack();
for(int i=0;i<n*2-1;i++){
while(!stack.isEmpty()&&nums[stack.peek()]<nums[i%n]){
ret[stack.pop()]=nums[i%n];
}
if(ret[i%n]==-1)
stack.push(i%n);//存索引,绝了
}
return ret;
}
}
静态数组
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] ans = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(ans, -1);
// 使用数组模拟栈,hh 代表栈底,tt 代表栈顶
int[] d = new int[n * 2];
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n * 2; i++) {
while (hh <= tt && nums[i % n] > nums[d[tt]]) {
int u = d[tt--];
ans[u] = nums[i % n];
}
d[++tt] = i % n;
}
return ans;
}
}
12 456. 132 模式
给你一个整数数组 nums ,数组中共有 n 个整数。132 模式的子序列 由三个整数 nums[i]、nums[j] 和 nums[k] 组成,并同时满足:i < j < k 和 nums[i] < nums[k] < nums[j] 。
如果 nums 中存在 132 模式的子序列 ,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。

参考:图解单调栈
class Solution {
public boolean find132pattern(int[] nums) {
int len=nums.length;
if(len<3) return false;
Stack<Integer> st=new Stack<>();
int K=-1;
for(int I=len-1;I>=0;I--){
if(K>-1&&nums[K]>nums[I]) return true;
while(!st.isEmpty()&&nums[st.peek()]<nums[I]){
K=st.pop();
}
st.push(I);
}
return false;
}
}
2021.08.16 第6天 数字
13 119. 杨辉三角 II
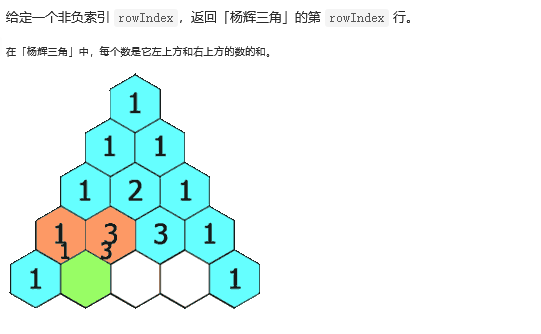
class Solution {
public List<Integer> getRow(int rowIndex) {
List<List<Integer>>list=new ArrayList();
for(int i=0;i<=rowIndex;i++){
List list2=new ArrayList();
for(int j=0;j<=i;j++){
if(j==0||j==i){
list2.add(1);
}else{
list2.add(list.get(i-1).get(j-1)+list.get(i-1).get(j));
}
}
list.add(list2);
}
return list.get(rowIndex);
}
}
class Solution {
public List<Integer> getRow(int rowIndex) {
List<Integer> pre = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i <= rowIndex; ++i) {
List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int j = 0; j <= i; ++j) {
if (j == 0 || j == i) {
cur.add(1);
} else {
cur.add(pre.get(j - 1) + pre.get(j));
}
}
pre = cur;
}
return pre;
}
}
14 279. 完全平方数

解题思路:先判断当前i是不是完全平方数,如果是,dp[i]=1;如果不是,依次遍历前面的dp,找出dp[j]+dp[i-j]中最小的,即组成j最少的平方数数目加上组成i-j最小的平方数数目,加到1/2就可以了,因为后面会重复
class Solution {
public int numSquares(int n) {
int dp[]=new int[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if((int)Math.sqrt(i)*(int)Math.sqrt(i)==i){
dp[i]=1;
}
else{
dp[i]=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int j=1;j<=i/2;j++){
dp[i]=Math.min(dp[j]+dp[i-j],dp[i]);
}
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}

解题思路2

class Solution {
public int numSquares(int n) {
int[] f = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int minn = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 1; j * j <= i; j++) {
minn = Math.min(minn, f[i - j * j]);
}
f[i] = minn + 1;
}
return f[n];
}
}
解题思路3 BFS
每一个节点的值都是从根节点到当前节点的累加。而平方数的个数其实就是遍历到第几层的时候累加和等于target。我们只需要一层一层的遍历,也就是常说的BFS,当遇到累加的和等于target的时候直接返回当前的层数即可。
参考:【数据结构和算法】BFS,动态规划,拉格朗日四平方和定理等4种方式解决
class Solution{
public int numSquares(int n) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//记录访问过的节点值
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
queue.offer(0);
visited.add(0);
//树的第几层
int level = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//每一层的节点数量
int size = queue.size();
level++;
//遍历当前层的所有节点
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
//节点的值
int digit = queue.poll();
//访问当前节点的子节点,类比于二叉树的左右子节点
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
//子节点的值
int nodeValue = digit + j * j;
//nodeValue始终是完全平方数的和,当他等于n的
//时候直接返回
if (nodeValue == n)
return level;
//如果大于n,终止内层循环
if (nodeValue > n)
break;
if (!visited.contains(nodeValue)) {
queue.offer(nodeValue);
visited.add(nodeValue);
}
}
}
}
return level;
}
}
15 483. 最小好进制

2021.08.17 第7天 树
16 112. 路径总和
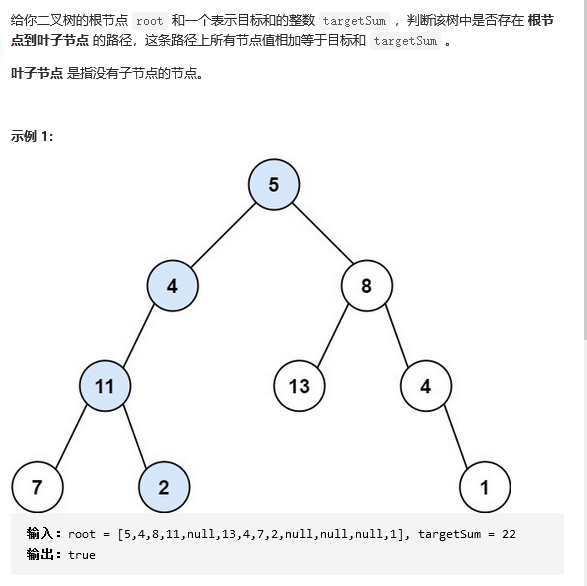
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if(root==null)
return false;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null)
return root.val==sum;
return hasPathSum(root.right, sum-root.val)|| hasPathSum(root.left, sum-root.val);
}
}
思路2:层序遍历,一个队列存储节点,另一个队列存储加上当前节点val的时候的sum值
17 230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
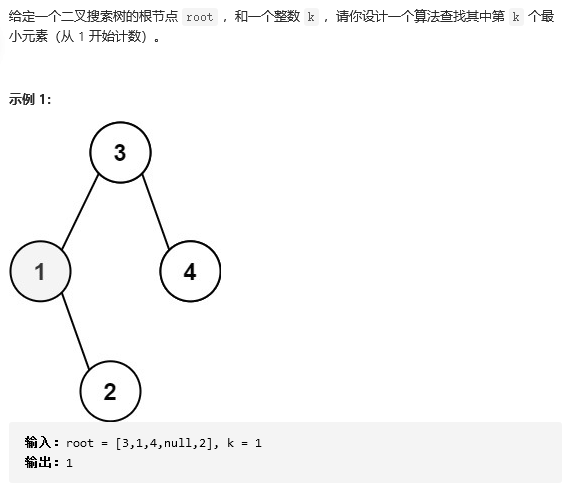
解题思路1.既然是二叉搜索树,那么中序遍历就是有序的升序序列,我们直接中序遍历就好了
class Solution {
int count=0;
int val=-1;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
inOrder(root,k);
return val;
}
public void inOrder(TreeNode root, int k){
if(root==null)
return ;
inOrder(root.left, k);
count++;
if(count==k){
val= root.val;
return;
}
inOrder(root.right, k);
}
}
思路2;:迭代中序遍历
18 968. 监控二叉树
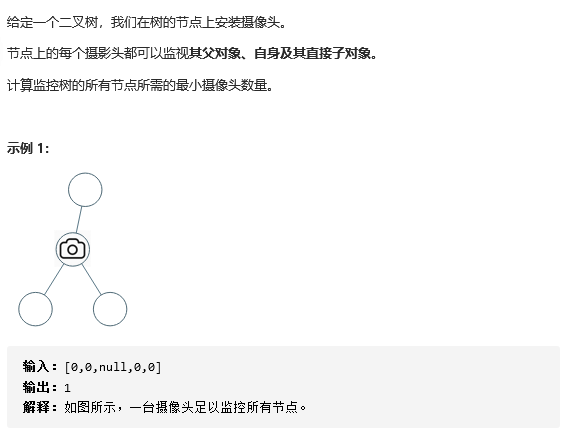
解题思路参考:968. 监控二叉树:【递归上的状态转移】详解
class Solution {
int res=0;
public int minCameraCover(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root)==0?res+1:res;//如果父节点是无覆盖状态,那么需要在父节点添加一台摄像机
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root==null)
return 2;//节点有覆盖
int left=dfs(root.left);
int right=dfs(root.right);
//0表示无覆盖,1表示有相机,2表示有覆盖,左右节点可以组成9种状态
//(00,01,02,10,11,12,20,21,22)
//只要有一个无覆盖,父节点就需要相机来覆盖这个子节点 00,01,10,20,02
if(left==0||right==0){
res++;
return 1;
}
//子节点其中只要有一个有相机,那么父节点就会是有覆盖的状态11,21,12
if(left==1||right==1){
return 2;
}
//还有一个就是22,两个子节点都是有覆盖的状态,父节点可以没有相机,可以借助它自己的父节点
return 0;
}
}
2021.08.18 第8天 字符串
()19 720. 词典中最长的单词

解题思路
20 3. 无重复字符的最长子串
给定一个字符串 s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
解题思路:遍历字符数组,如果map里面没有这个字符,直接把字符放入容器中,同时定义一个左指针和一个max.
如果遍历到当前字符在容器中已经存在,那么记录一个而当前的max值max=Math.max(i-left,max);
此时左指针也应当判断是否需要移动到重复字符的后一个,对于abba这种,先是b重复,left指向2,现在a重复,left不能指向1,而是继续指向2.所以, left=Math.max(left,map.get(arr[i])+1);即左指针不能后移
最后还需要判断最后一个字符是非重复的数的情况 max=Math.max(arr.length-left,max);
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
if(s.length()<=1)
return s.length();
int left=0;int max=0;
Map<Character,Integer>map=new HashMap();
char arr[]=s.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(!map.containsKey(arr[i])){
map.put(arr[i],i);
}
else{
max=Math.max(i-left,max);
left=Math.max(left,map.get(arr[i])+1);
map.put(arr[i],i);
}
}
max=Math.max(arr.length-left,max);
return max;
}
}
修改第二版代码如下
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int left=0;int max=0;
Map<Character,Integer>map=new HashMap();
char arr[]=s.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(map.containsKey(arr[i])){
max=Math.max(i-left,max);
left=Math.max(left,map.get(arr[i])+1);
}
map.put(arr[i],i);
}
max=Math.max(arr.length-left,max);
return max;
}
}
解题思路2,把每一个字符映射到数组里面
看滑动窗内是否有字符的出现次数大于1,大于1就做一次max判断,同时移动left指针,直到没有字符的出现次数大于1.
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int arr[]=new int[128];
char arr1[]=s.toCharArray();
int left=0;int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr1.length;i++){
arr[arr1[i]-32]++;
if(arr[arr1[i]-32]>1){
max=Math.max(max,i-left);
while(arr[arr1[i]-32]>1){
arr[arr1[left]-32]--;
left++;
}
}
}
return max=Math.max(max,s.length()-left);
}
}
21 97. 交错字符串
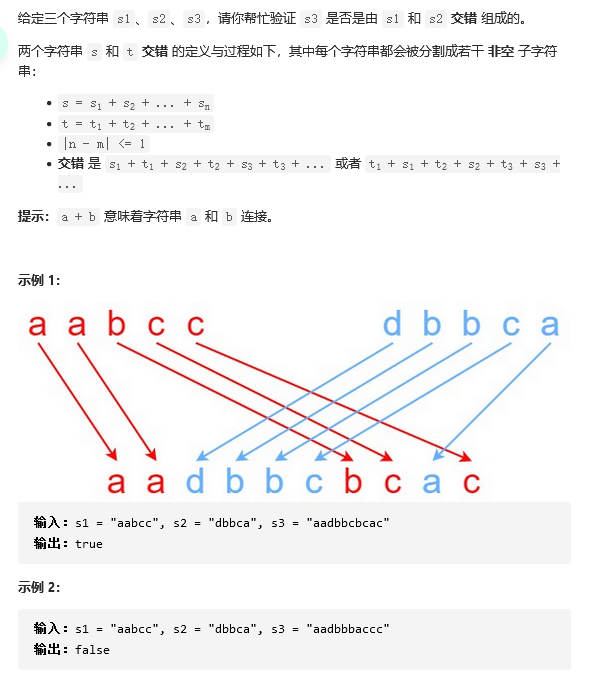
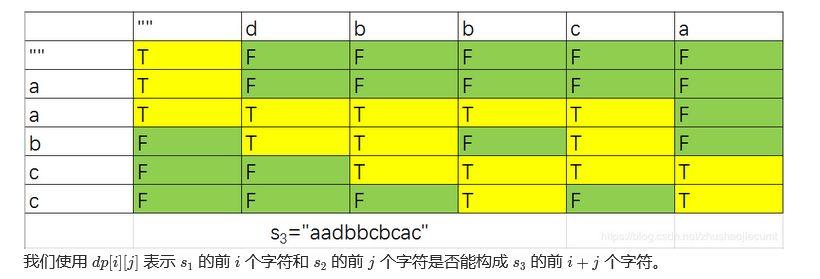
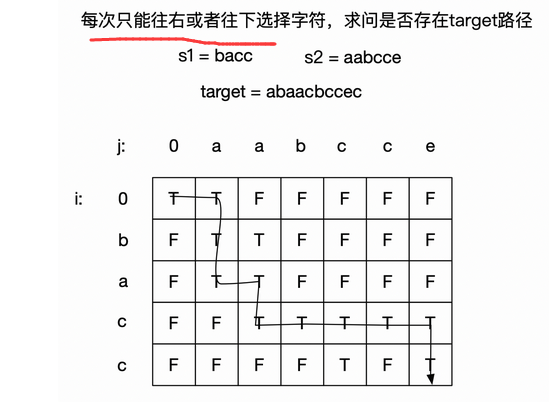
解题思路:动态规划,看s1的钱i个字符和s2的前j个字符能否组成s3的前i+j个字符
参考:动态规划 逐行解释 python3
class Solution {
public boolean isInterleave(String s1, String s2, String s3) {
int m=s1.length();
int n=s2.length();
int p=s3.length();
if(m+n!=p)
return false;
boolean dp[][]=new boolean[m+1][n+1];
//dp[i][j]表示s1的钱i个字符和s2的前j个字符能否组成s3的前i+j个字符
dp[0][0]=true;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)//填第一列
dp[i][0]=dp[i-1][0]&&s1.charAt(i-1)==s3.charAt(i-1);
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)//填第一行
dp[0][j]=dp[0][j-1]&&s2.charAt(j-1)==s3.charAt(j-1);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
//dp[i][j]可以由dp[i-1][j]和dp[i][j-1]变化而来
dp[i][j]=(dp[i-1][j]&&s1.charAt(i-1)==s3.charAt(i+j-1))||
(dp[i][j-1]&&s2.charAt(j-1)==s3.charAt(i+j-1));
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
}
解题思路2,深度优先遍历,在s1和s2中搜索s3的每一个字符,本质上是路径搜索
参考:
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/interleaving-string/solution/lei-si-lu-jing-wen-ti-zhao-zhun-zhuang-tai-fang-ch/
class Solution {
private boolean[][] visited;
public boolean isInterleave(String s1, String s2, String s3) {
if (s1.length() + s2.length() != s3.length())
return false;
visited = new boolean[s1.length() + 1][s2.length() + 1];
return backtrack(s1, s2, s3, 0, 0, 0);
}
private boolean backtrack(String s1, String s2, String s3, int i, int j, int k) {
if (k == s3.length())//说明s3的所有字符都被匹配了
return true;
if (visited[i][j])//如果当前节点已经被访问过,说明上一条路径从这经过走不通,即使是换一条路,经过相同的节点,依然是走不通的
return false;//在二维矩阵里面,这个元素访问过,说明它的右边和下边都被访问过了,但是行不通,那我们换条路又经过了这个点肯定还是走不通的
visited[i][j] = true;
if (i < s1.length() && s1.charAt(i) == s3.charAt(k)
&& backtrack(s1, s2, s3, i + 1, j, k + 1)
|| j < s2.length() && s2.charAt(j) == s3.charAt(k)
&& backtrack(s1, s2, s3, i, j + 1, k + 1))
return true;
return false;
}
}
2021.08.19 第9天
()22 28. 实现 strStr()
23 524. 通过删除字母匹配到字典里最长单词
给你一个字符串 s 和一个字符串数组 dictionary 作为字典,找出并返回字典中最长的字符串,该字符串可以通过删除 s 中的某些字符得到。
如果答案不止一个,返回长度最长且字典序最小的字符串。如果答案不存在,则返回空字符串。
示例 1:
输入:s = “abpcplea”, dictionary = [“ale”,“apple”,“monkey”,“plea”]
输出:“apple”
示例 2:
输入:s = “abpcplea”, dictionary = [“a”,“b”,“c”]
输出:“a”
解题思路

public class Solution {
public boolean isSubsequence(String x, String y) {
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < y.length() && j < x.length(); i++)
if (x.charAt(j) == y.charAt(i))
j++;
return j == x.length();
}
public String findLongestWord(String s, List < String > d) {
String max_str = "";
for (String str: d) {
if (isSubsequence(str, s)) {
if (str.length() > max_str.length() || (str.length() == max_str.length() && str.compareTo(max_str) < 0))
max_str = str;
}
}
return max_str;
}
}
()24 1392. 最长快乐前缀

2021.08.20 第10天
25 1042. 不邻接植花

解题思路:构建邻接矩阵,然后比那里每一个节点,查看他的邻接节点用了哪些花,它就放其他的一种花就行了,由于每个花园的路径最多3条,而花有4种,所以肯定能找到匹配的答案。
参考:思路很简单,实现起来难(着色问题)
class Solution {
public int[] gardenNoAdj(int n, int[][] paths) {
Map<Integer,Set<Integer>>graph=new HashMap();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
graph.put(i,new HashSet());
for(int []path:paths){
graph.get(path[0]).add(path[1]);
graph.get(path[1]).add(path[0]);
}
int res[]=new int[n];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
boolean[]used=new boolean[5];
for(int adj:graph.get(i))
used[res[adj-1]]=true;//找出相邻的点还未使用的 1-4 的部份;//比如adj=1,res[0]=0说明
//res本来都是0,如果不为0,说明有一种花被放进res里面了
for(int j=1;j<=4;j++){
if(!used[j])
res[i-1]=j;
}
}
return res;
}
}

class Solution {
public int[] gardenNoAdj(int n, int[][] paths) {
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) graph.add(new ArrayList<>(3));
for (int[] path : paths) {
graph.get(path[0] - 1).add(path[1] - 1);
graph.get(path[1] - 1).add(path[0] - 1);
}
int[] ans = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
boolean[] used = new boolean[5];
for (int j : graph.get(i)) used[ans[j]] = true;
int t = 1;
while (used[t]) ++t;
ans[i] = t;
}
return ans;
}
}
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public int[] gardenNoAdj(int n, int[][] paths) {
int[] res = new int[n];
if(paths.length == 0){
Arrays.fill(res,1);
return res;
}
int[][] adjoinGarden = new int[n + 1][3];
int[] gardenSize = new int[n + 1];
for (int[] p : paths) {
int v1 = p[0];
int v2 = p[1];
adjoinGarden[v1][gardenSize[v1]++] = v2;
adjoinGarden[v2][gardenSize[v2]++] = v1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
boolean[] color = new boolean[4];
for (int j : adjoinGarden[i]) {
if (j != 0 && res[j - 1] != 0) {
color[res[j - 1] - 1] = true;
}
}
if (!color[0]) {
res[i - 1] = 1;
} else if (!color[1]) {
res[i - 1] = 2;
} else if (!color[2]) {
res[i - 1] = 3;
} else {
res[i - 1] = 4;
}
}
return res;
}
}
26 787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班

解题思路,在回溯的过程汇总不断改变src,同时记录cost
超时,如果我用记忆化搜索memo[][]的话,还会出错,因为memo[][]只能表示上一个点从这里经过时,memo的最小值,而不是memo[][]到dst的最小值
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>>graph=new ArrayList();
int[][]costs;
// Integer[][]memo;
boolean visited[];
int max;
//
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
costs=new int[n][n];
// memo=new Integer[n][n];
visited=new boolean[n];
max=n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
graph.add(new ArrayList());//添加n个临界表
for(int[] flight:flights){
costs[flight[0]][flight[1]]=flight[2];//初始化花费
// costs[flight[1]][flight[0]]=flight[2];//初始化花费//注意是有向图
graph.get(flight[0]).add(flight[1]);//初始化邻接表
// graph.get(flight[1]).add(flight[0]);//初始化邻接表
}
int result=dfs(src,dst,k+2,0);
return (result ==max*10000) ?-1:result;
}
public int dfs(int src,int dst,int k, int cost){
if((src==dst)&&k>0){
//已经到达终点,记录当前花费
// return memo[src][dst]=cost;
return cost;
}
if(k<=0)//已经超过k个中转站了,不符合要求,返回一个较大的值
return max*10000;
// if(memo[src][dst]!=null)
// return memo[src][dst];
if(visited[src])
return max*10000 ; //不能反向访问
visited[src]=true;
int result= max*10000 ;
for(int i=0;i<graph.get(src).size();i++){
if(costs[src][graph.get(src).get(i)]>0){//注意是有向图,如果不大于0,说明两点之前没有连线,无法起飞
int temp1= dfs(graph.get(src).get(i),dst,k-1,cost+costs[src][graph.get(src).get(i)]);
result=Math.min(result,temp1);
}
}
visited[src]=false;
return result;
// return memo[src][dst]=result;
}
}
官方的深搜,虽然也超时,但是能通过的例子更多,是因为多了剪枝吧res取最小值就是在这里体现的
public class Solution {
private int[][] graph;
private boolean[] visited;
private int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int K) {
K = Math.min(K, n - 2);
this.graph = new int[n][n];
for (int[] flight : flights) {
graph[flight[0]][flight[1]] = flight[2];
}
this.visited = new boolean[n];
// 开始深度优先遍历,注意:这里传 K + 1,这是因为 K 次经停,总共 K + 1 个站
dfs(src, dst, K + 1, 0);
if (res == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
return -1;
}
return res;
}
/**
* 从 src 出发,到 dst 为止,最多经过 k 站(这里 k 包括 src)
*
* @param src 起点站
* @param dst 终点站
* @param k 经过的站点数限制
* @param cost 已经花费的价格
*/
private void dfs(int src, int dst, int k, int cost) {
if (src == dst) {
res = cost;
return;
}
if (k == 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < graph[src].length; i++) {
if (graph[src][i] > 0) {
if (visited[i]) {
continue;
}
// 剪枝:跳过可能产生较高费用的路径,从而选出最少价格
if (cost + graph[src][i] > res) {
continue;
}
visited[i] = true;
dfs(i, dst, k - 1, cost + graph[src][i]);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
作者:LeetCode
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/cheapest-flights-within-k-stops/solution/k-zhan-zhong-zhuan-nei-zui-bian-yi-de-hang-ban-b-2/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
一个老哥的记忆化搜索
class Solution {
// 看到了DAG
// dp[i][j][k],从i站到j站最多中转k站的最小代价!看题目描述自然想到这个状态
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int K) {
int[][] cost = new int[n][n];
for(int i = 0; i < flights.length; i++){
int st = flights[i][0];
int en = flights[i][1];
int price = flights[i][2];
cost[st][en] = price;
}
int[][][] dp = new int[n][n][K+2];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
Arrays.fill(dp[i][j], -1);
}
}
int res = f(cost, src, dst, K+1, dp);
return res >= 1000000 ? -1 : res;
}
private int f(int[][] cost, int src, int dst, int K, int[][][] dp){
if(K < 0){
return 1000000;
}
if(dp[src][dst][K] != -1){
return dp[src][dst][K];
}
if(src == dst){
return dp[src][dst][K] = 0;
}
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i = 0; i < cost.length; i++){
if(cost[src][i] != 0){
ans = Math.min(ans, cost[src][i] + f(cost, i, dst, K-1, dp));
}
}
return dp[src][dst][K] = (ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 1000000 : ans);
}
}

动态规划
class Solution {
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int K) {
// dp[i][k]是经过k个中转站后到达站 i 的最小费用
int[][] dp = new int[n][K + 1];
// 循环初始化整个二维数组。
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) Arrays.fill(dp[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 利用flights中的信息初始化src可直达的班次
for(int[] flight : flights) {
if(flight[0] == src){
dp[flight[1]][0] = flight[2];
}
}
// 循环初始化数组中dst == src的行
for(int i = 0; i <= K; i++){
dp[src][i] = 0;
}
//动态规划状态转移方程,开始填表
//直达的已经初始化了(即k = 0的情况),现在从k = 1 的开始,即只有一个中转站开始
for(int k = 1; k <= K; k++){
for(int[] flight : flights){
//结合题目理解
if(dp[flight[0]][k - 1] != Integer.MAX_VALUE){
dp[flight[1]][k] = Math.min(dp[flight[1]][k], dp[flight[0]][k - 1] + flight[2]);
}
}
}
return dp[dst][K] == Integer.MAX_VALUE? -1: dp[dst][K];
}
}

广度优先搜索,也超时?
我还想着标记搜索过的节点,看来不行
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>>graph=new ArrayList();
int[][]costs;
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
costs=new int[n][n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
graph.add(new ArrayList());//添加n个临界表
for(int[] flight:flights){
costs[flight[0]][flight[1]]=flight[2];//初始化花费
graph.get(flight[0]).add(flight[1]);//初始化邻接表
}
boolean visited[]=new boolean[n];
Queue<Integer>queue=new LinkedList();
Queue<Integer>cost=new LinkedList();
int result=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
queue.offer(src);
visited[src]=true;
cost.offer(0);
int count=0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size=queue.size();
count++;
if(count>k+2){
break;
}
for(int j=0;j<size;j++){
int temp=queue.poll();
int tempCost=cost.poll();
if(temp==dst){
result=Math.min(result,tempCost);
}
for(int i=0;i<graph.get(temp).size();i++){
if(!visited[graph.get(temp).get(i)]){
queue.offer(graph.get(temp).get(i));
cost.offer(tempCost+costs[temp][graph.get(temp).get(i)]);
}
}
}
}
return result==Integer.MAX_VALUE?-1:result;
}
}
剪枝之后,能通过更多例子了
这有个8ms的,可以通过
class Solution {
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int K) {
// 用来记录(当前城市,可以飞往城市的信息列表(每一项包含[城市坐标,费用]))
Map<Integer, List<int[]>> map = new HashMap<>();
// 建立map信息
for(int[] flight: flights) {
List<int[]> list = map.getOrDefault(flight[0], new ArrayList<>());
list.add(new int[]{flight[1], flight[2]});
map.put(flight[0], list);
}
// 用来记录飞到该城市的时候,最小的费用
int[] minValues = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(minValues, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 起始点的费用是0
minValues[src] = 0;
// 两个队列:记录城市坐标和当前累积的费用
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<Integer> queueValue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(src);
queueValue.offer(0);
// 记录当前经过的站数,大于K直接跳出
int count = 0;
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
if(count > K) break;
int size = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int f = queue.poll();
int v = queueValue.poll();
List<int[]> list = map.getOrDefault(f, new ArrayList<>());
// 遍历能飞往的下一个城市
for(int[] nextF: list) {
// 如果下一个城市是目的地,更新最小的费用
if(nextF[0] == dst) {
ans = Math.min(ans, v+nextF[1]);
continue;
}
// 如果飞往下一个城市的费用小于当前的最小值,才更新;如果已经大于现在的最小值,不放入队列中
if(minValues[nextF[0]] > v + nextF[1]) {
minValues[nextF[0]] = v + nextF[1];
queue.offer(nextF[0]);
queueValue.offer(v+nextF[1]);
}
}
}
count++;
}
// 说明在经过K站中转后,不能飞到目的地,返回-1
if(ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE) return -1;
return ans;
}
}
2021.08.21 第11天 图
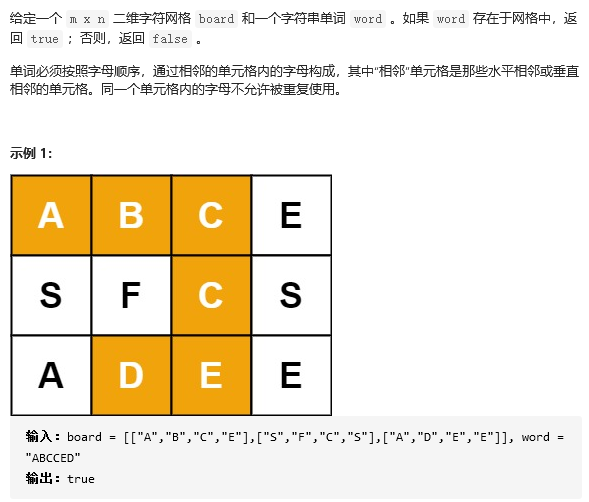
27 79. 单词搜索
class Solution {
int m;
int n;
boolean[][]visited;
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
m=board.length;
n=board[0].length;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(board[i][j]==word.charAt(0)){//从首字母开始搜索
visited=new boolean[m][n];
if(dfs(board,i,j,1,word)){
return true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean dfs(char[][]board,int i,int j,int curLen,String word){
if(i>=m||i<0||j>=n||j<0||curLen>word.length()||board[i][j]!=word.charAt(curLen-1))
return false;
if((curLen==word.length())&&board[i][j]==word.charAt(curLen-1))
return true;
if(visited[i][j])
return false;
// visited[i][j]=true;
char temp=board[i][j];
board[i][j]='*';
// boolean b1,b2,b3,b4;
boolean b1= dfs(board, i+1, j,curLen+1, word)||
dfs(board, i-1, j,curLen+1, word)||
dfs(board, i, j+1,curLen+1, word)||
dfs(board, i, j-1,curLen+1, word);
// visited[i][j]=false;
board[i][j]=temp;
return b1;
// return b1||b2||b3||b4;//这这里返回会多计算
}
}
之前尝试用visited数组标记,但是,下图两块代码写反了,导致出错,下图现在是对的
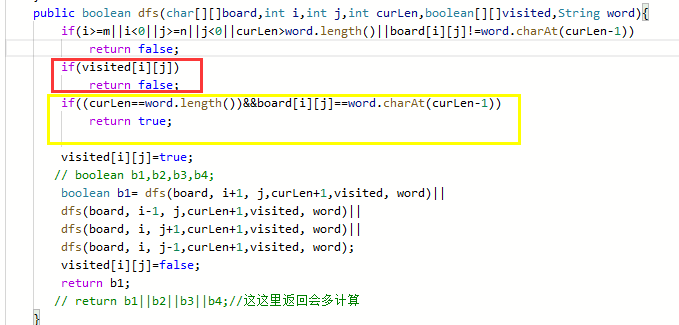
写反了会导致下图所示的回溯,一个字符用两次
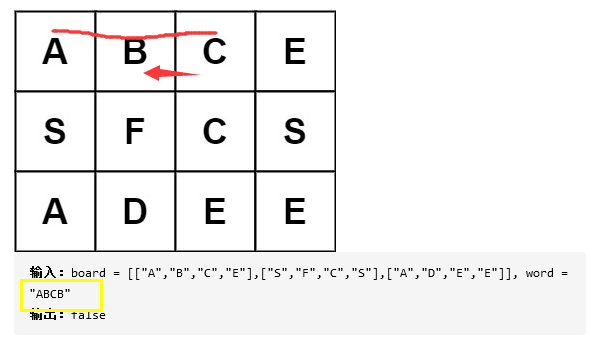
这有一个17ms的,就是先比较一下两个字符串中每种字符的数量
public class Solution {
private char[][] board;
private char[] word;
private int m;
private int n;
private int targetLen;
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String str) {
this.board = board;
this.m = board.length;
this.n = board[0].length;
this.word = str.toCharArray();
this.targetLen = word.length;
if(targetLen > m*n){
return false;
}
int[] f1 = new int[133];
int[] f2 = new int[133];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
++f1[board[i][j]];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < targetLen; i++) {
++f2[word[i]] ;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 133; i++) {
if(f1[i] < f2[i]) {
return false;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == word[0]) {
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[m][n];
boolean res = dfs(i, j, 0,visit);
if (res) {
return true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean dfs(int i, int j, int index,boolean [][]visit) {
if (index == targetLen) {
return true;
}
if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n) {
return false;
}
if(visit[i][j]){
return false;
}
if (board[i][j] == word[index]) {
visit[i][j] = true;
boolean res = dfs(i - 1, j, index + 1,visit)
||
dfs(i + 1, j, index + 1,visit)
||
dfs(i, j - 1, index + 1,visit)
||
dfs(i, j + 1, index + 1,visit);
visit[i][j] = false;
return res;
}
return false;
}
}
28 329. 矩阵中的最长递增路径
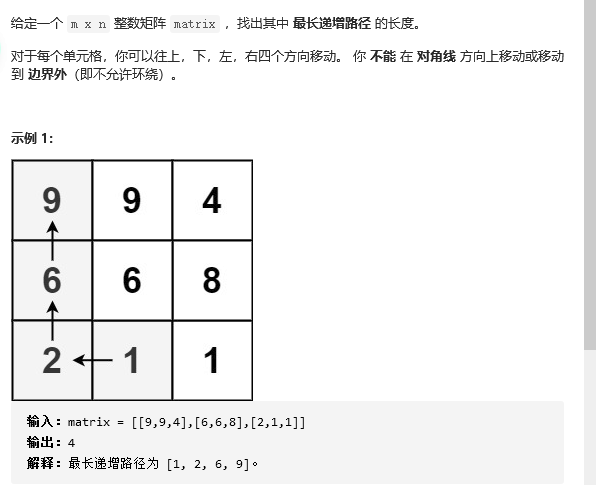
解题思路:枚举每一个点,找出每一个点的最长递增路径
第一版代码如下
class Solution {
int m;
int n;
boolean [][]visited;
int dr[]={0,1,0,-1};
public int longestIncreasingPath(int[][] matrix) {
m=matrix.length;
n=matrix[0].length;
visited=new boolean[m][n];
int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
max=Math.max(max,dfs(matrix,i,j,0,-1));
}
}
return max;
}
public int dfs(int [][]matrix,int i,int j,int curLen,int last){
if(i<0||i>=m||j<0||j>=n||matrix[i][j]<=last)
return curLen;
if(visited[i][j])
return 0;
visited[i][j]=true;
int cur=0;
for(int p=0;p<4;p++){
int newX=i+dr[p];int newY=j+dr[(p+1)%4];
int a=dfs(matrix,newX, newY, curLen+1, matrix[i][j]);
cur=Math.max(cur,a);
}
visited[i][j]=false;
return cur;
}
}
代码超时,因为有大量的重复计算,但是不能直接这样用memo[][],应为我这样计算出来的memo是带有方向性的,是上一个点寻找路径从这里经过时,当前元素给上一个元素返回的最大长度,而不是从当前点出发能够得到的最大长度
实际上,本题可以不用visited数组,应为题目要求是递增路径,我们的判断条件会给出这有条件,不满足自然不会反向访问。
我们可以以从当前点出发,找到他的相邻的比它小的元素的最长递增路径,取其中最大的
class Solution {
int m;
int n;
int dr[]={0,1,0,-1};
int maxValue;
public int longestIncreasingPath(int[][] matrix) {
m=matrix.length;
n=matrix[0].length;
int memo[][]=new int[m][n];
int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
max=Math.max(max,dfs(matrix,i,j,memo));
}
}
return max;
}
public int dfs(int [][]matrix,int i,int j,int memo[][]){
if(memo[i][j]!=0)
return memo[i][j];
memo[i][j]=1;
int cur=0;
for(int p=0;p<4;p++){
int newX=i+dr[p];int newY=j+dr[(p+1)%4];
if(newX>=0&&newX<m&&newY>=0&&newY<n&&matrix[newX][newY]>matrix[i][j]){
memo[i][j]=Math.max(memo[i][j],dfs(matrix,newX, newY,memo)+1);
}
}
return memo[i][j];
}
}
参考:矩阵中的最长递增路径

矩阵深度优先搜索里的回溯(backtracking)常常是必要的,由于这类题目通常要求每个元素只能使用1次,因此我们需要维护一个seen矩阵(记录访问过的元素,并且在dfs压栈和退栈的时候反复设置状态),而每次选定的起始位置不同,seen的状态就不一样了,导致计算的结果不可重用(因为计算结果只代表在seen的某一种确定状态下的结果,所以我们不能进行缓存)。
最终,我们只能采用回溯的方式去求解,得到的时间复杂度正是指数级别。比如经典的Word Search II,不管我们使用不使用字典树(Trie),回溯是不可避免的。
这题的每个元素只能用1次的条件是隐含的——因为要求(严格)递增路径,所以有效路径里,同一个位置的元素是不可能出现两次的。然而递增路径带来的buff却不止前面前面这个隐含条件。因为在内循环里,mat[ii][jj] > mat[i][j]确保了之前已经访问过的元素根本就不会出现在后续的路径里,所以seen就没有存在的意义,甚至可以直接缓存每一个子调用的计算结果,因为不管你从哪个位置开始迭代,因为没有状态(没有seen),计算结果变成唯一的了——因此变得可以缓存了。
2021.08.22 第12天 生活趣题
29 121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
给定一个数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 表示一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
你只能选择 某一天 买入这只股票,并选择在 未来的某一个不同的日子 卖出该股票。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回 0 。
解题思路:枚举每一天卖出去的利润,就要找到每一天之前的最小值
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<prices.length;i++){
min=Math.min(min,prices[i]);
max=Math.max(max,prices[i]-min);
}
return max;
}
}
30 122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II

class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int max=0;
for(int i=1;i<prices.length;i++){
if(prices[i]-prices[i-1]>0){
max=max+prices[i]-prices[i-1];
}
}
return max;
}
}
最后
以上就是活泼芝麻最近收集整理的关于leetcode 14天刷题计划-高效面试备战总结2021.08.11 第1 天 求和问题2021.08.12 第2天 求和问题2021.08.13 第3天 斐波拉契数列2021.08.14 第4天 动态规划法2021.08.15 第5 天 堆栈2021.08.16 第6天 数字2021.08.17 第7天 树2021.08.18 第8天 字符串2021.08.19 第9天2021.08.20 第10天2021.08.21 第11天 图2021.08.22 第12天 生活趣题的全部内容,更多相关leetcode内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复