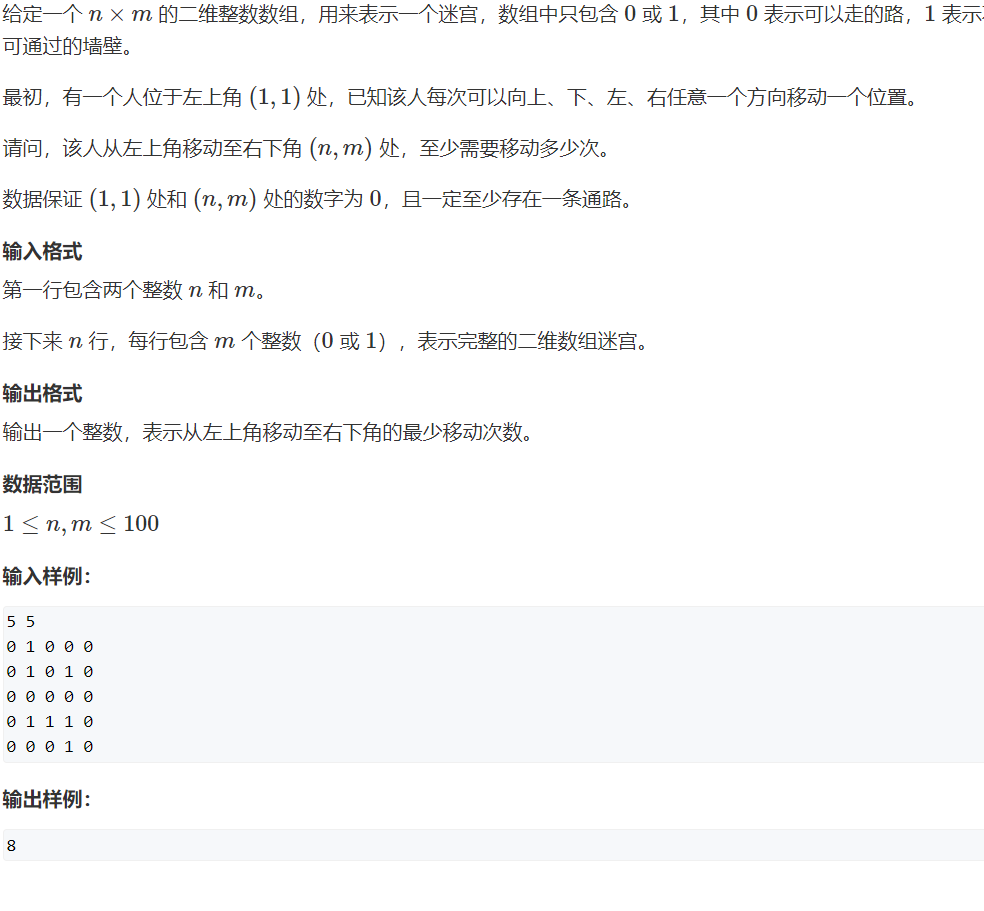
模拟队列版本:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int n, m;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
PII q[N * N]; //定义一个队列, 队列里面的元素表示二维数组里面的点
int g[N][N]; //用二维数组表示地图
int d[N][N]; //d数组里面的下标表二维数组里面的点,值表示每个点的距离
int bfs()
{
int hh = 0, tt = 0; //定义出队头队尾
q[0] = {0, 0};
//初始化d数组,方便后面选择没有走过的点
memset(d, -1, sizeof(d));
d[0][0] = 0; //一开始处于处于原点,设置下标为(0, 0)的点的值为1
//向四个方向延申
int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
while(hh <= tt)
{
auto t = q[hh++];
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int x = t.first + dx[i], y = t.second + dy[i];
if(x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && g[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == -1)
{
d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1;
q[++tt] = {x, y};
}
}
}
return d[n - 1][m - 1];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) cin >> g[i][j];
}
cout << bfs() << endl;
return 0;
}队列版本:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int n, m;
int g[N][N];
int d[N][N];
int bfs()
{
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({0, 0});
memset(d, -1, sizeof(d));
d[0][0] = 0;
int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
while(q.empty() == false)
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int x = t.first + dx[i], y = t.second + dy[i];
if(x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && g[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == -1)
{
d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1;
q.push({x, y});
}
}
}
return d[n - 1][m - 1];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) cin >> g[i][j];
}
cout << bfs() << endl;
return 0;
}最后
以上就是激情菠萝最近收集整理的关于C++实现BFS宽搜解决走迷宫问题的全部内容,更多相关C++实现BFS宽搜解决走迷宫问题内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复