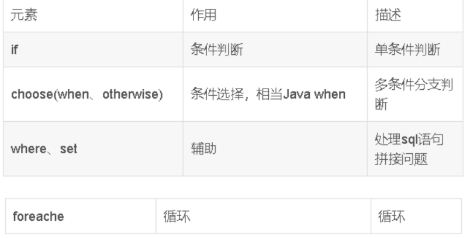
1、Mybatis实现多表联查询方式
- 业务装配对两个表写单独的sql语句,在业务(service)把查询结果进行联合。
- 使用Auto Mapping特性,在实现两个表联合查询时通过别名完成自动映射。
- 使用Mybatis的<resultMap>标签进行实现
2、多表查询时类中包含另一个对象的分类
- 单个对象
- 集合对象
二、resultMap标签
1、写在<select>标签中,不用写resultType属性,可以单独的在<resultMap>中将数据库字段与java属性不匹配进行映射。
2、使用<resultMap>标签在两个表中关联单个对象(N+1方式)
- N+1查询的方式,先查询出一个表的全部信息,根据这个表的信息查询另一个表的信息。
- 实现步骤在Student类中包含一个Teacher对象
- 在StudentMapper.xml文件中写上查询学生的sql,然后通过<resultMap>来完成Teacher对象的查询
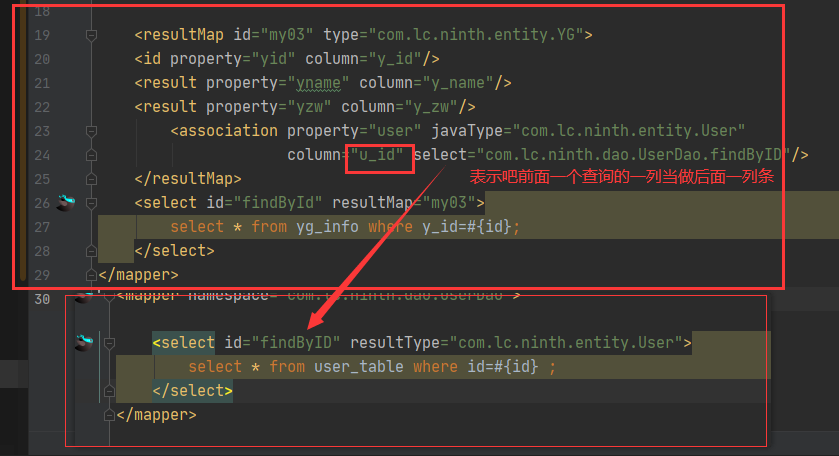
多表联查之嵌套查询
java代码 员工类
@Data
public class YG {
private Integer yid;
private String yname;
private String yzw;
private User user;
}部门类
@Data
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String realname;
}2在StudentMapper.xml中写上查询员工信息:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.lc.ninth.dao.YGDao">
<resultMap id="my03" type="com.lc.ninth.entity.YG">
<id property="yid" column="y_id"/>
<result property="yname" column="y_name"/>
<result property="yzw" column="y_zw"/>
<association property="user" javaType="com.lc.ninth.entity.User"
column="u_id" select="com.lc.ninth.dao.UserDao.findByID"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="findById" resultMap="my03">
select * from yg_info where y_id=#{id};
</select>
</mapper>3TeacherMapper.xml文件中提供一个查询部门对象的sql:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.lc.ninth.dao.UserDao">
<select id="findByID" resultType="com.lc.ninth.entity.User">
select * from user_table where id=#{id} ;
</select>
</mapper>综合
2 多表联查之 链表查询
只需要写一条SQL,在StudentMapper.xml中完成,对于学生属性直接用<id>或<result>进行装配(将字段别名与属性匹配),对于Teacher对象直接用<association>标签来映射,其中 property还是代表在类中该对象属性的名称 另外要设置javaType表示返回值类型,其它的还一次对应匹配即可
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.lc.ninth.dao.YGDao">
<!--association:表示多对一
property:表示对象属性名
javaType:表示该对象所属的类型
autoMapping必须写
-->
<resultMap id="my02" type="com.lc.ninth.entity.YG">
<id property="yid" column="y_id"/>
<result property="yname" column="y_name"/>
<result property="yzw" column="y_zw"/>
<association property="user" javaType="com.lc.ninth.entity.User" autoMapping="true">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="username" column="username"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<!--注意:使用了resultMap不能在使用resultType-->
<select id="findId" resultMap="my02">
select * from yg_info y join user_table u on y.u_id=u.id
</select>
</mapper>3一对多查询 (了解)
1.从一的一方查询多的一方。
比如: 班级--1---n-->学生.
数据库代码如下
CREATE TABLE class(
c_id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
c_name VARCHAR(20),
);
INSERT INTO class(c_name) VALUES('QY145');
INSERT INTO class(c_name) VALUES('QY143');
INSERT INTO class(c_name) VALUES('QY142');
CREATE TABLE student(
s_id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
s_name VARCHAR(20),
class_id INT
);
INSERT INTO student(s_name, class_id) VALUES('xs_A', 1);
INSERT INTO student(s_name, class_id) VALUES('xs_B', 1);
INSERT INTO student(s_name, class_id) VALUES('xs_C', 2);
INSERT INTO student(s_name, class_id) VALUES('xs_D', 2);
INSERT INTO student(s_name, class_id) VALUES('xs_E', 3);
INSERT INTO student(s_name, class_id) VALUES('xs_F', 3);
例子:根据班级id查询班级信息以及该班级下所有的学生信息。
<resultMap id="My03" type="com.ykq.entity.Clazz">
<id column="c_id" property="cid"/>
<result property="cname" column="c_name"/>
<!--
collection: 集合的意思 多的意思
property:集合对象名
ofType: 集合的泛型
-->
<collection property="students" ofType="com.ykq.entity.Student" autoMapping="true">
<id property="id" column="s_id"/>
<result property="name" column="s_name"/>
<result property="classId" column="class_id"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!--这里的id必须和Dao中的方法名一致。-->
<select id="findById" resultMap="My03">
select * from class c join student s on c.c_id=s.class_id where c_id=#{id}
</select>4 动态Sql
MyBatis 的强大特性之一便是它的动态 SQL。如果你有使用 JDBC 或其它类似框架的经验,你就能体会到根据不同条件拼接 SQL 语句的痛苦。例如拼接时要确保不能忘记添加必要的空格,还要注意去掉列表最后一个列名的逗号。利用动态 SQL 这一特性可以彻底摆脱这种痛苦。动态 SQL 元素和 JSTL 或基于类似 XML 的文本处理器相似.MyBatis 采用功能强大的基于 OGNL 的表达式来淘汰其它大部分元素。
5.1 if和where 一起使用
<!--如果传入了书名 则按照书名进行查询 如果没有传入书名 则查询所有
where:可以帮你添加where关键 并且把第一个and | or去除
-->
<select id="findByCondition" resultMap="map">
select * from book_info
<where>
<if test="bookname!=null and bookname!=''">
and book_name=#{bookname}
</if>
<if test="author!=null and author!=''">
and book_author=#{author}
</if>
</where>
</select>测试类
@Test
public void test(){
BookDao mapper = session.getMapper(BookDao.class);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("bookname","西游记");
map.put("bookauthor","吴承恩");
List<Book> idMap = mapper.findIdMap(map);
System.out.println(idMap);
}5.2 [choose when otherwise] 和where
<!--choose +where
when:当条件满足时不会执行下面的when和other 都不满足则执行otherwise
-->
<select id="findByCondition2" resultMap="map">
select * from book_info
<where>
<choose>
<when test="bookname!=null and bookname!=''">
and book_name=#{bookname}
</when>
<when test="author!=null and author!=''">
and book_author=#{author}
</when>
<otherwise>
and book_price>35
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>测试
@Test
public void test1() {
BookDao mapper = session.getMapper(BookDao.class);
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
//map.put("bookname","红高粱");
map.put("bookauthor","老舍");
List<Book> idMap1 = mapper.findIdMap1(map);
System.out.println(idMap1);
}3)set标签。修改部分字段。
<!--修改部分列的值。
set 可以帮你添加set关键字 并且去除最后的逗号。
-->
<update id="update">
update book_info
<set>
<if test="name!=null and name!=''">
book_name=#{name},
</if>
<if test="author!=null and author!=''">
book_author=#{author},
</if>
<if test="pub!=null and pub!=''">
book_pub=#{pub},
</if>
<if test="price!=null">
book_price=#{price},
</if>
</set>
where book_id=#{id}
</update>测试
@Test
public void update(){
BookDao mapper = session.getMapper(BookDao.class);
Book book = new Book();
book.setName("嘻游记");
book.setPrice(56);
book.setId(1001);
int update = mapper.update(book);
session.commit();
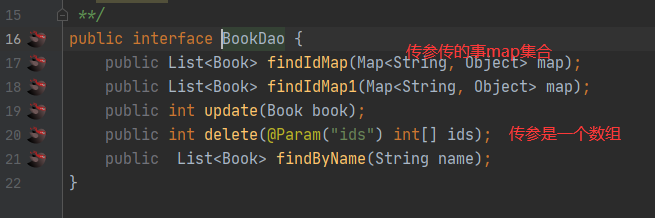
}5.4foreach 批量删除。
<!--
delete from book_info where id in(1001,1002,1003)
in (1001,1002,1003)
foreach:
collection:要遍历的集合和数组名
item: 每次遍历时赋值的元素变量名
open: 以什么开始
close:以什么结束
separator: 分隔符
-->
<delete id="batchDelete">
delete from book_info where book_id in
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>测试
@Test
public void delete(){
BookDao mapper = session.getMapper(BookDao.class);
int [] arr ={1001,1002,1003};
int delete = mapper.delete(arr);
session.commit();
}
6模糊查询
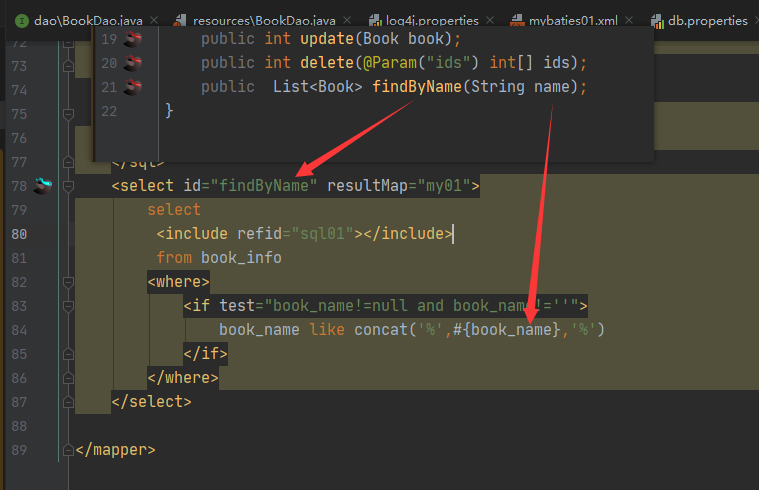
补充一下
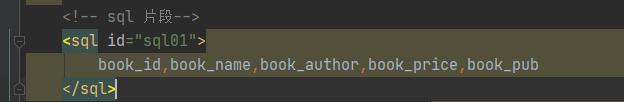
使用sql片段
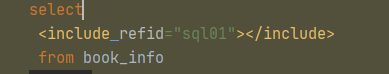
7 分页插件--PageHelper
(1)引入分页PageHelper依赖
<!--分页插件的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>5.1.11</version>
</dependency>(2) 加入拦截
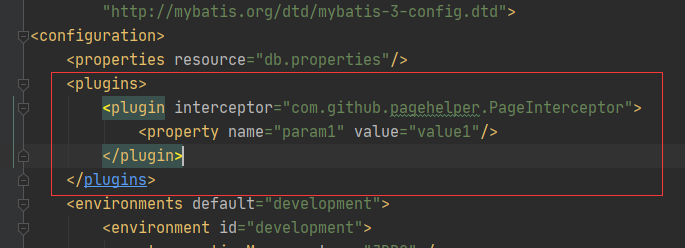

测试
@Test
public void testUpdate3(){
EmpDao empDao = session.getMapper(EmpDao.class);
//使用分页功能 request.getParamter("page") request.getParamter("pageSize")
PageHelper.startPage(2,10);
List<Emp> list = empDao.findAll3("王");
//可以把查询的结果封装到PageInfo类中 包含你想要的任何信息
PageInfo<Emp> pageInfo=new PageInfo<Emp>(list);
System.out.println("总条数:"+pageInfo.getTotal());
System.out.println("当前页码的数据:"+pageInfo.getList());
}8 介绍几个好用的插件
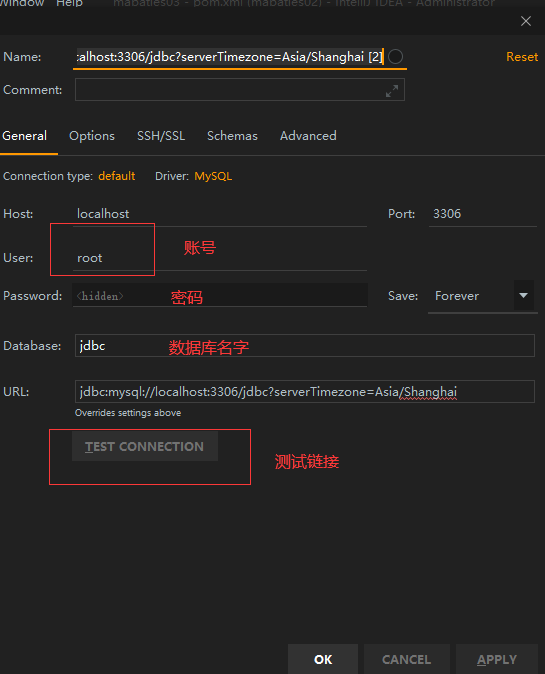
(1)mybatis插件----dao和映射文件之间的关联
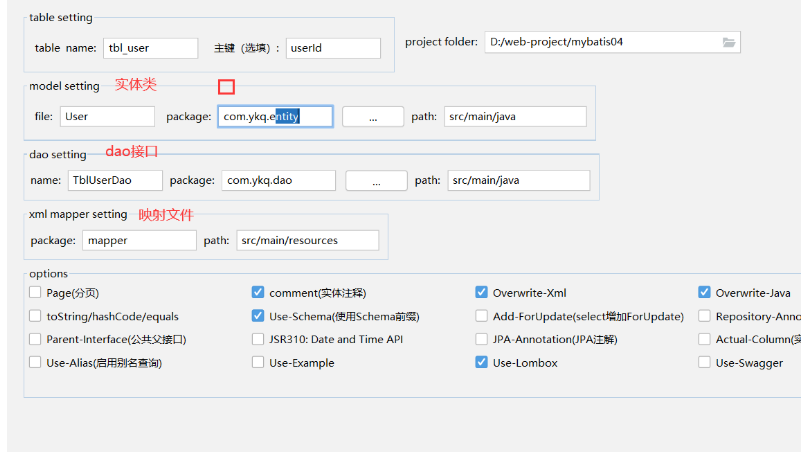
(2) easycode插件----代码单表的crud----entity dao 映射。
.作用域(Scope)和生命周期

最后
以上就是单身手套最近收集整理的关于mybatis多表联合和嵌套查询的全部内容,更多相关mybatis多表联合和嵌套查询内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复