背景
请求超时机制如何实现?订单回滚如何实现?心跳机制如何实现呢?如何实现在一段时间后触发一些事件呢?问题是有了,如何更好的去实现的?
文章目录
- 1.Thread.sleep
- 2.Timer
- 3.DelayQueue
- 4.ScheduledExecutorService
- 5.quartz
- 6.HashedWheelTimer
- 7.redis失效监听
- 7.1redis失效机制测试
- 7.2redis失效机制项目中使用
- 8.rocketmq延迟消息
1.Thread.sleep
当完成某些事之后,需要休眠一段时间再向下执行的时候,可以使用此类。一般在测试的时候会使用此方法,在生产环境中,暂时没发现哪里有使用过。
public class SleepTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("第一次输出");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000l);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第二次输出");
}
}
如上,在第一次输入完成之后,等待3秒后,在进行第二次输出。此方法简单,不做过多解释。
2.Timer
此类为任务调度工具,任务可以安排为一次性执行,也可以安排为定期重复执行。对应于每个计时器对象的是一个单独的后台线程,用于按顺序执行计时器的所有任务。这个类是线程安全的:多个线程可以共享一个计时器对象,而不需要外部同步。
| 修饰和类型 | 方法说明 |
|---|---|
void | **cancel**()Terminates this timer, discarding any currently scheduled tasks.终止此计时器,放弃任何当前计划的任务 |
int | **purge**()Removes all cancelled tasks from this timer’s task queue.从此计时器的任务队列中删除所有已取消的任务。 |
void | **schedule**(TimerTask task, Date time)Schedules the specified task for execution at the specified time.计划指定的任务以在指定的时间执行。 |
void | **schedule**(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period)Schedules the specified task for repeated fixed-delay execution, beginning at the specified time.从指定的时间开始,调度指定的任务以重复执行固定延迟。 |
void | **schedule**(TimerTask task, long delay)Schedules the specified task for execution after the specified delay.计划指定的任务以在指定的延迟后执行。 |
void | **schedule**(TimerTask task, long delay, long period)Schedules the specified task for repeated fixed-delay execution, beginning after the specified delay.调度指定的任务,以在指定的延迟之后开始重复执行固定延迟。 |
void | **scheduleAtFixedRate**(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period)Schedules the specified task for repeated fixed-rate execution, beginning at the specified time.从指定的时间开始计划指定的任务以重复执行固定速率。 |
void | **scheduleAtFixedRate**(TimerTask task, long delay, long period)Schedules the specified task for repeated fixed-rate execution, beginning after the specified delay.从指定的延迟后开始,调度指定的任务以重复执行固定速率。 |
更详细说明: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Timer.html
使用示例:
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
/**
* Created by likuo on 2020/6/6.
*/
public class TimerTaskTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer();
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("哈哈");
}
}, 0, 1000); // 每隔1秒执行一次
//--------------示例--------------------------------
System.out.println("任务在5秒执行");
Date date = new Date(new Date().getTime() + 5000);
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("任务已经执行");
}
}, date); // 5秒钟后执行
//---------------示例-------------------------------
System.out.println("任务在5秒后,每隔1秒执行一次");
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("任务每隔一秒执行一次");
}
}, date,1000); // 5秒钟后,每隔一秒执行一次
}
}
由于Timer是单线程的,如果任务太多就会有排队的情况,导致原本间隔很短的任务,需要等待很长时间才能执行。如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date(new Date().getTime() + 2000);
Timer timer = new Timer();
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println( "我1秒一次,"+LocalTime.now());
}
}, date, 1000); // 每隔1秒执行一次
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 休眠5秒
Thread.sleep(5000l);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println( "我5秒一次,"+LocalTime.now());
}
}, date, 1000); // 每隔1秒执行一次
}
其中有两个任务,一个每个的执行间隔都是1秒,但是任务2特别耗费时间,执行时间就5秒。所以就会有如下输出:
我1秒一次,20:10:24.040
我5秒一次,20:10:29.041
我1秒一次,20:10:29.041
原本任务1是一秒一次,但是由于任务2执行时间太久,导致任务1也需要等很久才能执行。
3.DelayQueue
《java多线程编程实战指南》中介绍了ArrayBlockingQueue,LinkedBlockingQueue和SynchronousQueue这三种队列。DelayQueue和这三种类似,这个的特点是延迟队列。也就是可以实现某些任务在一段时间后执行的。队列中的元素,需要实现Delayed接口,实现getDelay方法和compareTo方法。getDelay返回任务剩余时间。 compareTo方法定义了元素排序规则,注意,元素的排序规则影响了元素的获取顺序
使用示例:
public class DelayQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建延时队列
DelayQueue<Message> queue = new DelayQueue<Message>();
// 添加延时消息,m1 延时3s
Message m1 = new Message(1, "world", 3000);
// 添加延时消息,m2 延时10s
Message m2 = new Message(2, "hello", 10000);
//将延时消息放到延时队列中
queue.offer(m2);
queue.offer(m1);
// 启动消费线程 消费添加到延时队列中的消息,前提是任务到了延期时间
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
exec.execute(new Consumer(queue));
exec.shutdown();
}
static class Message implements Delayed {
public long excuteTime;
public int id;
public String body;
public Message(int id, String body, long delayTime) {
this.excuteTime = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.convert(delayTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) + System.nanoTime();
this.id = id;
this.body = body;
}
// 返回剩余时间
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert(this.excuteTime - System.nanoTime(), TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
}
public int compareTo(Delayed delayed) {
Message msg = (Message) delayed;
return Integer.valueOf(this.id) > Integer.valueOf(msg.id) ? 1
: (Integer.valueOf(this.id) < Integer.valueOf(msg.id) ? -1 : 0);
}
}
static class Consumer implements Runnable {
// 延时队列 ,消费者从其中获取消息进行消费
private DelayQueue<Message> queue;
public Consumer(DelayQueue<Message> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Message take = queue.take();
System.out.println("消费消息id:" + take.id + " 消息体:" + take.body);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
4.ScheduledExecutorService
线程池的返回值ExecutorService简介:
ExecutorService是Java提供的用于管理线程池的类。该类的两个作用:控制线程数量和重用线程
- Executors.newCacheThreadPool():可缓存线程池,先查看池中有没有以前建立的线程,如果有,就直接使用。如果没有,就建一个新的线程加入池中,缓存型池子通常用于执行一些生存期很短的异步型任务
- Executors.newFixedThreadPool(int n):创建一个可重用固定个数的线程池,以共享的无界队列方式来运行这些线程。
- Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(int n):创建一个定长线程池,支持定时及周期性任务执行
- Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor():创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务按照指定顺序(FIFO, LIFO, 优先级)执行。
先列举下常用的线程池,前两个是比较常见的,newSingleThreadExecutor这个用的也不多,曾经有一个面试题说:如何让线程有顺序的执行,可以用这个线程池来实现。
newScheduledThreadPool是一个线程池。由于内部使用的是延迟队列,所以提供了延迟队列的功能。
ScheduledExecutorService 可以解决Timer单线程任务排队的问题。示例:
public static ScheduledExecutorService mScheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(10);
public static void main(String[] args) {
mScheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println( "我1秒一次,"+ LocalTime.now());
}
}, 0,1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
mScheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000l);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println( "我5秒一次,"+LocalTime.now());
}
}, 0,1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
同样是一个任务1秒一次,一个任务5秒一次。输出:
我1秒一次,20:38:51.571
我1秒一次,20:38:52.462
我1秒一次,20:38:53.464
我1秒一次,20:38:54.464
我1秒一次,20:38:55.462
我1秒一次,20:38:56.463
我5秒一次,20:38:56.463
我1秒一次,20:38:57.464
我1秒一次,20:38:58.462
我1秒一次,20:38:59.462
我1秒一次,20:39:00.464
我1秒一次,20:39:01.463
我5秒一次,20:39:01.464
此方法在进行服务之间的心跳检测的时候极为常见。比如nacos在进行续约时就有。在com.alibaba.nacos.client.naming.beat.BeatReactor可见。
//创建任务线程池
private ScheduledExecutorService executorService = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1, new ThreadFactory() {
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread thread = new Thread(r);
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.setName("com.alibaba.nacos.naming.beat.sender");
return thread;
}
});
//心跳时间
private long clientBeatInterval = 5000L;
private NamingProxy serverProxy;
public final Map<String, BeatInfo> dom2Beat = new ConcurrentHashMap();
public BeatReactor(NamingProxy serverProxy) {
this.serverProxy = serverProxy;
// 执行任务,进行心跳,告诉nacos,当前服务还是存活状态
this.executorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new BeatReactor.BeatProcessor(), 0L, this.clientBeatInterval, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
5.quartz
quartz框架是用的较多的任务调度框架。应该都见过类似0/5 * * ? * *这样的配置。比如:每隔一周需要做一些事情,每天凌晨做一些事情等等,即可在项目中进行配置。简单使用示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws SchedulerException, InterruptedException {
// 1、创建调度器Scheduler
SchedulerFactory schedulerFactory = new StdSchedulerFactory();
Scheduler scheduler = schedulerFactory.getScheduler();
// 2、创建JobDetail实例,并与PrintWordsJob类绑定(Job执行内容)
JobDetail jobDetail = JobBuilder.newJob(TaskDemo.class)
.withIdentity("job1", "group1").build();
// 3、构建Trigger实例,每隔1s执行一次
Trigger trigger = TriggerBuilder.newTrigger().withIdentity("trigger1", "triggerGroup1")
.startNow()//立即生效
.withSchedule(SimpleScheduleBuilder.simpleSchedule()
.withIntervalInSeconds(1)//每隔1s执行一次
.repeatForever()).build();//一直执行
//4、执行
scheduler.scheduleJob(jobDetail, trigger);
System.out.println("--------scheduler start ! ------------");
scheduler.start();
//睡眠
TimeUnit.MINUTES.sleep(1);
scheduler.shutdown();
System.out.println("--------scheduler shutdown ! ------------");
}
import org.quartz.Job;
import org.quartz.JobExecutionContext;
import org.quartz.JobExecutionException;
public class TaskDemo implements Job {
public void execute(JobExecutionContext jobExecutionContext) throws JobExecutionException {
System.out.println("执行定时任务");
}
}
6.HashedWheelTimer
如果简单的服务之间的心跳机制,用上面的那些都可以的,但是如果dubbo服务之间调用的时候超时机制呢?当dubbo消费端调用服务端时,如果3秒还没有返回,则进行超时异常处理。这种情况用jdk自带的任务调度器可能不能更好的实现了。HashedWheelTimer是netty框架的一个工具类,主要是用来高效处理大量的定时任务的。这里不做过多的解释。
详细:https://www.cnblogs.com/zemliu/p/3928285.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/db138d40c3c5
7.redis失效监听
场景:订单30分钟如果还没有支付,则进行库存回滚操作。
在现在大部分互联网公司都是会进行多机部署,那么如果使用jvm自带的定时器进行处理的话,一旦服务宕机,就会出现所有的定时器也就失效了。想想如果大量的订单因为服务宕机导致不能回滚,是多么的可怕。
redis在2.8之后支持对Key过期通知。也就是说,如果key消失的时候会有一个推送。那么就可以利用这个机制,设置key的value为订单id,超时时间为30分钟,在30分钟的时候,会有一个推送。
7.1redis失效机制测试
1.设置redis.conf或者redis.windows.conf的notify-keyspace-events值
2.修改为`notify-keyspace-events Ex
3.启动一个客户端,执行 psubscribe __keyevent@0__:expired
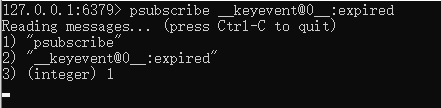
4再启动一个客户端,设置一个key,并且设置过期时间
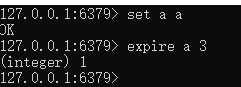
5.3秒钟后会有通知到第一个客户端。
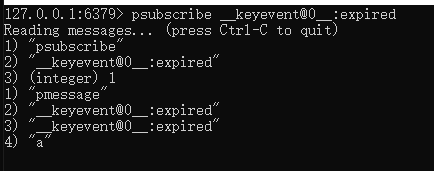
7.2redis失效机制项目中使用
引入jar
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>2.2.13</version>
</dependency>
@Configuration
public class RedisListenerConfig {
@Bean
RedisMessageListenerContainer container(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisMessageListenerContainer container = new RedisMessageListenerContainer();
container.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
return container;
}
}
@Service
public class RedisTest extends KeyExpirationEventMessageListener {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public RedisTest(RedisMessageListenerContainer listenerContainer) {
super(listenerContainer);
}
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message, byte[] pattern) {
System.out.println(new String(message.getChannel())+":"+message.toString());
}
}
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
如上,三个类即可实现redis失效机制的使用。
8.rocketmq延迟消息
虽然redis可以解决服务器宕机后jdk自带的延迟任务失效问题。但是如果是redis宕机了呢?或者redis失效的监听机制没有收到呢?毕竟redis的消息消失了,就什么都没有了,日志都没有。订单这种敏感的数据,如果出现问题,没日志查,那太难受了。
rocketmq提供了延迟消息,可以更好的来实现订单超时回滚。
阿里云rocketMq定时消息和延迟消息说明文档:
https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/43349.html?spm=a2c4g.11186623.6.552.533e30300FOeTX
https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/29549.html?spm=a2c4g.11186623.6.599.909378b4KEfHZ3
下一篇:分布式任务调度——xxl-job
最后
以上就是干净哑铃最近收集整理的关于【开发经验】任务调度实现方式的全部内容,更多相关【开发经验】任务调度实现方式内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复