一、 难以理解的场景
postgresql源码学习(十九)—— MVCC④-可见性判断 HeapTupleSatisfiesMVCC函数_Hehuyi_In的博客-CSDN博客
在前篇的可见性判断中有个一直没想明白的问题 —— 本事务插入的数据,什么场景可能会出现去查询获取快照后插入的数据这种情况?因为理论上事务内顺序的插入和查询,查的都是快照插入前的数据。今天终于发现了答案,愉快地记录下来~
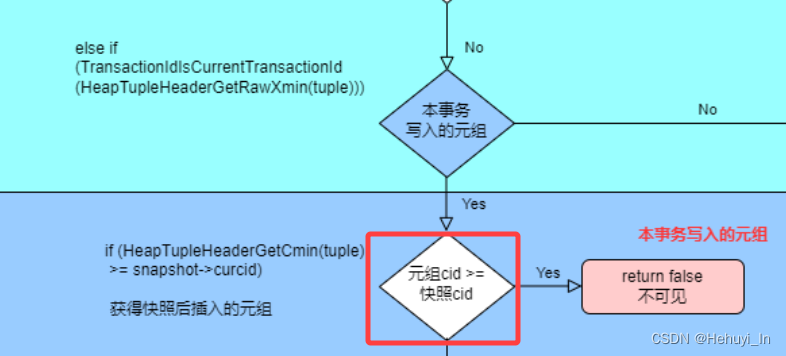

经过好多文章和资料的查找,终于查到了一个案例 —— 游标,下面案例参考自
一文搞懂费解的cmin和cmax
游标在声明时就获取一个快照,后续对于表的更改不影响到游标的取值,所以这也存在类似不同事务交替执行产生的数据可见性的问题。如下示例,Fetch游标时看到的是声明游标时的数据快照而不是Fetch执行时,即声明游标后对数据的变更对该游标不可见:
create table cur_test(a int);
begin;
insert into cur_test values(1);
select xmin,xmax,cmin,cmax,a from cur_test;
declare mycursor cursor for select xmin,xmax,cmin,cmax,a from cur_test ;
insert into cur_test values(2);
fetch all from mycursor;
select xmin,xmax,cmin,cmax,a from cur_test;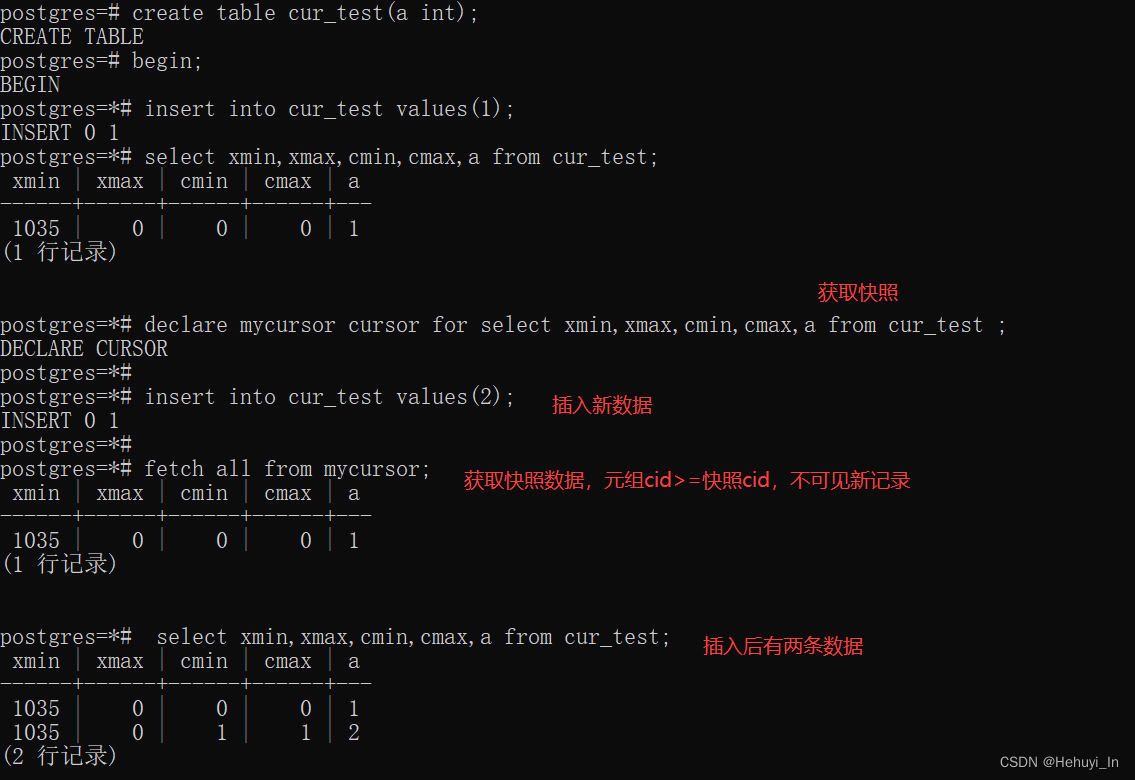
后来在postgresql_internals书中也找到了这种场景的介绍
a cursor that was opened at a particular point in time must not see any changes that happened later, regardless of the isolation level.
To address such situations, tuple headers provide a special field (displayed as cmin and cmax pseudocolumns) that shows the sequence number of the operation within the transaction.
二、 cid是什么
在不同事务中,可以根据xmin和xmax判断事务可见性。那同一个事务内怎么办?就需要用到cid(command id),cid 表示在该事务中,执行当前dml前还执行过几条dml,因此cid越大,写入顺序越靠后。 再回顾一下它的定义:
postgresql源码学习(十六)—— MVCC①-元组上的版本信息_Hehuyi_In的博客-CSDN博客_pgsql 怎么查看元组中的txid
/*
* We store five "virtual" fields Xmin, Cmin, Xmax, Cmax, and Xvac in three
* physical fields. Xmin and Xmax are always really stored, but Cmin, Cmax
* and Xvac share a field. This works because we know that Cmin and Cmax
* are only interesting for the lifetime of the inserting and deleting
* transaction respectively. If a tuple is inserted and deleted in the same
* transaction, we store a "combo" command id that can be mapped to the real
* cmin and cmax, but only by use of local state within the originating
* backend. See combocid.c for more details. Meanwhile, Xvac is only set by
* old-style VACUUM FULL, which does not have any command sub-structure and so
* does not need either Cmin or Cmax. (This requires that old-style VACUUM
* FULL never try to move a tuple whose Cmin or Cmax is still interesting,
* ie, an insert-in-progress or delete-in-progress tuple.)
*/
typedef struct HeapTupleFields
{
TransactionId t_xmin; /* inserting xact ID */
TransactionId t_xmax; /* deleting or locking xact ID */
union
{
CommandId t_cid; /* inserting or deleting command ID, or both */
TransactionId t_xvac; /* old-style VACUUM FULL xact ID */
} t_field3;
} HeapTupleFields;可以看到,虽然在前面的select中它是cmin,cmax两个值,但在源代码中,就是一个t_cid。
主要特点如下:
- cmin和cmax则分别代表插入、删除操作
- 在8.4以前,cmin和cmax分开存储,后来考虑到对同一事务内的同一行既执行插入又执行删除情况不多见,所以就合并成了一个字段,节省资源
- 如果真的出现同一事务中对同一行既执行插入、又执行删除,则通过combo cid 查找真正的cmin和cmax
- cmin和cmax始终是一致的,因为本质上都是 t_cid 字段
- vacuum full只设置t_xvac字段,而不需要cmin和cmax,可以合并存储两者,进一步节省资源
- CommandId是uint32类型,最大支持2^32 - 1个命令,为了节省资源,查询不会增加cid(类似事务id分配)
三、 获取cmin与cmax
1. HeapTupleHeaderGetCmin和HeapTupleHeaderGetCmax
在HeapTupleSatisfiesMVCC函数中,获取元组cmin与cmax相关的主要是HeapTupleHeaderGetCmin和HeapTupleHeaderGetCmax两个函数。
/*
* GetCmin and GetCmax assert that they are only called in situations where
* they make sense, that is, can deliver a useful answer. If you have
* reason to examine a tuple's t_cid field from a transaction other than
* the originating one, use HeapTupleHeaderGetRawCommandId() directly.
*/
CommandId
HeapTupleHeaderGetCmin(HeapTupleHeader tup)
{
CommandId cid = HeapTupleHeaderGetRawCommandId(tup);
Assert(!(tup->t_infomask & HEAP_MOVED));
Assert(TransactionIdIsCurrentTransactionId(HeapTupleHeaderGetXmin(tup)));
if (tup->t_infomask & HEAP_COMBOCID)
return GetRealCmin(cid);
else
return cid;
}CommandId
HeapTupleHeaderGetCmax(HeapTupleHeader tup)
{
CommandId cid = HeapTupleHeaderGetRawCommandId(tup);
Assert(!(tup->t_infomask & HEAP_MOVED));
/*
* Because GetUpdateXid() performs memory allocations if xmax is a
* multixact we can't Assert() if we're inside a critical section. This
* weakens the check, but not using GetCmax() inside one would complicate
* things too much.
*/
Assert(CritSectionCount > 0 ||
TransactionIdIsCurrentTransactionId(HeapTupleHeaderGetUpdateXid(tup)));
if (tup->t_infomask & HEAP_COMBOCID)
return GetRealCmax(cid);
else
return cid;
}可以看到,它们很类似:
- 对于非COMBOCID,核心函数都是 HeapTupleHeaderGetRawCommandId
- COMBOCID使用的是标记位t_infomask判断
- COMBOCID情况下分别使用GetRealCmin和GetRealCmax
- 无论哪个函数,最后返回的都是cid一个字段,因此cmin和cmax始终是一致的
2. HeapTupleHeaderGetRawCommandId函数
可以看到,其实就是去获取元组的t_cid
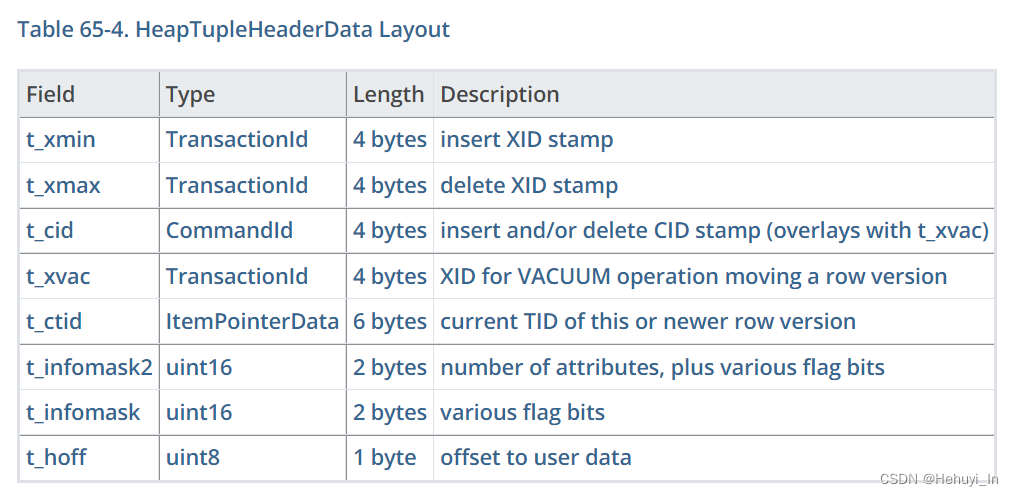
/*
* HeapTupleHeaderGetRawCommandId will give you what's in the header whether
* it is useful or not. Most code should use HeapTupleHeaderGetCmin or
* HeapTupleHeaderGetCmax instead, but note that those Assert that you can
* get a legitimate(合法的) result, ie you are in the originating transaction!
*/
#define HeapTupleHeaderGetRawCommandId(tup)
(
(tup)->t_choice.t_heap.t_field3.t_cid
)四、 combo cid
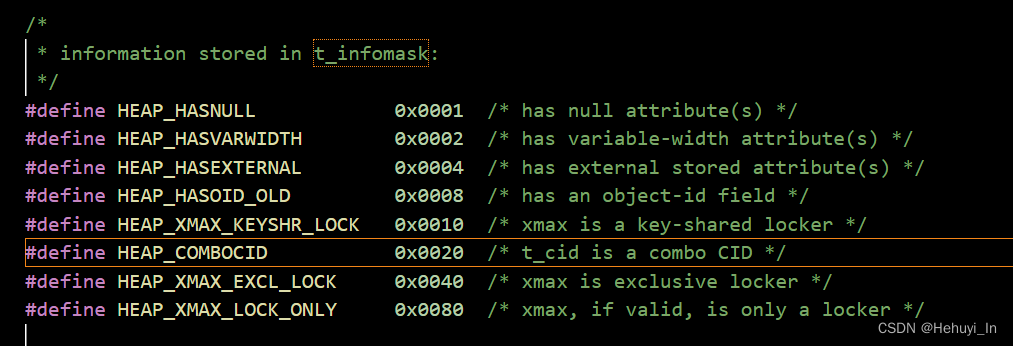
1. HEAP_COMBOCID标记位
从前面代码可以看到,COMBOCID使用的是标记位t_infomask判断,我们来验证一下。

t_infomask值为32,转成16进制就是0x0020,也就是HEAP_COMBOCID
2. 相关结构体
以下在combocid.c 文件中
/* Hash table to lookup combo CIDs by cmin and cmax,可以看到是通过哈希表去定位cmin,cmax的 */
static HTAB *comboHash = NULL;
/* Key and entry structures for the hash table,哈希表的key */
typedef struct
{
CommandId cmin;
CommandId cmax;
} ComboCidKeyData;
typedef ComboCidKeyData *ComboCidKey;
/* 哈希表的value */
typedef struct
{
ComboCidKeyData key;
CommandId combocid;
} ComboCidEntryData;
typedef ComboCidEntryData *ComboCidEntry;3. GetRealCmin和GetRealCmax函数
这两个函数相当简单,问题是过于简单好像看不出来什么东西...
static CommandId
GetRealCmin(CommandId combocid)
{
Assert(combocid < usedComboCids);
return comboCids[combocid].cmin;
}
static CommandId
GetRealCmax(CommandId combocid)
{
Assert(combocid < usedComboCids);
return comboCids[combocid].cmax;
}其中的usedComboCids和comboCids数组都来自GetComboCommandId函数
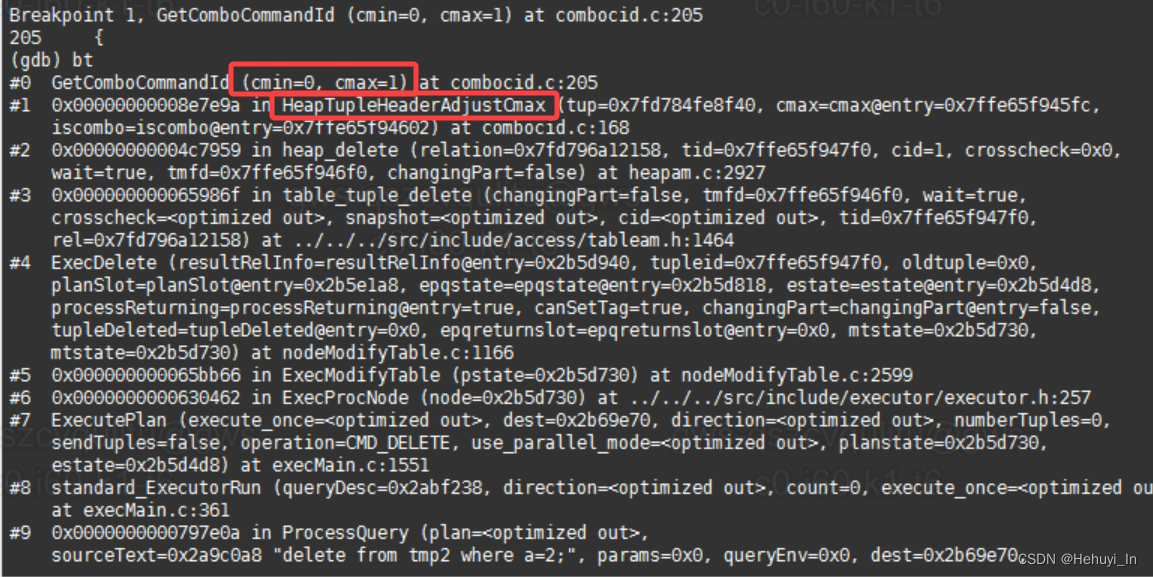
4. GetComboCommandId函数
从函数注释和调用栈都可以看到,它不是显式调用的,是一个内部函数,这里就有前面提到过的哈希表。
/**** Internal routines 内部流程 ****/
/*
* Get a combo command id that maps to cmin and cmax.
* We try to reuse old combo command ids when possible.
*/
static CommandId
GetComboCommandId(CommandId cmin, CommandId cmax)
{
CommandId combocid;
ComboCidKeyData key; // 哈希表key
ComboCidEntry entry; // 哈希表value
bool found;
/*
* Create the hash table and array the first time we need to use combo cids in the transaction.
* 第一次使用时哈希表不存在,需要先创建
*/
if (comboHash == NULL)
{
HASHCTL hash_ctl;
/* Make array first; existence of hash table asserts array exists
可以看到comboCids是ComboCidKeyData类型的数组(哈希表key数组) */
comboCids = (ComboCidKeyData *)
MemoryContextAlloc(TopTransactionContext,
sizeof(ComboCidKeyData) * CCID_ARRAY_SIZE);
sizeComboCids = CCID_ARRAY_SIZE;
usedComboCids = 0;
hash_ctl.keysize = sizeof(ComboCidKeyData);
hash_ctl.entrysize = sizeof(ComboCidEntryData);
hash_ctl.hcxt = TopTransactionContext;
/* 创建哈希表 */
comboHash = hash_create("Combo CIDs",
CCID_HASH_SIZE,
&hash_ctl,
HASH_ELEM | HASH_BLOBS | HASH_CONTEXT);
}
/*
* 超过长度则自动扩展数组
*/
if (usedComboCids >= sizeComboCids)
{
int newsize = sizeComboCids * 2;
comboCids = (ComboCidKeyData *)
repalloc(comboCids, sizeof(ComboCidKeyData) * newsize);
sizeComboCids = newsize;
}
/* Lookup or create a hash entry with the desired cmin/cmax,根据key值从哈希表中查找cmin/cmax */
/* We assume there is no struct padding in ComboCidKeyData! */
key.cmin = cmin;
key.cmax = cmax;
entry = (ComboCidEntry) hash_search(comboHash,
(void *) &key,
HASH_ENTER,
&found);
if (found)
{
/* Reuse an existing combo CID,找到则返回combocid */
return entry->combocid;
}
/* We have to create a new combo CID; we already made room in the array
否则需要新建一个combocid并以当前传入的cmin/cmax作为值,同时将计数器usedComboCids加一 */
combocid = usedComboCids;
comboCids[combocid].cmin = cmin;
comboCids[combocid].cmax = cmax;
usedComboCids++;
/* 保存到哈希表的value中并返回 */
entry->combocid = combocid;
return combocid;
}因此,前面的GetRealCmin和GetRealCmax函数,只需要一步return comboCids[combocid].cmin和 return comboCids[combocid].cmax 即可从哈希表获取所需值。
参考
一文搞懂费解的cmin和cmax
postgresql源码学习(十六)—— MVCC①-元组上的版本信息_Hehuyi_In的博客-CSDN博客_pgsql 怎么查看元组中的txid
pg事务篇(三)—— 事务状态与Hint Bits(t_infomask)_Hehuyi_In的博客-CSDN博客
postgresql源码学习(十九)—— MVCC④-可见性判断 HeapTupleSatisfiesMVCC函数_Hehuyi_In的博客-CSDN博客
最后
以上就是可爱百褶裙最近收集整理的关于postgresql源码学习(49)—— MVCC⑤-cmin与cmax 同事务内的可见性判断的全部内容,更多相关postgresql源码学习(49)——内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。

![Diagnosing Database Hanging Issues [ID 61552.1]](https://file2.kaopuke.com:8081/files_image/reation/bcimg8.png)






发表评论 取消回复