1.类之间的关联关系
- 组合关系:整体与部分的关系
- 继承关系:父子关系
2.组合与继承关系关系的特点
- 组合关系的特点
- 将其它类的对象作为当前类的成员使用
- 当前类的对象与成员对象的生命期相同
- 成员对象在用法上与普通对象完全一致
- 继承指类之间的父子关系
- 子类拥有父类的所有属性(成员变量)和行为(成员方法)
- 子类就是一种特殊的父类
- 子类对象可以当作父类对象使用
- 子类中可以添加父类没有的方法和属性
3.组合与继承的实例分析
- 组合关系的描述
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//内存类
class Memory
{
int MB;
public:
Memory() // 类的构造函数
{
MB = 512;
cout << "Memory()" << endl;
}
int value()
{
return MB;
}
~Memory()
{
cout << "~Memory()" << endl;
}
};
// 硬盘类
class Disk
{
public:
Disk()
{
cout << "Disk()" << endl;
}
~Disk()
{
cout << "~Disk()" << endl;
}
};
// CPU类
class CPU
{
public:
CPU()
{
cout << "CPU" << endl;
}
~CPU()
{
cout << "~CPU" << endl;
}
};
// 主板类
class MainBoard
{
public:
MainBoard()
{
cout << "MainBoard" << endl;
}
~MainBoard()
{
cout << "~MainBoard" << endl;
}
};
//计算机类
class Computer
{
//组合关系:部分-整体关系(与Computer对象同生命期)
Memory mMem;
Disk mDisk; // 就是直接将别的类在本类声明一个对象,拼凑在一起使用
CPU mCPU;
MainBoard mMainBoard;
public:
Computer()
{
cout << "Computer()" << endl;
}
int value()
{
return mMem.value();
}
void power()
{
cout << "power()" << endl;
}
void reset()
{
cout << "reset" << endl;
}
~Computer()
{
cout << "~Computer" << endl;
}
};
void run()
{
Computer c; // 组合初始化构造函数,先成员对象,再自己。
// 先构造成员对象,按照声明的顺序,再调用类构造函数
cout << c.value() << endl;
}
int main()
{
run();
system("pause");
return 0;
}- 运行结果
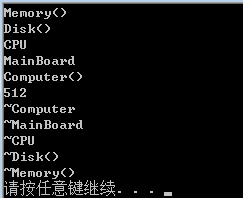
- 继承初体验
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Parent // 父类(基类)
{
int mv;
public:
Parent()
{
cout << "Parent()" << endl;
mv = 100; // 构造函数给mv赋值
}
void method()
{
cout << "mv = " << mv << endl;
}
};
class Child : public Parent // /子类(派生类),拥有父类所有的属性和方法
{
public:
void hello()
{
cout << "I am Child class !" << endl;
//cout << mv << endl; //测试,子类不能直接使用父类的私有变量
}
};
int main()
{
Child c;
c.hello();
c.method();
system("pause");
return 0;
}- 运行结果:
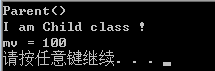
4.重要规则
- 子类就是一个特殊的父类
- 子类对象可以直接初始化父类对象(但子类对象不能直接使用父类的私有成员变量!可以用protected关键字改变private)
- 子类对象可以直接赋值给父类对象(父子兼容性)
5.继承的意义
- 继承是C++是代码复用的重要手段。通过继承,可以获得父类的所有功能,并且可以在子类中重写己有的功能,或者添加新功能。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//内存类
class Memory
{
public:
Memory()
{
cout << "Memory()" << endl;
}
~Memory()
{
cout << "~Memory()" << endl;
}
};
//硬盘类
class Disk
{
public:
Disk()
{
cout << "Disk()" << endl;
}
~Disk()
{
cout << "~Disk()" << endl;
}
};
//CPU类
class CPU
{
public:
CPU()
{
cout << "CPU()" << endl;
}
~CPU()
{
cout << "~CPU()" << endl;
}
};
//主板类
class MainBoard
{
public:
MainBoard()
{
cout << "MainBoard()" << endl;
}
~MainBoard()
{
cout << "~MainBoard()" << endl;
}
};
//计算机类
class Computer
{
//组合关系:部分-整体关系(与Computer对象同生命期)
Memory mMem;
Disk mDisk;
CPU mCPU; //想要在这个类的子类中使用这些成员方法。必须在这个类的public下面手工调用。
MainBoard mMainBoard;
int value;
public:
Computer()
{
cout << "Computer()" << endl;
}
void power()
{
cout << "power()" << endl;
}
void reset()
{
cout << "reset()" << endl;
}
~Computer()
{
cout << "~Computer()" << endl;
}
};
//惠普笔记本
class HPBook : public Computer
{
string mOS;
public:
HPBook()
{
mOS = "Windows 8"; // 预装Windows8 操作系统
}
void install(string os)
{
mOS = os; //更新操作系统
}
void OS()
{
cout << mOS << endl;
}
};
//苹果电脑
class MacBook : public Computer
{
public:
void OS()
{
//cout << Computer::value << endl; // 私有变量,不能直接访问
cout << "Mac OS" << endl;
}
};
void run()
{
HPBook hp; // 调用父类相应构造函数,再成员,最后自己。
hp.power(); // 可以使用公共的方法
hp.install("Ubuntu 16.04 LTS");
hp.OS();
cout << endl;
MacBook mac; // 调用父类相应构造函数,再成员,最后自己。
mac.OS();
}
int main()
{
run();
system("pause");
return 0;
}- 运行结果
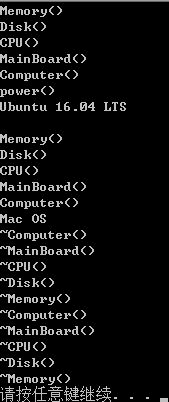
6.小结
- 继承是面向对象中类之间的一种关系
- 子类拥有父类的所有属性和行为
- 子类对象可以当作父类对象使用
- 子类中可以添加父类没有的方法和属性
- 继承是面向对象中代码复用的重要手段
ps:什么情况下用继承?什么情况下用组合呢?
- 继承:譬如你有一个电脑普通类,你想改造成苹果的,惠普的,联想的...这时候就要继承,添加别的功能。
- 组合:譬如你想要组装一台电脑,你有一堆硬件,硬盘,CPU,主机外壳,内存条,显示屏,他们之间没有任何重合的地方,彼此独立的,就可以组合,组合在一起干活。
最后
以上就是欣喜汉堡最近收集整理的关于C++深度解析(33)—继承的概念和意义的全部内容,更多相关C++深度解析(33)—继承内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复