单应变换相比平移变换,具有更广泛的场景适应性,但同时稳定性会有一定程度下降。
设计到的技术细节有:
- 特征检测与描述
- 特征匹配与单应矩阵估计
- opencv采集视频
- 渐入渐出图像融合
这个解决方案的硬件条件包括:有两个USB接口的计算机,两个合理放置的USB摄像头。
合理放置是指:两个摄像头分隔一定夹角,相机中心相距接近,所拍摄场景有足够的重叠部分。以上保证了单应变换的可用性。
代码实现:
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
# include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include"opencv2/nonfree/nonfree.hpp"
#include"opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
#include<iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
VideoCapture cap1(0);
VideoCapture cap2(1);
double rate = 60;
int delay = 1000 / rate;
bool stop(false);
Mat img1;
Mat img2;
Mat result;
int d = 200;//渐入渐出融合宽度
Mat homography;
int k = 0;
namedWindow("cam1", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
namedWindow("cam2", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
namedWindow("stitch", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
if (cap1.isOpened() && cap2.isOpened())
{
cout << "*** ***" << endl;
cout << "摄像头已启动!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "*** ***" << endl;
cout << "警告:请检查摄像头是否安装好!" << endl;
cout << "程序结束!" << endl << "*** ***" << endl;
return -1;
}
cap1.set(CV_CAP_PROP_FOCUS, 0);
cap2.set(CV_CAP_PROP_FOCUS, 0);
while (!stop)
{
if (cap1.read(img1) && cap2.read(img2))
{
imshow("cam1", img1);
imshow("cam2", img2);
//彩色帧转灰度
//cvtColor(img1, img1, CV_RGB2GRAY);
//cvtColor(img2, img2, CV_RGB2GRAY);
//计算单应矩阵
if (k < 1 || waitKey(delay) == 13)
{
cout << "正在匹配..." << endl;
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints1, keypoints2;
//构造检测器
//Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = new ORB(120);
Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = new SIFT(80);
detector->detect(img1, keypoints1);
detector->detect(img2, keypoints2);
//构造描述子提取器
Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = detector;
//提取描述子
Mat descriptors1, descriptors2;
descriptor->compute(img1, keypoints1, descriptors1);
descriptor->compute(img2, keypoints2, descriptors2);
//构造匹配器
BFMatcher matcher(NORM_L2, true);
//匹配描述子
vector<DMatch> matches;
matcher.match(descriptors1, descriptors2, matches);
vector<Point2f> selPoints1, selPoints2;
vector<int> pointIndexes1, pointIndexes2;
for (vector<DMatch>::const_iterator it = matches.begin(); it != matches.end(); ++it)
{
selPoints1.push_back(keypoints1.at(it->queryIdx).pt);
selPoints2.push_back(keypoints2.at(it->trainIdx).pt);
}
vector<uchar> inliers(selPoints1.size(), 0);
homography = findHomography(selPoints1, selPoints2, inliers, CV_FM_RANSAC, 1.0);
//根据RANSAC重新筛选匹配
vector<DMatch> outMatches;
vector<uchar>::const_iterator itIn = inliers.begin();
vector<DMatch>::const_iterator itM = matches.begin();
for (; itIn != inliers.end(); ++itIn, ++itM)
{
if (*itIn)
{
outMatches.push_back(*itM);
}
}
k++;
//画出匹配结果
//Mat matchImage;
//drawMatches(img1, keypoints1, img2, keypoints2, outMatches, matchImage, 255, 255);
//imshow("match", matchImage);
///
}
//拼接
double t = getTickCount();
warpPerspective(img1, result, homography, Size(2 * img1.cols-d, img1.rows));//Size设置结果图像宽度,宽度裁去一部分,d可调
Mat half(result, Rect(0, 0, img2.cols - d, img2.rows));
img2(Range::all(), Range(0, img2.cols - d)).copyTo(half);
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++)
{
result.col(img2.cols - d + i) = (d - i) / (float)d*img2.col(img2.cols - d + i) + i / (float)d*result.col(img2.cols - d + i);
}
imshow("stitch", result);
t = ((double)getTickCount() - t) / getTickFrequency();
//cout << t << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "----------------------" << endl;
cout << "waitting..." << endl;
}
if (waitKey(1) == 27)
{
stop = true;
cout << "程序结束!" << endl;
cout << "*** ***" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
实验效果:
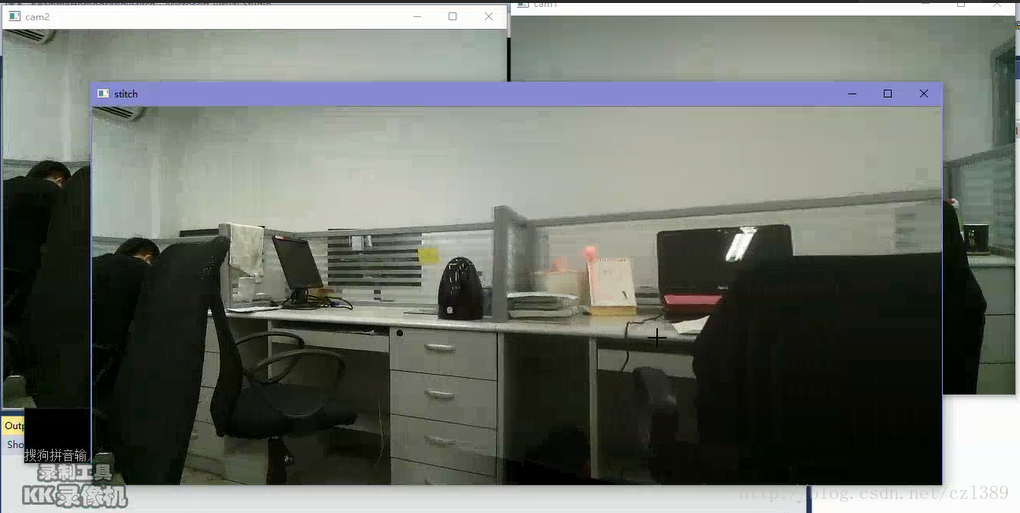
上述视频是用录屏软件录制的,分辨率会有下降。实际测试中,直接观察显示良好。两幅输入的源图像均为640*480分辨率,能够做到实时的实现。在我的具有i3处理器配置的笔记本上运行,拼接图像显示间隔为0.10″~0.12″。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/czl389/article/details/60757000
最后
以上就是愉快大山最近收集整理的关于图像拼接(九):双摄像头实时视频拼接(单应变换模型)的全部内容,更多相关图像拼接(九)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复