MNIST数据集的识别:实现模型保存与调用模型进行测试
完整代码
参考代码
网络部分
def __init__(self):
# 定义两个placeholder
self.x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784], name='x-input')
self.y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10], name='y-input')
# 将数据集转变乘4D的向量[batch, in_height. in_width, in_channels]
x_image = tf.reshape(self.x, [-1, 28, 28, 1], name='x_image')
# 第一个卷积层
# 定义卷积层权值和偏置值
w_conv1 = self.weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32], name='W_conv1') # 5*5的采样窗口,当前深度为1,卷积层深度为32
b_conv1 = self.bias_variable([32], name='b_conv1') # 卷积深度为32 所以偏置值也是32
conv2d_1 = self.conv2d(x_image, w_conv1) + b_conv1
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d_1) # 通过relu激活函数线性化
h_pool1 = self.max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) # max_pooling
# 第二个卷积层
# 定义卷积层权值和偏置值
w_conv2 = self.weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64], name='W_conv1') # 5*5的采样窗口,当前深度为64,卷积层深度为64
b_conv2 = self.bias_variable([64], name='b_conv1') # 卷积深度为64 所以偏置值也是64
conv2d_2 = self.conv2d(h_pool1, w_conv2) + b_conv2
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d_2) # 通过relu激活函数线性化
h_pool2 = self.max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) # max_pooling
# 28*28的图片经过第一次卷积后仍然是28*28,第一次池化后变成14*14
# 第二次卷积后为14*14,池化后为7*7
# 经过上面的操作最后得到64张7*7的平面
# 第一个全连接层
w_fc1 = self.weight_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024], name='w_fc1') # 前面输出为 7*7*64个神经元,所以全连接层有 1024 个神经元
b_fc1 = self.bias_variable([1024], name='b_fc1') # 1024个节点
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64], name='h_pool2_flat') # 将输出扁平化为1维
wx_plus_b1 = tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, w_fc1) + b_fc1
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(wx_plus_b1)
# 去除过拟合
self.keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name='keep_prob')
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, self.keep_prob, name='h_fc1_drop')
# 第二个全连接层
w_fc2 = self.weight_variable([1024, 10], name='w_fc2') # 前面输出为 7*7*64个神经元,所以全连接层有 1024 个神经元
b_fc2 = self.bias_variable([10], name='b_fc2') # 1024个节点
wx_plus_b2 = tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, w_fc2) + b_fc2
# 计算输出
self.prediction = tf.nn.softmax(wx_plus_b2)
# loss function
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=self.y, logits=self.prediction))
# 优化
self.train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.0001).minimize(cross_entropy)
# 求准确率
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(self.prediction, 1), tf.argmax(self.y, 1))
self.accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
def weight_variable(self, shape, name): # 定义权值
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1) # 生成一个截断的正态分布
return tf.Variable(initial, name=name)
def bias_variable(self, shape, name): # 定义偏置值
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial, name=name)
def conv2d(self, x, W): # 定义卷积层
# x为输入,大小为 [batch, height, width, channels]
# W为filter大小,shape `[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]`
# 前两项代表了过滤器的尺寸,第三个维度代表了当前的深度,第四个维度表示过滤器的深度
# strides[0]=strides[3]=1, strides[1]代表x方向的步长,strides[2]代表y方向的步长
# padding = 'SAME' 代表了填充的方式为补 0
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
def max_pool_2x2(self, x): # 定义池化层
# x 为输入
# ksize 提供了滤波器的尺寸,虽然给出了四个维度,但是第一个和最后一个数必须为1。这意味着池化层的过滤器
# 是不可以跨不同节点矩阵深度的。。
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
网络部分,是一个简单的CNN网络,值得注意的是,由于训练的数据并不是很多,所以经过这样的CNN网络后,准确率不会到0.8,所以加入了一个过拟合模块,keep_prob = 0.5 表示在此全连接层中,只有一半的神经元被传递到下一层。可以简化网络。
训练部分
’‘’
class Train(object):
def __init__(self):
self.net = Network()
self.sess = tf.Session()
self.sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
self.data = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True)
def train(self):
# 一个循环需要训练多少个batch
n_batch = self.data.train.num_examples // batch_size
saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=1) # 只保留最近一次的模型
# 训练模型
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) # 初始化变量
for i in range(1001):
batch_xs, batch_ys = self.data.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(self.net.train_step, feed_dict={self.net.x: batch_xs, self.net.y: batch_ys, self.net.keep_prob: 0.5})
if i % 100 == 0:
saver.save(sess, CKPT_DIR + '/model', global_step=i)
test_acc = sess.run(self.net.accuracy,
feed_dict={self.net.x: self.data.test.images, self.net.y: self.data.test.labels, self.net.keep_prob: 1.0})
print("当前训练到{}batch,准确率为{}".format(i, test_acc))
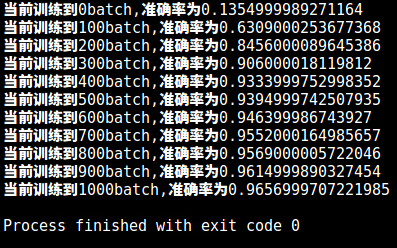
训练结果
这里保存了最后一次的训练模型
测试部分
这里的测试部分并没有使用 mnist 处理好的test_batch,而是将 mnist 的jpg格式进行测试。
‘’‘
def __init__(self):
# 清除默认图的堆栈,并设置全局图为默认图
# 若不进行清楚则在第二次加载的时候报错,因为相当于重新加载了两次
tf.reset_default_graph()
self.net = Network()
self.sess = tf.Session()
self.sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# 加载模型到sess中
self.restore()
print('load susess')
def restore(self):
saver = tf.train.Saver()
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(CKPT_DIR)
print(ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
saver.restore(self.sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
else:
raise FileNotFoundError('未保存模型')
def predict(self, image_path):
# 读取图片并灰度化
img = Image.open(image_path).convert('L')
x = np.reshape(img, [1, 784])
y = self.sess.run(self.net.prediction, feed_dict={self.net.x: x, self.net.keep_prob: 1.0})
print(image_path)
print(' Predict digit', np.argmax(y[0])) # 提取出可能性最大的值
最后
以上就是愉快鱼最近收集整理的关于用简单的CNN网络实现MNIST数据集的识别:实现模型保存与调用模型进行测试的全部内容,更多相关用简单内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复