Tensorflow–基本数据结构与运算
Tensor是Tensorflow中最基础,最重要的数据结构,常翻译为张量,是管理数据的一种形式
一.张量
1.张量的定义
所谓张量,可以理解为n维数组或者矩阵,Tensorflow提供函数:
constant(value,dtype=None,shape=None,name="Const",verify_shape=False)
2.Tensor与Numpy的ndarray转换
Tensor转换为ndarray
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
t=tf.constant([1,2,3],tf.float32)
session=tf.Session()
array=session.run(t)
print(type(array))
print(array)
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
[ 1. 2. 3.]
也可以先创建会话,然后利用Tensor的成员函数eval,将Tensor转换为ndarray,代码如下;
session=tf.Session()
array=t.eval(session=session)
print(array)
以上代码的另一种写法如下:
with tf.Session() as session:
array=t.eval()
print(array)
ndarray 转换为 Tensor
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
array=np.array([1,2,3],np.float32)
t=tf.convert_to_tensor(array,tf.float32,name="t")
print(t)
Tensor("t:0", shape=(3,), dtype=float32)
3.张量的尺寸
张量的尺寸,又称张量的形状
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
t=tf.constant(
[
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]
]
,tf.float32
)
session=tf.Session()
s=tf.shape(t)
print("张量的形状:",session.run(s))
张量的形状: [2 3]
利用成员函数get_shape()或者成员变量shape得到张量的尺寸
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
t=tf.constant(
[
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]
],
tf.float32
)
s=t.get_shape()
print("s的值:",s)
print(type(s))
print("s[0]的值:",s[0])
print("s[0]的数据结构类型:",type(s[0]))
print("将s[0]的值转换为整数型:")
print(s[0].value)
print(type(s[0].value))
s的值: (2, 3)
<class 'tensorflow.python.framework.tensor_shape.TensorShape'>
s[0]的值: 2
s[0]的数据结构类型: <class 'tensorflow.python.framework.tensor_shape.Dimension'>
将s[0]的值转换为整数型:
2
<class 'int'>
4.图像转换为张量
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
image=tf.read_file("LQ6H.png","r")
image_tensor=tf.image.decode_jpeg(image)
shape=tf.shape(image_tensor)
session=tf.Session()
print("图像的形状:",session.run(shape))
image_ndarray=image_tensor.eval(session=session)
plt.imshow(image_ndarray)
plt.show()
图像的形状: [180 180 3]

二.随机数
Tensorflow提供了很多产生不同概率分布的随机数的函数,如产生均匀分布随机数的函数random_uniform,产生正态分布随机数的函数random_norm,产生泊松分布随机数和正态分布随机数
1.平均分布随机数
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=tf.random_uniform([10,4,20,5],minval=0,maxval=10,dtype=tf.float32)
session=tf.Session()
array=session.run(x)
array1d=array.reshape([-1])
plt.hist(array1d)
plt.show()

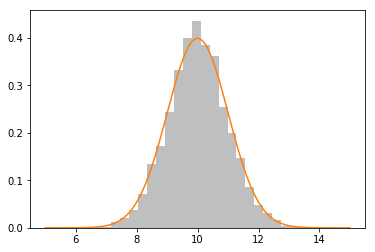
2.态(高斯)分布随机数
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import math
sigma=1
mu=10
result=tf.random_normal([10,4,20,5],mu,sigma,tf.float32)
session=tf.Session()
array=session.run(result)
array1d=array.reshape([-1])
histogram,bins,patch=plt.hist(array1d,25,facecolor="gray",alpha=0.5,normed=True)
x=np.arange(5,15,0.01)
y=1.0/(math.sqrt(2*np.pi)*sigma)*np.exp(-np.power(x-mu,2.0)/(2*math.pow(sigma,2)))
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.show()
E:Anacondaenvsmytensorflowlibsite-packagesmatplotlibaxes_axes.py:6521: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning:
The 'normed' kwarg was deprecated in Matplotlib 2.1 and will be removed in 3.1. Use 'density' instead.
alternative="'density'", removal="3.1")
三.单个张量的运算
1.改变张量的数据类型
数值型转换为bool型
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
t=tf.constant(
[
[0,2,0],
[0,0,1]
]
,tf.float32
)
session=tf.Session()
r=tf.cast(t,tf.bool)
print(session.run(r))
[[False True False]
[False False True]]
bool型转换为数值型
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
t=tf.constant(
[
[False,True,False],
[False,False,True]
]
,tf.bool
)
session=tf.Session()
r=tf.cast(t,tf.float32)
print(session.run(r))
[[ 0. 1. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 1.]]
2.访问张量中某一个区域的值
一维张量中某一个区域的值
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
t1=tf.constant([1,2,3,4,5],tf.float32)
t=tf.slice(t1,[1],[3])
session=tf.Session()
print(session.run(t))
[ 2. 3. 4.]
二维张量中某个区域的值
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
t2=tf.constant(
[
[1,2,3,4],
[5,6,7,8],
[9,10,11,12]
]
,tf.float32
)
t=tf.slice(t2,[0,1],[2,2])
session=tf.Session()
print(session.run(t))
[[ 2. 3.]
[ 6. 7.]]
三维张量中某个区域的值
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
t3d=tf.constant(
[
[[2,5],[3,3],[8,2]],
[[6,1],[1,2],[5,4]],
[[7,9],[2,-3],[-1,3]]
]
,tf.float32
)
t=tf.slice(t3d,[1,0,1],[2,2,1])
session=tf.Session()
print(session.run(t))
[[[ 1.]
[ 2.]]
[[ 9.]
[-3.]]]
3.转置
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
x=tf.constant(
[
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]
]
,tf.float32
)
session=tf.Session()
r=tf.transpose(x,perm=[1,0])
print(session.run(r))
[[ 1. 4.]
[ 2. 5.]
[ 3. 6.]]
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
x=tf.constant(
[
[[2,5],[3,4],[8,2]],
[[6,1],[1,2],[5,4]]
]
,tf.float32
)
session=tf.Session()
r=tf.transpose(x,perm=[1,0,2])
print(session.run(r))
[[[ 2. 5.]
[ 6. 1.]]
[[ 3. 4.]
[ 1. 2.]]
[[ 8. 2.]
[ 5. 4.]]]
4.改变形状
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
t3d=tf.constant(
[
[[1,2],[4,5],[6,7]],
[[8,9],[10,11],[12,13]]
]
,tf.float32
)
session=tf.Session()
t1=tf.reshape(t3d,[4,1,-1])
print(session.run(t1))
[[[ 1. 2. 4.]]
[[ 5. 6. 7.]]
[[ 8. 9. 10.]]
[[ 11. 12. 13.]]]
注意程序中t1=tf.reshape(t3d,[4,1,-1])等价于t1=tf.reshape(t3d,[4,1,3])
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
t4d=tf.constant(
[
[
[[2,5],[3,3],[8,2]],
[[6,1],[1,2],[5,4]]
],
[
[[1,2],[3,6],[1,2]],
[[3,1],[1,2],[2,1]]
]
]
,tf.float32
)
t2d=tf.reshape(t4d,[2,-1])
#t2d=tf.reshape(t4d,[-1,3*3*2])
session=tf.Session()
print(session.run(t2d))
[[ 2. 5. 3. 3. 8. 2. 6. 1. 1. 2. 5. 4.]
[ 1. 2. 3. 6. 1. 2. 3. 1. 1. 2. 2. 1.]]
5.归约运算
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
t1d=tf.constant([3,4,1,5],tf.float32)
sum0=tf.reduce_sum(t1d)
# sum0=tf.reduce_sum(t1d,axis=0)
session=tf.Session()
print(session.run(sum0))
13.0
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
value2d=tf.constant(
[
[5,1,4,2],
[3,9,5,7]
]
,tf.float32
)
session=tf.Session()
sum0=tf.reduce_sum(value2d,axis=0)
print("沿0轴方向的和:")
print(session.run(sum0))
sum1=tf.reduce_sum(value2d,axis=1)
print("沿1轴方向的和:")
print(session.run(sum1))
sum01=tf.reduce_sum(value2d,axis=(0,1))
print("沿(0,1)平面的和:")
print(session.run(sum01))
沿0轴方向的和:
[ 8. 10. 9. 9.]
沿1轴方向的和:
[ 12. 24.]
沿(0,1)平面的和:
36.0
四.对个张量之间的运算
1.二维张量的加法
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
value1=tf.constant(
[
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]
]
,tf.float32
)
value2=tf.constant(
[
[10],
[20]
]
,tf.float32
)
result=tf.add(value1,value2)
session=tf.Session()
print(session.run(result))
[[ 11. 12. 13.]
[ 24. 25. 26.]]
2.乘法
Tensorflow除了提供乘法函数multiply,还提供关于矩阵(二维张量)乘法的函数matmul
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
x=tf.constant(
[
[1,2],
[3,4]
]
,tf.float32
)
w=tf.constant([[-1],[-2]],tf.float32)
y=tf.matmul(x,w)
session=tf.Session()
print(session.run(y))
[[ -5.]
[-11.]]
3.张量的堆叠
一维张量的堆叠
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
t1=tf.constant([1,2,3],tf.float32)
t2=tf.constant([7,8,9],tf.float32)
t=tf.stack([t1,t2],0)
session=tf.Session()
print(session.run(t))
[[ 1. 2. 3.]
[ 7. 8. 9.]]
二维张量的堆叠
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
t1=tf.constant(
[
[11,12,13],
[14,15,16]
]
,tf.float32
)
t2=tf.constant(
[
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9]
]
,tf.float32
)
session=tf.Session()
t=tf.stack([t1,t2],1)
print(session.run(t))
[[[ 11. 12. 13.]
[ 4. 5. 6.]]
[[ 14. 15. 16.]
[ 7. 8. 9.]]]
五.占位符(placeholder)
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[2,None],name="x")
w=tf.constant(
[
[1,2],
[3,4],
[5,6]
]
,tf.float32
)
y=tf.matmul(w,x)
session=tf.Session()
result1=session.run(y,feed_dict={x:np.array([[2,1],[1,2]],np.float32)})
print(result1)
result2=session.run(y,feed_dict={x:np.array([[-1],[2]],np.float32)})
print(result2)
[[ 4. 5.]
[ 10. 11.]
[ 16. 17.]]
[[ 3.]
[ 5.]
[ 7.]]
六.Variable对象
Tensor对象的值是不可变的,Tensor类并没有提供任何成员函数改变其值,而且无法用同一个Tensor对象记录一个随时变化的值。Tensorflow中的Variable类可以解决该问题,保存随时变化的值
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author LQ6H
import tensorflow as tf
v=tf.Variable(tf.constant([2,3],tf.float32))
session=tf.Session()
session.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
print("v初始化的值")
print(session.run(v))
session.run(v.assign_add([10,20]))
print("v的当前值")
print(session.run(v))
v初始化的值
[ 2. 3.]
v的当前值
[ 12. 23.]
注意:创建Variable对象后,要调用方法global_variables_initializer(),才可以使用Variable对象的值,否则会报错
最后
以上就是疯狂哈密瓜最近收集整理的关于Tensorflow--基本数据结构与运算Tensorflow–基本数据结构与运算的全部内容,更多相关Tensorflow--基本数据结构与运算Tensorflow–基本数据结构与运算内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复