最近一直在复习java,写一下其中自己的疑惑点。第一个讲Int和Integer。
首先,应该明确的式Int是数据类型,Integer是封装Int的一个类。
八大数据类型,java都有封装。boolean->Boolean;char->Character;byte->Byte;short->Short;int->Integer;long->Long;float->Float;double->Double;
后者就成了类。
区别一:
在比较两个数大小的时候两者就体现出了区别:
127下,数值均相等:
int a=100;
int b=100;
System.out.println("a=100,b-100,a.b均为int类型");
if(a==b){
System.out.println("a==b");
}else{
System.out.println("a!=b");
}
Integer c=100;
Integer d=100;
System.out.println("c=100,d=100,c.d均为Integer类");
if(c==d){
System.out.println("c==d");
}else{
System.out.println("c!=d");
}
if(c.equals(d)){
System.out.println("c.equals(d)");
}else{
System.out.println("!c.equals(d)");
}
System.out.println("a=100,d=100,a为int,d为Integer");
if(a==d){
System.out.println("a==d");
}else{
System.out.println("a!=d");
}
if(d.equals(a)){
System.out.println("d.equals(a)");
}else{
System.out.println("!d.equals(a)");
}
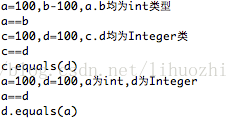
127以上数值:
a=200;
b=200;
System.out.println("a=200,b=200,a.b均为int类型");
if(a==b){
System.out.println("a==b");
}else{
System.out.println("a!=b");
}
System.out.println("c=200,d=200,c.d均为Integer类");
c=200;
d=200;
if(c==d){
System.out.println("c==d");
}else{
System.out.println("c!=d");
}
if(c.equals(d)){
System.out.println("c.equals(d)");
}else{
System.out.println("!c.equals(d)");
}
System.out.println("a=200,d=200,a为int,d为Integer");
a=200;
d=200;
if(a==d){
System.out.println("a==d");
}else{
System.out.println("a!=d");
}
if(d.equals(a)){
System.out.println("d.equals(a)");
}else{
System.out.println("!d.equals(a)");
}
}
运行结果:
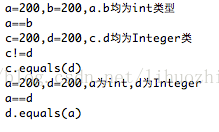
区别二:
初始值不一样,int类型初始化值为0;Integer初始化值为null
int[] a1=new int[5];
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
System.out.println(a1[i]);
}
Integer[] b1=new Integer[5];
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
System.out.println(b1[i]);
}运行结果:

区别三:
int可直接转char类型但是Integer不行需要转成int型:
int[] a2={85,89,90,97,126};
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
System.out.println((char)a2[i]);
}
Integer[] b2={85,89,90,97,126};
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
System.out.println((char)(b2[i].intValue()));
}
}
区别四:
这也就看出了类型之间的转化:
int->Integer
Integer a=new Integer(33);
String->Integer
Integer a=Integer.valueOf(s);
String -> int
int a=Integer.parseInt(s);
Integer a=Integer.valueOf(s).intVlaue();
int->String
String s=String.valueOf(a);
String s=Integer.toString(a);
String s=""+a;
区别五:
在List<>中,需要的是类,需要定义为List<Integer>而不是List<int>
基本总结到这,以后在添加。谢谢!~~
最后
以上就是野性铃铛最近收集整理的关于Int与Integer(Java复习一)的全部内容,更多相关Int与Integer(Java复习一)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复