常用类介绍01
A.Object
1)概述
类Object是类层次结构的根类
每个类都使用Object作为超类(父类)
所有对象(数组)都实现这个类的方法
系统默认继承Objiect类,因此一般都省略后半段:class Student extends Object{}
class Student {}
2)public int hashCode():
返回的是该对象的哈希码值
是通过哈希表里面的哈希算法算出来的,可以理解为地址值(整数)
package text; class Student extends Object {} // 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { /* * 地址值每次输出都不一样 */ Student s1 = new Student(); System.out.println(s1);// text.Student@4160ce61 System.out.println(s1.hashCode());// 1096863329 Student s2 = new Student(); System.out.println(s2.hashCode());// 982344655 Student s3 = s1; System.out.println(s3.hashCode());// 1096863329 } }
3)public final Class<?> getClass():
返回次Object正在运行的类
Class类中有一个方法:getName()
public String getName()以String的形式返回次Class对象所表示的实体名称
package text; class Student extends Object {} // 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Student s = new Student(); Class c = s.getClass(); System.out.println(c);// class text.Student String str = c.getName(); System.out.println(str);// text.Student:表示当前Student类的一个全路径名称 } }
4)public String toString():
返回该对象的字符串表示
通常,该方法会返回一个"以文本方式表示"此对象的字符串
Interger类:是int类的一个包装类类型
public static String toHexString(int i)
以十六进制无符号整数形式返回一个整数参数的字符串表示形式
注意:直接输出对象名称,和toString()一样,前提是在自定义的类中没有重写toString()方法
自己手动添加toString()方法,不需要手动添加
在自定义一个类的时候,可以在适当的情况重写toString()方法
创建对象,直接输出对象名,该类如果没有重写toString()方法,那么打印出来的是地址值:
包名.类名@16进制数据:地址值
a.没有重写toString()
//测试类package text; public class Student { /** * 分析源码: * public String toString() { * return getClass().getName + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode)); * } * getClass():返回的当前正在运行的类:Student类 * getName():返回的是全路径名称,是以String字符串形式显示出来text.Student * @:地址标记 * Integet.toHexString(hashCode()):返回一个整数的16进制数据 */ //成员变量 private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
package text; // 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Student s = new Student("Tom", 5); System.out.println(s);// text.Student@39126d91 System.out.println(s.hashCode());// 1176485512 System.out.println(s.toString());// text.Student@39126d91 /* * toString:相当于: s.getClass().getName+"@"+(该方法所在类名.toHexString(int i)) */ // getClass()是Object中的方法,getName是Class类中的方法 System.out.println(s.getClass().getName());// text.Student System.out.print("@"); System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(s.hashCode()));// 39126d91 } }b.重写toString()
//测试类package text; public class Student { /** * 分析源码: * public String toString() { * return getClass().getName + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode)); * } * getClass():返回的当前正在运行的类:Student类 * getName():返回的是全路径名称,是以String字符串形式显示出来text.Student * @:地址标记 * Integet.toHexString(hashCode()):返回一个整数的16进制数据 */ //成员变量 private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } //重写toString() // @Override // public String toString() { // return "姓名是:"+name+",年龄是:"+age; // } //自动生成toString()方法:Alt+Shift+s+s @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }
package text; // 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Student s = new Student("Tom", 5); System.out.println(s);// Student [name=Tom, age=5] } }
5)public boolean equals(Object obj):
指示其他某个对象是否与此对象“相等”
equals:默认比较的是地址值
Object类中的源码:
判断此对象(当前类的对象this),obj实际的对象,判断对象是否相等
public boolean equals(Object obj) { return (this == obj); }比较两个对象是否相等,看两个对象中的内容是否相同,就需要在Objiect类中去重写equal()
//测试类package text; public class Student { // 成员变量 private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } // toString()方法 @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } // 手动重写 // @Override // public boolean equals(Object obj) { // return (this == obj); // } @Override public int hashCode() { final int prime = 31; int result = 1; result = prime * result + age; result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); return result; } // 自动生成,默认的去去重写equals():Alt+Shift+S+H(执行两次,第一次生成hashCode(),第二次生成equals()) @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj)// this:Student当前类对象 return true; if (obj == null)// 如果obj对象是空对象,Student类具体对象和空对象比较,没有意义 return false; if (getClass() != obj.getClass())// getClass().equals(obj.getClass) return false; Student other = (Student) obj;// 将父类引用强制转换子类对象 if (age != other.age) return false; if (name == null) { if (other.name != null) return false; } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) return false; return true;// ==比较的地址值 两个对象做一个== } // getClass() != obj.getClass()有些版本是: // obj insataceof Student:作用就是obj是否是Student的实例化 }
package text; // 测试类 class Demo {} public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Student s1 = new Student("Tom", 5); Student s2 = new Student("Tom", 5); /* * 在Student类中没有重写equals()方法:输出false 在Student类中重写了equals()方法:输出true */ System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); Student s3 = new Student(); Demo d = new Demo(); System.out.println(s3.equals(d));// false } }
6)protected void finalize():
当垃圾回收器确定不再对该对象更多引用时,由对象的垃圾回收器调用此方法
什么时候调用这个方法不确定,要看GC垃圾回收器这个线程什么时候空闲(System类)
7)protected Object clone():
创建并返回此对象的一个副本,返回的是Object类型
Object类的clone方法执行特定的复制操作
首先,如果此对象的类不能实现接口 Cloneable,则会抛出CloneNotSupportedException
//测试类package text; public class Student extends Object implements Cloneable { // 成员变量 private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } // 重写了clone,但前提是该类必须实现Cloneable接口! @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } }
package text; // 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Student s = new Student(); s.setName("Tom"); s.setAge(27); System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // 使用clone创建该Student对象的一个副本 Object obj = s.clone();// 报错,选择抛出异常:Ctrl+1,选择第一个 Student s2 = (Student) obj;// 将父类的引用强制转换成子类对象 System.out.println(s2.getName() + "---" + s2.getAge()); // 没有学习过clone方法的时候 Student s3 = s; System.out.println("-------------------------"); System.out.println(s3.getName() + "---" + s3.getAge()); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // 其实有区别 Student s4 = new Student();// 重新创建对象,地址值发生变化,赋值,输出成员变量 s4.setName("张三"); s4.setAge(20); System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); System.out.println(s3.getName() + "---" + s3.getAge()); System.out.println(s4.getName() + "---" + s4.getAge()); } }
B.Scanner
1)java.util包下:需要导包
简单的文本扫描器:一般情况用于键盘录入
创建键盘录入对象:Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.in:System类中,包含一些有用的类字段和方法,不能被实例化
public static final InputStream in()
System.in = InputStream is; //标准输入流 = 字节输入流
2)两个常用方法:
public int nextInt():接受一个int类型的数据
public String nextInt():接受一个String类型数据
出现了一个问题:
先接收了一个int类型的数据,然后再接收字符串类型,发现String类型的数据没有接收到
出现的原因:换行符的问题,在接收数据完成后然后要手动的回车,出现了这个问题
public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); //先去接收int类型数据,在接受字符串类型 System.out.println("请先输入int类型,再输入字符串类型:"); int a = sc.nextInt(); String str = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println(a+","+str); } }解决办法:
1)将中间间隔"回车"改为"空格"
2)若要继续用"回车"作为间隔
则将:Strinng str = sc.nextLine();改为String str = sc.next();
3)再创建一个键盘录入对象
自行测试
3)public boolean hasNextxxx();
返回的是一个布尔类型,当前扫描器是否含有下一个类型的标记
public xxx nextxxx();获取这个标记值
异常:InputMismatchException:输入的和数据类型不一致
public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // 先去接收int类型数据,在接受字符串类型 System.out.println("请输入一个数据:"); if (sc.hasNextInt()) { int a = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println(a); } else { System.out.println("对不起,数据类型错误"); } } }
C.String
1)概述
String 类代表字符串
2)特点
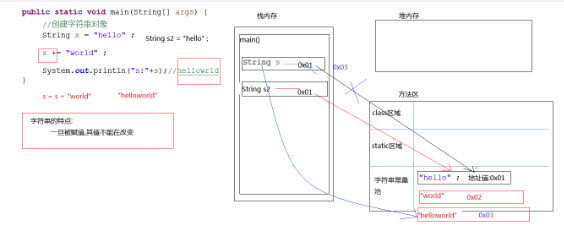
一旦被赋值,其值不能被改变
方法去:有一个内存区域:字符串常量池
如果我们创建一个字符串对象,给他赋值,这个值会在常量池找
有就返回,没有就开辟新的空间
有些同学说我确实改变了呀,,,,
只不过是在常量去重新开辟了一个地址,之前地址里的值并未被覆盖掉
3)常用构造方法
public String();无参构造
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = new String(); System.out.println(s);//空字符序列 System.out.println(s.length());// 0 } }public String(byte[] byte);将字节数组转换成字符串
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { byte[] b = { 97, 98, 99, 100, 101 };// 对应的ACSII码表 String s = new String(b); System.out.println(s);// abcde System.out.println(s.length());// 5 } }public String(byte[] byte, int offset, int length);将字符数组的一部分转换成字符串
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { byte[] b = { 97, 98, 99, 100, 101 };// 对应的ACSII码表 String s = new String(b, 1, 3); System.out.println(s);// bcd System.out.println(s.length());// 3 } }public String(char[] value);将字符数组转换成字符串
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { char[] c = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D' }; String s = new String(c); System.out.println(s);// abcdeABCD System.out.println(s.length());// 9 } }public String(char[] value, int offset, int count);将字符数组一部分转换成字符串
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { char[] c = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D' }; String s = new String(c, 5, 4); System.out.println(s);//ABCD System.out.println(s.length());// 4 } }public String(String original);将一个常量转换字符串,String是不可改变的,所以无需使用此方法
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = new String("hello"); System.out.println(s);// hello System.out.println(s.length());// 5 //也可以以下方法 String s1 = "hello"; System.out.println(s1); System.out.println(s1.length()); } }
4)数组中有没有length()? 字符串中有没有length()?
length:数组长度属性 -------数组中不存在这个方法
字符串中有length():返回字符串长度
5)面试题
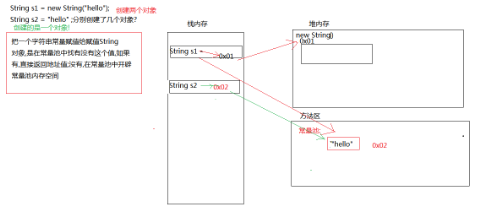
String s1 = new String("hello");创建了几个对象
String s2 = "hello";
s1创建了两个对象
s2创建了一个对象,直接指向常量池中的
6)equals和==的区别
==:默认比较的是地址值
equals:默认比较的是地址值,String类型底层已经重写了equals,比较的是内容是否相等
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = new String("hello"); String s2 = new String("hello"); System.out.println(s1 == s2);// false System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));// true String s3 = new String("hello"); String s4 = "hello"; System.out.println(s3 == s4);// false System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));// true String s5 = "hello"; String s6 = "hello"; System.out.println(s5 == s6);// true System.out.println(s5.equals(s6));// true } }看程序写结果
字符串变量相加,先开辟空间,再相加
字符串常量相加,先相加,然后在常量池中查找是否有这个值,有返回,没有开辟新空间
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "hello"; String s2 = "world"; String s3 = "helloworld"; System.out.println(s3 == s1 + s2);// false System.out.println(s3.equals((s1 + s2)));// true System.out.println(s3 == "hello" + "world");// true System.out.println(s3.equals("hello" + "world"));// true } }
7)常用的判断功能
boolean equals(Object obj);将此字符串与指定的对象比较
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "helloworld"; String s2 = "helloworld"; String s3 = "helloWorld"; System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));// true System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));// false } }boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str);将此字符串和另一个字符串进行比较,忽略大小写
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "helloworld"; String s2 = "helloworld"; String s3 = "helloWorld"; System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2));// true System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3));// true } }boolean contains(String str);判断此字符串中是否包含str这个子字符串
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "helloworld"; String s2 = "helloworld"; String s3 = "helloWorld"; System.out.println(s2.contains("hello"));// true } }boolean startsWith(String str);判断是否以str子字符串开头
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "helloworld"; String s2 = "helloworld"; String s3 = "helloWorld"; System.out.println(s2.startsWith("h"));// true } }boolean endsWith(String str);判断是否以str字符串结尾
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "helloworld"; String s2 = "helloworld"; String s3 = "helloWorld"; System.out.println(s2.endsWith("d"));// true } }boolean isEmpoty();判断字符串是否为空
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "helloworld"; String s2 = "helloworld"; String s3 = "helloWorld"; System.out.println(s1.isEmpty());// false } }注意:
String s = " ";表示s字符串是空字符串
String s = null;空对象,连对象都没有
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = " "; System.out.println(s1.isEmpty());// false String s2 = null;// 空指针异常 // 非空判断 if (s2 != null) { System.out.println(s2.isEmpty()); } } }
8)获取功能
int length();获取字符串长度
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "helloworld"; System.out.println(s.length());// 10 } }char charAt(int index);返回指定索引处的字符(重点)
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "helloworld"; System.out.println(s.charAt(1));// e } }int indexOf(int ch);返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现的索引(重点)
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "helloworld"; System.out.println(s.indexOf('l'));// 2 System.out.println(s.indexOf('f'));// -1 没找到 } }int indexOf(String str);返回指定字符串在此字符串第一次出现的索引
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "helloworld"; System.out.println(s.indexOf("owo"));// 4 } }int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex);返回此字符中从指定位置开始后第一次出现的索引
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "helloworld"; System.out.println(s.indexOf('o', 5));// 6 } }in substring(int start);截取,从指定位置开始截取,默认截取到结尾,包含start
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "helloworld"; System.out.println(s.substring(5));// world } }int substring(int start, int end);从指定位置开始截取到指定位置结束:包左(start这个索引),不包右
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "helloworld"; System.out.println(s.substring(5, 8));// wor } }
9)转换功能(重点)
byte[] getBytes;讲一个字符串转换成字节数组
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "javeSE"; byte[] b = s.getBytes(); for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) { System.out.print(b[i]+" ");// ASCII码表转换 106 97 118 101 83 69 } } }char[] toCharArray();讲一个字符串数组转换成字符数组(重点)
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "javeSE"; char[] c = s.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) { System.out.print(c[i]);// javeSE } } }static String valueOf(char[] chs);将字符数组转换成字符串
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { char[] c = { 'j', 'a', 's', 'e', 'S', 'E' }; String s = String.valueOf(c); System.out.println(s);// javaSE } }static String valueOf(int i);将int类型的数据转换成字符串
ValueOf可以将任何数据类型转换成字符串
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 100; String s = String.valueOf(i); System.out.println(s);// 100 } }String toLowerCase();将字符串转换成小写
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "JavaSE"; String s1 = s.toLowerCase(); System.out.println(s1);// javase } }String toUpperCase();将字符串转换成大写
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "JavaSE"; String s1 = s.toUpperCase(); System.out.println(s1);// JAVASE } }String concat(String str);字符串拼接功能
// 测试类 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "hello"; String s2 = "world"; String s3 = s1 + s2; String s4 = s1.concat(s2); System.out.println(s3);// helloworld System.out.println(s4);// helloworld } }
最后
以上就是殷勤枕头最近收集整理的关于【JavaSE学习笔记】常用类介绍_01_Object,Scanner,String的全部内容,更多相关【JavaSE学习笔记】常用类介绍_01_Object内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复