首先看一下 DispatcherServlet 的继承关系图
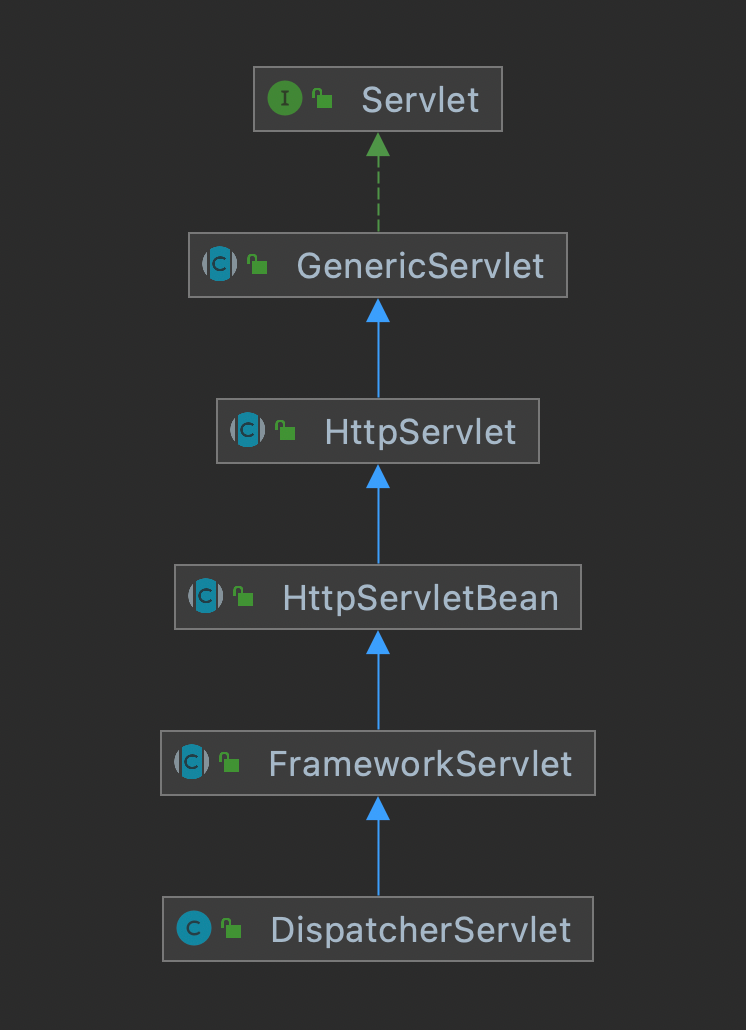
可以看出 DispatcherServlet 本质上就是一个 Servlet,那么它就应当具备 Servlet 的特征。
1、在 web.xml 中配置 DispatcherServlet
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springMVC</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springMVC.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springMVC</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
当<servlet></servlet>标签中配置有load-on-startup属性时,如果属性值大于等于 0 时,servlet会在启动的时候就初始化。如果未配置或者属性值小于0,servlet 则会在有请求的时候才会初始化。
2、复习Servlet 接口
在 Servlet 接口中定义了 5 个方法,其中有 3 个方法都由 Servlet 容器来调用,容器会在 Servlet 的生命周期的不同阶段调用特定的方法:
-
init(ServletConfig config)方法:该方法负责初始化 Servlet 对象,容器在创建好 Servlet 对象后,就会调用该方法。 -
service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)方法:负责响应客户的请求,为客户提供相应服务。容器接收到客户端要求访问特定 Servlet 对象请求时,就会调用该 Servlet 对象的 service() 方法。 -
destory()方法:负责释放 Servlet 对象占用的资源。当 Servlet 对象结束生命周期时,容器会调用此方法。
剩下的两个方法用于获得 Servlet 的配置信息以及其他相关信息。 -
getServletConfig():返回一个 ServletConfig 对象,该对象中包含了 Servlet 的初始化参数信息。 -
getServletInfo():返回一个字符串,该字符串中包含了 Servlet 的创建者、版本和授权等信息。
3、初始化操作方法调用关系图
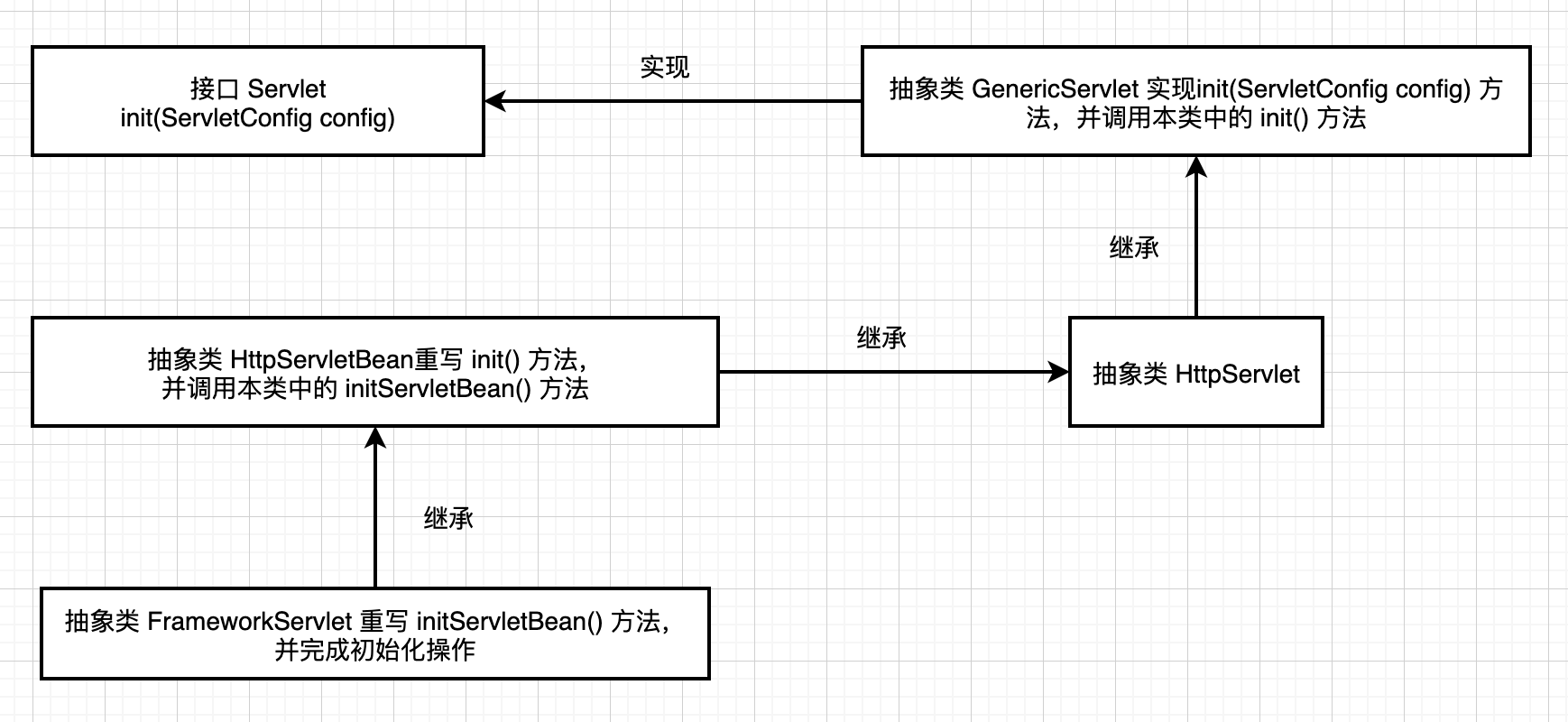
4、源码分析
1)接口 Servlet
package javax.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
public interface Servlet {
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException;
}
2)GenericServlet
public abstract class GenericServlet
implements Servlet, ServletConfig, java.io.Serializable {
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
this.config = config;
this.init();
}
public void init() throws ServletException {
}
}
3)HttpServletBean
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware {
private static class ServletConfigPropertyValues extends MutablePropertyValues {
public ServletConfigPropertyValues(ServletConfig config, Set<String> requiredProperties)
throws ServletException {
Set<String> missingProps = (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(requiredProperties) ?
new HashSet<>(requiredProperties) : null);
Enumeration<String> paramNames = config.getInitParameterNames(); // 获取web.xml中的初始化参数名
while (paramNames.hasMoreElements()) { // 遍历
String property = paramNames.nextElement();
Object value = config.getInitParameter(property); // 获取初始化参数值
addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(property, value));
if (missingProps != null) {
missingProps.remove(property);
}
}
// Fail if we are still missing properties.
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(missingProps)) {
throw new ServletException(
"Initialization from ServletConfig for servlet '" + config.getServletName() +
"' failed; the following required properties were missing: " +
StringUtils.collectionToDelimitedString(missingProps, ", "));
}
}
}
/**
* 将配置参数映射到此servlet的bean属性上,并调用子类初始化。
*/
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// 获取 web.xml 中 init-param 标签中的参数信息,
// 将其封装到set集合中
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
}
protected void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
}
}
分析:
HttpServletBean 主要做了三件事
- 获取 web.xml 文件中 init-param 中配置的参数信息,并将参数信息封装进一个 set 集合
- 创建 BeanWrapper 对象 bw(即 DispatcherServlet),将该参数信息设置到 bw中
通过断点分析可以看出,BeanWrapper本质上就是DispatcherServlet
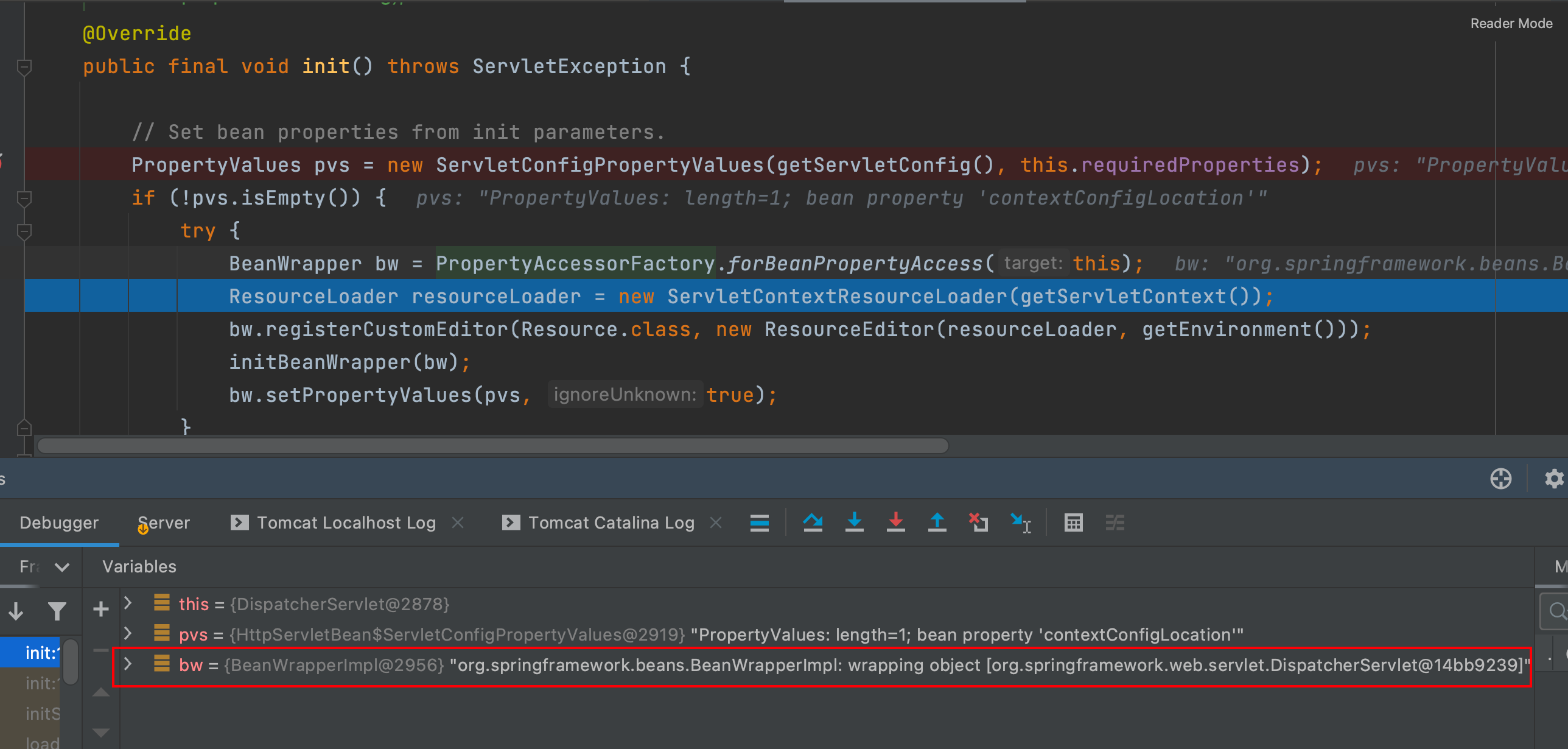
- 调用子类的initServletBean()
4)FrameworkServlet
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
// HttpServletBean 的重写方法,会在 bean 属性设置完成后调用。
// 同时该方法将会创建当前 servlet 的 WebApplicationContext
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 创建当前 servlet 的 WebApplicationContext
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
//在构建时注入了一个上下文实例
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { // 如果 wac 为 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 的一个实例,执行以下逻辑
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// 当上下文实例没有明确父级的情况时,将根应用程序上下文作为父级
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
// 刷新WebApplicationContext的内容信息
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// 调用 createWebApplicationContext 方法,创建 WebApplicationContext 实例
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
// 调用子类的 onrefresh 方法
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
// 创建 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 实例
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
// 设置环境
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
// 设置父级
wac.setParent(parent);
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
// 设置上下文配置
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
// 刷新容器 ApplicationContext
// 该方法中会调用 wac.refresh();
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// 设置容器id值
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// 默认的容器id
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
// 调用抽象类AbstractApplicationContext的 refresh() 方法,刷新容器
// refresh() 方法的作用:如果容器不存在,则创建容器,
// 如果已存在容器,则将旧容器销毁,重新创建容器,类似于容器的重启
wac.refresh();
}
}
分析
initServletBean 方法主要做了一件事,就是创建容器,即applicationContext,并未容器设置一些基本的信息,如容器id,环境,父级容器等。重点是AbstractApplicationContext类中的 refresh() 方法,该方法主要作用就是:如果容器不存在,则创建容器,如果已存在容器,则将旧容器销毁,重新创建容器,类似于容器的重启。
5)AbstractApplicationContext
AbstractApplicationContext 是一个抽象类,它实现了ConfigurableApplicationContext接口中的 refresh() 方法
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// 为刷新当前容器做准备
prepareRefresh();
// 告诉子类刷新内部bean工厂
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 准备bean工厂,以便在此上下文中使用
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 允许在上下文子类中对bean工厂进行后处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// 调用上下文中注册为bean的工厂处理器
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册拦截bean创建的bean处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// 初始化此上下文的消息源
initMessageSource();
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 初始化特定上下文子类中的其他特殊 bean
onRefresh();
// 检查侦听器bean并注册它们
registerListeners();
// 实例化所有剩余的(非惰性初始化)单例
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 最后一步:发布相应的事件
// 调用 DispatcherServlet 中的 onrefresh() 方法
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// 销毁已经创建的单例,以避免挂起资源。
destroyBeans();
// 重置“活跃”标识
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
}
6)DispatcherServlet
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context); // 初始化文件上传解析器
initLocaleResolver(context); // 初始化国际化解析器
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context); // 初始化处理器映射器
initHandlerAdapters(context); // 初始化处理器适配器
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); // 初始化处理器异常解析器
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context); // 初始化视图解析器
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
至此整个初始化过程结束
最后
以上就是天真火车最近收集整理的关于SpringMVC 中 DispatcherServlet 初始化过程源码解析的全部内容,更多相关SpringMVC内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。






![[翻译].NET framework 4.0并行编程:入门](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg8.png)

发表评论 取消回复