Spring的web MVC框架与其他许多web MVC框架一样,是由请求驱动的,围绕一个中央Servlet设计,它将请求分派给控制器,并提供其他功能促进web应用程序的开发。然而,Spring的DispatcherServlet却做得更多,不仅仅是这一点它与Spring IoC容器完全集成,因此允许您使用它spring的其他特征。
介绍了Spring Web MVC DispatcherServlet的请求处理工作流如下图。可以认识到DispatcherServlet是一个“前端控制器”。
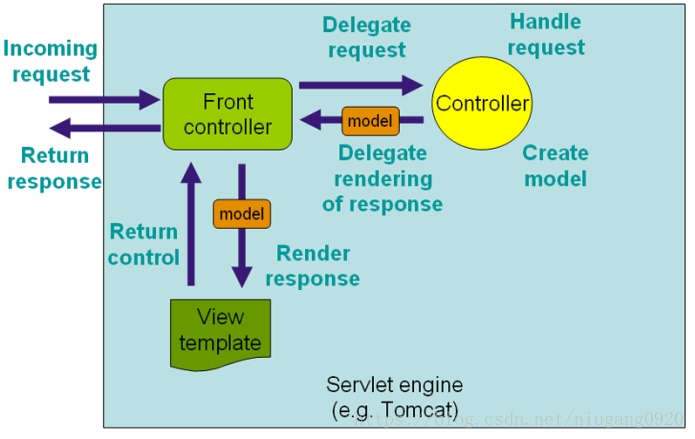
官方图解
DispatcherServlet是一个实际的Servlet(它从HttpServlet基类继承),正如在web应用程序中声明的那样。您需要映射您想要的请求。DispatcherServlet处理,通过使用URL映射。这是一个标准的Java EE Servlet。Servlet 3.0+环境中的配置如下:
public class MyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext container) {
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = container.addServlet("example", new
DispatcherServlet());
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping("/example/*");
}
}WebApplicationInitializer 介绍
在Servlet 3.0+环境中实现的接口,以便以编程方式配置ServletContext——而不是(或可能与)传统web相结合基于xml的方法。
基于xml的配置:
构建web应用程序的大多数Spring用户都需要注册Spring的DispatcherServlet
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/dispatcher-config.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>编程式配置:
基于代码的方法与WebApplicationInitializer这里是等效的DispatcherServlet注册逻辑
public class MyWebAppInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext container) {
XmlWebApplicationContext appContext = new XmlWebApplicationContext();
appContext.setConfigLocation("/WEB-INF/spring/dispatcher-config.xml");
ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher =
container.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(appContext));
dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(1);
dispatcher.addMapping("/");
}
}100%基于代码的配置方法
在上面的例子中,WEB-INF /web.xml成功地以WebApplicationInitializer的形式替换了代码,但是实际的dispatcher-config.xml Spring配置仍然是基于xml的。WebApplicationInitializer是一个非常适合使用Spring的基于代码的@Configuration类。下面的示例演示了重构,以使用Spring的AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext代替XmlWebApplicationContext,以及用户定义的@Configuration类AppConfig和DispatcherConfig,而不是Spring XML文件。这个示例也超出了上面的部分,以演示“根”应用程序上下文的典型配置和ContextLoaderListener的注册
public class MyWebAppInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext container) {
// Create the 'root' Spring application context 创建根上下文
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext rootContext =
new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
rootContext.register(AppConfig.class);
// Manage the lifecycle of the root application context
container.addListener(new ContextLoaderListener(rootContext));
// Create the dispatcher servlet's Spring application context
//创建DispatcherServlet上下文,即web上下文
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext dispatcherContext =
new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
dispatcherContext.register(DispatcherConfig.class);
// Register and map the dispatcher servlet
//注册映射
ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher =
container.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(dispatcherContext));
dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(1);
dispatcher.addMapping("/");
}
}WebApplicationInitializer是由Spring MVC提供的一个接口。基于代码的配置被检测到并自动用于初始化任何Servlet3.0容器。这个接口的一个抽象基类实现命名。AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer使得注册更容易。通过简单地指定它的servlet映射和列出配置类,DispatcherServlet甚至是设置Spring MVC应用程序的推荐方法,建议配置如下。
public class GolfingWebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
// GolfingAppConfig defines beans that would be in root-context.xml
//配置root
return new Class[] { GolfingAppConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
// GolfingWebConfig defines beans that would be in golfing-servlet.xml
//配置web
return new Class[] { GolfingWebConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/golfing/*" };
}
}
Spring的ApplicationContext实例可以作用域范围。在Web MVC框架中,每个DispatcherServlet都有自己的WebApplicationContext,它继承了在根WebApplicationContext中定义的所有bean。根WebApplicationContext应该包含应该在其他上下文和Servlet实例之间共享的所有基础结构bean。这些继承的bean可以在Servlet特定的范围内被覆盖,并且您可以在给定的Servlet实例中定义新的特定于范围的bean。
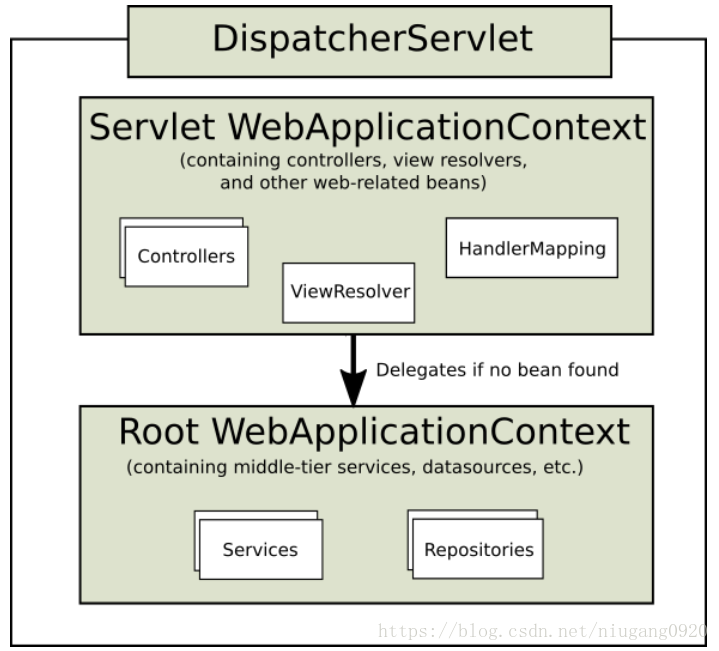
从上图可以看到Servlet WebApplicationContext 主要是配置web相关的,如controller 、视图解析器、处理器映射。Root WebApplicationContext主要是来配置service和repsoitories.这就是我们常用的分开配置.
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:root-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!--默认路径实在WEB-INF下放着,默认命名为servletName-servlet.xml-->
<param-value>
classpath*:dispatcher-servlet.xml
</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>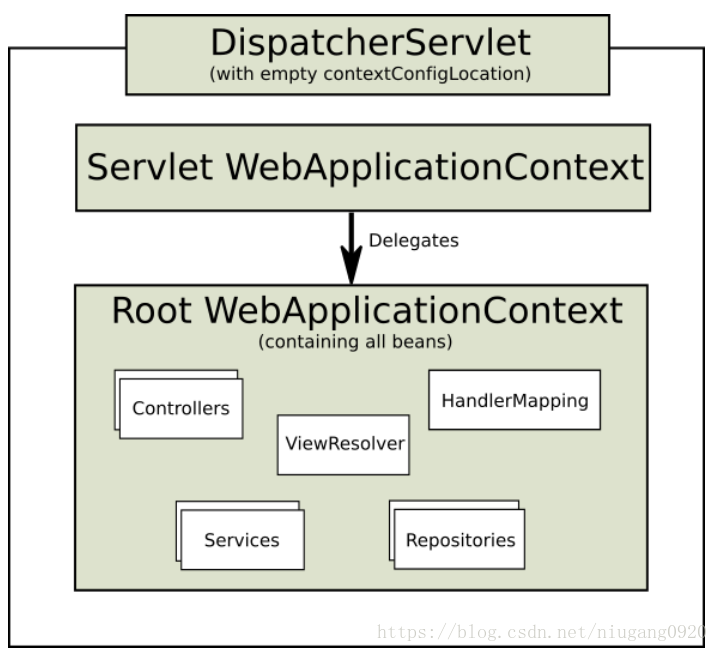
上图这种是Root WebApplicationContext承担了所有的配置
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
微信公众号:

JAVA程序猿成长之路
分享资源,记录程序猿成长点滴。专注于Java,Spring,SpringBoot,SpringCloud,分布式,微服务。
最后
以上就是专一背包最近收集整理的关于1.Spring4.3官方文档整理之DispatcherServlet的全部内容,更多相关1内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复