SpringBoot入门
学尚硅谷springboot2做的笔记
简介
Spring Boot 是用来简化 Spring 的搭建和开发过程的全新框架。Spring Boot 去除了大量的 xml 配置文件,简化了复杂的依赖管理,配合各种 starter 使用,基本上可以做到自动化配置。Spring 可以做的事情,现在用 Spring boot 都可以做。
SpringBoot所具备的特征有:
1)可以创建独立的Spring应用程序,并且基于其Maven或Gradle插件,可以创建可执行的JARs和WARs;
2)内嵌Tomcat或Jetty等Servlet容器;
3)提供自动配置的“starter”项目对象模型(POMS)以简化Maven配置;
4)尽可能自动配置Spring容器;
5)提供准备好的特性,如指标、健康检查和外部化配置;
6)绝对没有代码生成,不需要XML配置。
spring真的是配置地狱,光个SSM整合就要配半天.
springBoot贯彻一个思想:约定大于配置
第一个程序
本机环境:
- java 12
- maven 3.8.1
- idea 2021.3.1
创建Maven 配置如下
<!-- 继承spring-boot-starter-parent 便于统一版本号-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.4</version>
</parent>
<!-- 我用的jdk是12,就默认设置为12-->
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>12</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>12</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- 导入web模块依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
创建springBoot主程序
/*
* 主程序类
*@SpringBootApplication注解用来标识这是一个springBoot应用
* */
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainSpringBoot {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainSpringBoot.class,args);
}
}想要改变扫描路径,可以加上@SpringBootApplication注解加上scanBasePackages属性
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages="com.HeShiJia")//通过scanBasePackages可以改变包扫描路径编写控制层
//复合注解相当于@ResponseBody+@Controller
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String HelloTest(){
return "Hello SpringBoot";
}
}测试
直接运行springBoot主程序的main方法
然后打开浏览器,进入 http://localhost:8080/hello
SpringBoot特性
1.简化配置
只需在resources创建application.properties文件(固定写法)
几乎所有配置都可以在这个文件里配置
具体参考官方文档: Common Application Properties
例:将端口默认8080修改为8888
#修改端口号
server.port=8888 2.简化部署
在pom.xml中添加:
<!-- 创建可执行 Jar-->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>然后使用idea的maven插件打成jar包到target文件夹下
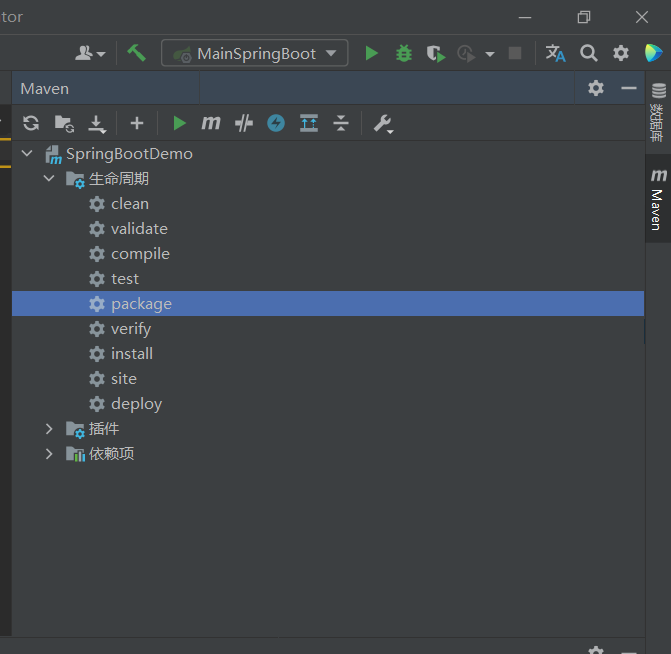
cmd执行测试,效果同springBoot主程序的main方法
容器功能
1.组件添加
@Configuration() 配置类注解
默认proxyBeanMethods属性为ture 保证是单实例的
/*
proxyBeanMethods:代理bean的方法
Full(proxyBeanMethods = true)、【保证每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是单实例的】
Lite(proxyBeanMethods = false)【每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是新创建的】
组件依赖必须使用Full模式默认。其他默认是否Lite模式
因为 Full模式启动容器时要检查,性能: Full< Lite
*/
//@Import({department.class,employee.class}) 给容器中自动创建出这两个类型的组件、默认组件的名字就是全类名
//@ConditionalOnBean(name ="tom") 只有容器中存在名字为tom的bean时才会创建 beanConfig 中的组件
//@ImportResource("classpath:springBean.xml") 可以导入原生的springXML文件,获取其中的组件
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)//告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类
public class beanConfig {
@Bean
public employee getEmployee(){
return new employee();
}
@Bean
public department getDepartment(){
return new department();
}
}@Import()注解
配合@Configuration使用,可以创建类型组件,默认组件名为全类名
@Import({department.class,employee.class}) //给容器中自动创建出这两个类型的组件、默认组件的名字就是全类名@Conditional注解
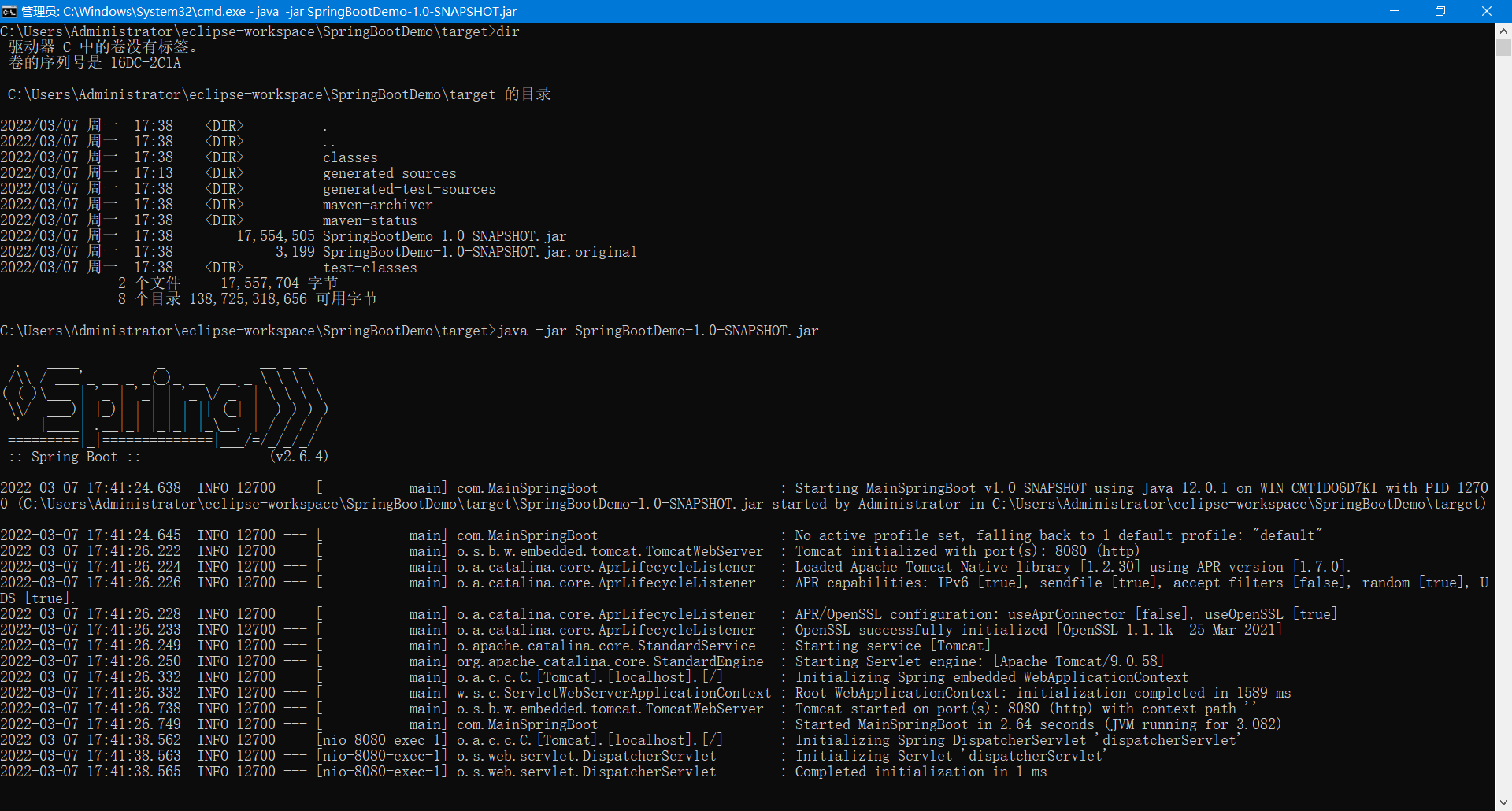
条件装配:满足Conditional指定的条件,则进行组件注入
Conditional其他注解
@ConditionalOnBean(name = "cat")
//如果没有名为cat的组件,那这个类的@Bean不会进入组件注入
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class MyConfig {
}2.原生配置文件引入
@ImportResource()
可以引入原生spring配置文件
@ImportResource("classpath:springBean.xml") // 可以导入原生的springXML文件,获取其中的组件3.配置绑定
使用Java读取到properties文件中的内容,并且把它封装到JavaBean中,随时使用,跟@Value差不多
@Component //用配置绑定一定要将其添加到ioc,不然识别不到
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "dep")
public class department {
private Integer d_id;
private String d_name;
public department(Integer d_id, String d_name) {
this.d_id = d_id;
this.d_name = d_name;
}
public department() {
}
public Integer getD_id() {
return d_id;
}
public void setD_id(Integer d_id) {
this.d_id = d_id;
}
public String getD_name() {
return d_name;
}
public void setD_name(String d_name) {
this.d_name = d_name;
}
}
application.properties
dep.d_id=1
dep.d_name=GLBSpringBoot 核心功能
配置文件
1.1 properties
properties的语法简单来说就是 key=value
1.2 yaml
简介
YAML 是 "YAML Ain't Markup Language"(YAML 不是一种标记语言)的递归缩写。
非常适合用来做以数据为中心的配置文件
语法示例
- key: value;kv之间有空格
- 大小写敏感
- 使用缩进表示层级关系
- 缩进不允许使用tab,只允许空格
- 缩进的空格数不重要,只要相同层级的元素左对齐即可
- '#'表示注释
- 字符串无需加引号,如果要加,''与""表示字符串内容 会被 转义/不转义
person:
Name: hsj #String
boss: true #Boolean
birth: 2020/10/23 #Date
age: 21 #Integer
department: #对象 department
d_id: 1
d_name: 业务部
interests: [篮球,游泳] #数组
animal: [兔子,老虎] #List集合
score: #Map集合
math: 90
English: 60
salarys: [4500,13000,25000] #Set集合
alldep:
dep: [{d_id: 2,d_name: 管理部},{d_id: 3,d_name: 开发部}]@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String Name;
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Integer age;
private department department;
private String[] interests;
private List<String> animal;
private Map<String, Object> score;
private Set<Double> salarys;
private Map<String, List<department>> alldep;
}1.3 配置提示
加上这个依赖,让配置文件有提示。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>web开发
1)静态资源
1.1 静态资源的访问
只要将静态资源放在类路径下static文件夹下,可以直接通过http://localhost:8080/静态资源名 访问
资源前缀
spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/resources/** #给静态资源加上前缀改变默认资源路径
spring.web.resources.static-locations=[classpath:/img/] #改变资源存放路径 1.2 Webjar
WebJars - Web Libraries in Jars
这个网址将一些前端框架打成了jar包,引入依赖后,可以通过http://localhost:8080/webjar/jquery/3.5.1/jquery.js (后面地址要按照依赖里面的包路径) 来访问
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>1.3 欢迎页的访问
将index.html 放在静态资源路径下 默认http://localhost:8080/ 就是欢迎页
1.4 自定义 Favicon
将favicon.ico 放在静态资源路径下就行
1.5 项目前缀路径设置
server.servlet.context-path=/springboot2)请求处理
基本的springMvc注解就不讲述了
2.1 Rest风格的使用
Rest风格
- /user GET-用户
- /user POST-保存用户
- /user PUT-修改用户
- /user DELETE-删除用户
用法
表单设置method=post,表单控件 <input type="hidden" name="_method" value="delete">
SpringBoot配置文件手动开启Rest支持:
spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter.enabled=true2.2 矩阵变量使用
Springboot 默认不能用矩阵变量来传递参数,需要手动开启,在配置类加上:
// 开启矩阵变量
@Bean // WebConfigurer
public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer() {
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper();
urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false);
configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper);
}
};
}
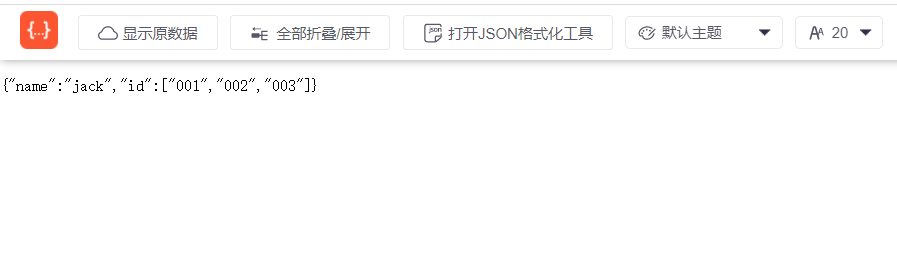
矩阵变量格式:
矩阵变量需要写在路径片段中,每个矩阵变量需要用分号隔开,如"/matrix/pathVariable;name=joe;id=01",多个值可以用逗号隔开,比如 “name=joe,jack,Lucy”
<a href="http://localhost:8080/matrix/path;name=jack;id=001,002,003">
matrixVariable演示
</a>控制器
// 测试矩阵变量
@GetMapping("/matrix/{path}")
public Map matrix(@MatrixVariable(value = "name") String name,@MatrixVariable(value = "id") String[] id){
HashMap<String, Object> HashMap = new HashMap<>();
HashMap.put("name",name);
HashMap.put("id",id);
return HashMap;
}页面返回
3)Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf是一个流行的模板引擎,该模板引擎采用Java语言开发.
Thymeleaf的主要目标在于提供一种可被浏览器正确显示的、格式良好的模板创建方式,因此也可以用作静态建模。你可以使用它创建经过验证的XML与HTML模板。
表达式
| 变量取值 | ${...} | 获取请求域、session域、对象等值 |
| 选择变量 | *{...} | 获取上下文对象值 |
| 消息 | #{...} | 获取国际化等值 |
| 链接 | @{...} | 生成链接 |
| 片段表达式 | ~{...} | jsp:include 作用,引入公共页面片段 |
| 行内表达式 | [[${...}]] | 跟el表达式类似,可以在行内获取请求域、session域、对象等值 |
thymeleaf依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>设置前缀后缀
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/view/ #前缀 默认是templates文件夹下
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html #后缀名称空间
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"页面抽取
抽取
th:fragment="片段名" 或 id="选择器"
table_Extract.html
<div th:fragment="hello">
<p>hello</p>
</div>引入
th:insert=“模板名::片段名” 或 th:insert=“模板名::选择器” 同下
th:replace=“模板名::片段名”
th:include=“模板名::片段名”
<div th:include="table_Extract :: hello"></div>4)自定义异常
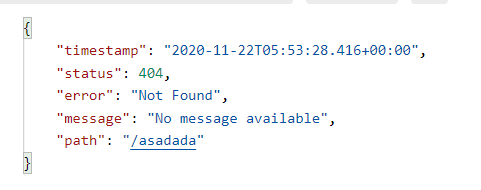
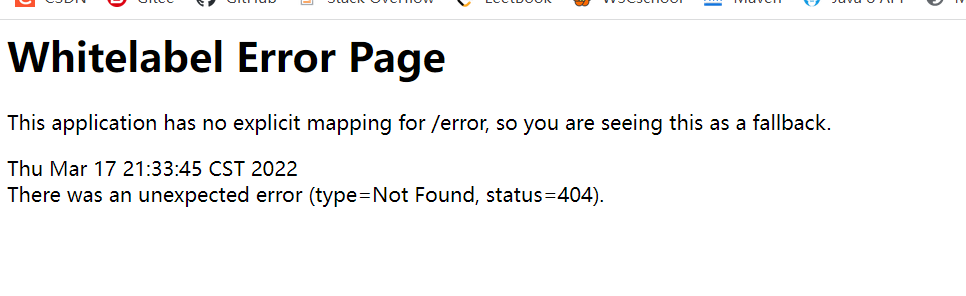
- 默认情况下,Spring Boot提供
/error处理所有错误的映射 - 对于机器客户端,它将生成JSON响应,其中包含错误,HTTP状态和异常消息的详细信息。对于浏览器客户端,响应一个“ whitelabel”错误视图,以HTML格式呈现相同的数据
自定义错误页
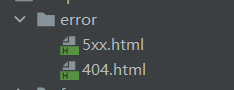
在目录
src/main/resources/templates/下创建一个叫error的文件夹,文件名设置为状态码
error/下的4xx,5xx页面会被自动解析
@ControllerAdvice+@ExceptionHandler处理全局异常
@ControllerAdvice //异常控制类
public class ErrorControllerZhujie {
@ExceptionHandler(value = {ArithmeticException.class}) //异常处理注解 value值的类型为Class数组
public String ExceptionHandler(Exception exception, Model model){ //通过Exception这个类来接收异常信息
model.addAttribute("ex",exception);
return "error";
}
}
5)原生组件注入
1.原生注解
主配置类扫描组件
@ServletComponentScan(value = "com.example.demo.servlet")原生注解Servlet
@WebServlet(value = {"/myServlet","/my"})
public class myServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("doGet方法");
resp.getWriter().write("hello Servlet");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("doPost方法");
}
}原生注解Filter
@WebFilter(urlPatterns = {"/css/*","/images/*"})
public class myFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("myFiler初始化");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("myFiler放行");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("myFiler销毁");
}
}原生注解Listener
@WebListener
public class myListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("监听器启动");
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("监听器销毁");
}
}2.spring方式注入
@Configuration
public class servletConfig {
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean(){
myServlet myServlet = new myServlet();
ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(myServlet,"/myServlet");
return servletRegistrationBean;
}
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean FilterRegistrationBean(){
myFilter myFilter = new myFilter();
FilterRegistrationBean<Filter> filterFilterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>();
filterFilterRegistrationBean.setFilter(myFilter);
filterFilterRegistrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/css/*","/images/*");
return filterFilterRegistrationBean;
}
@Bean
public ServletListenerRegistrationBean ServletListenerRegistrationBean(){
myListener myListener = new myListener();
ServletListenerRegistrationBean servletListenerRegistrationBean = new ServletListenerRegistrationBean(myListener);
return servletListenerRegistrationBean;
}
}
6)定制化
1.定制化的常见方式
-
修改配置文件
- 编写自定义的配置类 xxxConfiguration;+ @Bean替换、增加容器中默认组件
- Web应用 编写一个配置类实现 WebMvcConfigurer 即可定制化web功能;+ @Bean给容器中再扩展一些组件
@Configuration
//@EnableWebMvc 完全代理Mvc配置 慎用
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//添加拦截器
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/**")
.excludePathPatterns("/login","/","/css/**","/js/**","/images/**","/fonts/**");
}
}2.原理
场景starter - xxxxAutoConfiguration - 导入xxx组件 - 绑定xxxProperties -- 绑定配置文件项
数据访问
1)SQL
1.使用JDBC
导入依赖启动项
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>配置文件yaml
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_crud?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #可以不写,自动其实已经加载驱动了测试
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
Integer integer = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("SELECT count(*) FROM department_table", Integer.class);
System.out.println("共有"+integer+"条记录");
}
}
2.使用Druid数据源
中文文档
常见问题 · alibaba/druid Wiki · GitHub
导入启动项依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.17</version>
</dependency>配置文件yaml
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_crud?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
druid:
aop-patterns: com.example.demo.* #监控SpringBean
filters: stat,wall # 底层开启功能,stat(sql监控),wall(防火墙)
stat-view-servlet: # 配置监控页功能
enabled: true # 是否启用
login-password: root # 登录密码
login-username: root # 登录用户名
resetEnable: false # 是否启用重置按钮
web-stat-filter: # 对上面filters里面的stat的详细配置
enabled: true
url-pattern: /*
exclusions: '*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*'
filter:
stat:
slow-sql-millis: 1000 #毫秒
log-slow-sql: true
enabled: true
wall:
enabled: true
config:
drop-table-allow: false #不允许执行删除表的操作3、整合MyBatis
导入启动器依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4</version>
</dependency>配置文件配置
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_crud?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
mybatis:
# config-location: classpath:myBatisConfig.xml
# configuration:
# map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
# 可以不写全局;配置文件,所有全局配置文件的配置都放在configuration配置项中即可
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/**.xml #映射文件路径编写映射文件并在接口上添加@Mapper注解
@Mapper
public interface departmentMapper {
List<department> getDepList();
@Select("SELECT * FROM `department_table`WHERE dep_id=#{id}") //也可以不写映射文件直接用注解
department getDep(Integer id);
}
也可以不写@Mapper,在主配置类上加上@MapperScan注解扫描即可
4.整合 MyBatis-Plus
添加启动依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.1</version>
</dependency>Mapper继承 BaseMapper
public interface StuMapper extends BaseMapper<Stu> {
}单元测试
1.JUnit5 的变化
Spring Boot 2.2.0 版本开始引入 JUnit 5 作为单元测试默认库
作为最新版本的JUnit框架,JUnit5与之前版本的Junit框架有很大的不同。由三个不同子项目的几个不同模块组成。
JUnit 5 = JUnit Platform + JUnit Jupiter + JUnit Vintage
JUnit Platform: Junit Platform是在JVM上启动测试框架的基础,不仅支持Junit自制的测试引擎,其他测试引擎也都可以接入。
JUnit Jupiter: JUnit Jupiter提供了JUnit5的新的编程模型,是JUnit5新特性的核心。内部 包含了一个测试引擎,用于在Junit Platform上运行。
JUnit Vintage: 由于JUint已经发展多年,为了照顾老的项目,JUnit Vintage提供了兼容JUnit4.x,Junit3.x的测试引擎。
pringBoot 2.4 以上版本移除了默认对 Vintage 的依赖。如果需要兼容junit4需要自行引入(不能使用junit4的功能 @Test)
JUnit 5’s Vintage Engine Removed from spring-boot-starter-test,如果需要继续兼容junit4需要自行引入vintage
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.hamcrest</groupId>
<artifactId>hamcrest-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>2.JUnit5使用
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>@SpringBootTest
class Boot05WebAdminApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
}
- Junit类具有Spring的功能,@Autowired、比如 @Transactional 标注测试方法,测试完成后自动回滚
3.JUnit5 常用注解
JUnit 5 User Guide
- @Test :表示方法是测试方法。但是与JUnit4的@Test不同,他的职责非常单一不能声明任何属性,拓展的测试将会由Jupiter提供额外测试
- @ParameterizedTest :表示方法是参数化测试,下方会有详细介绍
- @RepeatedTest :表示方法可重复执行,下方会有详细介绍
- @DisplayName :为测试类或者测试方法设置展示名称
- @BeforeEach :表示在每个单元测试之前执行
- @AfterEach :表示在每个单元测试之后执行
- @BeforeAll :表示在所有单元测试之前执行
- @AfterAll :表示在所有单元测试之后执行
- @Tag :表示单元测试类别,类似于JUnit4中的@Categories
- @Disabled :表示测试类或测试方法不执行,类似于JUnit4中的@Ignore
- @Timeout :表示测试方法运行如果超过了指定时间将会返回错误
- @ExtendWith :为测试类或测试方法提供扩展类引用
@DisplayName("测试类")
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@BeforeAll
static void BeforeAll() {
System.out.println("前置ALL方法");
}
@BeforeEach
void Before() {
System.out.println("前置方法");
}
@DisplayName("测试方法1")
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println("测试1");
}
@AfterEach
void After() {
System.out.println("后缀方法");
}
@AfterAll
static void AfterALL() {
System.out.println("后缀ALL方法");
}
}
4.断言 assertions
断言(assertions)是测试方法中的核心部分,用来对测试需要满足的条件进行验证。这些断言方法都是 org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions 的静态方法。JUnit 5 内置的断言可以分成如下几个类别:检查业务逻辑返回的数据是否合理。
所有的测试运行结束以后,会有一个详细的测试报告;
简单断言
用来对单个值进行简单的验证。如:
| 方法 | 说明 |
| assertEquals | 判断两个对象或两个原始类型是否相等 |
| assertNotEquals | 判断两个对象或两个原始类型是否不相等 |
| assertSame | 判断两个对象引用是否指向同一个对象 |
| assertNotSame | 判断两个对象引用是否指向不同的对象 |
| assertTrue | 判断给定的布尔值是否为 true |
| assertFalse | 判断给定的布尔值是否为 false |
| assertNull | 判断给定的对象引用是否为 null |
| assertNotNull | 判断给定的对象引用是否不为 null |
| assertArrayEquals | 判断两个对象或原始类型的数组是否相等 |
@DisplayName("测试类")
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@DisplayName("断言测试")
@Test
void test01() {
Stu stu = new Stu();
Assertions.assertEquals(1,1,"数值不相等");
Assertions.assertSame( stu, stu,"不是同一对象");
Assertions.assertFalse(false,"不为false");
Assertions.assertNull(null,"不为空");
Assertions.assertArrayEquals(new int[]{1,2},new int[]{1,2},"数组不相等");
System.out.println("断言测试");
}
}
组合断言
assertAll 方法接受多个 org.junit.jupiter.api.Executable 函数式接口的实例作为要验证的断言,可以通过 lambda 表达式很容易的提供这些断言
@Test
@DisplayName("组合断言")
void test1() {
Assertions.assertAll(
()-> Assertions.assertArrayEquals(new Integer[]{1,2,3},new Integer[]{1,2,3},"数组不相等")
, ()-> Assertions.assertTrue(1>0));
}
超时和异常断言
在JUnit4时期,想要测试方法的异常情况时,需要用@Rule注解的ExpectedException变量还是比较麻烦的。而JUnit5提供了一种新的断言方式Assertions.assertThrows() ,配合函数式编程就可以进行使用。
Junit5提供了Assertions.assertTimeout() 为测试方法设置了超时时间
@Test
void test2() {
//扔出断言异常
Assertions.assertThrows(ArithmeticException.class,()-> System.out.println(10/0));
//如果测试方法时间超过3s将会异常
Assertions.assertTimeout(Duration.ofMillis(3000),()->Thread.sleep(1000));
}快速失败
通过 fail 方法直接使得测试失败
@Test
public void shouldFail() {
fail("马上失败");
}前置条件assumptions
JUnit 5 中的前置条件(assumptions【假设】)类似于断言,不同之处在于不满足的断言会使得测试方法失败,而不满足的前置条件只会使得测试方法的执行终止。前置条件可以看成是测试方法执行的前提,当该前提不满足时,就没有继续执行的必要。
@Test
@DisplayName("假设")
void test4() {
//如果不为true后面的输出语句不会执行
Assumptions.assumeTrue(1<0);
System.out.println("测试6");
}嵌套测试
JUnit 5 可以通过 Java 中的内部类和@Nested 注解实现嵌套测试,从而可以更好的把相关的测试方法组织在一起。在内部类中可以使用@BeforeEach 和@AfterEach 注解,而且嵌套的层次没有限制。
@DisplayName("测试类")
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Nested
@DisplayName("嵌套测试")
class nestedTest{
@BeforeEach
void nestedBefore(){
System.out.println("嵌套测试前缀");
}
@Test
void nestedTest1(){
System.out.println("嵌套测试1");
}
@AfterEach
void nestedAfter(){
System.out.println("嵌套测试后缀");
}
}
}
参数化测试
参数化测试是JUnit5很重要的一个新特性,它使得用不同的参数多次运行测试成为了可能,也为我们的单元测试带来许多便利。
利用@ValueSource等注解,指定入参,我们将可以使用不同的参数进行多次单元测试,而不需要每新增一个参数就新增一个单元测试,省去了很多冗余代码。
@ValueSource: 为参数化测试指定入参来源,支持八大基础类以及String类型,Class类型
@NullSource: 表示为参数化测试提供一个null的入参
@EnumSource: 表示为参数化测试提供一个枚举入参
@CsvFileSource:表示读取指定CSV文件内容作为参数化测试入参
@MethodSource:表示读取指定方法的返回值作为参数化测试入参(注意方法返回需要是一个流)
@ParameterizedTest
@DisplayName("参数化测试")
@ValueSource(ints={1,2,3,4})
void ParameterizedTest(Integer id) {
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println("参数化测试");
}多环境适配
1.Profile功能
为了方便多环境适配,springboot简化了profile功能。
application-profile功能
- 默认配置文件 application.yaml;任何时候都会加载
- 指定环境配置文件 application-{env}.yaml
- 激活指定环境
- 配置文件激活
1.命令行激活:java -jar xxx.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod --person.name=haha
2. 修改配置文件的任意值,命令行优先
- 默认配置与环境配置同时生效
- 同名配置项,profile配置优先
@Profile条件装配功能
@ConfigurationProperties("person")
@Data
@Component
@Profile("prod")
public class Staff implements Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
profile分组
#spring.profiles.active=test
spring.profiles.group.myprod[0]=prod
使用:--spring.profiles.active=myprod 激活
2.外部化配置
1、外部配置源
常用:Java属性文件、YAML文件、环境变量、命令行参数;
2、配置文件查找位置
(1) classpath 根路径
(2) classpath 根路径下config目录
(3) jar包当前目录
(4) jar包当前目录的config目录
(5) /config子目录的直接子目录
3、配置文件加载顺序:
- 当前jar包内部的application.properties和application.yml
- 当前jar包内部的application-{profile}.properties 和 application-{profile}.yml
- 引用的外部jar包的application.properties和application.yml
- 引用的外部jar包的application-{profile}.properties 和 application-{profile}.yml
4、指定环境优先,外部优先,后面的可以覆盖前面的同名配置项
最后
以上就是腼腆歌曲最近收集整理的关于SpringBoot笔记SpringBoot入门SpringBoot 核心功能的全部内容,更多相关SpringBoot笔记SpringBoot入门SpringBoot内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复