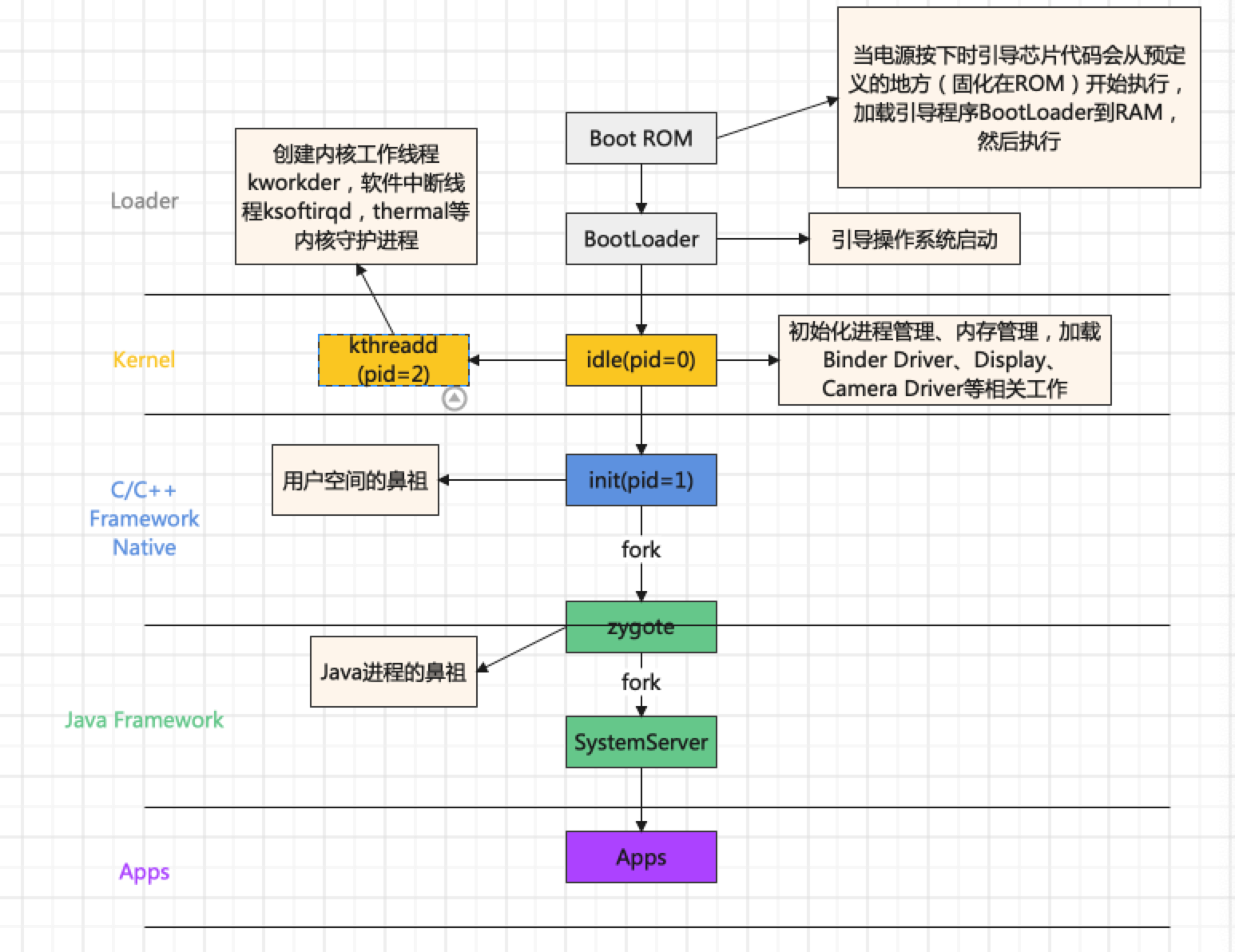
总流程:
第一步:加载引导程序BootLoader到RAM中,引导操作系统启动
第二步:有一个初始化idle进程,主要是初始化进程管理、内存管理等工作;还会创建threadd进程、init进程
第三步:init进程(用户空间的鼻祖)主要做的是:
第四步:从init进程中fork一个zygote进程(Java进程的鼻祖)
第五步:zygote进程fork一个systemserver进程
第六步:systemserver进程创建APP进程
init进程启动:
1、挂载文件
2、设置selinux -- 安全策略
3、开启属性服务,注册到epoll中
4、解析init.rc
5、循环处理脚本 -- 启动zygote
6、循环等待
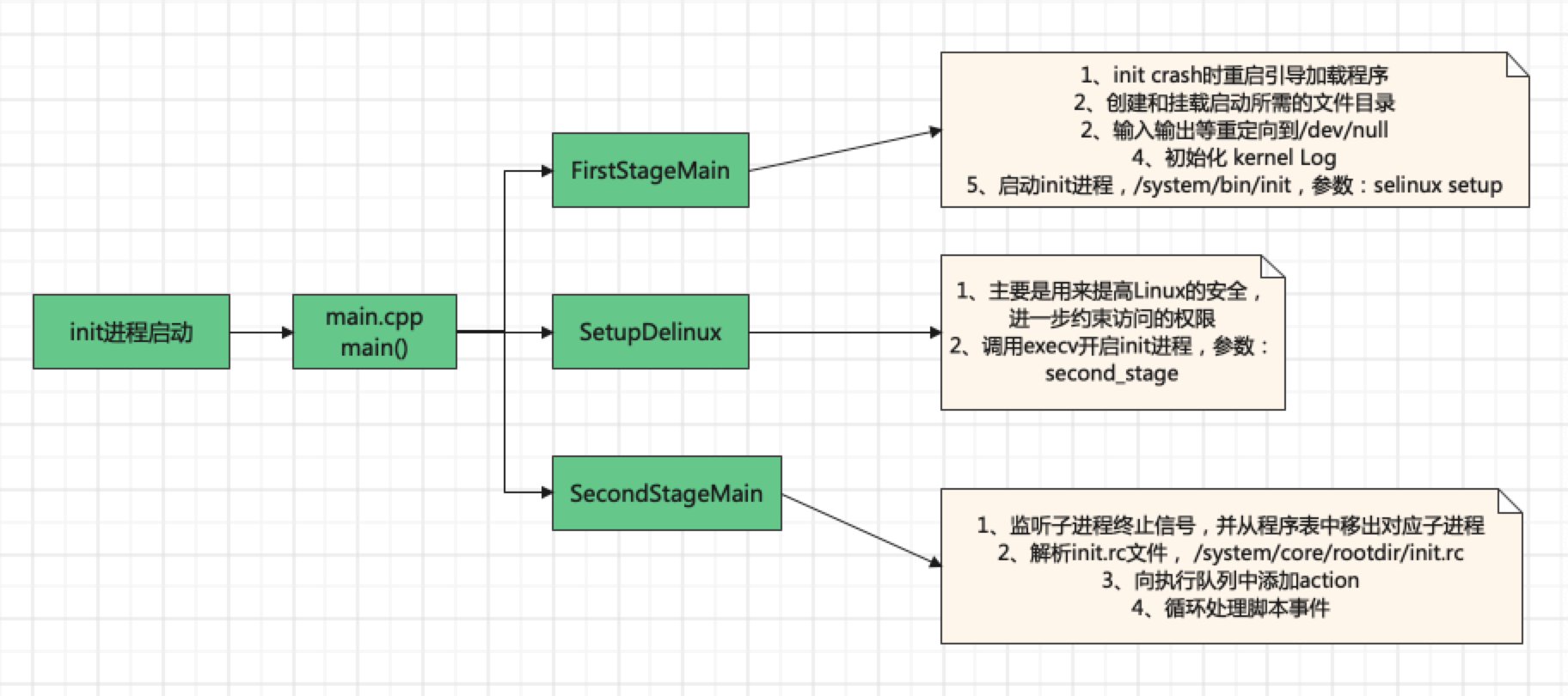
在system/core/init/main.cpp的main方法中循环调用这个main方法,顺序:FirstStageMain->SetupSelinux->SecondStageMain。以下都是kernel代码
FirstStageMain:
我们手机的system的bin目录下有一个init程序,这个地方就是入口
第一步:
根据路径kernel/common/init/main.c
static int __ref kernel_init(void *unused)
{
......
if (!try_to_run_init_process("/sbin/init") ||
!try_to_run_init_process("/etc/init") ||
// 找到了init
!try_to_run_init_process("/bin/init") ||
!try_to_run_init_process("/bin/sh"))
return 0;
}
static int try_to_run_init_process(const char *init_filename)
{
int ret;
// 这个处理/bin/init
ret = run_init_process(init_filename);
if (ret && ret != -ENOENT) {
pr_err("Starting init: %s exists but couldn't execute it (error %d)n",
init_filename, ret);
}
return ret;
}
static int run_init_process(const char *init_filename)
{
const char *const *p;
argv_init[0] = init_filename;
pr_info("Run %s as init processn", init_filename);
pr_debug(" with arguments:n");
for (p = argv_init; *p; p++)
pr_debug(" %sn", *p);
pr_debug(" with environment:n");
for (p = envp_init; *p; p++)
pr_debug(" %sn", *p);
// 执行init
return kernel_execve(init_filename, argv_init, envp_init);
}
//init的方法入口在哪?
//通过路径system/core/init/Android.bp文件找到:
srcs: ["main.cpp "],
//在system/core/init/main.cpp,这就是了
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
#if __has_feature(address_sanitizer)
__asan_set_error_report_callback(AsanReportCallback);
#endif
if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "ueventd")) {
return ueventd_main(argc, argv);
}
if (argc > 1) {
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "subcontext")) {
android::base::InitLogging(argv, &android::base::KernelLogger);
const BuiltinFunctionMap& function_map = GetBuiltinFunctionMap();
return SubcontextMain(argc, argv, &function_map);
}
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "selinux_setup")) {
return SetupSelinux(argv);
}
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "second_stage")) {
return SecondStageMain(argc, argv);
}
}
return FirstStageMain(argc, argv);
}
// 首先我们看FirstStageMain(argc, argv),第一阶段方法
// 路径在在system/core/init/first_stage_init.cpp
//这些CHECKCALL()方法就包含了:
/*1、文件挂载 也就是创建所需的文件
* 2、重定向 输入、输出
* 3、初始化内核的日志打印
* 4、启动selinux_setup --linux的安全策略
*/
int FirstStageMain(int argc, char** argv) {
if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) {
InstallRebootSignalHandlers();
}
boot_clock::time_point start_time = boot_clock::now();
std::vector<std::pair<std::string, int>> errors;
#define CHECKCALL(x)
if ((x) != 0) errors.emplace_back(#x " failed", errno);
// Clear the umask.
umask(0);
CHECKCALL(clearenv());
CHECKCALL(setenv("PATH", _PATH_DEFPATH, 1));
// Get the basic filesystem setup we need put together in the initramdisk
// on / and then we'll let the rc file figure out the rest.
CHECKCALL(mount("tmpfs", "/dev", "tmpfs", MS_NOSUID, "mode=0755"));
CHECKCALL(mkdir("/dev/pts", 0755));
CHECKCALL(mkdir("/dev/socket", 0755));
CHECKCALL(mount("devpts", "/dev/pts", "devpts", 0, NULL));
#define MAKE_STR(x) __STRING(x)
CHECKCALL(mount("proc", "/proc", "proc", 0, "hidepid=2,gid=" MAKE_STR(AID_READPROC)));
#undef MAKE_STR
// Don't expose the raw commandline to unprivileged processes.
CHECKCALL(chmod("/proc/cmdline", 0440));
std::string cmdline;
android::base::ReadFileToString("/proc/cmdline", &cmdline);
gid_t groups[] = {AID_READPROC};
CHECKCALL(setgroups(arraysize(groups), groups));
CHECKCALL(mount("sysfs", "/sys", "sysfs", 0, NULL));
CHECKCALL(mount("selinuxfs", "/sys/fs/selinux", "selinuxfs", 0, NULL));
CHECKCALL(mknod("/dev/kmsg", S_IFCHR | 0600, makedev(1, 11)));
......
}SetupSelinux:
int SetupSelinux(char** argv) {
SetStdioToDevNull(argv);
InitKernelLogging(argv);
if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) {
InstallRebootSignalHandlers();
}
boot_clock::time_point start_time = boot_clock::now();
MountMissingSystemPartitions();
// Set up SELinux, loading the SELinux policy.
SelinuxSetupKernelLogging();
SelinuxInitialize();
// We're in the kernel domain and want to transition to the init domain. File systems that
// store SELabels in their xattrs, such as ext4 do not need an explicit restorecon here,
// but other file systems do. In particular, this is needed for ramdisks such as the
// recovery image for A/B devices.
if (selinux_android_restorecon("/system/bin/init", 0) == -1) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "restorecon failed of /system/bin/init failed";
}
setenv(kEnvSelinuxStartedAt, std::to_string(start_time.time_since_epoch().count()).c_str(), 1);
const char* path = "/system/bin/init";
const char* args[] = {path, "second_stage", nullptr};
execv(path, const_cast<char**>(args));
// execv() only returns if an error happened, in which case we
// panic and never return from this function.
PLOG(FATAL) << "execv("" << path << "") failed";
return 1;
}SecondStageMain:
int SecondStageMain(int argc, char** argv) {
if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) {
InstallRebootSignalHandlers();
}
boot_clock::time_point start_time = boot_clock::now();
trigger_shutdown = [](const std::string& command) { shutdown_state.TriggerShutdown(command); };
SetStdioToDevNull(argv);
InitKernelLogging(argv);
LOG(INFO) << "init second stage started!";
....
// 初始化属性域
PropertyInit();
...
// 为第二阶段设置SELinux
// Now set up SELinux for second stage.
SelinuxSetupKernelLogging();
SelabelInitialize();
SelinuxRestoreContext();
Epoll epoll;
if (auto result = epoll.Open(); !result.ok()) {
PLOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
// 处理子进程终止信号 -- 僵尸进程
InstallSignalFdHandler(&epoll);
InstallInitNotifier(&epoll);
StartPropertyService(&property_fd);
...
// 匹配命令和函数之间的关系
const BuiltinFunctionMap& function_map = GetBuiltinFunctionMap();
...
//解析init.rc
LoadBootScripts(am, sm);
}
static void LoadBootScripts(ActionManager& action_manager, ServiceList& service_list) {
Parser parser = CreateParser(action_manager, service_list);
std::string bootscript = GetProperty("ro.boot.init_rc", "");
if (bootscript.empty()) {
// 获取Parser解析器后,解析init.rc
parser.ParseConfig("/system/etc/init/hw/init.rc");
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/system/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/system/etc/init");
}
// late_import is available only in Q and earlier release. As we don't
// have system_ext in those versions, skip late_import for system_ext.
parser.ParseConfig("/system_ext/etc/init");
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/product/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/product/etc/init");
}
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/odm/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/odm/etc/init");
}
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/vendor/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/vendor/etc/init");
}
} else {
parser.ParseConfig(bootscript);
}
...
while (true) {
// By default, sleep until something happens.
auto epoll_timeout = std::optional<std::chrono::milliseconds>{};
auto shutdown_command = shutdown_state.CheckShutdown();
...
//循环等待
auto pending_functions = epoll.Wait(epoll_timeout);
...
}
}解析init.rc
//如果是文件夹就ParseConfigDir(path)
bool Parser::ParseConfig(const std::string& path) {
if (is_dir(path.c_str())) {
return ParseConfigDir(path);
}
return ParseConfigFile(path);
}
//在文件夹中循环解析文件
bool Parser::ParseConfigDir(const std::string& path) {
LOG(INFO) << "Parsing directory " << path << "...";
std::unique_ptr<DIR, decltype(&closedir)> config_dir(opendir(path.c_str()), closedir);
if (!config_dir) {
PLOG(INFO) << "Could not import directory '" << path << "'";
return false;
}
dirent* current_file;
std::vector<std::string> files;
while ((current_file = readdir(config_dir.get()))) {
// Ignore directories and only process regular files.
if (current_file->d_type == DT_REG) {
std::string current_path =
android::base::StringPrintf("%s/%s", path.c_str(), current_file->d_name);
files.emplace_back(current_path);
}
}
// Sort first so we load files in a consistent order (bug 31996208)
std::sort(files.begin(), files.end());
for (const auto& file : files) {
//在文件夹中解析文件
if (!ParseConfigFile(file)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "could not import file '" << file << "'";
}
}
return true;
}
//解析文件
bool Parser::ParseConfigFile(const std::string& path) {
LOG(INFO) << "Parsing file " << path << "...";
android::base::Timer t;
auto config_contents = ReadFile(path);
if (!config_contents.ok()) {
LOG(INFO) << "Unable to read config file '" << path << "': " << config_contents.error();
return false;
}
//解析数据
ParseData(path, &config_contents.value());
LOG(VERBOSE) << "(Parsing " << path << " took " << t << ".)";
return true;
}
// 解析数据
void Parser::ParseData(const std::string& filename, std::string* data) {
data->push_back('n'); // TODO: fix tokenizer
data->push_back('�');
....
}zygote进程启动:
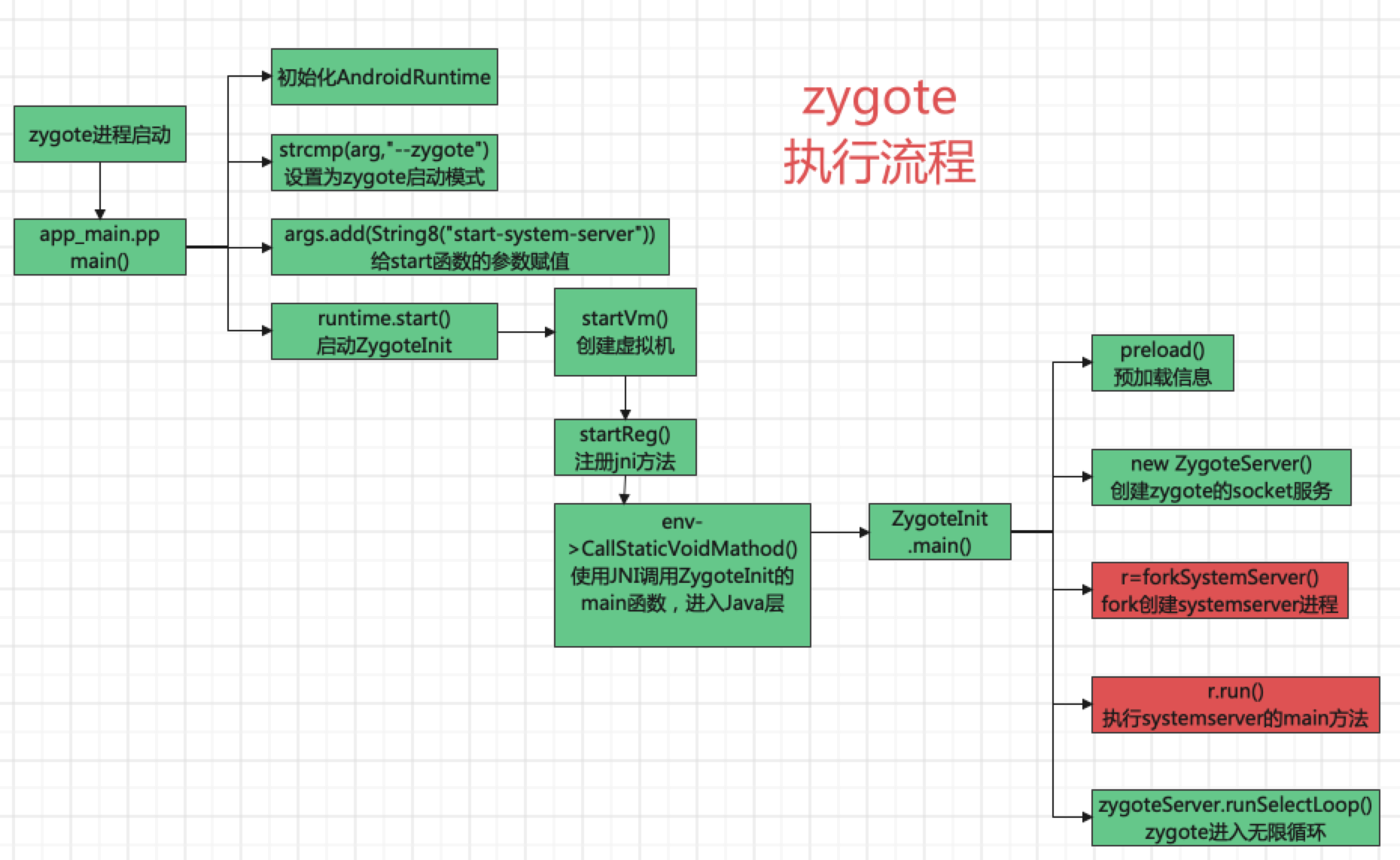
native层:
1、初始化运行环境,创建JVM
2、注册jni
3、调用zygoteInit.main
java层:
1、预加载 -- 加快进程启动
2、创建socket,等待通知
3、循环等待
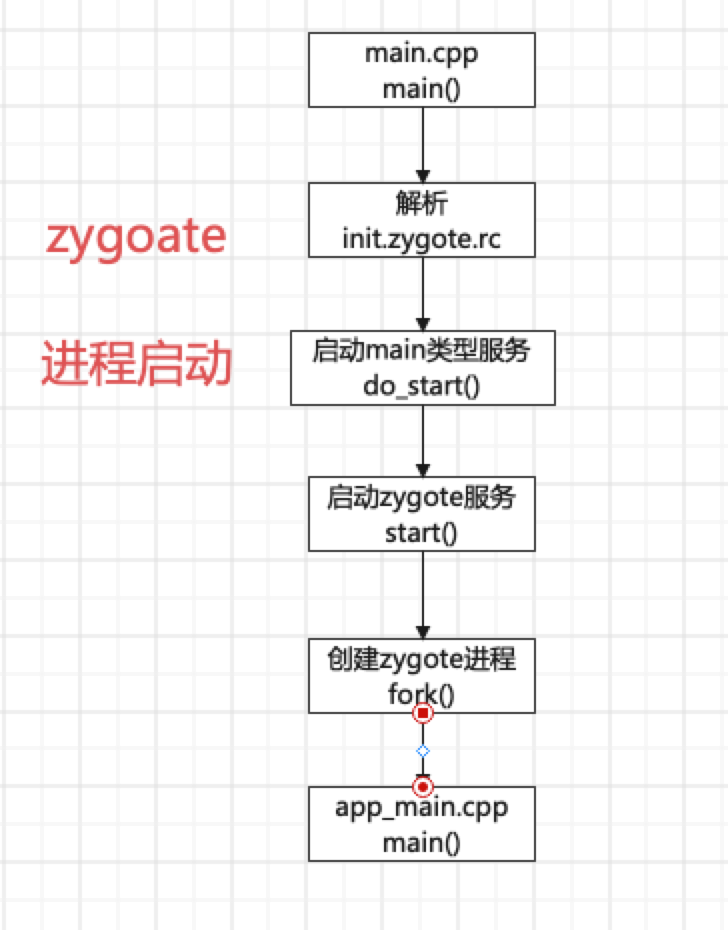
通过system/core/rootdir/init.rc找到init.rc文件,启动zygote
mport /init.environ.rc
import /system/etc/init/hw/init.usb.rc
import /init.${ro.hardware}.rc
import /vendor/etc/init/hw/init.${ro.hardware}.rc
import /system/etc/init/hw/init.usb.configfs.rc
//导入ro.zygote启动zygote
import /system/etc/init/hw/init.${ro.zygote}.rc
...
trigger zygote-start
...
on zygote-start && property:ro.crypto.state=unsupported
# A/B update verifier that marks a successful boot.
exec_start update_verifier_nonencrypted
start statsd
start netd
//启动zygote
start zygote
start zygote_secondary启动zygote就是对应启动我们手机目录下的sysytem/bin/app_process(zygote),与之对应的就是
上面的32、64就是我们的系统的多少位的,是32 还是64或者主32副64或者主64副32。
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
class main
priority -20
user root
group root readproc reserved_disk
socket zygote stream 660 root system
socket usap_pool_primary stream 660 root system
//各种onrestart就是重启zygote进程,Android系统崩溃后就会调用
onrestart exec_background - system system -- /system/bin/vdc volume abort_fuse
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart cameraserver
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
onrestart restart wificond
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks各种onrestart就是重启zygote进程,Android系统崩溃后就会调用。
我们进入到app_process/android.bp:
cc_binary {
name: "app_process",
// zygote的启动文件
srcs: ["app_main.cpp"],
multilib: {
lib32: {
version_script: ":art_sigchain_version_script32.txt",
suffix: "32",
},
lib64: {
version_script: ":art_sigchain_version_script64.txt",
suffix: "64",
},
},再进入app_main.cpp:
main方法的参数:service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
if (!LOG_NDEBUG) {
String8 argv_String;
for (int i = 0; i < argc; ++i) {
argv_String.append(""");
argv_String.append(argv[i]);
argv_String.append("" ");
}
ALOGV("app_process main with argv: %s", argv_String.string());
}
// 这个就开始启动Java层
AppRuntime runtime(argv[0], computeArgBlockSize(argc, argv));
// Process command line arguments
// ignore argv[0]
argc--;
argv++;
...
nt i;
for (i = 0; i < argc; i++) {
...
// 解析传进来的参数
while (i < argc) {
const char* arg = argv[i++];
// zygote
if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) {
zygote = true;
niceName = ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME;
// startsystemserver
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0) {
application = true;
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--nice-name=", 12) == 0) {
niceName.setTo(arg + 12);
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--", 2) != 0) {
className.setTo(arg);
break;
} else {
--i;
break;
}
}
...
}
...
// 启动Android运行时环境
if (zygote) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
} else if (className) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
}
}我们看一下runtime.start()方法,进入frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp,传入的参数:runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote)里面的参数:
这是zygote的native的启动,
oid AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote)
{
...
//启动虚拟机
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote, primary_zygote) != 0) {
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);
/*
* 注册jni,就是Java与C/C++互调功能
* Register android functions.
*/
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android nativesn");
return;
}
...
if (startClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'n", slashClassName);
/* keep going */
} else {
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'n", className);
/* keep going */
} else {
// 这个地方执行runtime.start
// ("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote)
// 的ZygoteInit中的main方法
//ZygoteInit是一个Java文件,这时候就到我们的Java层了
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
#if 0
if (env->ExceptionCheck())
threadExitUncaughtException(env);
#endif
}
}
...
}进入zygoteInit.java
public class ZygoteInit {
//预加载。加快进程的启动
static void preload(TimingsTraceLog bootTimingsTraceLog) {
}
//main方法
public static void main(String argv[]) {
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = null;
...
if (!enableLazyPreload) {
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygotePreload");
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
// 预加载
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygotePreload
}
...
// 创建ZygoteServer -- 就是socket的服务端,AMS通过这个socket创建socket的客户端
zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer(isPrimaryZygote);
if (startSystemServer) {
// 启动 systemserver进程,AMS
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, zygoteSocketName
,zygoteServer);
// {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and
{@code r != null} in the
// child (system_server) process.
if (r != null) {
r.run();
return;
}
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
// The select loop returns early in the child process after a fork and
// loops forever in the zygote.
// 死循环,接收AMS传过来的消息
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
}
}整个过程通过zygote进程从native层走到了Java层。
最后
以上就是稳重蜻蜓最近收集整理的关于Android启动流程的全部内容,更多相关Android启动流程内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复