1.接着来 ConfigFileApplicationListener中的postProcessEnvironment,等等,我差点要跳过了,原来这个EnvironmentPostProcessor才是加载配置文件的关键1
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplication application) {
addPropertySources(environment, application.getResourceLoader());
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment, application);
}2.进入 addPropertySources方法,入参environment 为StandardServletEnvironment
resourceLoader 为 null,
protected void addPropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
}2.1且看RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);方法
public static void addToEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
environment.getPropertySources().addAfter(
StandardEnvironment.SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
new RandomValuePropertySource(RANDOM_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
logger.trace("RandomValuePropertySource add to Environment");
}这个方法就是将RandomValuePropertySource加在SystemEnvironmentPropertySource {name='systemEnvironment'}之后
的第一个
2.2 再看 new Loader(environment, resourceLoader)方法
Loader(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.environment = environment;
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader == null ? new DefaultResourceLoader()
: resourceLoader;
}注意这个Loader是ConfigFileApplicationListener中的内部类
该类的注释为Loads candidate property sources and configures the active profiles.
中文的意思是加载候选属性源并配置活动配置文件
这里的resourceLoader 附上了 new DefaultResourceLoader(),已不再为null
2.3 重点就是load方法了
public void load() {
this.propertiesLoader = new PropertySourcesLoader();
this.activatedProfiles = false;
this.profiles = Collections.asLifoQueue(new LinkedList<Profile>());
this.processedProfiles = new LinkedList<Profile>();
// Pre-existing active profiles set via Environment.setActiveProfiles()
// are additional profiles and config files are allowed to add more if
// they want to, so don't call addActiveProfiles() here.
Set<Profile> initialActiveProfiles = initializeActiveProfiles();
this.profiles.addAll(getUnprocessedActiveProfiles(initialActiveProfiles));
if (this.profiles.isEmpty()) {
for (String defaultProfileName : this.environment.getDefaultProfiles()) {
Profile defaultProfile = new Profile(defaultProfileName, true);
if (!this.profiles.contains(defaultProfile)) {
this.profiles.add(defaultProfile);
}
}
}
// The default profile for these purposes is represented as null. We add it
// last so that it is first out of the queue (active profiles will then
// override any settings in the defaults when the list is reversed later).
this.profiles.add(null);
while (!this.profiles.isEmpty()) {
Profile profile = this.profiles.poll();
for (String location : getSearchLocations()) {
if (!location.endsWith("/")) {
// location is a filename already, so don't search for more
// filenames
load(location, null, profile);
}
else {
for (String name : getSearchNames()) {
load(location, name, profile);
}
}
}
this.processedProfiles.add(profile);
}
addConfigurationProperties(this.propertiesLoader.getPropertySources());
}2.3.1 来看 Set<Profile> initialActiveProfiles = initializeActiveProfiles();
private Set<Profile> initializeActiveProfiles() {
if (!this.environment.containsProperty(ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY)
&& !this.environment.containsProperty(INCLUDE_PROFILES_PROPERTY)) {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
// Any pre-existing active profiles set via property sources (e.g. System
// properties) take precedence over those added in config files.
SpringProfiles springProfiles = bindSpringProfiles(
this.environment.getPropertySources());
Set<Profile> activeProfiles = new LinkedHashSet<Profile>(
springProfiles.getActiveProfiles());
activeProfiles.addAll(springProfiles.getIncludeProfiles());
maybeActivateProfiles(activeProfiles);
return activeProfiles;
}
这个方法就是获取environment中 spring.profiles.active和spring.profiles.include的值并封装成initialActiveProfiles
2.3.2 this.profiles.addAll(getUnprocessedActiveProfiles(initialActiveProfiles));
getUnprocessedActiveProfiles(initialActiveProfiles)顾名思义,获取不能处理的激活文件,比如在key不是
spring.profiles.active和spring.profiles.include的环境
如果 this.profiles这都没有值 ,spring 会添加一个default 的profile,然后在指定的location循环遍历找配置文件
这个location的生存如下,在没有配置 spring.config.location的情况下,生成的location如下
private Set<String> getSearchLocations() {
Set<String> locations = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
// User-configured settings take precedence, so we do them first
if (this.environment.containsProperty(CONFIG_LOCATION_PROPERTY)) {
for (String path : asResolvedSet(
this.environment.getProperty(CONFIG_LOCATION_PROPERTY), null)) {
if (!path.contains("$")) {
path = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
if (!ResourceUtils.isUrl(path)) {
path = ResourceUtils.FILE_URL_PREFIX + path;
}
}
locations.add(path);
}
}
locations.addAll(
asResolvedSet(ConfigFileApplicationListener.this.searchLocations,
DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS));
return locations;
}
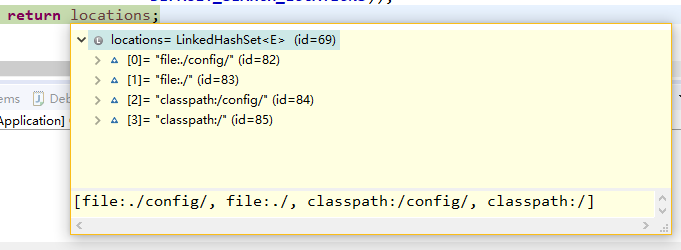
那它要读哪些文件呢getSearchNames方法给出了答案,在没有指定spring.config.name的值得时候
答案是[application] 也就是平时所说的application文件
private Set<String> getSearchNames() {
if (this.environment.containsProperty(CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY)) {
return asResolvedSet(this.environment.getProperty(CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY),
null);
}
return asResolvedSet(ConfigFileApplicationListener.this.names, DEFAULT_NAMES);
}
文件名有了,那文件的后缀名,默认为[properties, xml, yml, yaml]
public Set<String> getAllFileExtensions() {
Set<String> fileExtensions = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.loaders) {
fileExtensions.addAll(Arrays.asList(loader.getFileExtensions()));
}
return fileExtensions;
}
具体的加载方法为private void load(String location, String name, Profile profile)
private void load(String location, String name, Profile profile) {
String group = "profile=" + (profile == null ? "" : profile);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(name)) {
// Try to load directly from the location
loadIntoGroup(group, location, profile);
}
else {
// Search for a file with the given name
for (String ext : this.propertiesLoader.getAllFileExtensions()) {
if (profile != null) {
// Try the profile-specific file
loadIntoGroup(group, location + name + "-" + profile + "." + ext,
null);
for (Profile processedProfile : this.processedProfiles) {
if (processedProfile != null) {
loadIntoGroup(group, location + name + "-"
+ processedProfile + "." + ext, profile);
}
}
// Sometimes people put "spring.profiles: dev" in
// application-dev.yml (gh-340). Arguably we should try and error
// out on that, but we can be kind and load it anyway.
loadIntoGroup(group, location + name + "-" + profile + "." + ext,
profile);
}
// Also try the profile-specific section (if any) of the normal file
loadIntoGroup(group, location + name + "." + ext, profile);
}
}
}
2.3.3 在看看关键的loadIntoGroup(group, location, profile);方法
private PropertySource<?> loadIntoGroup(String identifier, String location,
Profile profile) {
try {
return doLoadIntoGroup(identifier, location, profile);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Failed to load property source from location '" + location + "'",
ex);
}
}进入doLoadIntoGroup方法
private PropertySource<?> doLoadIntoGroup(String identifier, String location,
Profile profile) throws IOException {
Resource resource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(location);
PropertySource<?> propertySource = null;
StringBuilder msg = new StringBuilder();
if (resource != null && resource.exists()) {
String name = "applicationConfig: [" + location + "]";
String group = "applicationConfig: [" + identifier + "]";
propertySource = this.propertiesLoader.load(resource, group, name,
(profile == null ? null : profile.getName()));
if (propertySource != null) {
msg.append("Loaded ");
handleProfileProperties(propertySource);
}
else {
msg.append("Skipped (empty) ");
}
}
else {
msg.append("Skipped ");
}
msg.append("config file ");
msg.append(getResourceDescription(location, resource));
if (profile != null) {
msg.append(" for profile ").append(profile);
}
if (resource == null || !resource.exists()) {
msg.append(" resource not found");
this.logger.trace(msg);
}
else {
this.logger.debug(msg);
}
return propertySource;
}这里存在三层for循环,location一层 name一层 ex扩展名一层,这里休息一下,明天有空继续
继续回来,为验证读取配置文件的顺序,在resources文件下我创建了两个配置文件application.properties 和application-dev.properties这两个文件
第一个进入doLoadIntoGroup中resource != null && resource.exists()判断中的代码是application.properties
2.3.4 随后进入propertySource = this.propertiesLoader.load(resource, group, name,(profile == null ? null : profile.getName()));
且看这个propertySource是什么对象,为org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource,
该类的说明大致为 该类为抽象封装键值对的基类,其中属性source 是泛型,可以是java.util.properties对象、java.util.map对象、servletContext和servletconfig对象等,一般这个对象不单独使用,结合org.springframework.core.env.PropertySources类结合使用,也就是PropertySources类来承载PropertySource类
public PropertySource<?> load(Resource resource, String group, String name,
String profile) throws IOException {
if (isFile(resource)) {
String sourceName = generatePropertySourceName(name, profile);
for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.loaders) {
if (canLoadFileExtension(loader, resource)) {
PropertySource<?> specific = loader.load(sourceName, resource,
profile);
addPropertySource(group, specific, profile);
return specific;
}
}
}
return null;
}具体解析文件的为PropertiesPropertySourceLoader 和YamlPropertySourceLoader ,后面就不看了,最终还是以文件的方式读出来,返回的是PropertySource的子类
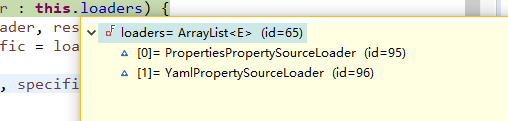
比如这里是PropertiesPropertySource,其中的source为Properties类
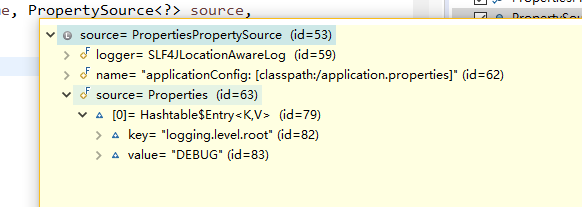
最后存储到了PropertySourcesLoader这个对象的private final MutablePropertySources propertySources;这个属性里面
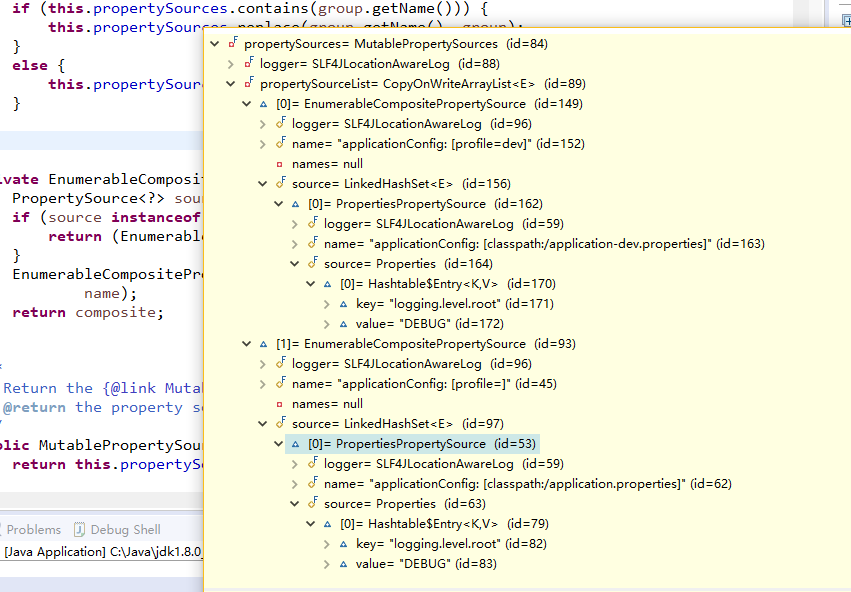
2.3.5 进入handleProfileProperties(propertySource);方法,目前不是很清楚他的作用
private void handleProfileProperties(PropertySource<?> propertySource) {
SpringProfiles springProfiles = bindSpringProfiles(propertySource);
maybeActivateProfiles(springProfiles.getActiveProfiles());
addProfiles(springProfiles.getIncludeProfiles());
}2.3.5 从一层方法返回出来,读取配置文件算是完成了,接下来进入addConfigurationProperties(this.propertiesLoader.getPropertySources()); 方法
这个方法大致就是把刚才读取到的所有配置文件绑定到 Loader对象里面
private final ConfigurableEnvironment environment;这个属性上
因为addPropertySources(environment, application.getResourceLoader());的参数是对象,即对象里面的属性改变也会改变,也会改变参数对象的属性值,也就是说,到这里,spring把刚才读到的配置文件信息无形之中封装了入参environment这个对象里面了,至此addPropertySources方法分析完毕。
3.进入configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);方法,方法入参为environment
private void configureIgnoreBeanInfo(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
if (System.getProperty(
CachedIntrospectionResults.IGNORE_BEANINFO_PROPERTY_NAME) == null) {
RelaxedPropertyResolver resolver = new RelaxedPropertyResolver(environment,
"spring.beaninfo.");
Boolean ignore = resolver.getProperty("ignore", Boolean.class, Boolean.TRUE);
System.setProperty(CachedIntrospectionResults.IGNORE_BEANINFO_PROPERTY_NAME,
ignore.toString());
}
}这个方法就是获取environment中关于spring.beaninfo.ignore 的配置,并把值放到System中去,默认值为true,至于这个系统参数有何作用,现在不得而知
4.接下来进入bindToSpringApplication(environment, application); 顾名思义,将environment绑定到application
protected void bindToSpringApplication(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplication application) {
PropertiesConfigurationFactory<SpringApplication> binder = new PropertiesConfigurationFactory<SpringApplication>(
application);
binder.setTargetName("spring.main");
binder.setConversionService(this.conversionService);
binder.setPropertySources(environment.getPropertySources());
try {
binder.bindPropertiesToTarget();
}
catch (BindException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot bind to SpringApplication", ex);
}
}这里首先构建了一个PropertiesConfigurationFactory对象
这个类的解释是Validate some Properties (or optionally PropertySources) by binding them to an object of a specified type and then optionally running a Validator over it.
理解一下就是他可以用来校验一些属性或是属性源通过绑定到一个指定类型的对象上,然后就选择性的在这个对象上实施他们
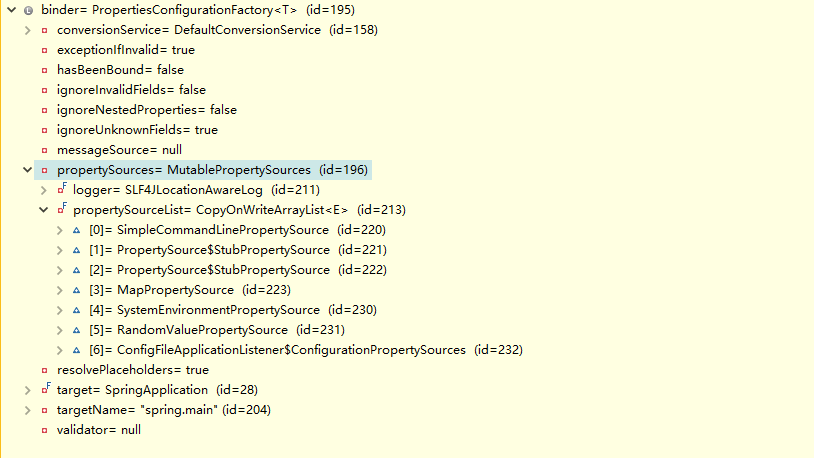
这里target 为之前最早创建的SpringApplication,
targetName为"spring.main"
propertySuorces为environment中的propertySuorces,也就包含我们读出来的配置文件
conversionService 为DefaultconversionService
接下来进入bindPropertiesToTarget()方法
public void bindPropertiesToTarget() throws BindException {
Assert.state(this.propertySources != null, "PropertySources should not be null");
try {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Property Sources: " + this.propertySources);
}
this.hasBeenBound = true;
doBindPropertiesToTarget();
}
catch (BindException ex) {
if (this.exceptionIfInvalid) {
throw ex;
}
PropertiesConfigurationFactory.logger
.error("Failed to load Properties validation bean. "
+ "Your Properties may be invalid.", ex);
}
}进入doBindPropertiesToTarget();方法,大致的意思就是将propertyValues绑定到SpringApplication这个对象上
private void doBindPropertiesToTarget() throws BindException {
RelaxedDataBinder dataBinder = (this.targetName != null
? new RelaxedDataBinder(this.target, this.targetName)
: new RelaxedDataBinder(this.target));
if (this.validator != null
&& this.validator.supports(dataBinder.getTarget().getClass())) {
dataBinder.setValidator(this.validator);
}
if (this.conversionService != null) {
dataBinder.setConversionService(this.conversionService);
}
dataBinder.setAutoGrowCollectionLimit(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
dataBinder.setIgnoreNestedProperties(this.ignoreNestedProperties);
dataBinder.setIgnoreInvalidFields(this.ignoreInvalidFields);
dataBinder.setIgnoreUnknownFields(this.ignoreUnknownFields);
customizeBinder(dataBinder);
Iterable<String> relaxedTargetNames = getRelaxedTargetNames();
Set<String> names = getNames(relaxedTargetNames);
PropertyValues propertyValues = getPropertySourcesPropertyValues(names,
relaxedTargetNames);
dataBinder.bind(propertyValues);
if (this.validator != null) {
dataBinder.validate();
}
checkForBindingErrors(dataBinder);
}到这里,postProcessEnvironment方法就结束了
总结一下,读取配置文件,目前支持properties和yml两种形式,默认文件名为application加或不加active,读取文件后封装到springApplication中去,设置系统参数spring.beaninfo.ignore,绑定数据到springApplication对象上
最后
以上就是兴奋冥王星最近收集整理的关于springBoot1.5.9.RELEASE启动源码分析之ConfigFileApplicationListener#postProcessEnvironment的全部内容,更多相关springBoot1内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复