我是靠谱客的博主 震动芹菜,这篇文章主要介绍不带缓存I/O操作写在前面的话不带缓存 I/O 操作create 函数open 函数read 函数write 函数lseek 函数close 函数文件复制的例子,现在分享给大家,希望可以做个参考。
文章目录
- 写在前面的话
- 不带缓存 I/O 操作
- create 函数
- open 函数
- read 函数
- write 函数
- lseek 函数
- close 函数
- 文件复制的例子
写在前面的话
- 文档没有任何商业因素,本着共享的精神进行分享,如有素材侵权,请给我留言;
- 文档都是自己平时看书或工作中的笔记,观点错误的地方欢迎留言;
不带缓存 I/O 操作
不带缓存的文件 I/O 操作,主要用到 6 个函数:
create;open;write;lseek;close;
这里不带缓存是指每个函数都只调用系统中的一个函数,这些函数虽然不是 ANSI C 的组成部分,但却是 POSIX 的组成部分;
create 函数
create 函数用于建立文件,详细说明如下表所示:
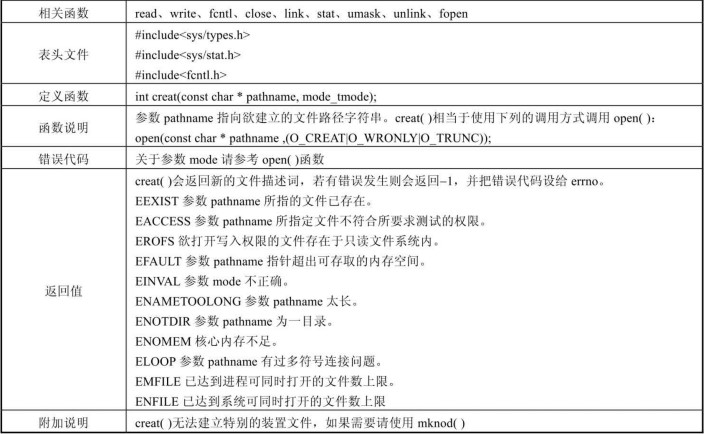
例子如下:
// create.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
void create_file(char *filename)
{
if(creat(filename, 0755) < 0) {
printf("%s: %d: create file %s failure!n", __FILE__, __LINE__, filename);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
else printf("%s: %d: create file %s success n", __FILE__, __LINE__, filename);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i;
if(argc < 2) {
perror("you haven't input the filename, please try againn");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for(int i = 1; i < argc; i++) create_file(argv[i]);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
open 函数
open 函数打开文件,详细参数见下表:

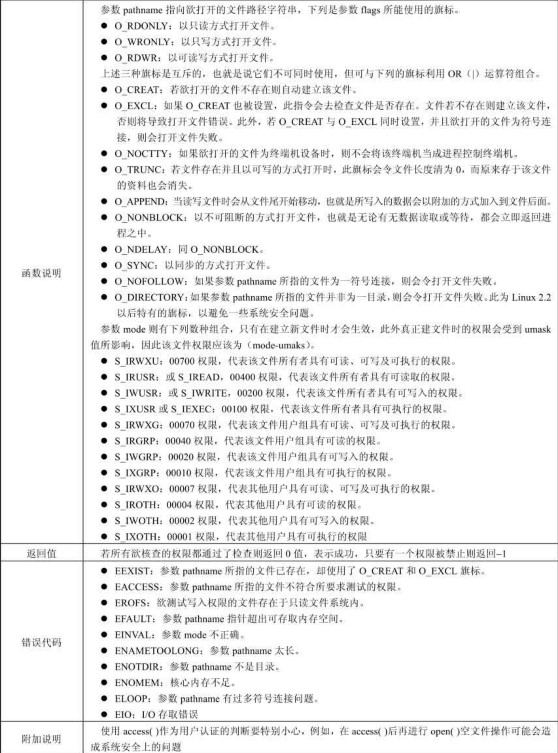
例子如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd;
if(argc < 2) {
perror("Please input the open file pathname!n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if((fd=open(argv[1], O_CREAT|O_RDWR, 0755)) < 0) {
perror("Open file failuren");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
else printf("%s: %d: Open file %d success!n", __FILE__, __LINE__, fd);
close(fd);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
read 函数
read 函数用于从已经打开的文件读取数据,具体参数如下表所示:
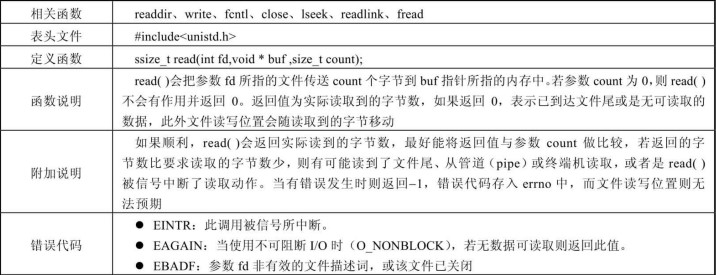
write 函数
write 函数用于将数据写入已经打开的文件中,具体参数如下所示:
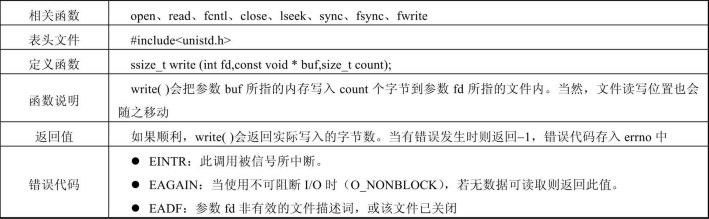
lseek 函数
lseek 函数用于移动读写指针的位置,具体参数如下所示:
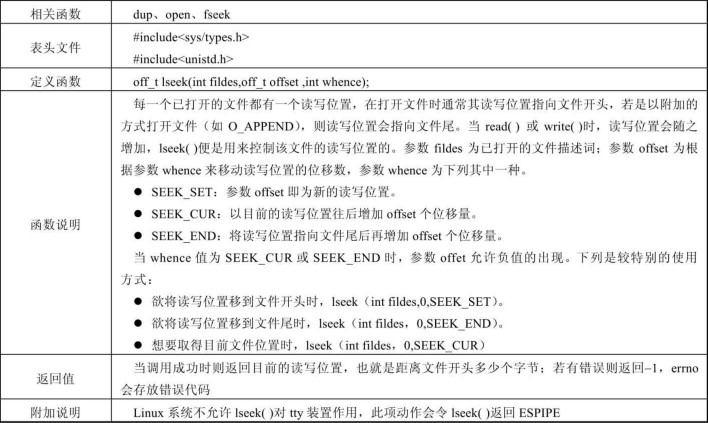
close 函数
close 函数用于关闭文件,具体参数如下所示:
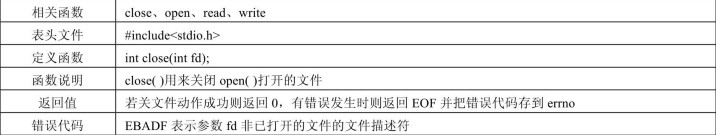
文件复制的例子
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1024
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int from_fd, to_fd;
int bytes_read, bytes_write;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
char *ptr = NULL;
if(argc != 3) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage:%s fromfile tofile/n/a", argv[0]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// open source file
if((from_fd=open(argv[1], O_RDONLY)) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Open %s Error: %s/n", argv[1], strerror(errno));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// create dst file
if((to_fd=open(argv[2], O_WRONLY|O_CREAT, S_IRUSR}S_IWUSR)) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Open %s Error: %sn", argv[2], strerror(errno));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// copying
while(bytes_read = read(from_id, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE)) {
// fetal error
if((bytes_read == -1) && (errno != EINTR)) break;
else if(bytes_read > 0) {
ptr = buffer;
while(bytes_write = write(to_fd, ptr, bytes_read)) {
// fetal error
if((bytes_Write == -1) && (errno != EINTR)) break;
else if(bytes_write == bytes_read) break;
else {
ptr += bytes_Write;
bytes_read -= bytes_Write;
}
}
// fetal error
if(bytes_write == -1) break;
}
}
close(from_fd);
close(to_fd);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
最后
以上就是震动芹菜最近收集整理的关于不带缓存I/O操作写在前面的话不带缓存 I/O 操作create 函数open 函数read 函数write 函数lseek 函数close 函数文件复制的例子的全部内容,更多相关不带缓存I/O操作写在前面的话不带缓存内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。






![[3 文件I/O(不带缓冲的I/O)]](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg5.png)

发表评论 取消回复