finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)这个方法是来实例化所有的非懒加载的Bean的,在前面已经将配置文件解析成了beanDefinition,现在准备生产,这个过程涉及来几个重要的概念
- bean的生命周期
- 循环依赖
- 三级缓存
- bean的后置处理器
- AOP时机
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
// 初始化类型转换
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor
// (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
// 支路的相关处理操作
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
// 某些bean不要修改了,冰冻他
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 实例化其他的非懒加载单例对象
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
主要看最后一行beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
// 日志死一边去
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
// 把获取到的beandefinitionNames转换成集合
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
// 是否实现了factorybean
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
这里主要逻辑就是判断当前bean定义是否实现了FactoryBean,第一篇文章提到了FactoryBean这个概念,如果实现了,说明得特殊处理,否则直接去getBean(beanName)->doGetBean(beanName);
protected <T> T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
// getSingleton()是个非常重要的方法,后续专门讲,现在了解大概流程,第一次进来这里肯定是拿不到如何bean,为空
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
// 现在的sharedInstance是一个完整对象,有可能是factorybean这个实现类本身,还得拿到另一个对象。有2个对象, 一定是先创建实现类再通过getObject方法创建所需的对象
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
// 当对象都是单例的时候会尝试解决循环依赖的问题,但是原型模式下如果存在循环依赖的情况,那么会直接抛异常
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
//表示要创建bean
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
是不是单例
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// lambda表达式,到时候某个类调用lambda表达式对象的时候,调用的其实是createBean()方法,创建开始
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
// 可能是factoryBean
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
注意这里重要的一个重载方法getSingleton,这里一堆逻辑就是三级缓存,循环依赖了,后面单独讲,现在先瞄一眼bean的生命周期
getSingleton(String beanName)肯定为空,我还没生产过,如果被生产过了直接返回,如果没有就准备生产,然后调用重载在的getSingleton(String beanName,ObjectFactory objectFactory),它的第二个参数是一个Lambda表达式,跟进去看看,
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// 先从一级缓存拿
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) {
throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName,
"Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " +
"(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
//拿不到,准备生产,设置标志位,singletonsCurrentlyInCreation:正在创建的bean,inCreationCheckExclusions:用来抛出异常,即构造函数循环依赖无法解决
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
boolean newSingleton = false;
boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null);
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
try {
// 这里调用的就是那个lambda的createBean方法
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime ->
// if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state.
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) {
ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);
}
}
throw ex;
}
finally {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = null;
}
// 创建bean完成,把标志位清除
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
// 加入一级缓存,remove2,3级缓存。
if (newSingleton) {
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
}
//这里调用的就是那个lambda的createBean方法
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
这句就是去生产bean了,生产完毕后加入一级缓存,移除二三级缓存
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
// bean后置处理器的实例化前方法,如果被返回了对象就为他执行初始化后方法并直接返回
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try {
// 核心方法,完成了创建生命周期的实例化,属性填充,初始化
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}
2个核心,一个是实例化前会去调用第一次Bean的后置处理器,比如你可以在此终端bean的生产,另一个就是doCreateBean()生产bean
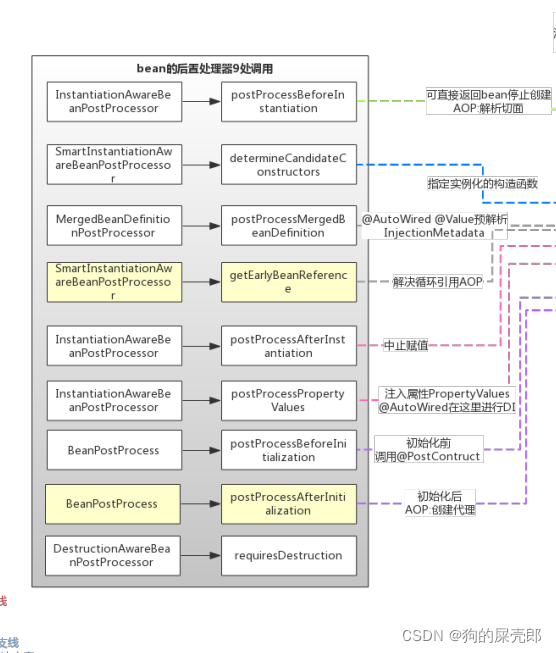
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 创建bean实例
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// 拿到原始对象
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
// 表示是否提前暴露,是否存在存在循环依赖beanA 满足条件
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}//放入三级缓存
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
// 原始bean,接着进行属性填充初始化
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 填充属性
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 初始化和初始化后
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
//一二级缓存能否拿到,能说明存在循环依赖且解决了,bean在二级缓存,如果是代理对象,需要把这个代理对象放入一级缓存
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
// 容器关闭,销毁对象,埋了一个钩子函数
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
这里开始反射创建对象,属性填充,初始化和aware,最后放入一级缓存,生产完毕。
- `instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);//创建bean的实例。核心
- populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);//填充属性,炒鸡重要,赋值过程中可能存在循环依赖
- exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);//一系列aware回调`
这里就是初始化的一系列逻辑
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 执行aware
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 执行一堆的postprocessBeforeInitialization:初始化前
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
// 执行initMethod方法,这里面调用了两个方法,一个是afterPropertiesSet方法,一个是init-method方法:
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//执行初始化后方法,AOP
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
// 完整的bean对象
return wrappedBean;
}
总结Bean的生命周期
- 实例化Bean对象,这个时候Bean的对象是非常低级的,基本不能够被我们使用,因为连最基本的属性都没有设置,可以理解为
连Autowired注解都是没有解析的; - 填充属性,当做完这一步,Bean对象基本是完整的了,可以理解为Autowired注解已经解析完毕,依赖注入完成了;
- 如果Bean实现了BeanNameAware接口,则调用setBeanName方法;
- 如果Bean实现了BeanClassLoaderAware接口,则调用setBeanClassLoader方法;
- 如果Bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,则调用setBeanFactory方法;
- 调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法;
- 如果Bean实现了InitializingBean接口,调用afterPropertiesSet方法;
- 如果Bean定义了init-method方法,则调用Bean的init-method方法;
- 调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法;当进行到这一步,Bean已经被准备就绪了,一直停留在应用的上下文中,直到被销毁;
- 如果应用的上下文被销毁了,如果Bean实现了DisposableBean接口,则调用destroy方法,如果Bean定义了destory-method
声明了销毁方法也会被调用。
最后
以上就是坚定白羊最近收集整理的关于refresh之finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)的全部内容,更多相关refresh之finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复