要知道spring的类型转换,我们首先需要知道两个接口。这两个接口就是类型转换的处理类,一个是spring自己定义的,一个是jdk定义的:
Spring定义的Converter接口:
@FunctionalInterface public interface Converter<S, T> { @Nullable T convert(S source); }
Jdk定义的PropertyEditor接口:
public interface PropertyEditor { void setValue(Object value); Object getValue(); boolean isPaintable(); void paintValue(java.awt.Graphics gfx, java.awt.Rectangle box); String getJavaInitializationString(); String getAsText(); void setAsText(String text) throws java.lang.IllegalArgumentException; String[] getTags(); java.awt.Component getCustomEditor(); boolean supportsCustomEditor(); void addPropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener); void removePropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener); }
这个PropertyEditor用于类型转换的是setAsText、getAsText、getValue、setValue这些方法。
可以看到Converter这里用了泛型、而PropertyEditor并没有。所以,如果调用getValue方法,获取的是Object对象。获取后还需要再转换为我们的目的对象。
这两个Converter、PropertyEditor接口只是接口,下面我们来看下其的实现类。
一、Converter接口
Converter接口只有一个convert方法,但我们知道,在进行类型转换前,我们一般会先判断其能不能转换为目的类型。所以其实Converter还会搭配ConditionalConverter接口,判断能不能转换:
public interface ConditionalConverter { boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType); }
这两个在组合为一个ConditionalGenericConverter接口:
public interface ConditionalGenericConverter extends GenericConverter, ConditionalConverter { }
这里GenericConverter接口,我们先将其看做为Converter接口(但其并有继承Converter接口,只是一个独立接口,在Spring的使用中,实现Converter接口的类最后还是会表叙为GenericConverter接口,这个到后面的代码就明白了),
public interface GenericConverter { @Nullable Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes(); @Nullable Object convert(@Nullable Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType); final class ConvertiblePair { private final Class<?> sourceType; private final Class<?> targetType; public ConvertiblePair(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType) { Assert.notNull(sourceType, "Source type must not be null"); Assert.notNull(targetType, "Target type must not be null"); this.sourceType = sourceType; this.targetType = targetType; } public Class<?> getSourceType() { return this.sourceType; } public Class<?> getTargetType() { return this.targetType; } ................ }
ConvertiblePair 就是哟本来存源类型,目标类型。
我们先简单看一个Converter接口的实现类:NumberToCharacterConverter ,将Number类型转换为Character类型
final class NumberToCharacterConverter implements Converter<Number, Character> { @Override public Character convert(Number source) { return (char) source.shortValue(); } }
通过这个我们可以知道Converter在Spring的实现过程。
接下来我们看下其的使用过程,我们看下这个转换器在哪里使用。其是在DefaultConversionService类中被注册:
private static void addScalarConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) { converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new NumberToNumberConverterFactory()); .............. converterRegistry.addConverter(new NumberToCharacterConverter()); converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new CharacterToNumberFactory()); converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToBooleanConverter()); ................ }public static void addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) { addScalarConverters(converterRegistry); addCollectionConverters(converterRegistry); converterRegistry.addConverter(new ByteBufferConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry)); .......... }
这里我们先了解DefaultConversionService、ConverterRegistry。
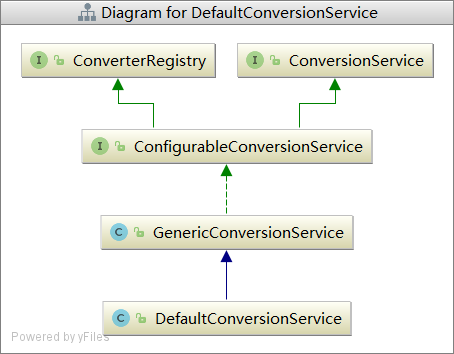
ConverterRegister,这个看名字就知道其是用来注册Converter的:

这里有四种类型注册。在这里我们看到可以注册Converter以及GenericConverter,还有ConverterFactory,就是生成Converter 的工厂。
public interface ConversionService { boolean canConvert(@Nullable Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType); boolean canConvert(@Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType); @Nullable <T> T convert(@Nullable Object source, Class<T> targetType); @Nullable Object convert(@Nullable Object source, @Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType); }
ConversionService 这个接口就是用来判断能不能进行转换,以及进行转换的。
public interface ConfigurableConversionService extends ConversionService, ConverterRegistry { }
其实现类GenericConversionService
GenericConversionService类有两个成员变量:
private final Converters converters = new Converters(); private final Map<ConverterCacheKey, GenericConverter> converterCache = new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>(64);
@Override public void addConverter(Converter<?, ?> converter) { ResolvableType[] typeInfo = getRequiredTypeInfo(converter.getClass(), Converter.class); if (typeInfo == null && converter instanceof DecoratingProxy) { typeInfo = getRequiredTypeInfo(((DecoratingProxy) converter).getDecoratedClass(), Converter.class); } .......... addConverter(new ConverterAdapter(converter, typeInfo[0], typeInfo[1])); }
@Nullable private ResolvableType[] getRequiredTypeInfo(Class<?> converterClass, Class<?> genericIfc) { ResolvableType resolvableType = ResolvableType.forClass(converterClass).as(genericIfc); ResolvableType[] generics = resolvableType.getGenerics(); if (generics.length < 2) { return null; } Class<?> sourceType = generics[0].resolve(); Class<?> targetType = generics[1].resolve(); if (sourceType == null || targetType == null) { return null; } return generics; }
可以看到这个getRequiredTypeInfo就用来获取Converter<?, ?>中的两个表示泛型的类型,例如前面的NumberToCharacterConverter implements Converter<Number, Character>,然后就会获取Number, Character,再与Converter以前转换为ConverterAdapter:
private final class ConverterAdapter implements ConditionalGenericConverter { private final Converter<Object, Object> converter; private final ConvertiblePair typeInfo; private final ResolvableType targetType; public ConverterAdapter(Converter<?, ?> converter, ResolvableType sourceType, ResolvableType targetType) { this.converter = (Converter<Object, Object>) converter; this.typeInfo = new ConvertiblePair(sourceType.resolve(Object.class), targetType.resolve(Object.class)); this.targetType = targetType; } @Override public Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes() { return Collections.singleton(this.typeInfo); } @Override public boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) { if (this.typeInfo.getTargetType() != targetType.getObjectType()) { return false; } ResolvableType rt = targetType.getResolvableType(); if (!(rt.getType() instanceof Class) && !rt.isAssignableFrom(this.targetType) && !this.targetType.hasUnresolvableGenerics()) { return false; } return !(this.converter instanceof ConditionalConverter) || ((ConditionalConverter) this.converter).matches(sourceType, targetType); } @Override @Nullable public Object convert(@Nullable Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) { if (source == null) { return convertNullSource(sourceType, targetType); } return this.converter.convert(source); } .............. }
ConverterAdapter是实现了ConditionalGenericConverter 接口,所以其需要实现GenericConverter的convert方法、以及ConditionalConverter的是否匹配,即是否能用本Converter去转换。同时会将Converter的源类型以及目标类型存到ConvertiblePair。所以这里就将前面的GenericConverter与Converter 的关系理清了。Converter会被转换到ConverterAdapter,ConverterAdapter实现了GenericConverter。
我们再回到 addConverter(new ConverterAdapter(converter, typeInfo[0], typeInfo[1]));方法:
其调用的是:
@Override public void addConverter(GenericConverter converter) { this.converters.add(converter); invalidateCache(); }
所以这里如果是添加GenericConverter类型,就将其直接添加到converters,如果是添加Converter就将其转换为ConverterAdapter(类型转换适配器)。再调用addConverter(GenericConverter converter)方法,ConverterAdapter实现统一的matchs方法。
private final Converters converters = new Converters();private static class Converters { private final Set<GenericConverter> globalConverters = new LinkedHashSet<>() private final Map<ConvertiblePair, ConvertersForPair> converters = new LinkedHashMap<>(36); public void add(GenericConverter converter) { Set<ConvertiblePair> convertibleTypes = converter.getConvertibleTypes(); if (convertibleTypes == null) { Assert.state(converter instanceof ConditionalConverter, "Only conditional converters may return null convertible types"); this.globalConverters.add(converter); } else { for (ConvertiblePair convertiblePair : convertibleTypes) { ConvertersForPair convertersForPair = getMatchableConverters(convertiblePair); convertersForPair.add(converter); } } } private ConvertersForPair getMatchableConverters(ConvertiblePair convertiblePair) { ConvertersForPair convertersForPair = this.converters.get(convertiblePair); if (convertersForPair == null) { convertersForPair = new ConvertersForPair(); this.converters.put(convertiblePair, convertersForPair); } return convertersForPair; }
可以看到这里的添加会分情况添加到两个地方:globalConverters、converters。要了解这两种的区别,我们看其find方法,即找到对应的GenericConverter:
首先下ConvertersForPair类
private static class ConvertersForPair { private final LinkedList<GenericConverter> converters = new LinkedList<>(); public void add(GenericConverter converter) { this.converters.addFirst(converter); } @Nullable public GenericConverter getConverter(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) { for (GenericConverter converter : this.converters) { if (!(converter instanceof ConditionalGenericConverter) || ((ConditionalGenericConverter) converter).matches(sourceType, targetType)) { return converter; } } return null; } }
public GenericConverter find(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) { ................... for (Class<?> sourceCandidate : sourceCandidates) { for (Class<?> targetCandidate : targetCandidates) { ConvertiblePair convertiblePair = new ConvertiblePair(sourceCandidate, targetCandidate); GenericConverter converter = getRegisteredConverter(sourceType, targetType, convertiblePair); if (converter != null) { return converter; } } } return null; }private GenericConverter getRegisteredConverter(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType, ConvertiblePair convertiblePair) { // Check specifically registered converters ConvertersForPair convertersForPair = this.converters.get(convertiblePair); if (convertersForPair != null) { GenericConverter converter = convertersForPair.getConverter(sourceType, targetType); if (converter != null) { return converter; } } // Check ConditionalConverters for a dynamic match for (GenericConverter globalConverter : this.globalConverters) { if (((ConditionalConverter) globalConverter).matches(sourceType, targetType)) { return globalConverter; } } return null; }
这里是先获取添加到converters中的,如果没有再获取globalConverters中的:
通过前面ConvertersForPair 的getConverter方法,可以知道其在matches是转换为ConditionalGenericConverter,而globalConverters是强转为ConditionalConverter。其中ConditionalGenericConverter继承了ConditionalConverter接口。
所以关于Converer接口,整个使用过程是如果实现Converter接口的类都转换为ConverterAdapter适配器,然后通过这个适配器实现的matches的方法去匹配,及调用converter的convert方法。而如果是添加的GenericConverter类型,通过find方法可以知道,要么同时一起继承ConditionalConverter接口(matches方法),要么直接实现ConditionalGenericConverter,因为
ConditionalGenericConverter继承了ConditionalConverter与GenericConverter接口。
这里Converter、GenericConverter、ConditionalConverter是怎样在GenericConversionService中使用的已经理清楚了。我们再来看其在Spring中使用过程。
我们再回到继承GenericConversionService类的DefaultConversionService:
public DefaultConversionService() { addDefaultConverters(this); }
其在初始化的时候就调用addDefaultConverters将默认的Converter添加到该类中,如果需要自己再添加,就可以调用前面介绍的addConverter方法,
哪里使用到这个DefaultConversionService类呢?这里就要知道TypeConverterSupport类,Spring中类型转换就是通过这个类去统筹调度的。先在这里不展开,因为这个类还会用到类型转换的另一个接口PropertyEditer接口。
二、PropertyEditor接口
这个接口 在Jdk中有个初步实现类:PropertyEditorSupport:
public class PropertyEditorSupport implements PropertyEditor {private Object value; private Object source; private java.util.Vector<PropertyChangeListener> listeners; .................. public void setValue(Object value) { this.value = value; firePropertyChange(); } public Object getValue() { return value; } public String getAsText() { return (this.value != null) ? this.value.toString() : null; } public void setAsText(String text) throws java.lang.IllegalArgumentException { if (value instanceof String) { setValue(text); return; } throw new java.lang.IllegalArgumentException(text); } ............. }
可以看到这里在setValue的时候会去通知Listener。我们看一个Spring关于PropertyEditerSupport的实现类:
public class ByteArrayPropertyEditor extends PropertyEditorSupport { @Override public void setAsText(@Nullable String text) { setValue(text != null ? text.getBytes() : null); } @Override public String getAsText() { byte[] value = (byte[]) getValue(); return (value != null ? new String(value) : ""); } }
这里就是将text设置为byte[],所以这个类的成员变量为byte[]。当调用getValue的时候返回的是byte[],调用getAsText的时候是获取转换为byte的String。看下Spring中的测试用例:
@Test public void sunnyDaySetAsText() throws Exception { final String text = "Hideous towns make me throw... up"; byteEditor.setAsText(text); Object value = byteEditor.getValue(); assertNotNull(value); assertTrue(value instanceof byte[]); byte[] bytes = (byte[]) value; for (int i = 0; i < text.length(); ++i) { assertEquals("cyte[] differs at index '" + i + "'", text.charAt(i), bytes[i]); } assertEquals(text, byteEditor.getAsText()); }
这里在getValue的时候要强转换为byte[]。
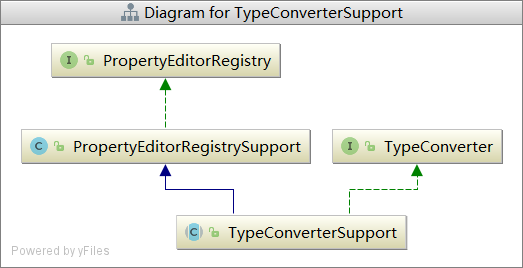
三、现在我们来看TypeConverterSupport类
public interface TypeConverter { @Nullable <T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType) throws TypeMismatchException; @Nullable <T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable MethodParameter methodParam) throws TypeMismatchException; @Nullable <T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Field field) throws TypeMismatchException; }
这个TypeConverter就是判断当前的转换器中能不能转换,能转换就调用对应方法进行转换:
public interface PropertyEditorRegistry { void registerCustomEditor(Class<?> requiredType, PropertyEditor propertyEditor); void registerCustomEditor(@Nullable Class<?> requiredType, @Nullable String propertyPath, PropertyEditor propertyEditor); @Nullable PropertyEditor findCustomEditor(@Nullable Class<?> requiredType, @Nullable String propertyPath); }
PropertyEditorRegistry ,通过参数就可以知道其是用来注册PropertyEditor 这种转换器的。
PropertyEditorRegistry 实现类PropertyEditorRegistrySupport:
public class PropertyEditorRegistrySupport implements PropertyEditorRegistry { @Nullable private ConversionService conversionService; private boolean defaultEditorsActive = false; private boolean configValueEditorsActive = false; @Nullable private Map<Class<?>, PropertyEditor> defaultEditors; @Nullable private Map<Class<?>, PropertyEditor> overriddenDefaultEditors; @Nullable private Map<Class<?>, PropertyEditor> customEditors; @Nullable private Map<String, CustomEditorHolder> customEditorsForPath; @Nullable private Map<Class<?>, PropertyEditor> customEditorCache; ................................ public PropertyEditor getDefaultEditor(Class<?> requiredType) { if (!this.defaultEditorsActive) { return null; } if (this.overriddenDefaultEditors != null) { PropertyEditor editor = this.overriddenDefaultEditors.get(requiredType); if (editor != null) { return editor; } } if (this.defaultEditors == null) { createDefaultEditors(); } return this.defaultEditors.get(requiredType); } private void createDefaultEditors() { this.defaultEditors = new HashMap<>(64); // Simple editors, without parameterization capabilities. // The JDK does not contain a default editor for any of these target types. this.defaultEditors.put(Charset.class, new CharsetEditor()); this.defaultEditors.put(Class.class, new ClassEditor()); } .............................. }
这里关注两种类型,defaultEditors这个就是Spring的默认添加的PropertyEditor,customEditors这个就是你自定义的propertyEditor是添加在这里,这里的ConversionService 就是赋值前面讲的用与管理GenericConverter类型转换的GenericConversionService及其子类
再回到TypeConverterSupport:
public abstract class TypeConverterSupport extends PropertyEditorRegistrySupport implements TypeConverter { @Nullable TypeConverterDelegate typeConverterDelegate; @Override @Nullable public <T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType) throws TypeMismatchException { return doConvert(value, requiredType, null, null); } @Override @Nullable public <T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable MethodParameter methodParam) throws TypeMismatchException { return doConvert(value, requiredType, methodParam, null); } @Override @Nullable public <T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Field field) throws TypeMismatchException { return doConvert(value, requiredType, null, field); } @Nullable private <T> T doConvert(@Nullable Object value,@Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable MethodParameter methodParam, @Nullable Field field) throws TypeMismatchException { Assert.state(this.typeConverterDelegate != null, "No TypeConverterDelegate"); try { if (field != null) { return this.typeConverterDelegate.convertIfNecessary(value, requiredType, field); } else { return this.typeConverterDelegate.convertIfNecessary(value, requiredType, methodParam); } } catch (ConverterNotFoundException | IllegalStateException ex) { throw new ConversionNotSupportedException(value, requiredType, ex); } catch (ConversionException | IllegalArgumentException ex) { throw new TypeMismatchException(value, requiredType, ex); } } }
可以看到这里convertIfNecessary最终是调用doConvert去转换的,而doConvert是调用typeConverterDelegate的convertIfNecessary。
class TypeConverterDelegate { private final PropertyEditorRegistrySupport propertyEditorRegistry; @Nullable private final Object targetObject; public TypeConverterDelegate(PropertyEditorRegistrySupport propertyEditorRegistry) { this(propertyEditorRegistry, null); } ................... }
可以看到TypeConverterDelegate的初始化是需要PropertyEditorRegistrySupport,而TypeConverterSupport实现了该类,并且TypeConverterSupport是抽象类,所以TypeConverterDelegate初始化的时候是TypeConverterSupport的实现类传的this,用代码验证下:
protected AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor(boolean registerDefaultEditors) { if (registerDefaultEditors) { registerDefaultEditors(); } this.typeConverterDelegate = new TypeConverterDelegate(this); } public class SimpleTypeConverter extends TypeConverterSupport { public SimpleTypeConverter() { this.typeConverterDelegate = new TypeConverterDelegate(this); registerDefaultEditors(); } }
AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor实现了TypeConverterSupport。所以这里得到了验证,就是将作为TypeConverterSupport成员的TypeConverterDelegate类的初始化传TypeConverterSupport本身。
我们看TypeConverterDelegate的convertIfNecessary方法:
public <T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable String propertyName, @Nullable Object oldValue, @Nullable Object newValue, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable TypeDescriptor typeDescriptor) throws IllegalArgumentException { // Custom editor for this type? PropertyEditor editor = this.propertyEditorRegistry.findCustomEditor(requiredType, propertyName); ConversionFailedException conversionAttemptEx = null; // No custom editor but custom ConversionService specified? ConversionService conversionService = this.propertyEditorRegistry.getConversionService(); if (editor == null && conversionService != null && newValue != null && typeDescriptor != null) { TypeDescriptor sourceTypeDesc = TypeDescriptor.forObject(newValue); if (conversionService.canConvert(sourceTypeDesc, typeDescriptor)) { try { return (T) conversionService.convert(newValue, sourceTypeDesc, typeDescriptor); } catch (ConversionFailedException ex) { // fallback to default conversion logic below conversionAttemptEx = ex; } } } Object convertedValue = newValue; .................. if (editor == null) { editor = findDefaultEditor(requiredType); } convertedValue = doConvertValue(oldValue, convertedValue, requiredType, editor); } ...............(这后面有一串很长的代码,不过一般用前面这一串就可以完成转换了) return (T) convertedValue; }
1、这里实现是获取自定义PropertyEditor。
2、如果ConversionService不为空,就是指如果存在Converter类型的转获取其,其这里找一下,看有没有符合的Converter转换器:
conversionService.canConvert(sourceTypeDesc, typeDescriptor),该放在在GenericConversionService的实现:
public boolean canConvert(@Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) { ........... GenericConverter converter = getConverter(sourceType, targetType); return (converter != null); } protected GenericConverter getConverter(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) { ConverterCacheKey key = new ConverterCacheKey(sourceType, targetType); GenericConverter converter = this.converterCache.get(key); if (converter != null) { return (converter != NO_MATCH ? converter : null); } converter = this.converters.find(sourceType, targetType); if (converter == null) { converter = getDefaultConverter(sourceType, targetType); } if (converter != null) { this.converterCache.put(key, converter); return converter; } this.converterCache.put(key, NO_MATCH); return null; }
这里是用了缓存,我们找到在放到缓存前的两个方法:
converter = this.converters.find(sourceType, targetType); if (converter == null) { converter = getDefaultConverter(sourceType, targetType); }
这里的find方法在前面已经讲GenericConversionService的时候就讲了,我们看下如果没有获取到,调用getDefaultConverter:
@Nullable protected GenericConverter getDefaultConverter(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) { return (sourceType.isAssignableTo(targetType) ? NO_OP_CONVERTER : null); } private static final GenericConverter NO_OP_CONVERTER = new NoOpConverter("NO_OP"); private static class NoOpConverter implements GenericConverter { private final String name; .......... @Nullable public Object convert(@Nullable Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) { return source; } }
我们再回到前面的convertIfNecessary,如果在这里找到了对应Converter类型的转换器,就去进行对应的转换:
public Object convert(@Nullable Object source, @Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) { ............... GenericConverter converter = getConverter(sourceType, targetType); if (converter != null) { Object result = ConversionUtils.invokeConverter(converter, source, sourceType, targetType); return handleResult(sourceType, targetType, result); } ................ }
获取对应的GenericConverter,然后通过ConversionUtils工具类ConversionUtils去转换:
public static Object invokeConverter(GenericConverter converter, @Nullable Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) { try { return converter.convert(source, sourceType, targetType); } catch (ConversionFailedException ex) { throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new ConversionFailedException(sourceType, targetType, source, ex); } }
再回到convertIfNecessary方法,如果没有对应的GenericConverter类型转换器,就会接着往下:
if (editor == null) { editor = findDefaultEditor(requiredType); } convertedValue = doConvertValue(oldValue, convertedValue, requiredType, editor);
如果没有自定义的PropertyEditor,就会获取默认的PropertyEditor,去转换:
private PropertyEditor findDefaultEditor(@Nullable Class<?> requiredType) { .............. editor = this.propertyEditorRegistry.getDefaultEditor(requiredType); .......... return editor; }
这里就回到前面讲propertyEditorRegistrySupport是时候的getDefaultEditor方法了,将所有的默认Editer,添加到defaultEditors。
自此,这个Spring的类型转换就梳理完毕了。Spring中如果要进行类型转换,就会持有TypeConverterDelegate,或者持有
TypeConverterSupport的子类。同时通过这个流程可以知道。进行类型转换的时候首先是使用Converter类型,如果该类型能完成转换,就不会去使用propertyEditor了。并且,在使用Converter类型的时候,是先使用实现ConditionalGenericConverter接口的类,如果没有才会再去使用实现ConditionalConverter类型的类。
最后
以上就是谨慎万宝路最近收集整理的关于Spring源码 --- Spring的类型转换(TypeConverterDelegate与TypeConverterSupport)的全部内容,更多相关Spring源码内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复