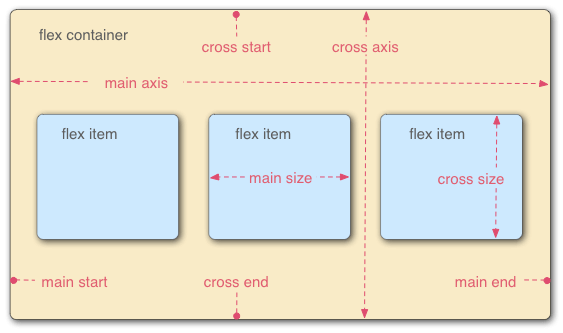
黄色框:容器
蓝色框:子项(项目)
main axis :主轴
cross axis:交叉轴
注意:设为Flex布局以后,子元素的 float 、 clear 和 vertical-align 属性将失效。
容器属性
1.flex-direction:定义主轴方向
flex-direction: row | row-reverse | column | column-reverse;
row (默认值):主轴为水平方向,起点在左端。
row-reverse :主轴为水平方向,起点在右端。
column :主轴为垂直方向,起点在上沿。
column-reverse :主轴为垂直方向,起点在下沿。
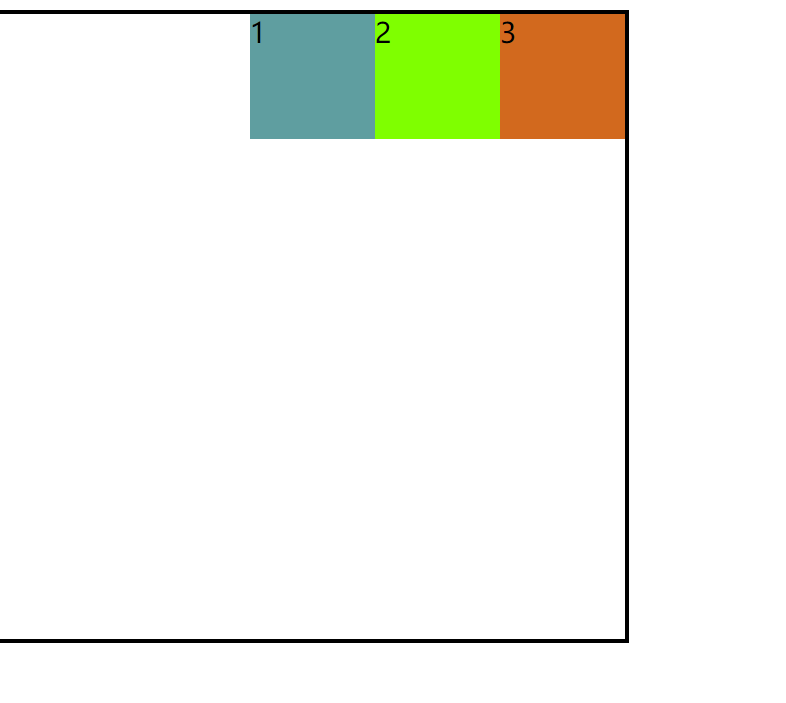
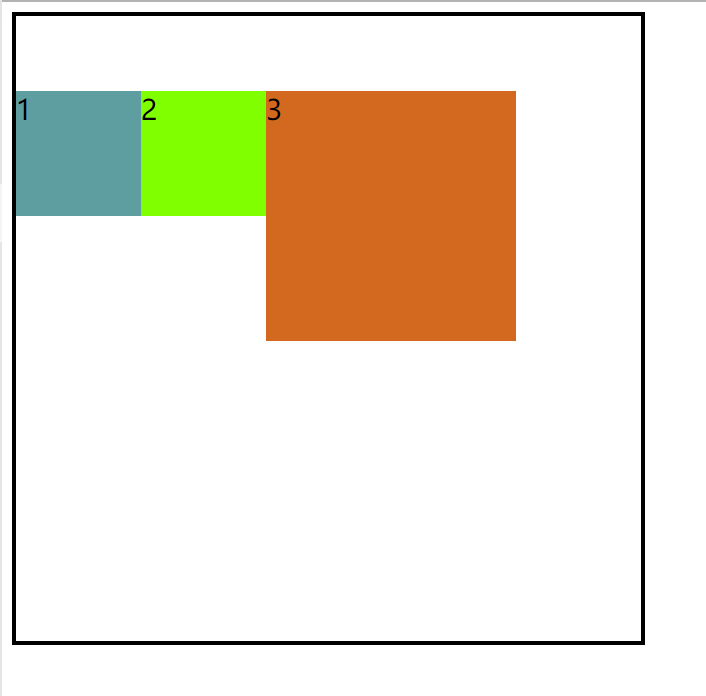
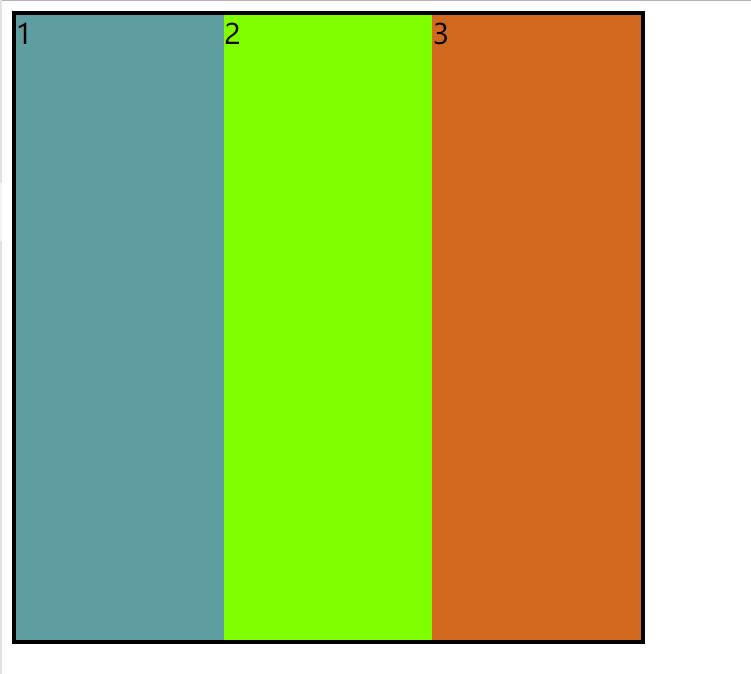
1.常规流布局:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>测试</title>
<style>
section{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
border:3px solid black;
}
.d1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: cadetblue;
}
.d2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:chartreuse;
}
.d3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: chocolate;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<section>
<div class="d1">1</div>
<div class="d2">2</div>
<div class="d3">3</div>
</section>
</body>
</html>
效果图:
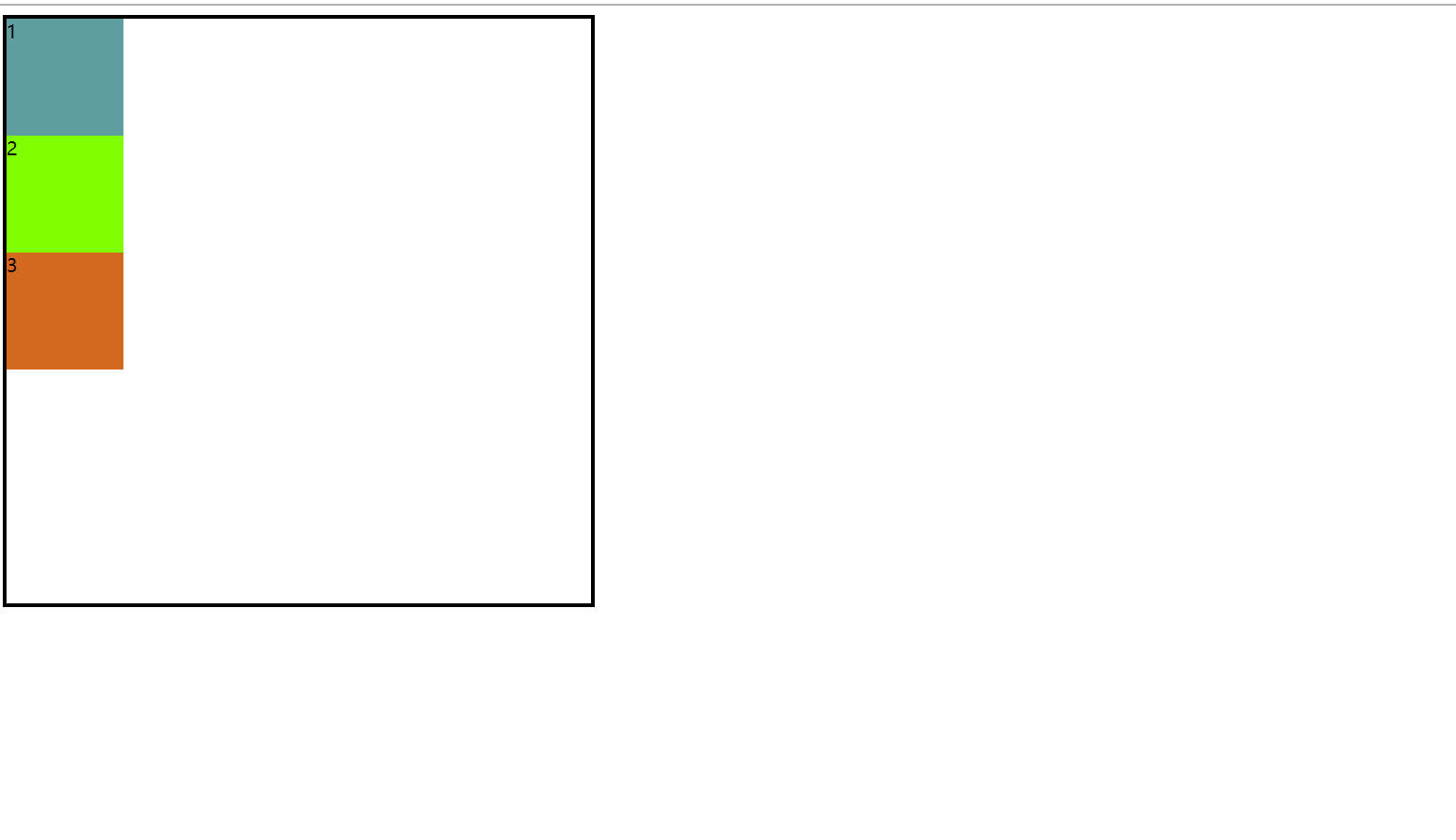
2.flex布局(默认轴)
section{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
border:3px solid black;
display: flex; /* 在父级容器使用flex布局 */
}
效果图:

此时flex-direction:row(默认)
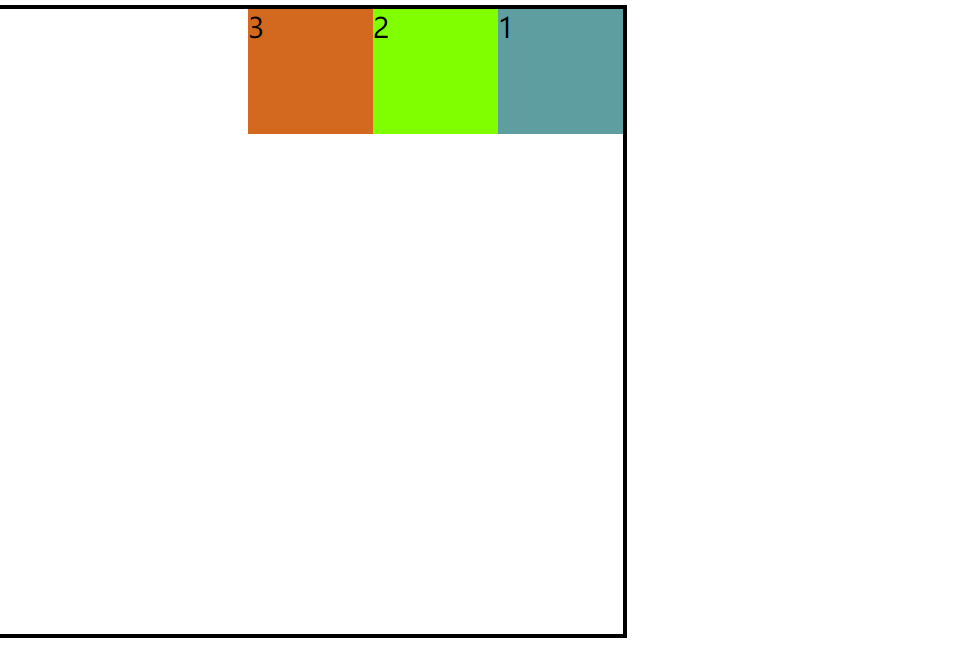
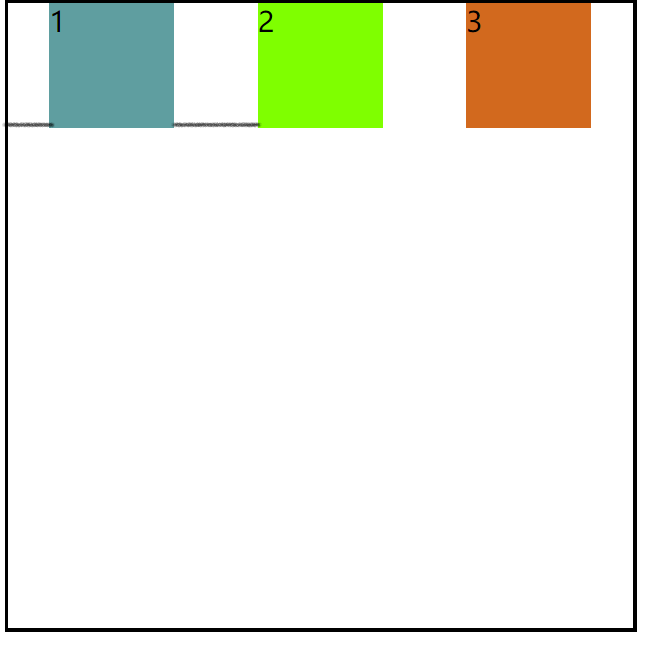
3. flex-direction:row-revers(主轴反方向)
代码:
section{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
font-size: 22px;
border:3px solid black;
display: flex; /* 在父级容器使用flex布局 */
flex-direction: row-reverse;
}
效果图:
4.flex-direction:column(主轴改为垂直方向)
代码:
flex-direction: column;
效果图:
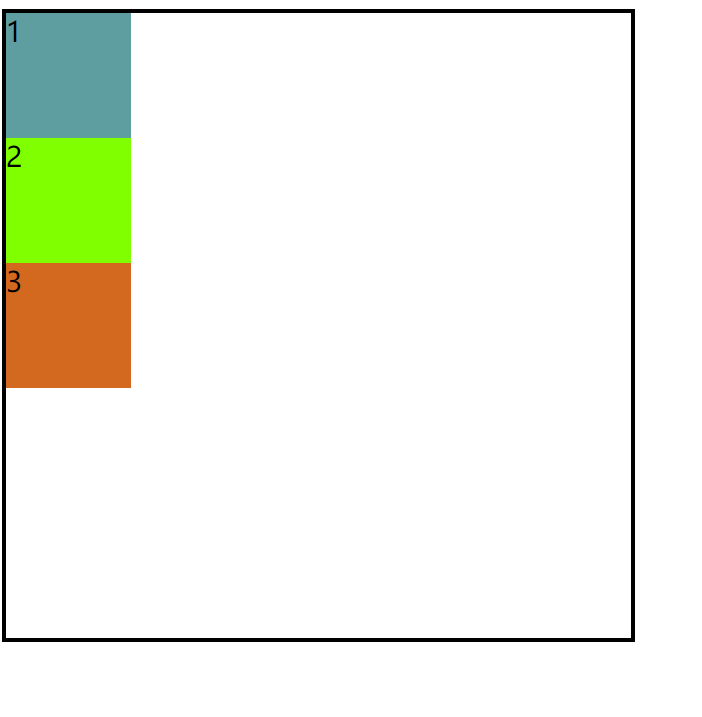
注意:这里我用的是块盒,默认变是垂直方向,并非没有效果
5.flex-direction:column-revers(主轴垂直反轴)
代码:
flex-direction: column-reverse;
效果图:
2.flex-wrap
flex-wrap: nowrap | wrap | wrap-reverse;
属性控制伸缩容器是单行还是多行,也就是换行与否。
nowrap (默认):不换行。
wrap :换行,第一行在上方。
wrap-reverse :换行,第一行在下方。
3.flex-flow
flex-flow: <flex-direction> || <flex-wrap>;
属性是 flex-direction 属性和 flex-wrap 属性的简写形式,默认值为
row nowrap 。
4.justify-content
justify-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between |
space-around | ;
注意:默认主轴是从左到右
flex-start (默认值):左对齐
flex-end :右对齐
center : 居中
space-between :两端对齐,项目之间的间隔都相等。
space-around :每个项目两侧的间隔相等。所以,项目之间的间隔
比项目与边框的间隔大一倍。
space-evenly:所有子项目之间间距等于父容器之间的间距,平均分配。
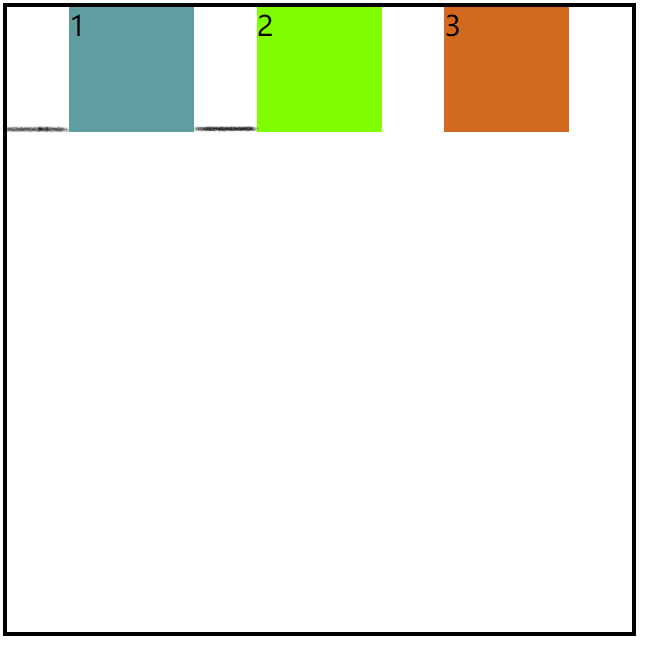
1.flex-end
代码:
section{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
font-size: 22px;
border:3px solid black;
display: flex; /* 在父级容器使用flex布局 */
/* flex-direction: column-reverse; */
justify-content:flex-end;/*注意数字*/
}
效果图:

注意:数字顺序
2.center
代码:
justify-content:center;
效果图:
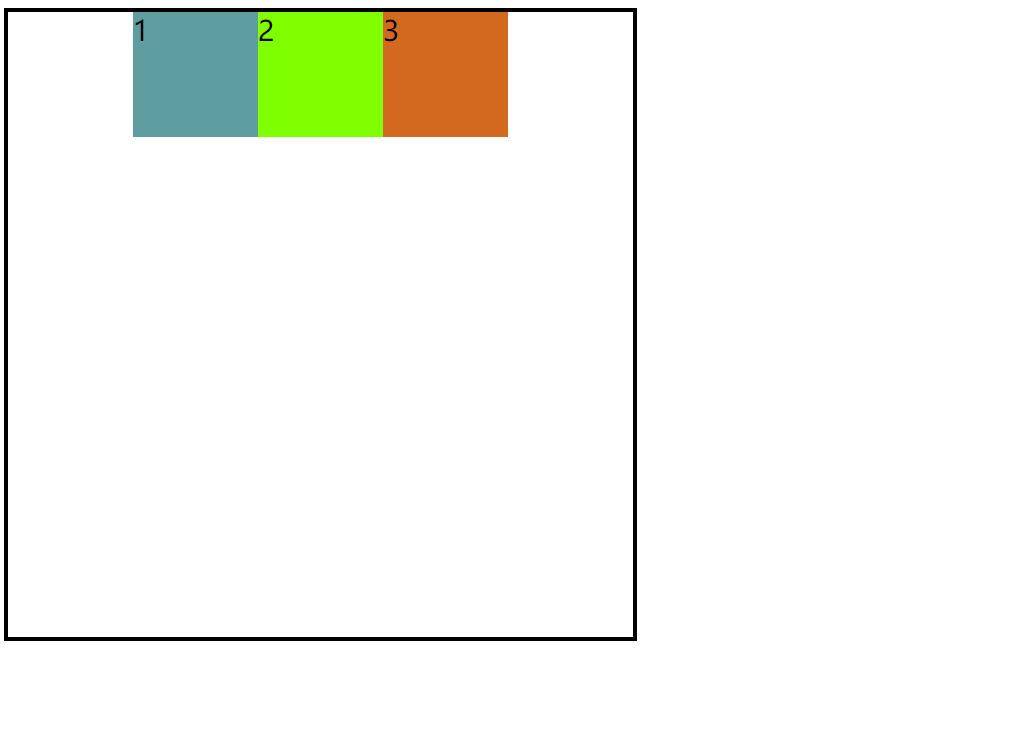
3.space-between(两端对齐)
代码
justify-content:center;
效果图:
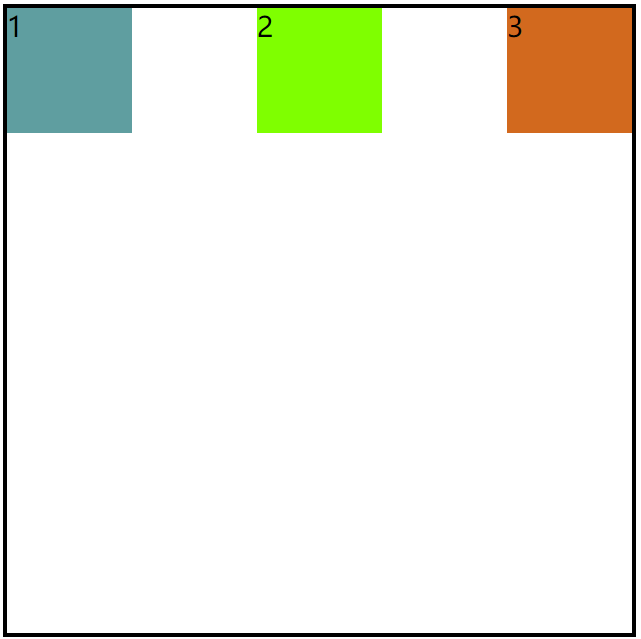
4.space-around
代码
justify-content:space-around;
效果图:

注意:如上图所视,子项目的间距,是它到父容器间距的两倍
5.space-evenly
代码:
justify-content:space-evenly;
效果图:

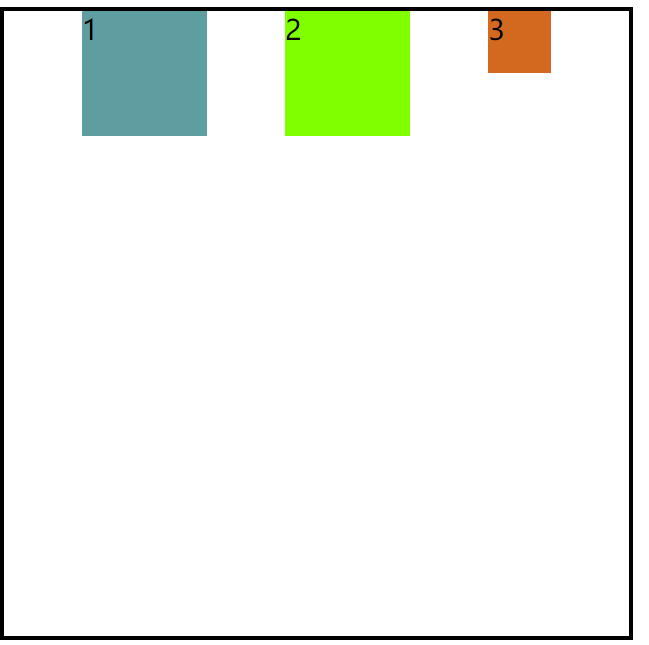
注意:space-evenly是平均分配剩余空间。
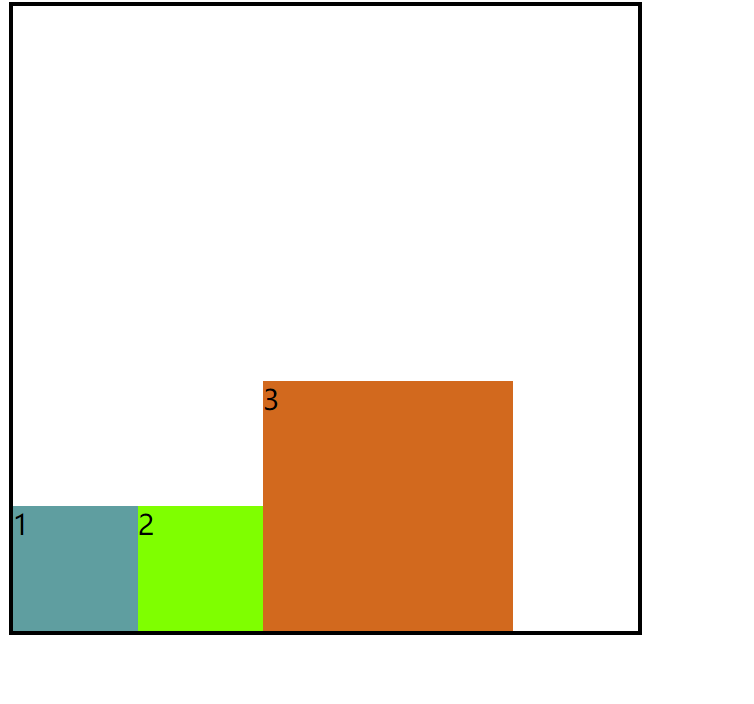
5.align-items
align-items: flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch;
flex-start :交叉轴的起点对齐。
flex-end :交叉轴的终点对齐。
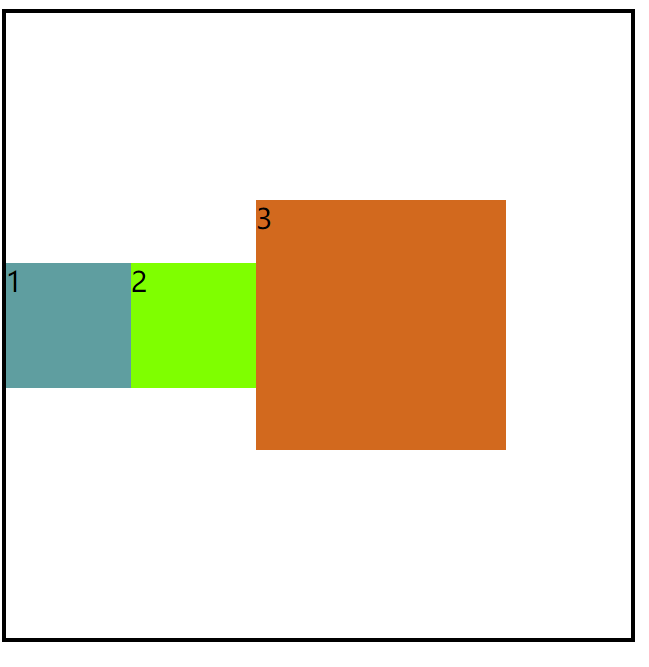
center :交叉轴的中点对齐。
baseline : 项目的第一行文字的基线对齐。
stretch (默认值):如果项目未设置高度或设为 auto ,将占满整个
容器的高度。
1.flex-end
效果图:
2.center
效果图:
3.baseline
代码:
.d1{
/* flex:1; */
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin-top: 60px;
background-color: cadetblue;
}
.d2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:chartreuse;
}
.d3{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
margin-top: 50px;
background-color: chocolate;
}
效果图:
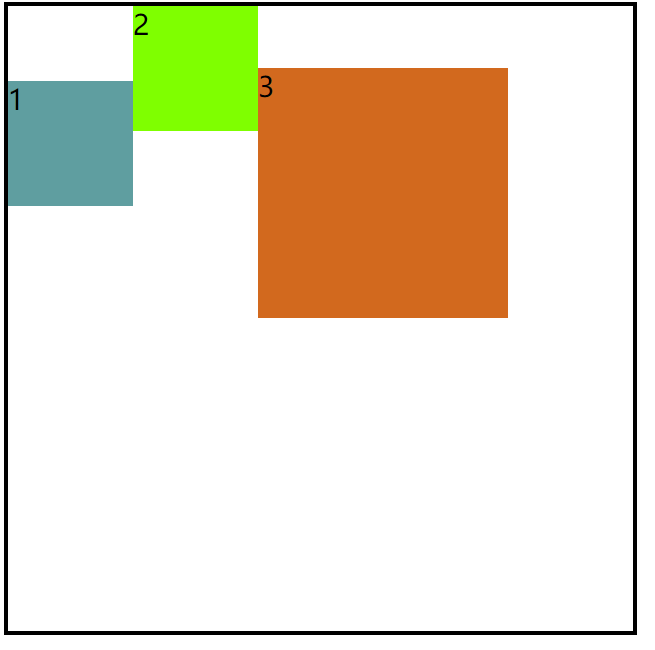
代码:
align-items: baseline;
使用baseline后的效果:
注意:他们是以第一行文字为基准
4.stretch
注意:在演示之前需要去掉三个div的宽高
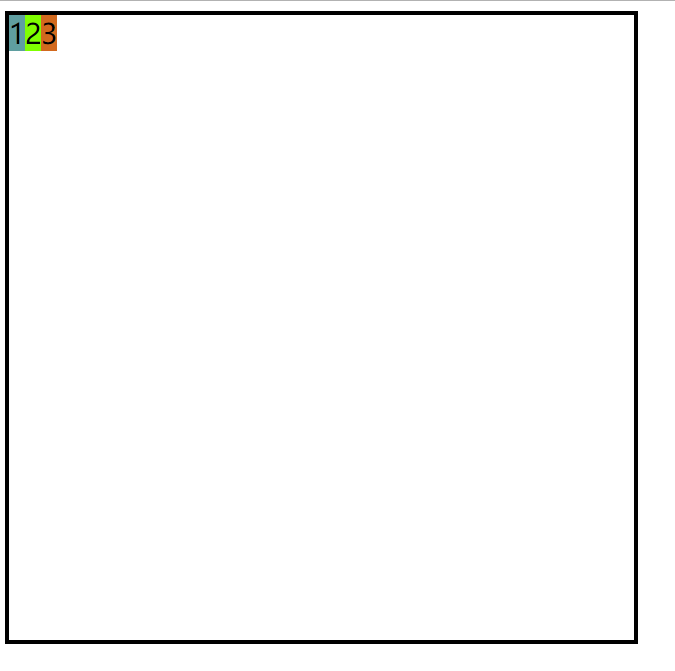
这时候的div默认为文字的宽高
接下来使用:
align-items: stretch;
效果图:
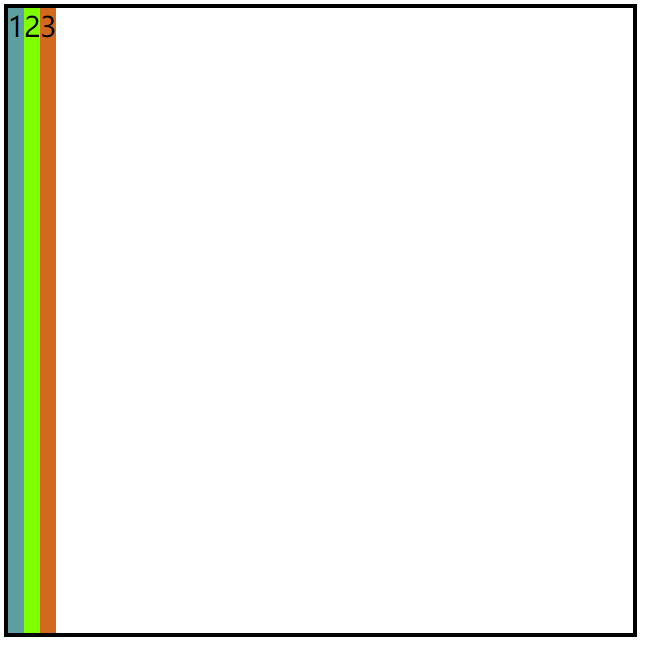
通常需要配合项目的东西来使用比如:flex:1;
.d1{
flex:1;
/* width: 100px;
height: 100px; */
/* margin-top: 60px; */
background-color: cadetblue;
}
.d2{
flex:1;
/* width: 100px;
height: 100px; */
background-color:chartreuse;
}
.d3{
flex:1;
/* width: 200px;
height: 200px; */
/* margin-top: 50px; */
background-color: chocolate;
}
就会变成这样:
如果这时候再将父容器的宽度注释掉
会变成什么样呢?
6.align-content
align-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between |
space-around | stretch;
flex-start :与交叉轴的起点对齐。
flex-end :与交叉轴的终点对齐。
center :与交叉轴的中点对齐。
space-between :与交叉轴两端对齐,轴线之间的间隔平均分布。
space-around :每根轴线两侧的间隔都相等。所以,轴线之间的
间隔比轴线与边框的间隔大一倍。
stretch (默认值):轴线占满整个交叉轴。
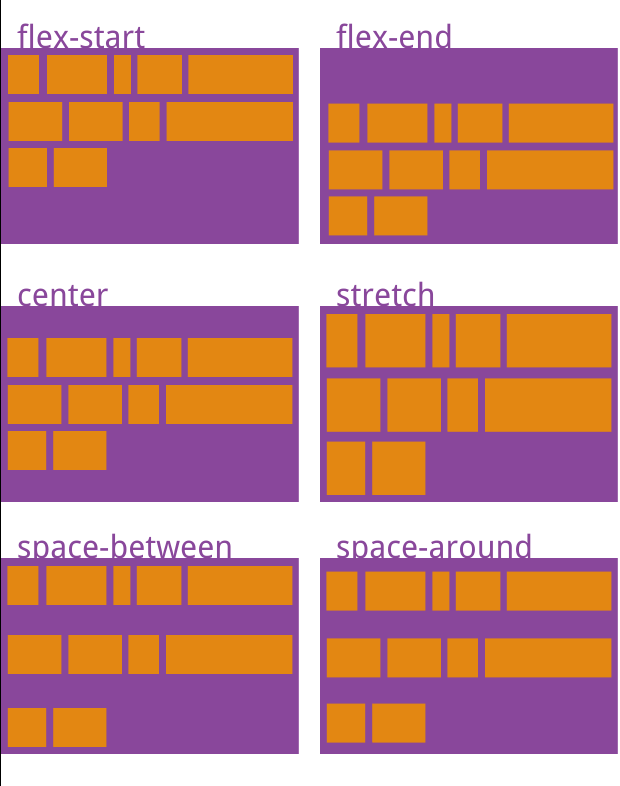
借了一张图,将就着看吧,这东西应该不常用,要用了看API文档就可以了……
今天就先写到容器这里吧~
最后
以上就是会撒娇大门最近收集整理的关于Flex Layout Box(弹性布局)容器属性的全部内容,更多相关Flex内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复