初次接触android的同学,最先接触的也就是android的布局了,因为android的代码与界面是分开的,因此想要界面显示什么,布局应该是第一步,就像一个孩子生下来你要给他穿衣服一样,因此,我们现在所写的布局就是你看到项目运行的界面。
LinearLayout是android五大布局之一,android还有RelativeLayout,FrameLayout,GridLayout,AbsoluteLayout(已过期),其实android开始支持一个布局,可能大家接触的比较少:百分比布局(这个稍后会分享)主要是为了适配而生的布局。LinearLayout是线性布局的控件,它相当于一个大容器,以后我们需要添加的一些控件比如说按钮之类的控件就要添加在它的里面,所谓的线性布局呢就是根据LinearLayout的一个属性来决定这个容器中所有的控件的排列顺序是横着排,还是竖着排。
LinearLayout的属性
- android:baselineAligned:是否允许用户调整它内容的基线。
- android:baselineAlignedChildIndex:当一个线性布局与另一个布局是按基线对齐的一部分,它可以指定其内容的基线对齐方式。
- android:gravity:指定如何在该对象中放置此对象的内容(x/y坐标值)。
- android:orientation:设置它内容的对其方向(横向/竖向)。
- gravity 这个英文单词是重心的意思,在这里就表示停靠位置的意思。
android:layout_gravity 和 android:gravity 的区别
从名字上可以看到,android:gravity是对元素本身说的,元素本身的文本显示在什么地方靠着换个属性设置,不过不设置默认是在左侧的。
android:layout_gravity是相对与它的父元素说的,说明元素显示在父元素的什么位置。
比如说button:android:layout_gravity 表示按钮在父控件上的位置。 android:gravity表示button上的字在button上的位置。
可选值
这两个属性可选的值有:top、bottom、left、right、center_vertical、fill_vertical、center_horizontal、fill_horizontal、center、fill、clip_vertical。
而且这些属性是可以多选的,用“|”分开。
Example 1:
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="48dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_dark"
//排列的顺序 horizontal:横向
vertical:纵向
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="button1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="button1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="button1"/>
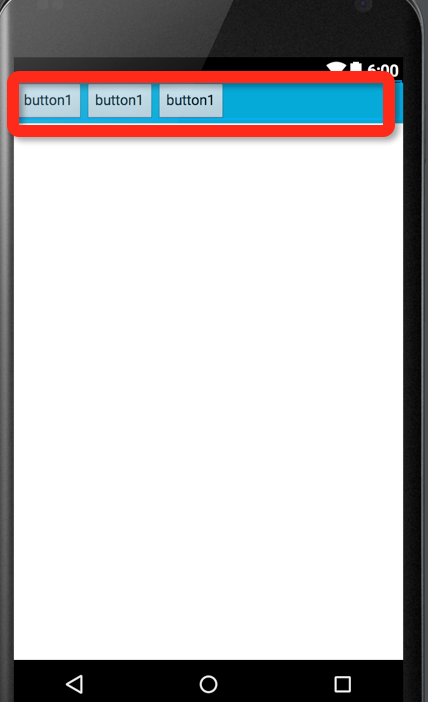
</LinearLayout>运行的结果:
像我们所预料的一样,这些button是打横排列的,可是有时候我们需要他们平分这些空白的位置,我们又该怎么做呢?
LinearLayout提供了这么一个方法,通常我们称它为权重。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_dark"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
//宽度设为0
android:layout_width="0dp"
//权重设为1
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:text="button1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:text="button1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:text="button1"/>
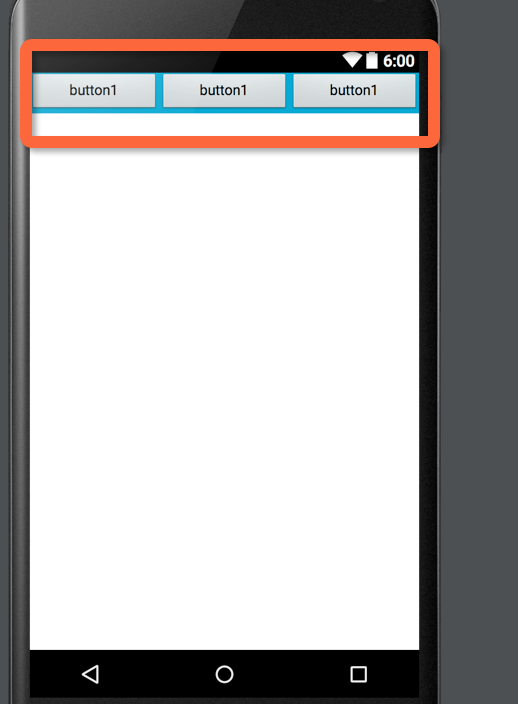
</LinearLayout>运行结果:
为什么这里的宽度要设为0呢?设成其他的数值是否可以呢?设成其他的数据,是否还能完成等分的效果呢?
LinearLayout的widget或者是container指定填充权值。好处就是允许其包含的widget或者是container可以填充屏幕上的剩余空间。这也避免了在一个大屏幕中,一串widgets或者是containers挤成一堆的情况,而是允许他们放大填充空白。剩余的空间会按这些widgets或者是containers指定的权值比例分配屏幕。
默认的 weight 值为0,表示按照widgets或者是containers实际大小来显示,若高于0的值,则将Container剩余可用空间分割,分割大小具体取决于每一个widget或者是container的layout_weight及该权值在所有widgets或者是containers中的比例。
例如,如果有三个文本框,其中两个指定的权值为1,那么,这两个文本框将等比例地放大,并填满剩余的空间,而第三个文本框不会放大,按实际大小来显示。如果前两个文本框的取值一个为2,一个为1,显示第三个文本框后剩余的空间的2/3给权值为2的,1/3大小给权值为1的。也就是权值越大,重要度越大。
如果LinearLayout包含子LinearLayout,子LinearLayout之间的权值越大的,重要度则越小。如果有LinearLayout A包含LinearLayout C,D,C的权值为2,D的权值为1,则屏幕的2/3空间分给权值为1的D,1/3分给权值为2的C。在LinearLayout嵌套的情况下,子LinearLayout必须要设置权值,否则默认的情况是未设置权值的子LinearLayout占据整个屏幕。
最后
以上就是迅速大侠最近收集整理的关于android五大布局之LinearLayout的全部内容,更多相关android五大布局之LinearLayout内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复