初步认识g2o的边
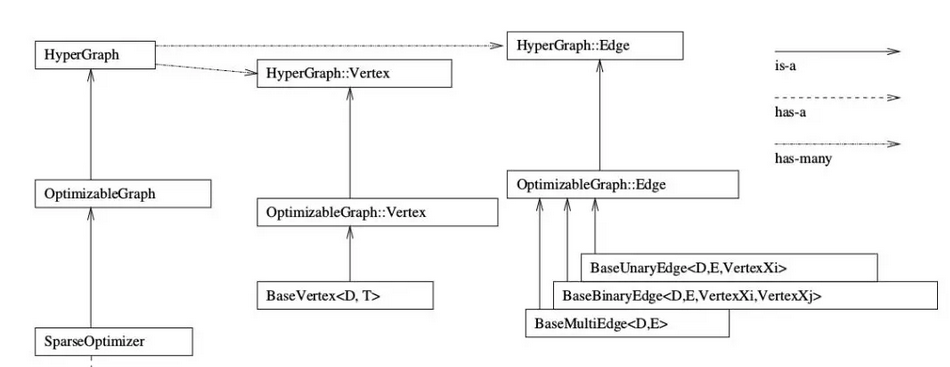 边的继承关系上图所示,对应的文件为:
边的继承关系上图所示,对应的文件为:
- g2o/g2o/core/hyper_graph.h
- g2o/g2o/core/optimizable_graph.h
- g2o/g2o/core/base_edge.h
BaseUnaryEdge,BaseBinaryE加粗样式dge,BaseMultiEdge 分别表示一元边,两元边,多元边。
一元边你可以理解为一条边只连接一个顶点,两元边理解为一条边连接两个顶点,也就是我们常见的边啦,多元边理解为一条边可以连接多个(3个以上)顶点
参数
主要就是 几个参数:D, E, VertexXi, VertexXj,他们的分别代表:
- D 是 int 型,表示测量值的维度 (dimension)
- E 表示测量值的数据类型
- VertexXi,VertexXj 分别表示不同顶点的类型
比如我们用边表示三维点投影到图像平面的重投影误差,就可以设置输入参数如下:
BaseBinaryEdge<2, Vector2D, VertexSBAPointXYZ, VertexSE3Expmap>
二元边。第1个2是说测量值是2维的,也就是图像像素坐标x,y的差值,对应测量值的类型是Vector2D,两个顶点也就是优化变量分别是空间点位置 VertexSBAPointXYZ,和李代数位姿VertexSE3Expmap
除了输入参数外,定义边我们通常需要复写一些重要的成员函数,顶点里主要复写了顶点更新函数oplusImpl和顶点重置函数setToOriginImpl
成员函数
virtual bool read(std::istream& is);
virtual bool write(std::ostream& os) const;
virtual void computeError();
virtual void linearizeOplus();
- read,write:分别是读盘、存盘函数,一般情况下不需要进行读/写操作的话,仅仅声明一下就可以
- computeError函数:非常重要,是使用当前顶点的值计算的测量值与真实的测量值之间的误差
- linearizeOplus函数:非常重要,是在当前顶点的值下,该误差对优化变量的偏导数,也就是我们说的Jacobian
除了上面几个成员函数,还有几个重要的成员变量和函数也一并解释一下:
_measurement:存储观测值
_error:存储computeError() 函数计算的误差
_vertices[]:存储顶点信息,比如二元边的话,_vertices[] 的大小为2,存储顺序和调用setVertex(int, vertex) 是设定的int 有关(0 或1)
setId(int):来定义边的编号(决定了在H矩阵中的位置)
setMeasurement(type) 函数来定义观测值
setVertex(int, vertex) 来定义顶点
setInformation() 来定义协方差矩阵的逆
定义g2o的边
模板如下,基本上定义g2o中的边,就是如下套路:
class myEdge: public g2o::BaseBinaryEdge<errorDim, errorType, Vertex1Type, Vertex2Type>
{
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
myEdge(){}
virtual bool read(istream& in) {}
virtual bool write(ostream& out) const {}
virtual void computeError() override
{
// ...
_error = _measurement - Something;
}
virtual void linearizeOplus() override
{
_jacobianOplusXi(pos, pos) = something;
// ...
/*
_jocobianOplusXj(pos, pos) = something;
...
*/
}
private:
// data
}
最重要的就是computeError(),linearizeOplus()两个函数了
eg1:
一元边,主要是定义误差函数
// 误差模型 模板参数:观测值维度,类型,连接顶点类型
class CurveFittingEdge: public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<1,double,CurveFittingVertex>
{
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
CurveFittingEdge( double x ): BaseUnaryEdge(), _x(x) {}
// 计算曲线模型误差
void computeError()
{
const CurveFittingVertex* v = static_cast<const CurveFittingVertex*> (_vertices[0]);
const Eigen::Vector3d abc = v->estimate();
_error(0,0) = _measurement - std::exp( abc(0,0)*_x*_x + abc(1,0)*_x + abc(2,0) ) ;
}
virtual bool read( istream& in ) {}
virtual bool write( ostream& out ) const {}
public:
double _x; // x 值, y 值为 _measurement
};
eg2:
二元边:3D-2D点的PnP 问题,也就是最小化重投影误差问题,。地址:g2o/types/sba/types_six_dof_expmap.h
//继承了BaseBinaryEdge类,观测值是2维,类型Vector2D,顶点分别是三维点、李群位姿
class G2O_TYPES_SBA_API EdgeProjectXYZ2UV : public BaseBinaryEdge<2, Vector2D, VertexSBAPointXYZ, VertexSE3Expmap>{
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
//1. 默认初始化
EdgeProjectXYZ2UV();
//2. 计算误差
void computeError() {
//李群相机位姿v1
const VertexSE3Expmap* v1 = static_cast<const VertexSE3Expmap*>(_vertices[1]);
// 顶点v2
const VertexSBAPointXYZ* v2 = static_cast<const VertexSBAPointXYZ*>(_vertices[0]);
//相机参数
const CameraParameters * cam
= static_cast<const CameraParameters *>(parameter(0));
//误差计算,测量值减去估计值,也就是重投影误差obs-cam
//估计值计算方法是T*p,得到相机坐标系下坐标,然后在利用camera2pixel()函数得到像素坐标。
Vector2D obs(_measurement);
_error = obs-cam->cam_map(v1->estimate().map(v2->estimate()));
}
//3. 线性增量函数,也就是雅克比矩阵J的计算方法
virtual void linearizeOplus();
//4. 相机参数
CameraParameters * _cam;
bool read(std::istream& is);
bool write(std::ostream& os) const;
};
cam_map 函数功能是把相机坐标系下三维点(输入)用内参转换为图像坐标(输出),函数在g2o/types/sba/types_six_dof_expmap.cpp,具体代码如下所示:
Vector2 CameraParameters::cam_map(const Vector3 & trans_xyz) const {
Vector2 proj = project2d(trans_xyz);
Vector2 res;
res[0] = proj[0]*focal_length + principle_point[0];
res[1] = proj[1]*focal_length + principle_point[1];
return res;
}
.map函数,它的功能是把世界坐标系下三维点变换到相机坐标系,函数在g2o/types/sim3/sim3.h
Vector3 map (const Vector3& xyz) const {
return s*(r*xyz) + t;
}
观测相机方程关于相机位姿与特征点的两个导数矩阵
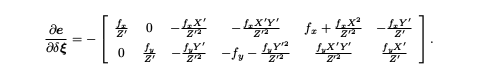
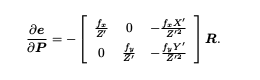
EdgeProjectXYZ2UV 的 linearizeOplus 函数
void EdgeProjectXYZ2UV::linearizeOplus() {
VertexSE3Expmap * vj = static_cast<VertexSE3Expmap *>(_vertices[1]);
SE3Quat T(vj->estimate());
VertexSBAPointXYZ* vi = static_cast<VertexSBAPointXYZ*>(_vertices[0]);
Vector3D xyz = vi->estimate();
Vector3D xyz_trans = T.map(xyz);
double x = xyz_trans[0];
double y = xyz_trans[1];
double z = xyz_trans[2];
double z_2 = z*z;
const CameraParameters * cam = static_cast<const CameraParameters *>(parameter(0));
Matrix<double,2,3,Eigen::ColMajor> tmp;
tmp(0,0) = cam->focal_length;
tmp(0,1) = 0;
tmp(0,2) = -x/z*cam->focal_length;
tmp(1,0) = 0;
tmp(1,1) = cam->focal_length;
tmp(1,2) = -y/z*cam->focal_length;
_jacobianOplusXi = -1./z * tmp * T.rotation().toRotationMatrix();
_jacobianOplusXj(0,0) = x*y/z_2 *cam->focal_length;
_jacobianOplusXj(0,1) = -(1+(x*x/z_2)) *cam->focal_length;
_jacobianOplusXj(0,2) = y/z *cam->focal_length;
_jacobianOplusXj(0,3) = -1./z *cam->focal_length;
_jacobianOplusXj(0,4) = 0;
_jacobianOplusXj(0,5) = x/z_2 *cam->focal_length;
_jacobianOplusXj(1,0) = (1+y*y/z_2) *cam->focal_length;
_jacobianOplusXj(1,1) = -x*y/z_2 *cam->focal_length;
_jacobianOplusXj(1,2) = -x/z *cam->focal_length;
_jacobianOplusXj(1,3) = 0;
_jacobianOplusXj(1,4) = -1./z *cam->focal_length;
_jacobianOplusXj(1,5) = y/z_2 *cam->focal_length;
}
向图中添加边
eg1:
曲线拟合的例子
// 往图中增加边
for ( int i=0; i<N; i++ )
{
CurveFittingEdge* edge = new CurveFittingEdge( x_data[i] );
edge->setId(i);
edge->setVertex( 0, v ); // 设置连接的顶点
edge->setMeasurement( y_data[i] ); // 观测数值
edge->setInformation( Eigen::Matrix<double,1,1>::Identity()*1/(w_sigma*w_sigma) ); // 信息矩阵:协方差矩阵之逆
optimizer.addEdge( edge );
}
eg2:
slambook/ch7/pose_estimation_3d2d.cpp
index = 1;
for ( const Point2f p:points_2d )
{
g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV* edge = new g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV();
edge->setId ( index );
edge->setVertex ( 0, dynamic_cast<g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ*> ( optimizer.vertex ( index ) ) );
edge->setVertex ( 1, pose );
edge->setMeasurement ( Eigen::Vector2d ( p.x, p.y ) );
edge->setParameterId ( 0,0 );
edge->setInformation ( Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity() );
optimizer.addEdge ( edge );
index++;
}
setVertex 定义顶点,有两个
- 一个是 0 和 VertexSBAPointXYZ 类型的顶点
- 一个是1 和pose
setVertex在g2o官网的定义:
// set the ith vertex on the hyper-edge to the pointer supplied
void setVertex(size_t i, Vertex* v) { assert(i < _vertices.size() && "index out of bounds"); _vertices[i]=v;}
_vertices[i] 里的i就是我们这里的0和1,再看看这里边的类型: g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV
的定义
class G2O_TYPES_SBA_API EdgeProjectXYZ2UV
.....
//李群相机位姿v1
const VertexSE3Expmap* v1 = static_cast<const VertexSE3Expmap*>(_vertices[1]);
// 顶点v2
const VertexSBAPointXYZ* v2 = static_cast<const VertexSBAPointXYZ*>(_vertices[0]);
_vertices[0] 对应的是 VertexSBAPointXYZ 类型的顶点,也就是三维点,_vertices[1] 对应的是VertexSE3Expmap 类型的顶点,也就是位姿pose。
实践.
题目:用直接法Bundle Adjustment 估计相机位姿。给定3张图片,两个txt文件
- poses.txt中存储3张图片对应的相机初始位姿(Tcw),格式为:timestamp, tx, ty, tz, qx, qy, qz, qw ,分别对应时间戳、平移、旋转(四元数)-
- points.txt中存储的是3D点集合以及该点周围 4x4 窗口的灰度值,记做 I§i,格式为:x, y, z, 灰度1,灰度2…,灰度16
我们把每个3D点投影到对应图像中,用投影后点周围的灰度值与原始窗口的灰度值差异作为待优化误差。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_binary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/dense/linear_solver_dense.h>
#include <g2o/core/robust_kernel.h>
#include <g2o/core/robust_kernel_impl.h>
#include <g2o/types/sba/types_six_dof_expmap.h>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <sophus/se3.h>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <pangolin/pangolin.h>
#include <boost/format.hpp>
using namespace Sophus;
using namespace pangolin;
using namespace g2o;
#define DEBUG false
typedef vector<Sophus::SE3, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Sophus::SE3>> VecSE3;
typedef vector<Eigen::Vector3d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Vector3d>> VecVec3d;
// global variables
string pose_file = "/home/xiaohu/learn_SLAM/zuoye18/练习18-g2o边代码框架/poses.txt";
string points_file = "/home/xiaohu/learn_SLAM/zuoye18/练习18-g2o边代码框架/points.txt";
// intrinsics
float fx = 277.34;
float fy = 291.402;
float cx = 312.234;
float cy = 239.777;
inline bool bInImage(float u, float v, int w, int h)
{
if(u>=0 && u<w && v>=0 && v<h)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// bilinear interpolation
inline float GetPixelValue(const cv::Mat &img, float x, float y) {
uchar *data = &img.data[int(y) * img.step + int(x)];
float xx = x - floor(x);
float yy = y - floor(y);
return float(
(1 - xx) * (1 - yy) * data[0] +
xx * (1 - yy) * data[1] +
(1 - xx) * yy * data[img.step] +
xx * yy * data[img.step + 1]
);
}
// g2o vertex that use sophus::SE3 as pose
class VertexSophus : public g2o::BaseVertex<6, Sophus::SE3> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
VertexSophus() {}
~VertexSophus() {}
bool read(std::istream &is) {}
bool write(std::ostream &os) const {}
virtual void setToOriginImpl() {
_estimate = Sophus::SE3();
}
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update_) {
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1>> update(update_);
setEstimate(Sophus::SE3::exp(update) * estimate());
}
};
// TODO edge of projection error, implement it
// 16x1 error, which is the errors in patch
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double,16,1> Vector16d;
class EdgeDirectProjection : public g2o::BaseBinaryEdge<16, Vector16d, g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ, VertexSophus> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
EdgeDirectProjection(float *color, cv::Mat &target) {
this->origColor = color;
this->targetImg = target;
this->w = targetImg.cols;
this->h = targetImg.rows;
}
~EdgeDirectProjection() {}
virtual void computeError() override {
// ---------------- 开始你的代码 ----------------------//
// 参考十四讲中直接法BA部分
// 空间点
const VertexSBAPointXYZ* vertexPw = static_cast<const VertexSBAPointXYZ* >(vertex(0));
//李群相机位姿
const VertexSophus* vertexTcw = static_cast<const VertexSophus* >(vertex(1));
Vector3d Pc = vertexTcw->estimate() * vertexPw->estimate();
float u = Pc[0]/Pc[2] * fx + cx;
float v = Pc[1]/Pc[2] * fy + cy;
if(!bInImage(u-3,v-3,w,h) || !bInImage(u+2,v+2,w,h)) {
this->setLevel(1);
for(int n=0;n<16;n++)
_error[n] = 0;
} else {
for(int i = -2; i<2; i++) {
for(int j = -2; j<2; j++) {
int num = 4 * i + j + 10;
_error[num] = origColor[num] - GetPixelValue(targetImg, u+i, v+j);
}
}
}
// ---------------- 结束你的代码 ----------------------//
}
// 下面函数不用自己写了,但是要能看懂
virtual void linearizeOplus() override
{
if(level()==1)
{
_jacobianOplusXi = Matrix<double,16,3>::Zero();
_jacobianOplusXj = Matrix<double,16,6>::Zero();
return;
}
const VertexSBAPointXYZ* vertexPw = static_cast<const VertexSBAPointXYZ* >(vertex(0));
const VertexSophus* vertexTcw = static_cast<const VertexSophus* >(vertex(1));
Vector3d Pc = vertexTcw->estimate() * vertexPw->estimate();
float x = Pc[0];
float y = Pc[1];
float z = Pc[2];
float inv_z = 1.0/z;
float inv_z2 = inv_z * inv_z;
float u = x * inv_z * fx + cx;
float v = y * inv_z * fy + cy;
Matrix<double,2,3> J_Puv_Pc;
J_Puv_Pc(0,0) = fx * inv_z;
J_Puv_Pc(0,1) = 0;
J_Puv_Pc(0,2) = -fx * x * inv_z2;
J_Puv_Pc(1,0) = 0;
J_Puv_Pc(1,1) = fy * inv_z;
J_Puv_Pc(1,2) = -fy * y * inv_z2;
Matrix<double,3,6> J_Pc_kesi = Matrix<double,3,6>::Zero();
J_Pc_kesi(0,0) = 1;
J_Pc_kesi(0,4) = z;
J_Pc_kesi(0,5) = -y;
J_Pc_kesi(1,1) = 1;
J_Pc_kesi(1,3) = -z;
J_Pc_kesi(1,5) = x;
J_Pc_kesi(2,2) = 1;
J_Pc_kesi(2,3) = y;
J_Pc_kesi(2,4) = -x;
Matrix<double,1,2> J_I_Puv;
for(int i = -2; i<2; i++)
for(int j = -2; j<2; j++) {
int num = 4 * i + j + 10;
J_I_Puv(0,0) = (GetPixelValue(targetImg,u+i+1,v+j) - GetPixelValue(targetImg,u+i-1,v+j))/2;
J_I_Puv(0,1) = (GetPixelValue(targetImg,u+i,v+j+1) - GetPixelValue(targetImg,u+i,v+j-1))/2;
_jacobianOplusXi.block<1,3>(num,0) = -J_I_Puv * J_Puv_Pc * vertexTcw->estimate().rotation_matrix();
_jacobianOplusXj.block<1,6>(num,0) = -J_I_Puv * J_Puv_Pc * J_Pc_kesi;
}
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {}
private:
cv::Mat targetImg; // the target image
float *origColor = nullptr; // 16 floats, the color of this point
int w;
int h;
};
// plot the poses and points for you, need pangolin
void Draw(const VecSE3 &poses, const VecVec3d &points);
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
// read poses and points
VecSE3 poses;
VecVec3d points;
ifstream fin(pose_file);
while (!fin.eof()) {
double timestamp = 0;
fin >> timestamp;
if (timestamp == 0) break;
double data[7];
for (auto &d: data) fin >> d;
poses.push_back(Sophus::SE3(
Eigen::Quaterniond(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]),
Eigen::Vector3d(data[0], data[1], data[2])
));
if (!fin.good()) break;
}
fin.close();
vector<float *> color;
fin.open(points_file);
while (!fin.eof()) {
double xyz[3] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) fin >> xyz[i];
if (xyz[0] == 0) break;
points.push_back(Eigen::Vector3d(xyz[0], xyz[1], xyz[2]));
float *c = new float[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) fin >> c[i];
color.push_back(c);
if (fin.good() == false) break;
}
fin.close();
cout << "poses: " << poses.size() << ", points: " << points.size() << ", color: "<<color.size()<<endl;
// read images
vector<cv::Mat> images;
boost::format fmt("../%d.png");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
images.push_back(cv::imread((fmt % i).str(), 0));
}
cout<<"images: "<<images.size()<<endl;
// typedef g2o::BlockSolver< g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6,3> > Block; // pose 维度为 6, landmark 维度为 3
// // 第1步:创建一个线性求解器LinearSolver
// Block::LinearSolverType* linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverDense<Block::PoseMatrixType>();
//
// // 第2步:创建BlockSolver。并用上面定义的线性求解器初始化
// Block* solver_ptr = new Block ( std::unique_ptr<Block::LinearSolverType>(linearSolver) );
//
// // 第3步:创建总求解器solver。并从GN, LM, DogLeg 中选一个,再用上述块求解器BlockSolver初始化
// g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg ( std::unique_ptr<Block>(solver_ptr) );
//
// // 第4步:创建稀疏优化器
// g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;
// optimizer.setAlgorithm ( solver );
// old g2o version
typedef g2o::BlockSolver< g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6,3> > Block; // pose 维度为 6, landmark 维度为 3
Block::LinearSolverType* linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverDense<Block::PoseMatrixType>(); // 线性方程求解器
Block* solver_ptr = new Block ( linearSolver ); // 矩阵块求解器
g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg ( solver_ptr );
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;
optimizer.setAlgorithm ( solver );
// 第5步:添加顶点和边
// ---------------- 开始你的代码 ----------------------//
for(int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {
VertexSBAPointXYZ* vertexPw = new VertexSBAPointXYZ();
vertexPw->setEstimate(points[i]);
vertexPw->setId(i);
vertexPw->setMarginalized(true);
optimizer.addVertex(vertexPw);
}
for(int j = 0; j < poses.size(); j++) {
VertexSophus* vertexTcw = new VertexSophus();
vertexTcw->setEstimate(poses[j]);
vertexTcw->setId(j + points.size());
optimizer.addVertex(vertexTcw);
}
for(int c = 0; c < poses.size(); c++)
for(int p = 0; p < points.size(); p++) {
EdgeDirectProjection* edge = new EdgeDirectProjection(color[p],images[c]);
edge->setVertex(0,dynamic_cast<VertexSBAPointXYZ*>(optimizer.vertex(p)));
edge->setVertex(1,dynamic_cast<VertexSophus*>(optimizer.vertex(c + points.size())));
edge->setInformation(Matrix<double,16,16>::Identity());
RobustKernelHuber* rk = new RobustKernelHuber;
rk->setDelta(1.0);
edge->setRobustKernel(rk);
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
}
// ---------------- 结束你的代码 ----------------------//
// 第6步:执行优化
optimizer.initializeOptimization(0);
optimizer.optimize(200);
// 从optimizer中获取结果
for(int c = 0; c < poses.size(); c++)
for(int p = 0; p < points.size(); p++) {
Vector3d Pw = dynamic_cast<VertexSBAPointXYZ*>(optimizer.vertex(p))->estimate();
points[p] = Pw;
SE3 Tcw = dynamic_cast<VertexSophus*>(optimizer.vertex(c + points.size()))->estimate();
poses[c] = Tcw;
}
// plot the optimized points and poses
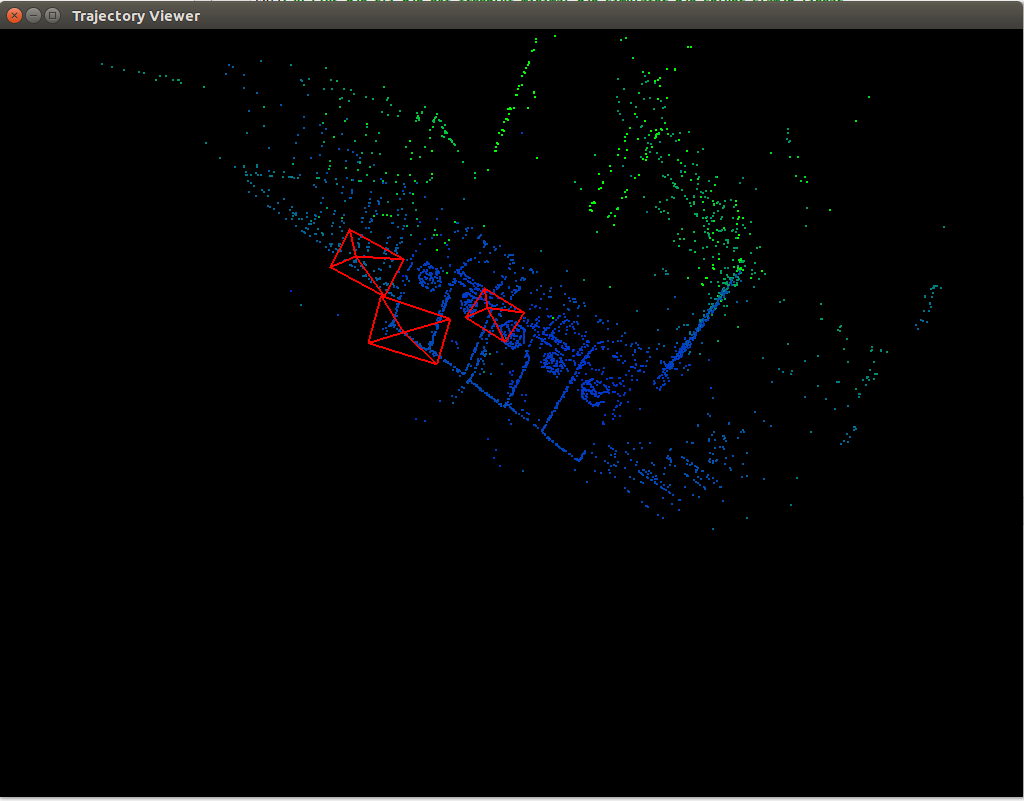
Draw(poses, points);
// delete color data
for (auto &c: color) delete[] c;
return 0;
}
// 画图函数,无需关注
void Draw(const VecSE3 &poses, const VecVec3d &points) {
if (poses.empty() || points.empty()) {
cerr << "parameter is empty!" << endl;
return;
}
cout<<"Draw poses: "<<poses.size()<<", points: "<<points.size()<<endl;
// create pangolin window and plot the trajectory
pangolin::CreateWindowAndBind("Trajectory Viewer", 1024, 768);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glEnable(GL_BLEND);
glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
pangolin::OpenGlRenderState s_cam(
pangolin::ProjectionMatrix(1024, 768, 500, 500, 512, 389, 0.1, 1000),
pangolin::ModelViewLookAt(0, -0.1, -1.8, 0, 0, 0, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0)
);
pangolin::View &d_cam = pangolin::CreateDisplay()
.SetBounds(0.0, 1.0, pangolin::Attach::Pix(175), 1.0, -1024.0f / 768.0f)
.SetHandler(new pangolin::Handler3D(s_cam));
while (pangolin::ShouldQuit() == false) {
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
d_cam.Activate(s_cam);
glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
// draw poses
float sz = 0.1;
int width = 640, height = 480;
for (auto &Tcw: poses) {
glPushMatrix();
Sophus::Matrix4f m = Tcw.inverse().matrix().cast<float>();
glMultMatrixf((GLfloat *) m.data());
glColor3f(1, 0, 0);
glLineWidth(2);
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glVertex3f(0, 0, 0);
glVertex3f(sz * (0 - cx) / fx, sz * (0 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(0, 0, 0);
glVertex3f(sz * (0 - cx) / fx, sz * (height - 1 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(0, 0, 0);
glVertex3f(sz * (width - 1 - cx) / fx, sz * (height - 1 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(0, 0, 0);
glVertex3f(sz * (width - 1 - cx) / fx, sz * (0 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (width - 1 - cx) / fx, sz * (0 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (width - 1 - cx) / fx, sz * (height - 1 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (width - 1 - cx) / fx, sz * (height - 1 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (0 - cx) / fx, sz * (height - 1 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (0 - cx) / fx, sz * (height - 1 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (0 - cx) / fx, sz * (0 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (0 - cx) / fx, sz * (0 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (width - 1 - cx) / fx, sz * (0 - cy) / fy, sz);
glEnd();
glPopMatrix();
}
// points
glPointSize(2);
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
for (size_t i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {
glColor3f(0.0, points[i][2]/4, 1.0-points[i][2]/4);
glVertex3d(points[i][0], points[i][1], points[i][2]);
}
glEnd();
pangolin::FinishFrame();
usleep(5000); // sleep 5 ms
}
}
最后
以上就是稳重羽毛最近收集整理的关于SLAM——入门到放弃:g2o定义边初步认识g2o的边定义g2o的边向图中添加边实践.的全部内容,更多相关SLAM——入门到放弃:g2o定义边初步认识g2o内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复