Android 界一直流传着一句话,想学习Service, 那么你就要写一个音乐播放器。
为什么要用 Service?
Service 是运行于幕后的,它并不轻易见人,而正巧,音乐也是只闻其声不见其人的,相信这就是它们在一起的原因。
大家都知道,从Activity中跟Service交互有两种方式:
1)startService。在Activity 中直接调用 startService的方法,我们就可以在后台看不见的地方(但还是在同一个进程里)创建一个叫Service 的东西,它能够在后面静悄悄地执行类似下载的任务,也能够热热闹闹地唱起“苍茫的天涯是你的爱...”,但是这种方式呢,我们就只能跟它说,“Service,做这件事吧”,而没办法在它做一半的时候跟它说,“Service,别做这事了,做那一件事吧”(其实也可以,但是每次都要重新创建一个Intent,里面定义我们要做的事情,然后再次调用startService,让它重新再做,但我觉得,这不科学)。
2)bindService。我们也可以通过 bindService的方法来将Activity 跟 Service 绑定在一起,为什么绑定Service了之后就能够随时叫Service做事了呢?因为通过绑定,从Service返回了一个继承于Binder的类给Activity,而通过这个继承类,可以在里面定义一些交互的回调函数,那么Activity就可以通过这些方法来随时告诉Service要做些啥事了,这才叫交互嘛。
那么,音乐播放器肯定是要用后面这种 bindService的方法了啊,因为我们要交互啊。先看一下界面:
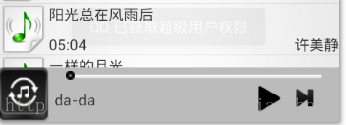
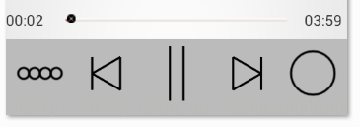
在列表界面上和歌词界面上有着不同的控制按钮,比如向前向后,模式改变,播放暂停等,所以我们得想想怎么去设计Service。
如何设计Service?
class NatureBinder extends Binder{
/**
* 唱吧,有人想听
*/
public void startPlay(int currentMusic, int currentPosition){}
/**
* 别唱了
*/
public void stopPlay(){}
/**
* 后一首
*/
public void toNext(){}
/**
* 前一首
*/
public void toPrevious(){}
/**
* 有人改变模式了,我得把它记下来
*/
public void changeMode(){}
/**
* 告诉别人,你现在到底是顺序播放,还是随机乱弹
* MODE_ONE_LOOP = 1;
* MODE_ALL_LOOP = 2;
* MODE_RANDOM = 3;
* MODE_SEQUENCE = 4;
* @return
*/
public int getCurrentMode(){}
/**
* 告诉调用者,到底有没有在做事。。。
* @return
*/
public boolean isPlaying(){}
/**
* 要告诉调用者,当前播哪首歌了,歌多长啊
*/
public void notifyActivity(){}
/**
* 有人拖动Seekbar了,要告诉service去改变播放的位置
* @param progress
*/
public void changeProgress(int progress){}
}mediaPlayer.setOnCompletionListener(new OnCompletionListener() {
@Override
public void onCompletion(MediaPlayer mp) {
...
});
}private void toUpdateProgress(){
if(mediaPlayer != null && isPlaying){
int progress = mediaPlayer.getCurrentPosition();
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(ACTION_UPDATE_PROGRESS);
intent.putExtra(ACTION_UPDATE_PROGRESS,progress);
sendBroadcast(intent);
handler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(updateProgress, 1000);
}
}
而相对应的,我们在Activity中,会接收到这样的广播,从而做相应的更新,当然,也别忘了要注册对应的Action,不然可收不到。代码如下:
private void registerReceiver(){
progressReceiver = new ProgressReceiver();
IntentFilter intentFilter = new IntentFilter();
intentFilter.addAction(NatureService.ACTION_UPDATE_PROGRESS);
...
registerReceiver(progressReceiver, intentFilter);
}
//上面是注册广播,下面是接收广播,最后别忘了,要注销广播
...
class ProgressReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver{
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String action = intent.getAction();
if(NatureService.ACTION_UPDATE_PROGRESS.equals(action)){
int progress = intent.getIntExtra(NatureService.ACTION_UPDATE_PROGRESS, 0);
if(progress > 0){
currentPosition = progress; // Remember the current position
pbDuration.setProgress(progress / 1000);
}
...
}
}Service该怎么用?
private NatureBinder natureBinder;
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
natureBinder = (NatureBinder) service;
}
};
private void connectToNatureService(){
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, NatureService.class);
bindService(intent, serviceConnection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
当然,也是有几步要走的:
natureBinder.startPlay(currentMusic,currentPosition);natureBinder.stopPlay();natureBinder.toNext();最后
以上就是过时硬币最近收集整理的关于Android 音乐播放器的实现(三)Service的实现为什么要用 Service?如何设计Service?Service该怎么用?的全部内容,更多相关Android内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复