神经网络架构搜索——可微分搜索(SGAS)
- 动机
- 方法
- 整体思路
- 三个指标
- 边的重要性
- 选择的准确性
- 选择的稳定性
- 两种评估准则
- 评估准则1:
- 评估准则2:
- 实验结果
- CIFAR-10(CNN)
- ImageNet(CNN)
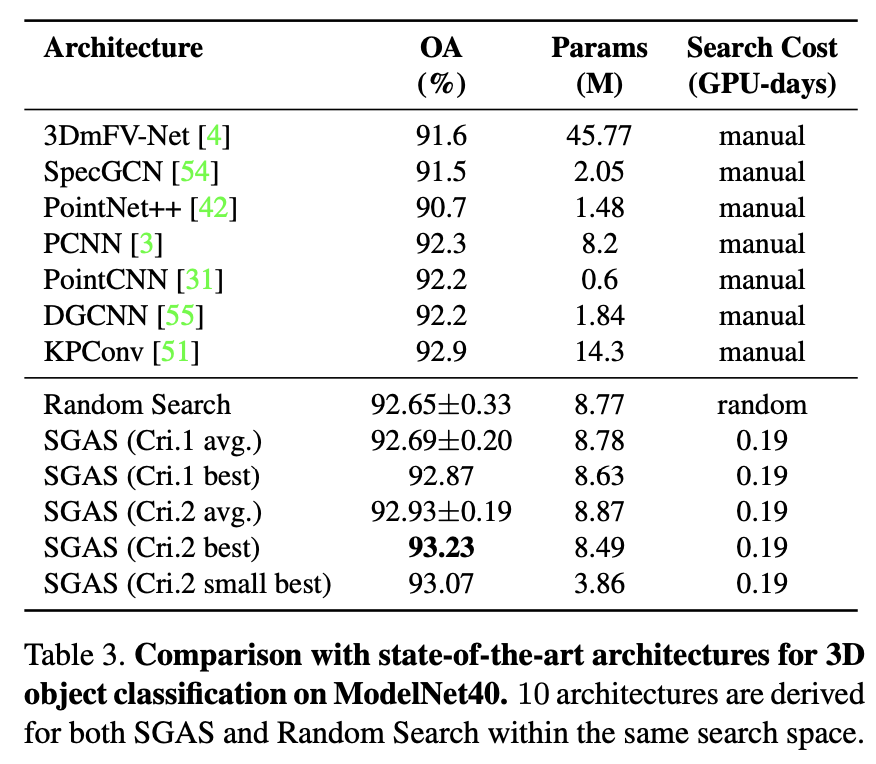
- ModelNet40(GCN)
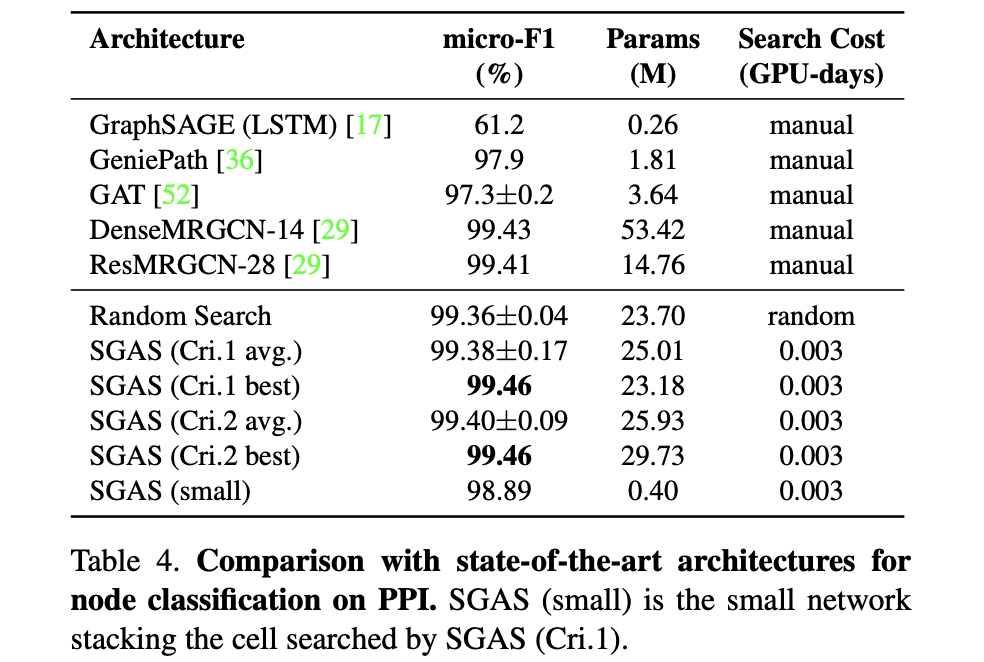
- PPI(GCN)
- 参考
KAUST&Intel发表在CVPR 2020上的NAS工作,针对现有DARTS框架在搜索阶段具有高验证集准确率的架构可能在评估阶段表现不好的问题,提出了分解神经网络架构搜索过程为一系列子问题,SGAS使用贪婪策略选择并剪枝候选操作的技术,在搜索CNN和GCN网络架构均达到了SOTA。
- Paper: SGAS: Sequential Greedy Architecture Search
- Code: https://github.com/lightaime/sgas
动机
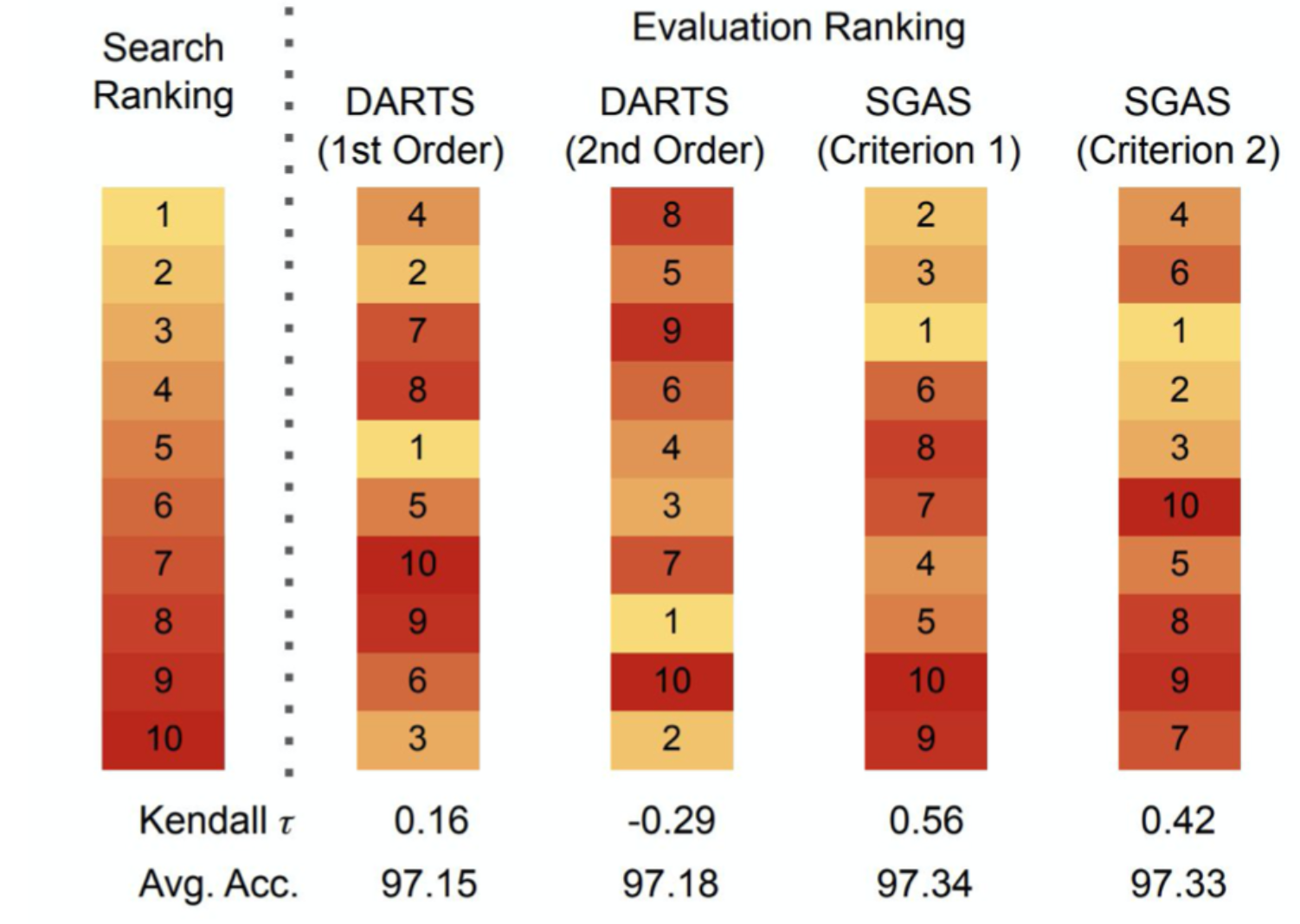
NAS技术都有一个通病:在搜索过程中验证精度较高,但是在实际测试精度却没有那么高。传统的基于梯度搜索的DARTS技术,是根据block构建更大的超网,由于搜索的过程中验证不充分,最终eval和test精度会出现鸿沟。从下图的Kendall系数来看,DARTS搜出的网络精度排名和实际训练完成的精度排名偏差还是比较大。
方法
整体思路
本文使用与DARTS相同的搜索空间,SGAS搜索过程简单易懂,如下图所示。类似DARTS搜索过程为每条边指定参数α,超网训练时通过文中判定规则逐渐确定每条边的具体操作,搜索结束后即可得到最终模型。
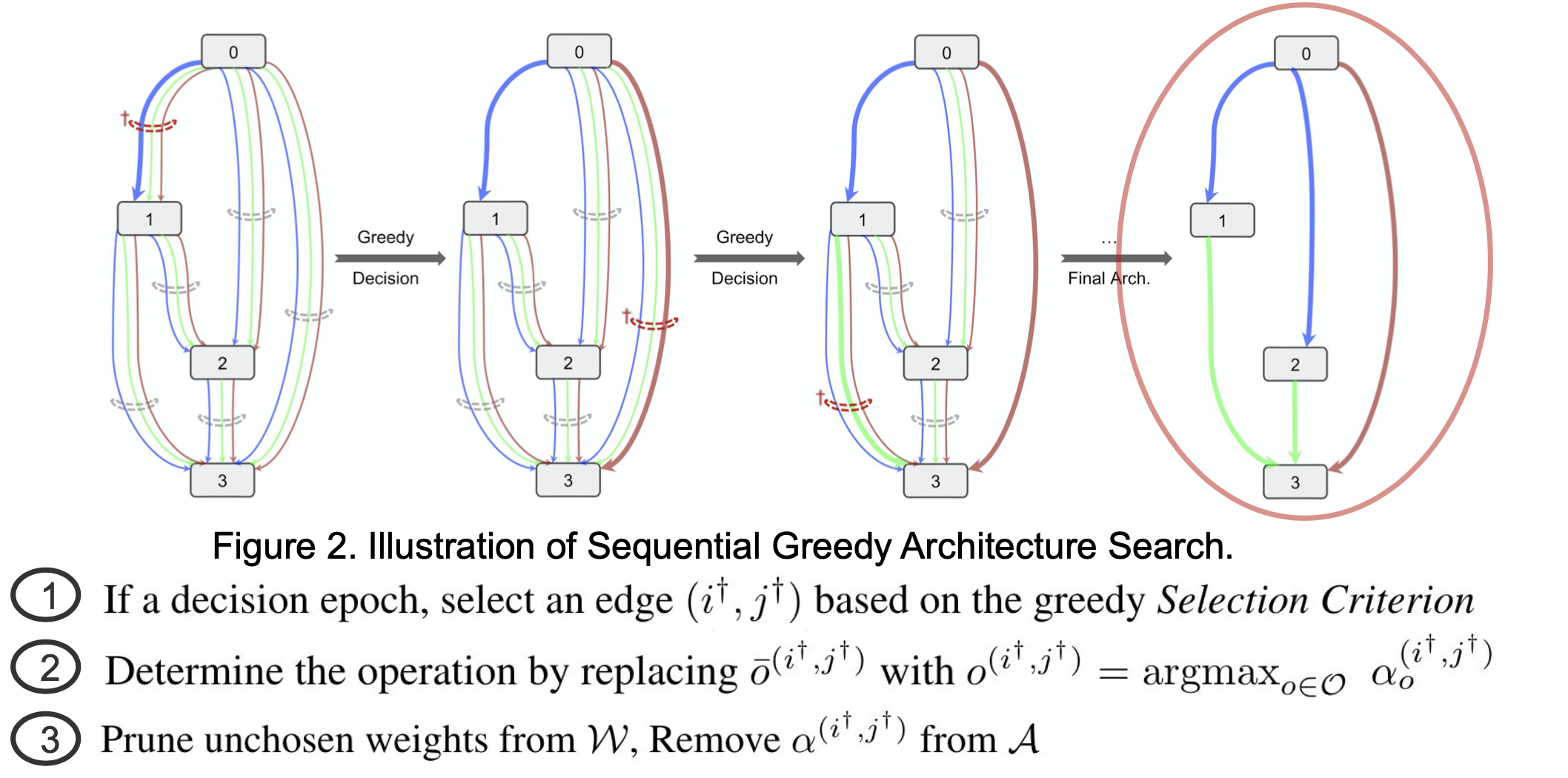
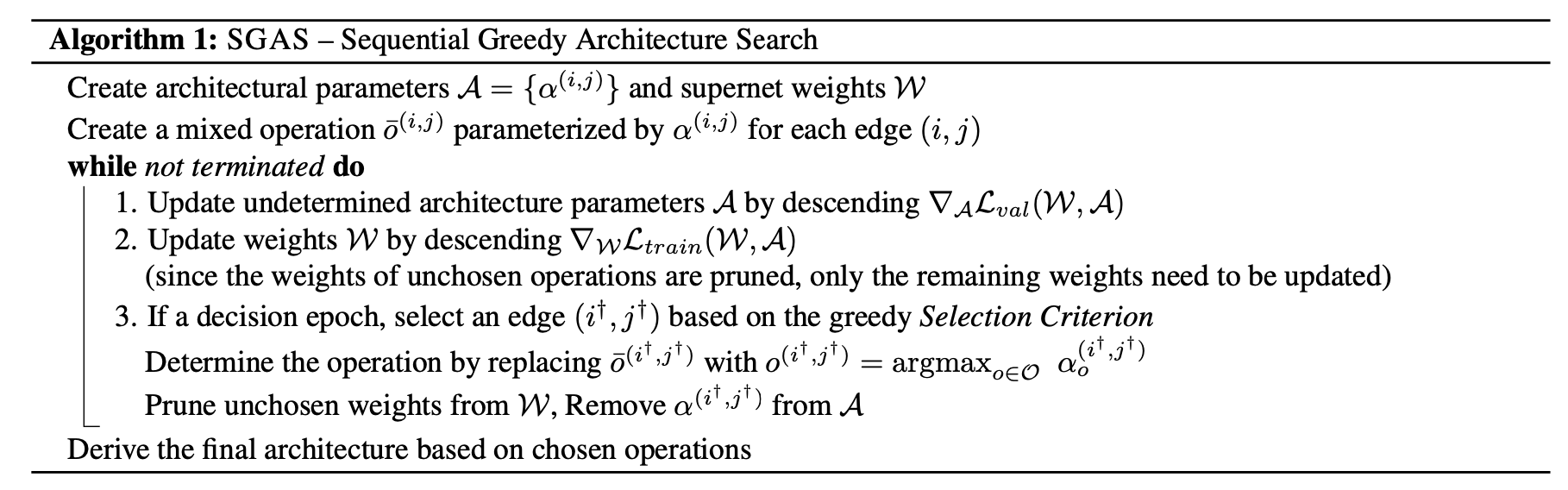
为了保证在贪心搜索的过程中能尽量保证搜索的全局最优性,进而引入了三个指标和两个评估准则。
三个指标
边的重要性
非零操作参数对应的softmax值求和,作为边的重要性衡量指标。
S
E
I
(
i
,
j
)
=
∑
o
∈
O
,
o
≠
z
e
r
o
exp
(
α
o
(
i
,
j
)
)
∑
o
′
∈
O
exp
(
α
o
′
(
i
,
j
)
)
S_{E I}^{(i, j)}=sum_{o in mathcal{O}, o neq z e r o} frac{exp left(alpha_{o}^{(i, j)}right)}{sum_{o^{prime} in mathcal{O}} exp left(alpha_{o^{prime}}^{(i, j)}right)}
SEI(i,j)=o∈O,o=zero∑∑o′∈Oexp(αo′(i,j))exp(αo(i,j))
alphas = []
for i in range(4):
for n in range(2 + i):
alphas.append(Variable(1e-3 * torch.randn(8)))
# alphas经过训练后
mat = F.softmax(torch.stack(alphas, dim=0), dim=-1).detach() # mat为14*8维度的二维列表,softmax归一化。
EI = torch.sum(mat[:, 1:], dim=-1) # EI为14个数的一维列表,去掉none后的7个ops对应alpha值相加
选择的准确性
计算操作分布的标准化熵,熵越小确定性越高;熵越高确定性越小。
p
o
(
i
,
j
)
=
exp
(
α
o
(
i
,
j
)
)
S
E
I
(
i
,
j
)
∑
o
′
∈
O
exp
(
α
o
′
(
i
,
j
)
)
,
o
∈
O
,
o
≠
z
e
r
o
S
S
C
(
i
,
j
)
=
1
−
−
∑
o
∈
O
,
o
≠
z
e
r
o
p
o
(
i
,
j
)
log
(
p
o
(
i
,
j
)
)
log
(
∣
O
∣
−
1
)
begin{array}{c} p_{o}^{(i, j)}=frac{exp left(alpha_{o}^{(i, j)}right)}{S_{E I}^{(i, j)} sum_{o^{prime} in mathcal{O}} exp left(alpha_{o^{prime}}^{(i, j)}right)}, o in mathcal{O}, o neq z e r o \ S_{S C}^{(i, j)}=1-frac{-sum_{o in mathcal{O}, o neq z e r o} p_{o}^{(i, j)} log left(p_{o}^{(i, j)}right)}{log (|mathcal{O}|-1)} end{array}
po(i,j)=SEI(i,j)∑o′∈Oexp(αo′(i,j))exp(αo(i,j)),o∈O,o=zeroSSC(i,j)=1−log(∣O∣−1)−∑o∈O,o=zeropo(i,j)log(po(i,j))
import torch.distributions.categorical as cate
probs = mat[:, 1:] / EI[:, None]
entropy = cate.Categorical(probs=probs).entropy() / math.log(probs.size()[1])
SC = 1-entropy
选择的稳定性
将历史信息纳入操作分布评估,使用直方图交叉核计算平均选择稳定性。直方图交叉核的原理详见(https://blog.csdn.net/hong__fang/article/details/50550656)。
S
S
S
(
i
,
j
)
=
1
K
∑
t
=
T
−
K
T
−
1
∑
o
t
∈
O
,
o
t
≠
z
e
r
o
min
(
p
o
t
(
i
,
j
)
,
p
o
T
(
i
,
j
)
)
S_{S S}^{(i, j)}=frac{1}{K} sum_{t=T-K}^{T-1} sum_{o_{t} in mathcal{O}, o_{t} neq z e r o} min left(p_{o_{t}}^{(i, j)}, p_{o_{T}}^{(i, j)}right)
SSS(i,j)=K1t=T−K∑T−1ot∈O,ot=zero∑min(pot(i,j),poT(i,j))
def histogram_intersection(a, b):
c = np.minimum(a.cpu().numpy(),b.cpu().numpy())
c = torch.from_numpy(c).cuda()
sums = c.sum(dim=1)
return sums
def histogram_average(history, probs):
histogram_inter = torch.zeros(probs.shape[0], dtype=torch.float).cuda()
if not history:
return histogram_inter
for hist in history:
histogram_inter += utils.histogram_intersection(hist, probs)
histogram_inter /= len(history)
return histogram_inter
probs_history = []
probs_history.append(probs)
if (len(probs_history) > args.history_size):
probs_history.pop(0)
histogram_inter = histogram_average(probs_history, probs)
SS = histogram_inter
两种评估准则
评估准则1:
选择具有高边缘重要性和高选择确定性的操作
S
1
(
i
,
j
)
=
normalize
(
S
E
I
(
i
,
j
)
)
∗
normalize
(
S
S
C
(
i
,
j
)
)
S_{1}^{(i, j)}=text { normalize }left(S_{E I}^{(i, j)}right) * text { normalize }left(S_{S C}^{(i, j)}right)
S1(i,j)= normalize (SEI(i,j))∗ normalize (SSC(i,j))
def normalize(v):
min_v = torch.min(v)
range_v = torch.max(v) - min_v
if range_v > 0:
normalized_v = (v - min_v) / range_v
else:
normalized_v = torch.zeros(v.size()).cuda()
return normalized_v
score = utils.normalize(EI) * utils.normalize(SC)
评估准则2:
在评估准则1的基础上,加入考虑选择稳定性
S
2
(
i
,
j
)
=
S
1
(
i
,
j
)
∗
normalize
(
S
S
S
(
i
,
j
)
)
S_{2}^{(i, j)}=S_{1}^{(i, j)} * text { normalize }left(S_{S S}^{(i, j)}right)
S2(i,j)=S1(i,j)∗ normalize (SSS(i,j))
score = utils.normalize(EI) * utils.normalize(SC) * utils.normalize(SS)
实验结果
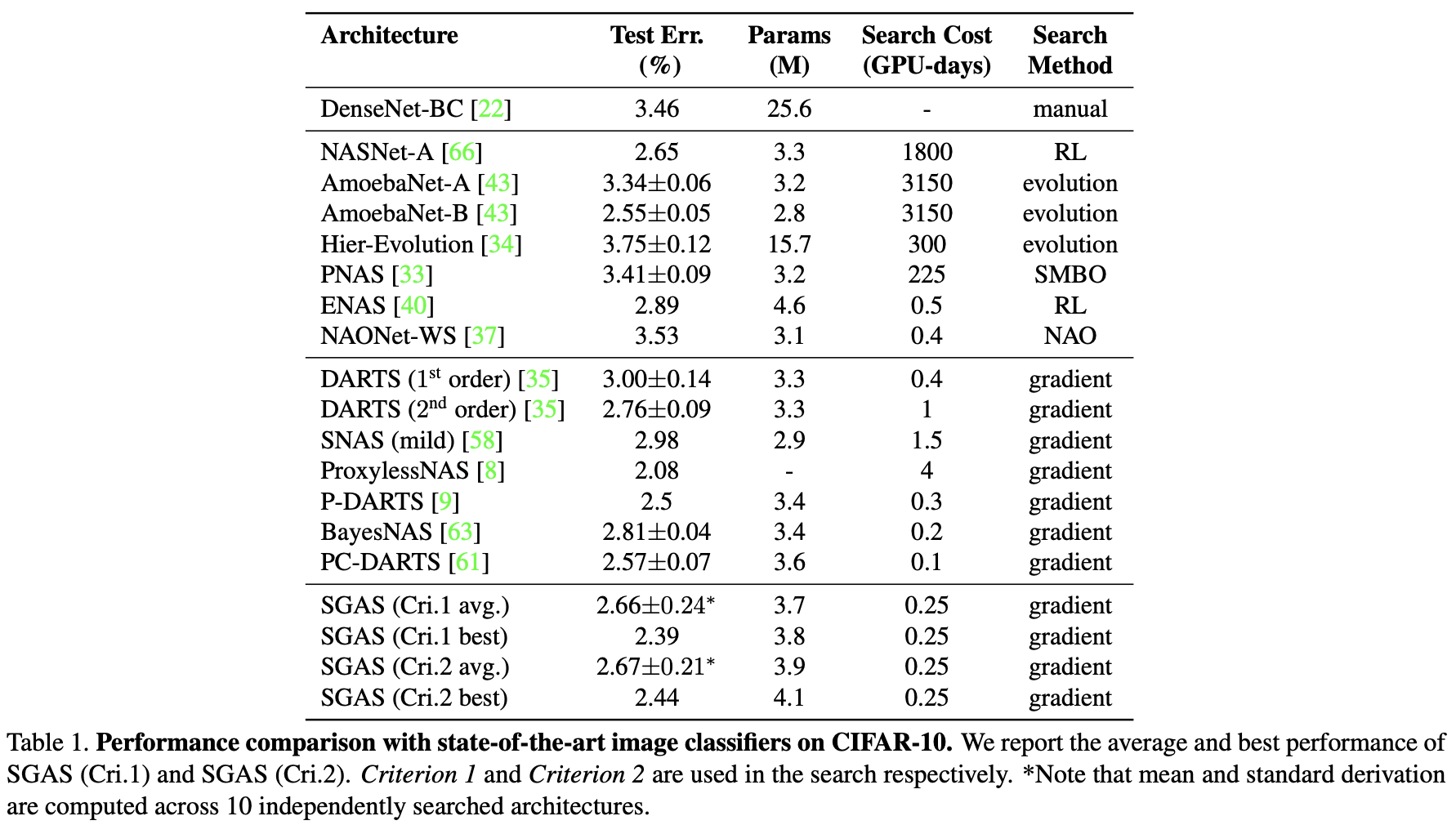
CIFAR-10(CNN)
ImageNet(CNN)
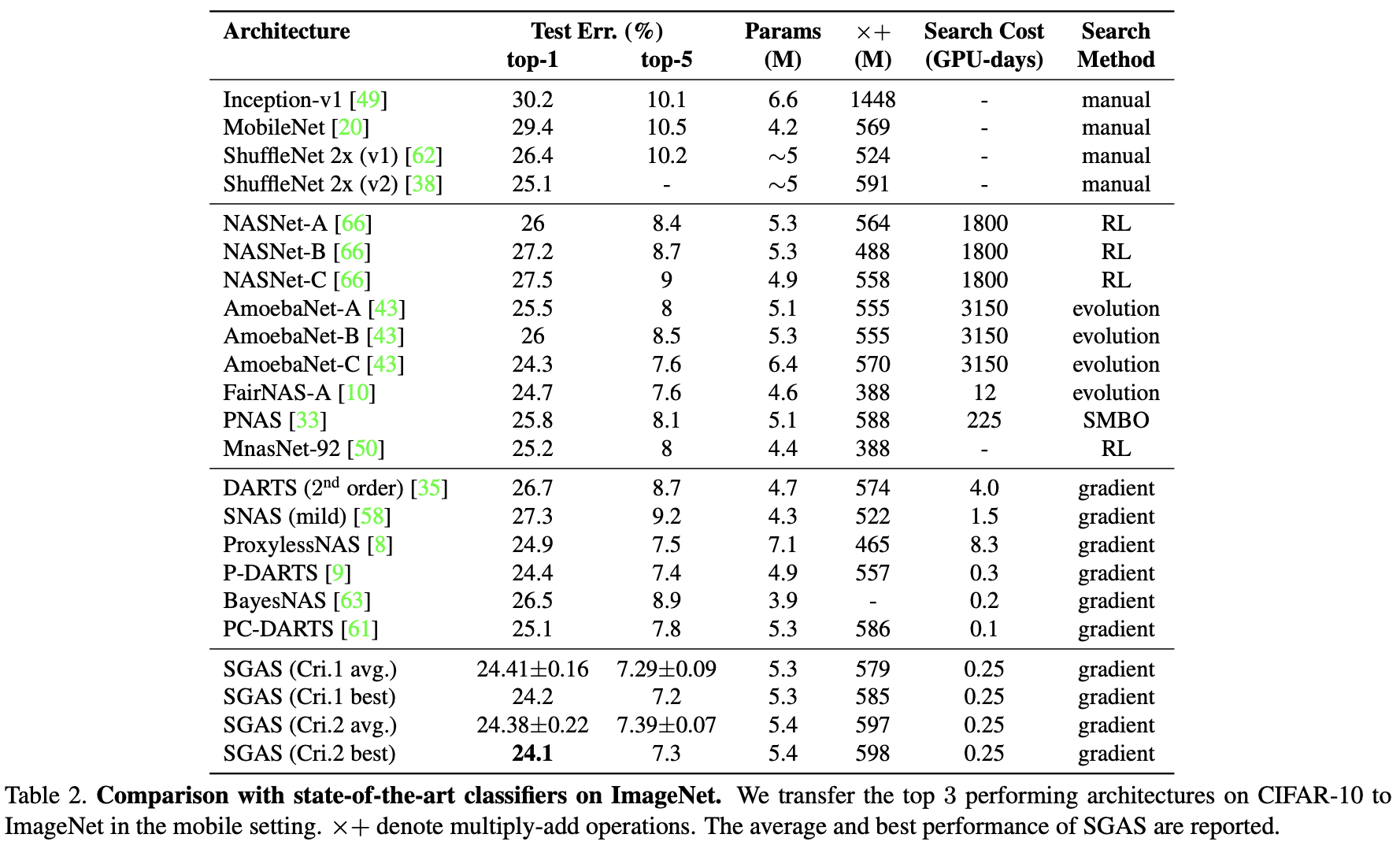
ModelNet40(GCN)
PPI(GCN)
参考
[1] Li, Guohao et al. ,SGAS: Sequential Greedy Architecture Search
[2] https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/134294068
[3] 直方图交叉核 https://blog.csdn.net/hong__fang/article/details/50550656

最后
以上就是迷人信封最近收集整理的关于神经网络架构搜索——可微分搜索(SGAS)的全部内容,更多相关神经网络架构搜索——可微分搜索(SGAS)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复