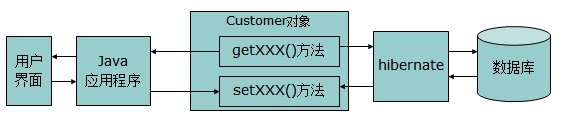
(一)、Hibernate中持久化类的访问者有两个:
- Java应用程序
- hibernate(何时调用get、set方法?)
- 注意:Java应用程序不能访问持久化类的private方法,而hibernate没有这个限制,它可以访问各种级别的方法。(例如提供私有的getXxx和setXxx方法,解决数据库字段跟domain属性不一致的问题而不影响设计)。
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String firstName;
private String secondName;
/*
* 问题:domain设计成了firstName 和
* secondName,但是数据库表中我们设计成了fullName,在hibernate中我们如何对应字段关系?
*
* 解决方案: 提供fullName的getter和setter,为了不影响业务需要(不被其他类访问),我们将其设置为private的,这样,
* 我们只需要将domain对应的映射文件中,对应的数据表的字段名称修改为fullName,就可以解决该问题
*/
private String getFullName() {
return firstName + "," + secondName;
}
private void setFullName(String fullName) {
String[] names = fullName.split(",");
this.firstName = names[0];
this.secondName = names[1];
}
...省略其他字段的getter和setter和tostring方法...
}<hibernate-mapping package="sun.domain">
<class name="User" table="user">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native" />
</id>
<property name="name" column="NAME" />
<!-- name为fullName,则hibernate会根据该名字去找getFullName和setFullName方法,即时是私有的方法 -->
<property name="fullName" column="FULL_NAME" />
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>测试代码:
@Test
public void testSave() {
Session s = util.getSession();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
Transaction tx = s.beginTransaction();
User e = new User();
e.setName("userName" + i);
e.setFirstName("firstName" + i);
e.setSecondName("secondName" + i);
// 保存
s.save(e);
tx.commit();
}
s.close();
}mysql> select * from user;
+-----+------------+--------------------------+
| id | NAME | FULL_NAME |
+-----+------------+--------------------------+
| 1 | userName0 | firstName0,secondName0 |
| 2 | userName1 | firstName1,secondName1 |
| 3 | userName2 | firstName2,secondName2 |
| 4 | userName3 | firstName3,secondName3 |
| 5 | userName4 | firstName4,secondName4 |
…………
(二)、Hibernate访问持久化类属性的策略
- property默认值:表明hibernate通过getXXX和setXXX来访问类属性。推荐使用。提高域模型透明性。
- field:hibernate通过java反射机制直接访问类属性。对于没有javabean方法的属性可设置该访问策略。
如:
<property name=“name” access=“field” />
注意:除了设置property属性的access为field和property之外,还可以自定义访问策略,需要创建实现org.hibernate.
property.PropertyAccessor接口的类.然后把类的完整名字赋值给<property>元素的access属性。
(三)、基本数据类型和包装类型的映射
基本数据类型和包装类型对应的hibernate映射类型相同.type属性为我们提供指定特殊的类型的入口,我们可以修改type
属性来重新修改数据表的字段属性。
<property name=“price” type=“double” column=“PRICE” />
- 基本类型可直接运算、无法表达null、数字类型的默认值为0。
- 包装类默认值是null。当对于默认值有业务意义的时候需要使用包装类。
hibernate的type属性与java数据类型对照表:
| Java数据类型 | Hibernate数据类型 | 标准SQL数据类型 对于不同的DB可能有所差异) |
| java.util.Date、java.sql.Timestamp | timestamp | TIMESTAMP |
| java.util.Calendar | calendar | TIMESTAMP |
| java.util.Calendar | calendar_date | DATE |
| byte[] | binary | VARBINARY、BLOB |
| java.lang.String | text | CLOB |
| java.io.Serializable | serializable | VARBINARY、BLOB |
| java.sql.Clob | clob | CLOB |
| java.sql.Blob | blob | BLOB |
| java.lang.Class | class | VARCHAR |
| java.util.Locale | locale | VARCHAR |
| java.util.TimeZone | timezone | VARCHAR |
| java.util.Currency | currency | VARCHAR |
private Date birthday;
private Date registerTime;
<property name="birthday" column="birthday" type="date"/>
<property name="registerTime" type="timestamp"/>
(四)、控制insert、update语句
| Java数据类型 | Hibernate数据类型 | 标准SQL数据类型 对于不同的DB可能有所差异) |
| byte、java.lang.Byte | byte | TINYINT |
| short、java.lang.Short | short | SMALLINT |
| int、java.lang.Integer | integer | INGEGER |
| long、java.lang.Long | long | BIGINT |
| float、java.lang.Float | float | FLOAT |
| double、java.lang.Double | double | DOUBLE |
| java.math.BigDecimal | big_decimal | NUMERIC |
| char、java.lang.Character | character | CHAR(1) |
| boolean、java.lang.Boolean | boolean | BIT |
| java.lang.String | string | VARCHAR |
| boolean、java.lang.Boolean | yes_no | CHAR(1)('Y'或'N') |
| boolean、java.lang.Boolean | true_false | CHAR(1)('Y'或'N') |
| java.util.Date、java.sql.Date | date | DATE |
| java.util.Date、java.sql.Time | time | TIME |
| 映射属性 | 作用 |
| <property> insert属性 | 若为false,在insert语句中不包含该字段,该字段永远不能被插入。默认值true。 |
| <property> update属性 | 若为false,update语句不包含该字段,该字段永远不能被更新。默认值为true。 |
| <class> mutable属性 | 若为false,等价于所有的<property>元素的update属性为false,整个实例不能被更新。默认为true。 |
| <class> dynamic-insert属性 | 若为true,保存一个对象时,动态生成insert语句,语句中仅包含取值不为null的字段。默认false。 |
| <class> dynamic-update属性 | 若为true,更新一个对象时,动态生成update语句,语句中仅包含取值不为null的字段。默认false。 |
(五)、处理sql标示符、关键字
在SQL语法中,标识符是指用于为数据库表、视图、字段或索引等命名的字符串,常规标识符不包括空格,也不包含特殊字符,因此无需使用引用符号。如果数据库表名或列名包含特殊字符,可以使用引用标识符。
<property name=“description” column=“`CUSTOMER DESCRIPTION`” />
当我们的项目在不同的包下有相同名称的两个类时,在插入数据的时候会出现错误:
java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError
at sun.domain2.TestUser.test(TestUser.java:15)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:39)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:597)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod$1.runReflectiveCall(FrameworkMethod.java:44)
at org.junit.internal.runners.model.ReflectiveCallable.run(ReflectiveCallable.java:15)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod.invokeExplosively(FrameworkMethod.java:41)
at org.junit.internal.runners.statements.RunBefores.evaluate(RunBefores.java:27)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runNotIgnored(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:79)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:71)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:49)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$3.run(ParentRunner.java:193)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$1.schedule(ParentRunner.java:52)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runChildren(ParentRunner.java:191)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.access$000(ParentRunner.java:42)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$2.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:184)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.run(ParentRunner.java:236)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit4.runner.JUnit4TestReference.run(JUnit4TestReference.java:50)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.TestExecution.run(TestExecution.java:38)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.runTests(RemoteTestRunner.java:467)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.runTests(RemoteTestRunner.java:683)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.run(RemoteTestRunner.java:390)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.main(RemoteTestRunner.java:197)
Caused by: org.hibernate.InvalidMappingException: Could not parse mapping document from resource sun/domain2/User.hbm.xml
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.addResource(Configuration.java:671)
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.parseMappingElement(Configuration.java:1679)
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.parseSessionFactory(Configuration.java:1647)
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.doConfigure(Configuration.java:1626)
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.doConfigure(Configuration.java:1600)
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.configure(Configuration.java:1520)
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.configure(Configuration.java:1506)
at sun.util.HibernateUtil.<init>(HibernateUtil.java:12)
at sun.util.HibernateUtil.<clinit>(HibernateUtil.java:8)
... 24 more
Caused by: org.hibernate.DuplicateMappingException: duplicate import: User refers to both sun.domain2.User and sun.domain.User (try using auto-import="false")
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration$MappingsImpl.addImport(Configuration.java:2418)
at org.hibernate.cfg.HbmBinder.bindPersistentClassCommonValues(HbmBinder.java:667)
at org.hibernate.cfg.HbmBinder.bindClass(HbmBinder.java:581)
at org.hibernate.cfg.HbmBinder.bindRootClass(HbmBinder.java:319)
at org.hibernate.cfg.HbmBinder.bindRoot(HbmBinder.java:172)
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.add(Configuration.java:771)
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.addInputStream(Configuration.java:606)
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.addResource(Configuration.java:668)
... 32 more
问题分析:hibernate为这两个相同类名的类生成了相同的简写名称,所以我们在Insert into User values(。。。)的时候,不能区别当前的User是对应哪一个类。
解决方案:将hibernate的自动导入功能取消,而改为手动导入,并为其指定不同的别名。
修改后的配置:
<!-- auto-import属性标示hibernate的导入类的方式,默认为true -->
<hibernate-mapping package="sun.domain2" auto-import="false">
<!-- 手动导入类并指定别名 -->
<import class="sun.domain2.User" rename="User2" />
<class name="User" table="user">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native" />
</id>
<property name="name" column="NAME" />
<!-- name为fullName,则hibernate会根据该名字去找getFullName和setFullName方法,即时是私有的方法 -->
<property name="fullName" column="FULL_NAME" />
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>最后
以上就是霸气花卷最近收集整理的关于hibernate对象关系映射的全部内容,更多相关hibernate对象关系映射内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复