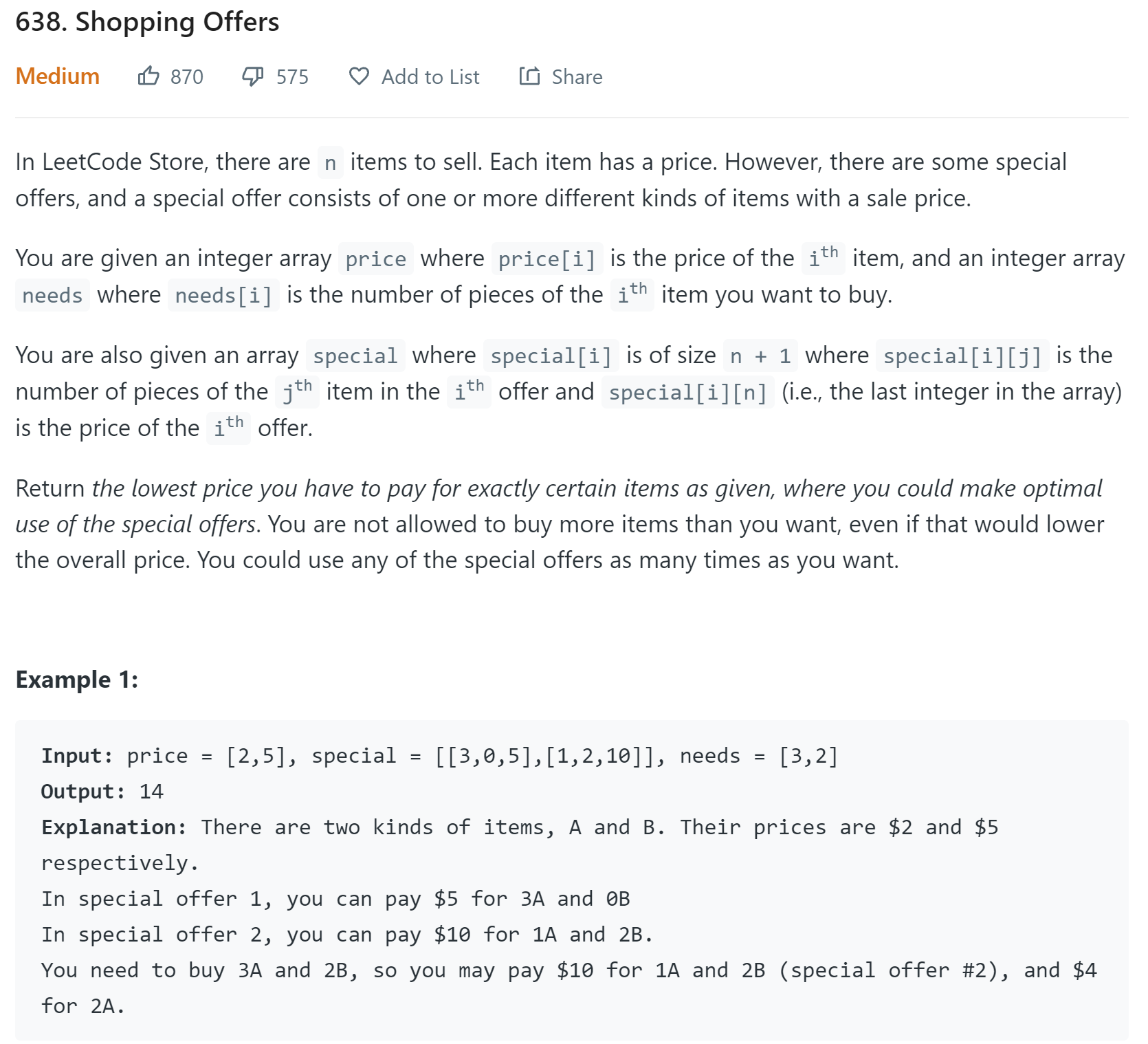
题目
https://leetcode.com/problems/shopping-offers/
题解
类似题目有:leetcode 474. Ones and Zeroes | 474. 一和零(双约束背包问题)
本题实质上是一个多约束(n<6)的背包问题,求解目标是,在背包刚好装满的情况下,希望让总的 price 最小。物品可以使用无限次。
参考左神体系班学习班第19节:剪贴纸问题(实际上没参考它,只是想到有这么个题)
给定一个字符串str,给定一个字符串类型的数组arr,出现的字符都是小写英文
arr每一个字符串,代表一张贴纸,你可以把单个字符剪开使用,目的是拼出str来
返回需要至少多少张贴纸可以完成这个任务。
例子:str= “babac”,arr = {“ba”,“c”,“abcd”}
ba + ba + c 3 abcd + abcd 2 abcd+ba 2
所以本题返回2
由于一些物品是以组合的形式给出的,所以我们先将 list 嵌套 list 转化成数组,方便索引查找。
然后,因为物品可以单独购买。为了统一方便,我们将可以单独购买的物品也转化成组合的形式,只不过让它们的系数都为 1。
如下图所示,前两行分别是单独购买 A 物品、单独购买 B 的价格,后两行是 AB 物品组合购买的价格。

然后就是经典的 暴力递归 -> 傻缓存了。本题应该是无法转化成 dp 的,因为它的状态太多了,详见 dp map 中的 key,我的处理方式是将状态压缩成了字符串。后来看题解发现,hashmap 可以直接用 list 作为 key。
还有,我这个效率超级低,(应该是我为了避免回溯而copy的数组开销比较大),删掉 import 的头文件的话,会超时(这又是 leetcode 的蜜汁特性,带头文件的话运行速度快一些),带着头文件可以 AC。
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
class Solution {
int M; // 套餐总数
int N; // 物品总数
public int shoppingOffers(List<Integer> price, List<List<Integer>> special, List<Integer> needs) {
N = price.size();
M = special.size() + price.size();
// 数组化 套餐列表
int[][] sp = new int[M][N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < special.size(); i++) {
List<Integer> list = special.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < N + 1; j++) {
sp[i][j] = list.get(j);
}
}
for (int i = special.size(), j = 0; i < M; i++, j++) {
sp[i][j] = 1;
sp[i][N] = price.get(j);
}
// 数组化 购物清单
int[] need = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
need[i] = needs.get(i);
}
Map<String, Integer> dp = new HashMap<>();
return process(sp, need, 0, dp);
}
// 多约束背包问题
// 物品列表在special中。当前可选择的物品在cur位置,还剩余needs要买的情况下,至少需要多少cost
public int process(int[][] special, int[] needs, int cur, Map<String, Integer> dp) {
// 查缓存
StringBuilder key = new StringBuilder();
for (int n : needs) { // 状态压缩成字符串
key.append(n).append(":");
}
key.append(cur);
if (dp.containsKey(key.toString())) return dp.get(key.toString());
if (allZero(needs)) {
dp.put(key.toString(), 0);
return 0;
}
int minCost = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int p = cur; p < M; p++) { // 当前购买special[p]套餐
for (int count = 0; canBuy(special, needs, count, p); count++) { // 购买count件p套餐
int[] newNeeds = buy(special, needs, count, p);
int newCost = process(special, newNeeds, p + 1, dp);
if (newCost != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
minCost = Math.min(minCost, count * special[p][N + 1 - 1] + newCost);
}
}
}
// 缓存
dp.put(key.toString(), minCost);
return minCost;
}
// 当前状态下,如果继续买count件p物品,是否买了不需要的
public boolean canBuy(int[][] special, int[] needs, int count, int p) {
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
if (needs[k] - count * special[p][k] < 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
public int[] buy(int[][] special, int[] needs, int count, int p) {
int[] newNeeds = new int[N];
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
newNeeds[k] = needs[k] - count * special[p][k];
}
return newNeeds;
}
public boolean allZero(int[] needs) {
for (int n : needs) {
if (n != 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
最后
以上就是长情水杯最近收集整理的关于leetcode 638. Shopping Offers | 638. 大礼包(动态规划,多约束背包问题)的全部内容,更多相关leetcode内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复