Trminology
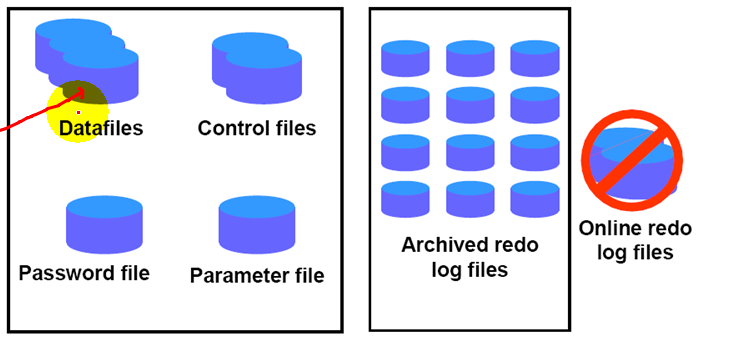
1.Whole database backup
a.Targt database may be open or closed
b. Backup of all datafiles and the control file
2.Partial database backups
a.Tablespace
b.Data file
c. Control file
3.Consisitent backups
4.Inconsistent backups
Get DB File Information
1.V$DATAFILE
2.V$CONTROFILE
3.V$LOGFILE
4.DBA_DATA_FILS
select name , status from v$datafile;
select name from v$controlfile;
slect member from v$logfile;select t.name tablespace, f.name datafile from v$tablespac t, v$datafile f where t.ts# =f.t.tst# order by t.name;
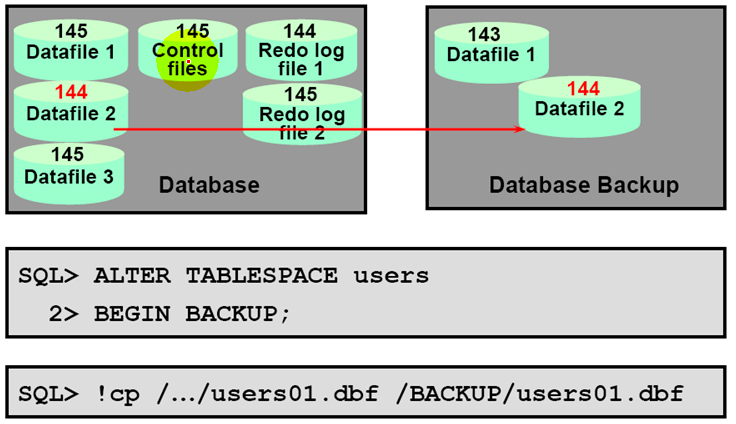
Consistent Whole DB Backup
Open Database Backup
1.Maintains high database availability
2.Can be done at a tablespace or datafile level
3.Supports nonstop business operations
热备需要在归档模式下
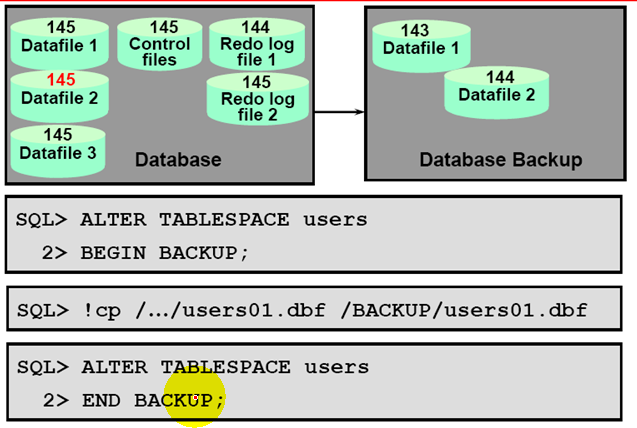
Ending Online TS Baskup
What does Backup Mode do?
The tablespace is checkpointed, the checkpoint SCN marker in the datafile headers case to increment with checkpoints , and full images of changed DB blocks are writeen to the redo logs.
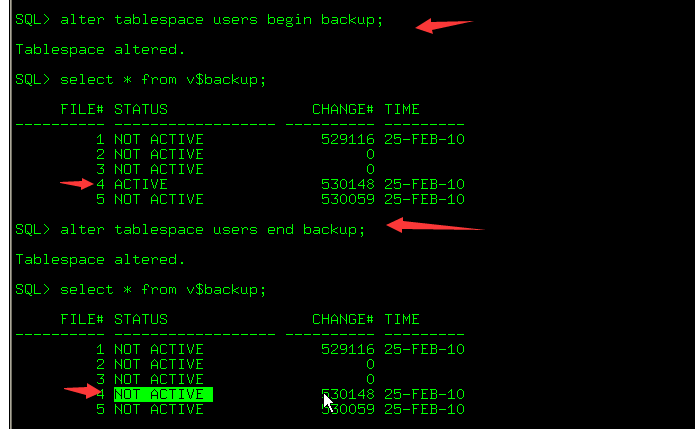
Backup Status Information
select * from v$backup;
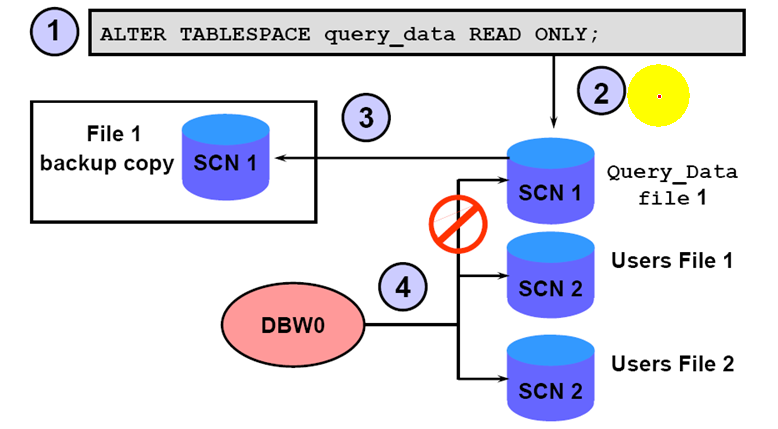
Read-Only TS Baskup
1.Only one backup is needed after altering the tablespace to read-only
2. resume a normal backup schedule for that tablespace after making it read-wirte
3.The control file must correctly indetify the tablespace in read-only mode; otherwise you must recover it.
Logging and Nologging
LOGGING NOLOGGING
ALL changes recorded to redo Minimal redo recorded
Fully recoverable from last backup Not recoverable from last backup
No additional backup May require additional backup
Manual Control File Backups
1.Creating a binary image
ALTER DATABASE BACKUP CONTROLFILE TO 'control1.bkp'
2.Creating a text trac file
ALTER DATABASE BACKUP CONTROLFILE TO TRACE AS '/tmp/con/cxxx.sql'
Backup the Init Param File
CREATE PFILE FROM SPFILE;
CREATE PFILE='/backup/init.ora' from SPFILE;
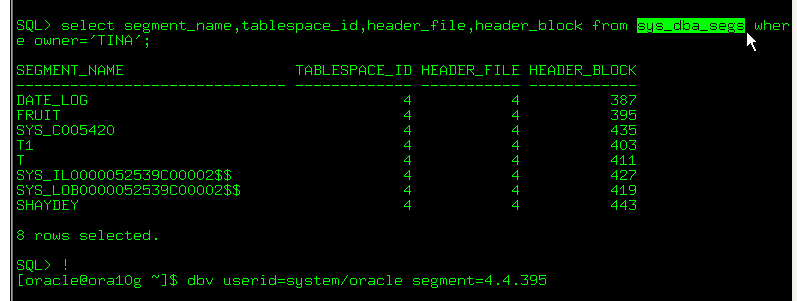
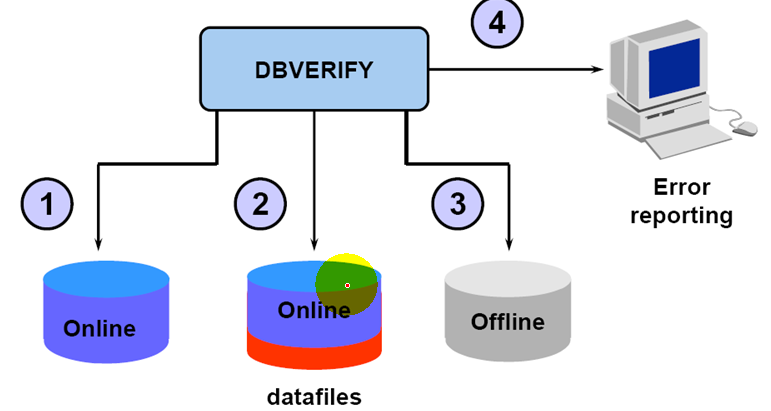
Using DBVERIFY
DBV 检查表空间
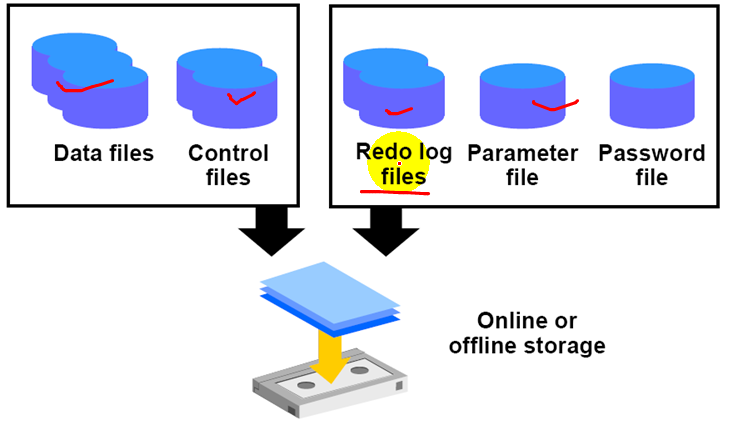
Recovery in NOARCHIVELOG
1.In NOARCHIVELOG mode, you must restor the following database files:
a.All datafiles
b.Control files
2.You can also restore the following files
a.Redo log files
b.Password file
c.Parameter file
3.Advatanges
a.Easy to perform, with low risk of error
b.Recovery time is the time is takes to restore all files
4.Disadvantages
a.Data is lost and must be reaplied manually
b.The entire database is restored to the point of the last whole closed backup
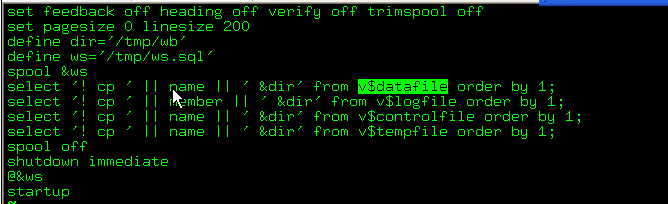
[oracle@localhost king]$ cp *.* ./backup/
[oracle@localhost king]$ cp /u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0/db_1/dbs/orapwking ./backup/
[oracle@localhost king]$ cp /u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0/db_1/dbs/spfileking.ora ./backup/
SQL> create pfile from spfile
[oracle@localhost dbs]$ pwd
/u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0/db_1/dbs
[oracle@localhost dbs]$ vi initking.ora
*.control_files='/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/backup/control01.ctl','/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/backup/control02.ctl','/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/backup/control03.ctl'
SQL> create spfile from pfile;
SQL> statup mount;
SQL> col name format a50;
SQL> select file#,name from v$datafile;
FILE# NAME
---------- --------------------------------------------------
1 /u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/system01.dbf
2 /u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/undotbs01.dbf
3 /u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/backup/sysaux01.dbf
4 /u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/users01.dbf
alter database rename file '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/system01.dbf' to
'/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/backup/system01.dbf';
alter database rename file '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/undotbs01.dbf' to
'/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/backup/undotbs01.dbf';
alter database rename file '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/sysaux01.dbf' to
'/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/backup/sysaux01.dbf';
alter database rename file '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/users01.dbf' to
'/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/backup/users01.dbf';
SQL> select file#,name from v$tempfile;
FILE# NAME
---------- --------------------------------------------------
1 /u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/temp01.dbf
alter database rename file '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/temp01.dbf' to
'/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/backup/temp01.dbf';
SQL> col member format a40;
SQL> select group#,member from v$logfile;
GROUP# MEMBER
---------- ----------------------------------------
3 /u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/redo03.log
2 /u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/redo02.log
1 /u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/redo01.log
alter database rename file '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/redo03.log' to
'/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/backup/redo03.log';
alter database rename file '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/redo02.log' to
'/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/backup/redo02.log';
alter database rename file '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/redo01.log' to
'/u01/app/oracle/oradata/king/backup/redo01.log';
SQL> alter database open;Without Redo Log File Backups
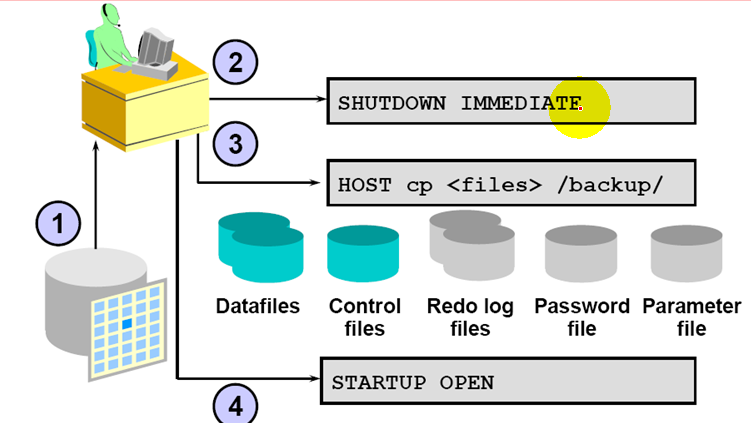
1.shut down the instance
2.Restore the datafiles and the control file from the most recent whole database backup
3.Perform cancel-based recovery
4.Open the database with the RESETLOGS option.
在mount下执行:
recover database until using backup controlfile;
alter database open resetlogs;
Complete Recovery
1.Make sure that datafiles for restore are offline.
2.Restore only lost or damaged datafiles.
3.Do not restore the control files ,redo log files, password files or parameter file.
4.Recover the datafiles
Datermine Files Need Recovery
1.View V$RECOVER_FILE to datermine which datafiles ndd recovery.
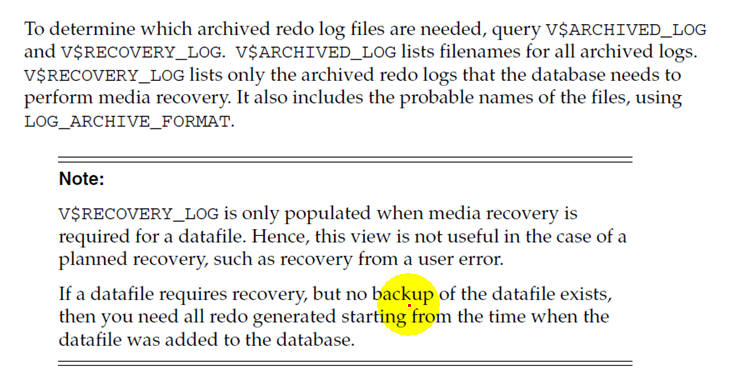
2.View V$ARCHIVED_LOG for a list of all archived redo logfiles for the database.
3.View V$RECOVERY_LOG for a list of all archived redo log files required for recovery
About V$RECOVERY_LOG
About v$recover_file
RECOVER Command
Recover a mounted database:
1.RECOVER DATABASE
2.RECOVER DATAFILE '/xxx/xxx/1.dbf'
Recover an open database:
1.RECOVER TABLESPACE users
2.RECOVER DATAFILE '/123/123/1.dbf'
Using Archived Redo Log Files
1.To change archive location, use the
ALTER SYSTEM ARCHIVE LOG...command
2.To apply redo log files automatically
a.Issue the SET AUTORECOVERY ON command before starting media recovery.
b.Enter auto when prompted for an archived log file
c.Use the Recover AUTOMATIC ... command
Restore Files to a New Location
1.Use operating system commands to restore the datafile to the new location
2.Use the ALTER DATABAS RENAME FILE command to record the change in the control file.
Complete Recovery Methods
1.Closed database recovery for :
a.System datafiles
b. undo segment datafiles
c. Whole database
2.Open database recovery,with database initailly opend (for file loss)
3.Open database recovery with database initailly closed(for hardware failure)
4.Data file recovery wit no datafile backup
最后
以上就是奋斗小松鼠最近收集整理的关于ORACLE_基础二十二(User-Managed Backup)TrminologyGet DB File InformationConsistent Whole DB BackupOpen Database BackupEnding Online TS BaskupWhat does Backup Mode do?Backup Status InformationRead-Only TS BaskupLogging and NologgingManual Control File Backu的全部内容,更多相关ORACLE_基础二十二(User-Managed内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。









发表评论 取消回复