工厂处理器是一种特殊的Bean,这种Bean并不对外提供服务,它甚至可以无需id属性,它主要负责对容器本身进行某些特殊的处理。Spring中有两类工厂后处理器,一个是BeanFactoryPostProcessor,它是所有工厂后处理器的顶层接口;另一个是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,它继承自BeanFactoryPostProcessor,设计它的目的是使用它向Bean注册表(一个BeanDefinitionRegistry 对象)中注册bean的配置信息——一个BeanDefinition对象。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor的定义
Spring工厂后处理器的顶层接口org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor的定义如下。
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}postProcessBeanFactory方法在BeanFactory对象实例化完成后,当所有的bean的BeanDefinition对象加载完成时(即,所有bean的配置信息都已经注册到bean注册表中)被调用。它允许覆盖或者设置bean的属性值,甚至是立即实例化bean,比如实例化bean后处理器对象。
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的定义
Spring还定义了一个工厂后处理器接口,那就是org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,该接口继承了BeanFactoryPostProcessor。下面是它的源码定义。
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean definition registry after its
* standard initialization. All regular bean definitions will have been loaded,
* but no beans will have been instantiated yet. This allows for adding further
* bean definitions before the next post-processing phase kicks in.
* @param registry the bean definition registry used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
}postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法用向bean注册表BeanDefinitionRegistry对象(一般是Spring默认的BeanFacotry对象——DefaultListableBeanFactory)中注册bean的配置信息,即注册BeanDefintion对象。
两类工厂bean的执行顺序
BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法在所有的bean的BeanDefinition对象加载到bean注册表中后被调用,而BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法用于向bean注册表中注册BeanDefinition对象。因此,这两个方法的执行顺序有严格的要求,下面我们通过Spring4的源码解释这个流程。
Spring4执行把通过PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate的静态方法invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法执行工厂后处理器的相关方法,此方法的代码如下。(这段代码有点长,看我的注释就是了)
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// 首先执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<String>();
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new LinkedList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryPostProcessors =
new LinkedList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();
// 遍历容器中的工厂后处理器
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryPostProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
// 执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的
// ->postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
registryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryPostProcessors.add(registryPostProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// 获取并执行bean工厂中定义的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor对象,这里分为三步,如下。
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// 首先,执行实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor对象
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
registryPostProcessors.addAll(priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, registry);
// 然后,执行实现了Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor对象
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
registryPostProcessors.addAll(orderedPostProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, registry);
// 最后执行其它的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor对象
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class);
registryPostProcessors.add(pp);
processedBeans.add(ppName);
pp.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
reiterate = true;
}
}
}
// 执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor工厂后处理器的postProcessBeanFactory方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 执行容器中普通的工厂后处理器的postProcessBeanFactory方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
} else {
// 执行容器中的bean工厂后处理器的postProcessBeanFactory方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// 获取定义在bean工厂中的bean工厂后处理器,下面执行postProcessBeanFactory方法也分成三步,如下。
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// 把bean工厂后处理器按PriorityOrdered、Ordered和其他来分类
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// 排除前面已经执行了的后处理器
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// 首先执行实现了PriorityOrdered接口的后处理器
sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 然后执行实现了Ordered接口的后处理器
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
//
最后执行其他的后处理器
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 清除工厂中的元数据缓存
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
/**
* 执行给定的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor beans.
*/
private static void invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> postProcessors, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
}
}
/**
* 执行给定的bean工厂
**/
private static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor> postProcessors, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
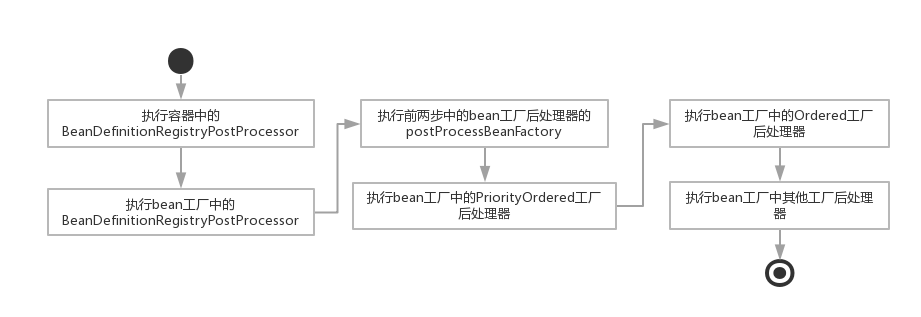
}上面的执行流程用图表达如下。
上图很明显的表达了bean工厂后处理器的执行顺序,但这里还有两点需要说明的。
a. 为什么要先执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor?因为实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口的后处理器可以在bean工厂创建其他bean之前添加更多的BeanDefinition对象到bean工厂中去。比如spring中ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类就是这样一种工厂后处理器,它主要把被@Configuration注解的类中定义的bean信息转换成BeanDefinition对象,并注册到bean工厂中。
b. 这个流程中有一个很明显的规定就是,不管是什么工厂后处理器,都必须先执行容器中的工厂后处理器后,才执行bean工厂中的工厂后处理器。这里的容器中的工厂后处理器是指ApplicationContext对象所持有的未注册到bean工厂中的。bean工厂中的工厂后处理器是指注册到BeanFactory对象中的后处理器。
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的实现类
spring-context-x.x.x模块下的org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor后处理器,用于加载基于java类配置的bean。
mybatis-spring包中的org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer:用于扫描指定包下的mapper接口。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的实现类
spring-beans-x.x.x模块下的PropertyOverrideConfigurer:加载属性文件中信息直接覆盖Spring配置文件中的元数据。
spring-beans-x.x.x模块下PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer及其子类PreferencesPlaceholderConfigurer:负责读取properties属性文件里的属性值,并将这些属性值设置成Spring配置文件的元数据。
spring-context-x.x.x模块下PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer:和PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer的作用一样,不过前者是spring3.1后<context:property-placeholder/>默认加载。后者是3.1以前默认加载的。
关于上面3个与加载属性文件相关的后处理器如何被引入到Spring容器中,请见解析context命名空间之property-placeholder和property-override标签
spring-beans-x.x.x模块下的CustomScopeConfigurer:用于向BeanFactory中注册自定义bean作用域Scope对象。
spring-beans-x.x.x模块下的CustomEditorConfigurer:用于向BeanFactory中注册自定义的PropertyEditorRegistrar对象和PropertyEditor对象。
最后
以上就是勤劳汽车最近收集整理的关于总结Spring中工厂后处理器的全部内容,更多相关总结Spring中工厂后处理器内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复