1、#error的用法
#error用于生成—个编译错误消息
用法 : #error message (message不需要用双引号包围)
#error编译指示字用于自定义程序员特有的编译错误消息
类似的,#warning用于生成编译警告。
#error是一种预编译器指示字
#error可用于提示编译条件是否满足
编译过程中的任意错误信息意味着无法生成最终的可执行程序。
2、实例分析
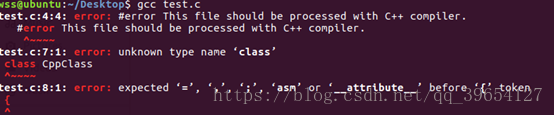
#error预处理初探 23-1.c
#include <stdio.h>
#ifndef __cplusplus
#error This file should be processed with C++ compiler.
#endif
class CppClass
{
private:
int m_value;
public:
CppClass() {}
~CppClass() {}
};
int main()
{
return 0;
} 
3、编程实验
#error在条件编译中的应用 23-2.c
#include <stdio.h>
void f()
{
#if ( PRODUCT == 1 )
printf("This is a low level product!n");
#elif ( PRODUCT == 2 )
printf("This is a middle level product!n");
#elif ( PRODUCT == 3 )
printf("This is a high level product!n");
#else
#error The "PRODUCT" is NOT defined!
#endif
}
int main()
{
f();
printf("1. Query Information.n");
printf("2. Record Information.n");
printf("3. Delete Information.n");
#if ( PRODUCT == 1 )
printf("4. Exit.n");
#elif ( PRODUCT == 2 )
printf("4. High Level Query.n");
printf("5. Exit.n");
#elif ( PRODUCT == 3 )
printf("4. High Level Query.n");
printf("5. Mannul Service.n");
printf("6. Exit.n");
#endif
return 0;
} #error不会产生可执行程序,#warnning会产生
4、#line的用法
#line用于强制指定新的行号和编译文件名,并对源程序
的代码重新编号
用法 :#line number filename (filename可省略)
#line编译指示字的本质是重定义__LINE__和__FILE__
5、编程实验
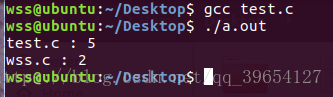
#line的使用 23-3.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("%s : %dn", __FILE__, __LINE__);
#line 1 "wss.c" //重新指定文件名,行号
printf("%s : %dn", __FILE__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
在以前的工程中由最初一个人写代码到多人合作,找出某个人的错误:
#include <stdio.h>
// The code section is written by A.
// Begin
#line 1 "a.c"
// End
// The code section is written by B.
// Begin
#line 1 "b.c"
// End
// The code section is written by Delphi.
// Begin
#line 1 "wss.c"
int main()
{
printf("%s : %dn", __FILE__, __LINE__);
printf("%s : %dn", __FILE__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
// End 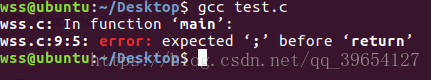
这是较为原始的方式,现代软件公司几乎很少见到这种方式了
6、小结
#error用于自定义—条编译错误信息
#warning用于自定义—条编译警告信息
#error和#warning常应用于条件编译的情形
#line用于强制指定新的行号和编译文件名
最后
以上就是唠叨冥王星最近收集整理的关于#error 和 #line 使用分析的全部内容,更多相关#error内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复