TensorFlow客户端以三种方式接收数据:
- 使用占位符placeholder,用python代码在算法的每个步骤中提供数据。
- 将数据预加载并存储为TensorFlow的张量
- 搭建输入管道
例:
代码:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python
2 # encoding: utf-8
3 import tensorflow as tf
4 import numpy as np
5 import os
6 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "3" #指定所用的GPU编号
8 #使用占位符提供数据
9 #以sigmoid为例
10 graph = tf.Graph()
11 session = tf.InteractiveSession(graph=graph)
12 x = tf.placeholder(shape=[1,10],dtype=tf.float32,name='x')
13 W = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform(shape=[10,5], minval=-0.1, maxval=0.1, dtype=tf.float32),name='W')
14 b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(shape=[5],dtype=tf.float32),name='b')
15 h = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.matmul(x,W) + b)
16 tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
17 h_eval = session.run(h,feed_dict={x: np.random.rand(1,10)})
18 print('W: ', W)
19 print('x: ', x)
20 print('b: ', b)
21 print('h_eval: ', h_eval)
22 session.close()
23
24 #使用张量提供数据
25 # 定义图结构
26 graph = tf.Graph()
27 session = tf.InteractiveSession(graph=graph)
28 x = tf.constant(value=[[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5,0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9,1.0]],dtype=tf.float32,name='x')
29 W = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform(shape=[10,5], minval=-0.1, maxval=0.1, dtype=tf.float32),name='W')
30 b = 0.1 * tf.Variable(tf.ones(shape=[5],dtype=tf.float32),name='b')
31 op1 = tf.matmul(x,W)
32 tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
33 #想打印中间结果需要拆分操作单独run
34 res1 = session.run(op1)
35 print('res1: ', res1)
36 op2 = tf.add(res1, b)
37 res2 = session.run(op2)
38 print('res2: ', res2)
39 op3 = tf.nn.relu(res2)
40 res3 = session.run(op3)
41 res4 = session.run([op1, op2, op3])
42 res5, g, k = session.run([op1, op2, op3])
43 print('res3: ', res3)
44 print('res4: ', res4)
45 print('res5: ', res5, g, k)
46
47 session.close()输出结果:
直接打印无法得到预期的中间结果:
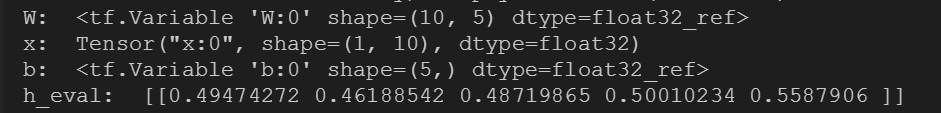
需使用session.run(operation)执行操作: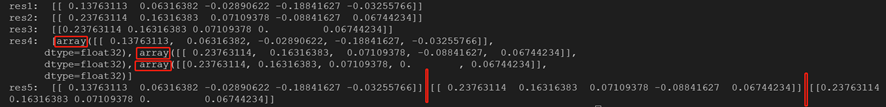
最后
以上就是活泼泥猴桃最近收集整理的关于TensorFlow基础(1)——数据的输入的全部内容,更多相关TensorFlow基础(1)——数据内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复