安卓学习笔记6——多线程下载器
- 一、项目整体介绍
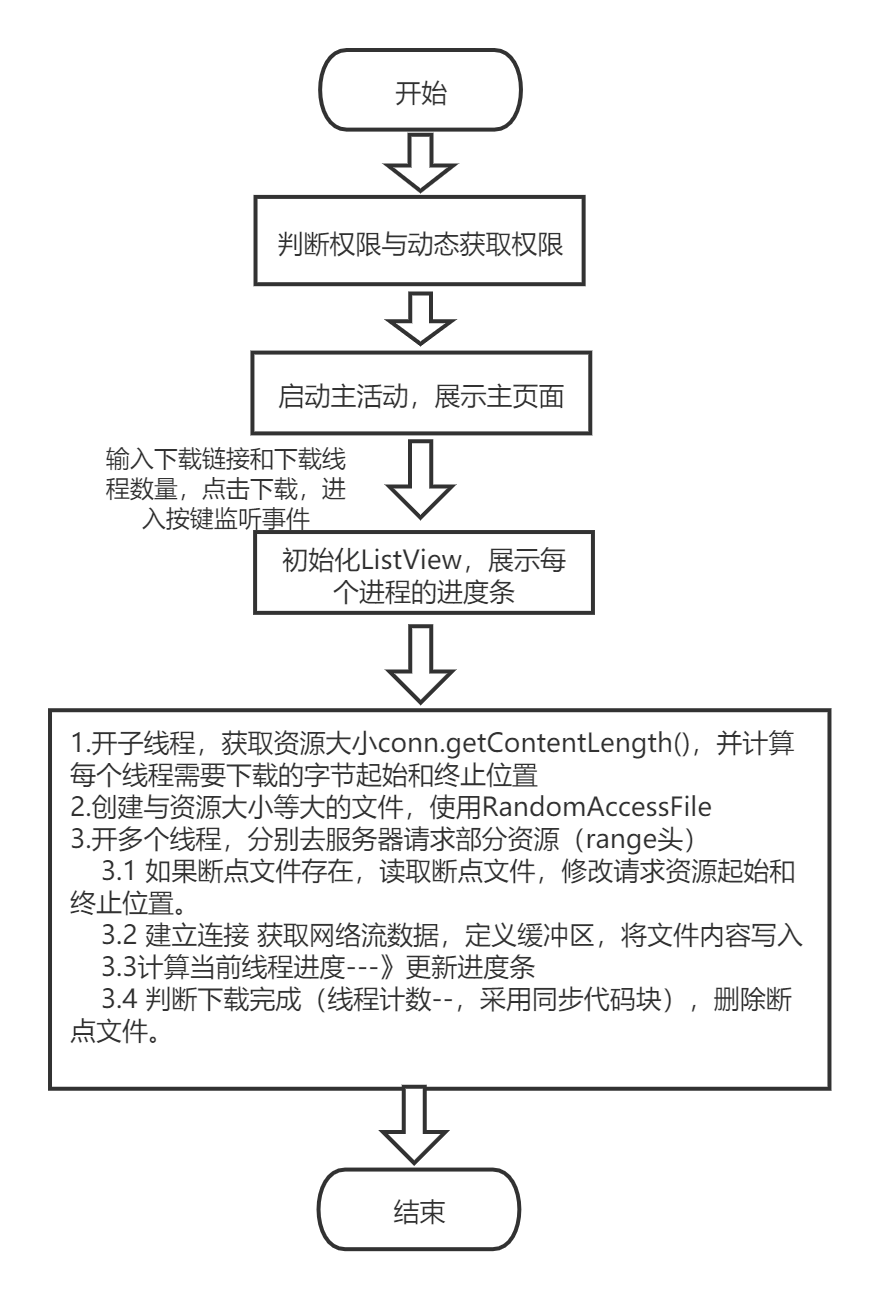
- 1、项目逻辑流程
- 2、项目目的:
- 二、项目代码
- 三、展示
一、项目整体介绍
使用HttpUrlConnection与服务器建立连接,获取文件长度,开多个线程下载资源,使用RandomAccessFile写入文件;
本项目没有使用高大上的OKhttp
1、项目逻辑流程
2、项目目的:
我把这个小demo写在简历中,有两次面试都问道为什么采用多线程下载,多线程下载比单线程下载的好处?我在这里总结了一下
- 多线程主要的优势是与服务器建立多个http链接
多线程下载有可能比单线程下载速度快,多线程主要的优势是与服务器建立多个http链接(目前底层都是tcp,编程就基于socket);相当于多个人搬东西,
- 限制下载速度的主要因素是带宽,而不是CPU执行速度
这个带宽指服务器和客户端两端的带宽;若服务器限制每个socket链接传输数据带宽时,多线程下载在服务器端可以获得更大的带宽,若是单个socket服务器端带宽就大于客户端的网络带宽,那么多线程是不会快过单线程的,因为TCP的拥塞控制和流量控制,服务器端发这么块,客户端接收慢,瓶颈就在客户端。
二、项目代码
主活动onCreate方法
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
et_path=(EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_path);
et_threadCount =(EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_threadCount);
ll_pb_layout=(LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ll_layout);
pbList=new ArrayList<ProgressBar>();
// 获取权限
String[] PERMISSIONS_STORAGE = {
Manifest.permission.INTERNET,
Manifest.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE,
Manifest.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE,
};
for (String str : PERMISSIONS_STORAGE){
int permission = ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission(MainActivity.this, str);
if(permission!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
// We don't have permission so prompt the user
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(
MainActivity.this,
PERMISSIONS_STORAGE,
1
);
}
}
}
下载资源线程
private class DownLoadThread extends Thread {
//通过构造方法把每个线程下载的开始位置和结束位置传递进来
private int startIndex;
private int endIndex;
private int threadId;
private int PbMaxSize;//代表当前线程下载的最大值
// 如果中断过获取上次下载的位置
private int pblastPostion;
public DownLoadThread(int startIndex, int endIndex, int threadId) {
this.startIndex = startIndex;
this.endIndex = endIndex;
this.threadId = threadId;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try{
//计算当前进度条的最大值
PbMaxSize=endIndex-startIndex;
URL url = new URL(path);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
conn.setConnectTimeout(5000);
//[4.0]如果中间断过继续上次的位置继续下载从文件中读取上次下载的位置
File file=new File(getFilename(path)+threadId+".txt");
if(file.exists() && file.length()>0){
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedReader bufr=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
String lastPositionn =bufr.readLine();
int lastPosition=Integer.parseInt(lastPositionn);
pblastPostion=lastPosition-startIndex;
startIndex=lastPosition+1;
System.out.println("线程id"+threadId+"真实下载的位置:"+startIndex+"---"+endIndex);
fis.close();
}
conn.setRequestProperty("Range","bytes="+startIndex+"-"+endIndex);
int code =conn.getResponseCode();
if(code==206){
RandomAccessFile raf=new RandomAccessFile(getFilename(path),"rw");
raf.seek(startIndex);
InputStream in=conn.getInputStream();
int len=-1;
byte[] buffer =new byte[1024*1024];
int total=0;
while((len=in.read(buffer))!=-1){
raf.write(buffer,0,len);
total+=len;
//实现断点续传就是把当前线程下载的位置给存起来下次再下载的时候就是按照上次下载的位置继续下载就可以了
int currentThreadPosition =startIndex+total;
RandomAccessFile raff=new RandomAccessFile(getFilename(path)+threadId+".txt","rwd");
raff.write(String.valueOf(currentThreadPosition).getBytes());
raff.close();
//[10]设置一下当前进度条的最大值和当前进度,无需在子线程中更新
pbList.get(threadId).setMax(PbMaxSize);
pbList.get(threadId).setProgress(pblastPostion+total);
}
raf.close();
System.out.println("线程id:"+threadId+"---下载完毕了");
//
synchronized (DownLoadThread.class){
runningThread--;
if(runningThread==0){
for (int i=0;i<threadCount;i++){
File delteFile =new File(getFilename(path)+i+".txt");
delteFile.delete();
}
}
}
}
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
其他
//获取文件的名字"http://192.168.11.73:8080/feiq.exe"
public String getFilename(String path) {
int start = path.lastIndexOf("/") + 1;
String substring =path.substring(start);
String filename = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getPath()+"/"+substring;
return filename;
}
按钮点击事件
public void click(View v){
//[2]获取下载的路径
path=et_path.getText().toString().trim();
//[3]获取线程的数量
String threadCountt =et_threadCount.getText().toString().trim();
threadCount=Integer.parseInt(threadCountt);
//先移除进度条在添加
ll_pb_layout.removeAllViews();
pbList.clear();
for(int i=0;i< threadCount;i++) {
//[3.1]把我定义的item布局转换成一个view对象
ProgressBar pbview = (ProgressBar) View.inflate(getApplicationContext(), R.layout.item, null);
pbList.add(pbview);
//[4]动态的添加进度条
ll_pb_layout.addView(pbview);
}
// 创建子线程去获取文件大小,
// 获取到大小后,根据线程下载数,再循环开多个线程去取部分资源
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
try {
URL url = new URL(path);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
conn.setConnectTimeout(5000);
int code = conn.getResponseCode();
if (code == 200)//200代表获取服务器资源全部成功206请求部分资源
{
//(6)获取服务器文件的大小
int length = conn.getContentLength();
runningThread = threadCount;
System.out.println("length:" + length);
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(getFilename(path), "rw");
randomAccessFile.setLength(length);
//(7)算出每个线程下载的大小|
int blockSize = length / threadCount;
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
int startIndex = i * blockSize;//每个线
//特殊情况就是最后一个线程
int endIndex = (i + 1) * blockSize - 1;
if (i == threadCount - 1) {
//说明是最后一个线程
endIndex = length - 1;
}
System.out.println("线程id:" + i + "理论下载的位置:" + startIndex + "-----" + endIndex);
DownLoadThread thread=new DownLoadThread(startIndex,endIndex,i);
thread.start();
}
}
}
catch(Exception e){
e. printStackTrace();
}
}
}.start();
}
三、展示
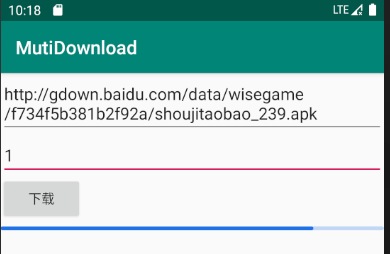
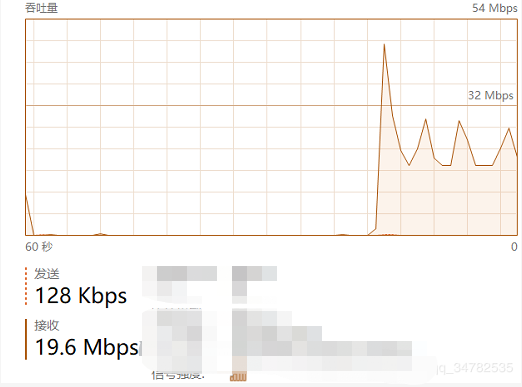
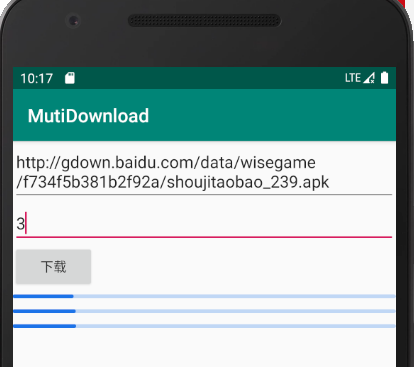
我的本地带宽是50M
单个线程
多个线程
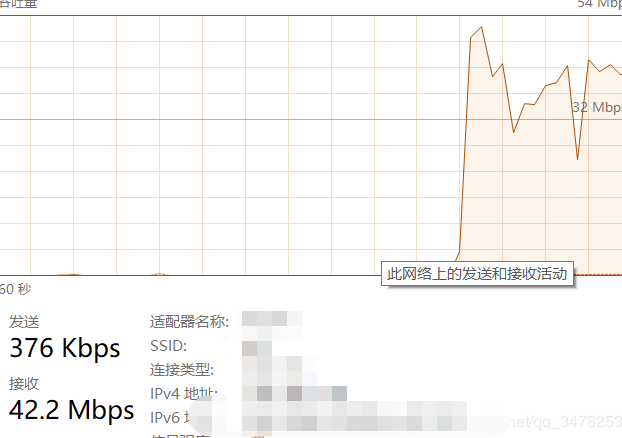
最后
以上就是和谐菠萝最近收集整理的关于安卓学习笔记6——多线程下载器一、项目整体介绍二、项目代码三、展示的全部内容,更多相关安卓学习笔记6——多线程下载器一、项目整体介绍二、项目代码三、展示内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复