1.快速排序的思路
1)在数组中选择一个数作为基准,为了避免性能恶化,可采用随机数来选择;
2)把随机选择的基准数交换到第一个位置或者最后一个位置;
3)顺序遍历数组,把小于基准数的放在基准的左边,大于基准数的放在基准数的右边,从而把数组分为两个子数组;
4)分别对两个子数组重复步骤1-3,直到所有的元素都排好序;
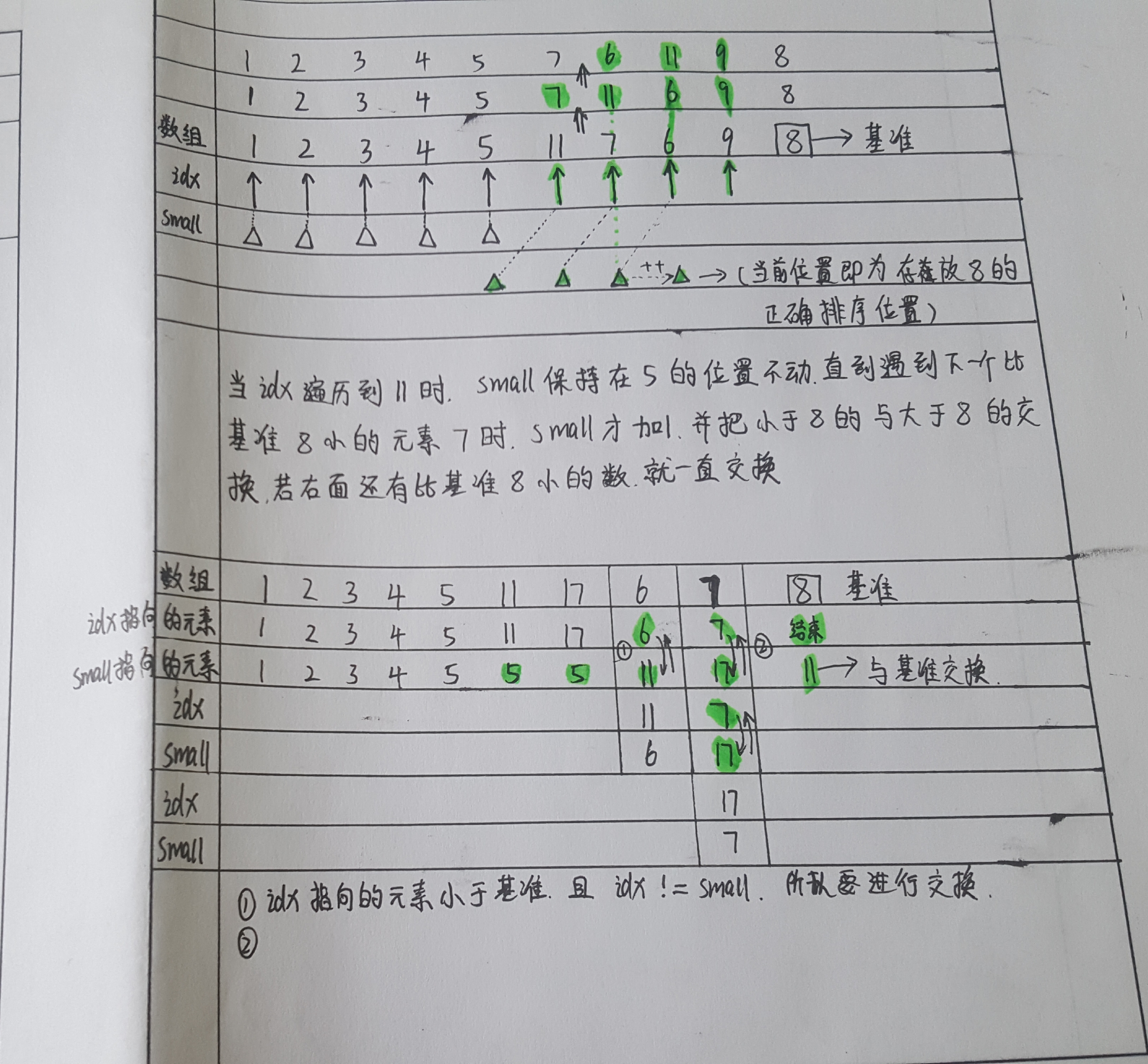
举例如下图所示:
2.代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include<random>
using namespace std;
int Partition(int arry[], int len, int start, int end)
{
if (arry == nullptr || len <= 0 || start < 0 || end > len)
throw new std::exception("invalid parameters");
//产生随机数idx
static default_random_engine e(1234);
//default_random_engine e(time(0));调用系统函数time来作为种子
int idx = e() % (end - start + 1) + start;
//选中的随机数arry[idx]交换到最后面,以跟其他所有的数进行比较
swap(arry[idx], arry[end]);
int small = start - 1;
for (idx = start; idx < end; idx++)
{
if (arry[idx] < arry[end])
{
//如果small == idx,则遍历到的都是比基准小的数
//small统计比基准元素小的元素的个数
small++;
if (small != idx)
{
swap(arry[idx], arry[small]);
}
}
}
//small+1并交换是为了把基准元素放在合适的位置,即所有比它小的数的后面
small++;
swap(arry[small], arry[end]);
return small;
}
void QuickSort(int arry[],int len, int start, int end){
if (start == end)
return;
//返回的位置为选中的基准点正确排列的位置,且它前面的数都比它小,后面的数都比它大
int idx = Partition(arry,len, start, end);
if (idx > start)
QuickSort(arry, len, start, idx - 1);
if (idx < end)
QuickSort(arry, len, idx + 1, end);
}最后
以上就是粗心大雁最近收集整理的关于快速排序的递归实现的全部内容,更多相关快速排序内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复