文章目录
- explain
- 1、explain之id、table
- 2、explain之select_type 查询类型
- 3、explain之type 索引类型
- 4、explain之possible_keys、key
- 5、explain之key_len
- 6、explain之ref、rows
- 7、explain之Extra
explain
a.分析SQL的执行计划(人为优化) : explain ,可以模拟SQL优化器执行SQL语句,从而让开发人员 知道自己编写的SQL状况
b.MySQL查询优化其会干扰我们的优化(系统优化,在服务层里的SQL优化器)
expalin分析SQl的执行计划:
explain可以模拟SQL优化器执行SQL语句,从而让开发人员知道自己编写的SQL
1、查询SQl的执行计划:explain + SQL语句:explain select * from city;

| 字段 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| id | select查询的序列号,是一组数字,表示的是查询中执行select子句或者是操作表的顺序。 |
| select_type | 表示 SELECT 的查询类型,常见的取值有 SIMPLE(简单表,即不使用表连接或者子查询)、PRIMARY(主查询,即外层的查询)、UNION(UNION 中的第二个或者后面的查询语句)、SUBQUERY(子查询中的第一个 SELECT)等 |
| table | 输出结果集的 表名 |
| type | 表示索引类型,性能由好到差的连接类型为( system —> const -----> eq_ref ------> ref -------> ref_or_null----> index_merge —> index_subquery -----> range -----> index ------> all ) |
| possible_keys | 表示查询时,可能使用的索引(预测使用的索引) |
| key | 表示实际使用的索引 |
| key_len | 实际使用索引字段的长度 该字段创建时类型长度 如vachar(8),根据长度判断是否使用索引 |
| ref | 表之间的引用 |
| rows | 通过索引查询到的数据量 ,扫描行的数量 |
| extra | 执行情况的说明和描述 |
2、创建表准备数据,目的是看explain中查询出的参数:
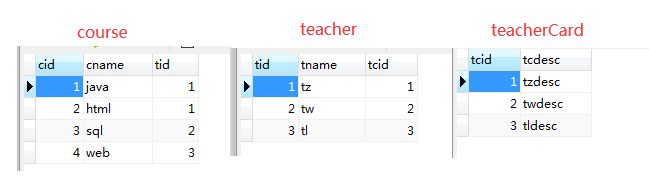
1、explain之id、table
id 字段是 select查询的序列号,是一组数字,表示的是查询中执行select子句或者是操作表的顺序。
table 查询的表
1、 id 相同表示加载表的顺序是从上到下:t、tc、c 数据量少的表优先查询
t当前的数据量为3,tc当前的数据量为3,c当前的数据量为4
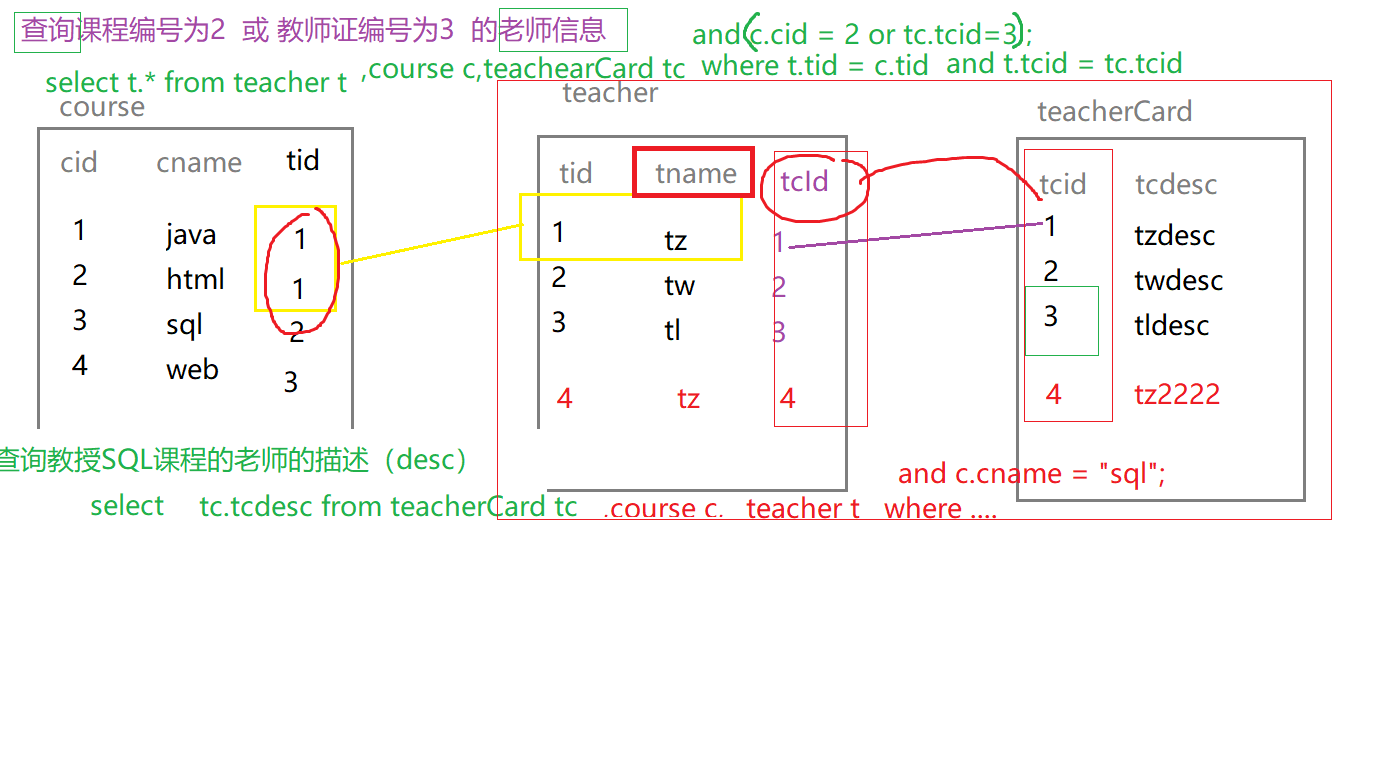
查询课程编号为2 或 教师证编号为3 的老师信息:
explain select t.*
from teacher t , course c , teacherCard tc
where t.tid=c.tid and t.tcid=tc.tcid and (c.cid=2 or tc.tcid=3);

t–>tc–>c 3-3-4
表的执行顺序 因数量的个数改变而改变的原因: 笛卡儿积(如下表a)
a b c 最终执行顺序
2 3 4 = 2*3=6 * 4 =24 (a-->b-->c)
4 3 2 = 3*4=12 * 2 =24 (c-->b-->a)
中间结果6<12(查询的数据量越少越好),因此数据量少的表优先查询
2、id 不同id值越大,优先级越高,越先被执行:c、t、tc
查询教授SQL课程的老师的描述(desc):
explain select tc.tcdesc from teacherCard tc,course c,teacher t where c.tid = t.tid
and t.tcid = tc.tcid and c.cname = 'sql' ;
将以上多表查询 转为子查询形式:(像数学的括号一样,总是先计算括号里的8-(2-(3+6))),因为c表在最内层,先查询c表;接着是t表;再接着是最外层tc表。下面嵌套select从内往外查。
explain select tc.tcdesc from teacherCard tc where tc.tcid =
(select t.tcid from teacher t where t.tid =
(select c.tid from course c where c.cname = 'sql')
);
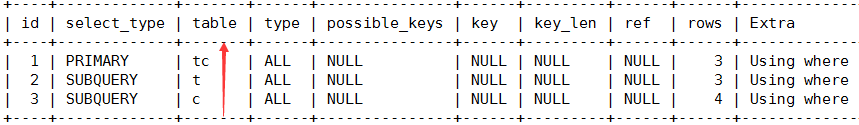
这个跟SQL语句的子查询有关:应给先查询最内层的表,然后查询外层的表,一层一层的查询。
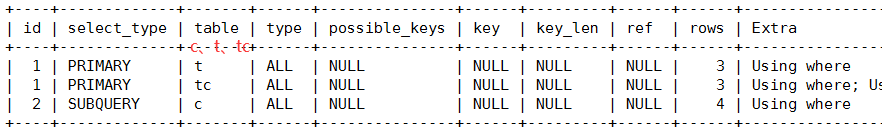
3、 id 有相同,也有不同。id相同的可以认为是一组,从上往下顺序执行;在所有的组中,id的值越大,优先级越高,越先执行:c、t、tc
子查询+多表:
explain select t.tname ,tc.tcdesc from teacher t,teacherCard tc
where t.tcid= tc.tcid and t.tid = (select c.tid from course c where cname = 'sql') ;
2、explain之select_type 查询类型
| select_type | 含义 |
|---|---|
| SIMPLE | 简单的select查询,查询中不包含子查询或者UNION (不包含子查询和联合查询) |
| PRIMARY | 查询中若包含任何复杂的子查询,最外层查询标记为该标识 (包含子查询 的最外层查询) |
| SUBQUERY | 在SELECT 或 WHERE 列表中包含了子查询,非最外层 (包含子查询中的 子查询) |
| DERIVED | 衍生查询(使用到了临时表) a.在from子查询中只有一张表 course就是derived衍生表 explain select cr.cname from ( select * from course where tid in (1,2) ) cr ; b.在from子查询中, 如果有table1 union table2 ,则table1 就是derived,table2就是union explain select cr.cname from ( select * from course where tid = 1 union select * from course where tid = 2 ) cr |
| UNION | 若第二个SELECT出现在UNION之后,则标记为UNION ,上例; 若UNION包含在FROM子句的子查询中,外层SELECT将被标记为 : DERIVED |
| UNION RESULT | 从UNION表获取结果的SELECT,告知开发人员,哪些表之间存在union查询 |
表示 select 的类型(查询类型),常见的取值:
1、simple:简单的select查询,查询中不包含子查询或者union(简单查询)
2、primary:查询中若包含复杂的子查询,最外层查询为PRIMARY(最外层的查询,主查询)
3、subquery:在select或where 列表中包含了子查询(非最外层的查询,子查询)
explain select t.tname ,tc.tcdesc from teacher t,teacherCard tc
where t.tcid= tc.tcid and t.tid = (select c.tid from course c where cname = 'sql') ;
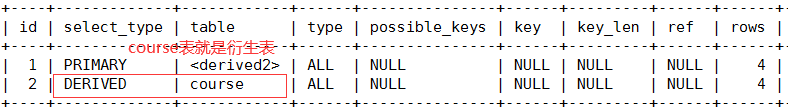
4、derived:在from列表中包含的子查询,使用到了临时表(衍生查询)
在from子查询中只有一张表,那么该表的查询就是DERIVED:
explain select cr.cname from ( select * from course where tid in(1,2) ) cr ;

在from子查询中,如果table1 union table2,那么table1就是DERIVED查询,table2就是UNION查询:
explain select cr.cname
from ( select * from course where tid = 1 union select * from course where tid = 2 ) cr ;
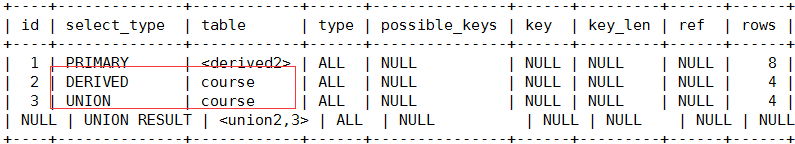
5、union:若第二个select出现在union之后,则标记为union ; (连接查询) 见上图
6、union result:从union表获取结果的select 见上图
3、explain之type 索引类型
system>const>eq_ref>ref>range>index>all ,要对type进行优化的前提:有索引
其中:system,const只是理想情况;索引实际优化只能达到 ref>range
system(忽略): 只有一条数据的系统表 ;或 衍生表只有一条数据的主查询
type 是索引类型,是较为重要的一个指标,可取值为:
| type | 含义 |
|---|---|
| NULL | MySQL不访问任何表,索引,直接返回结果 |
| system | 表只有一行记录(等于系统表),这是const类型的特例,一般不会出现 |
| const | 表示通过索引一次就找到了,const 用于比较primary key 或者 unique 索引。因为只匹配一行数据,所以很快。如将主键置于where列表中,MySQL 就能将该查询转换为一个常亮。const于将 “主键” 或 “唯一” 索引的所有部分与常量值进行比较 |
| eq_ref | 类似ref,区别在于使用的是唯一索引,使用主键的关联查询,关联查询出的记录只有一条。常见于主键或唯一索引扫描 |
| ref | 非唯一性索引扫描,返回匹配某个单独值的所有行。本质上也是一种索引访问,返回所有匹配某个单独值的所有行(多个) |
| range | 只检索给定返回的行,使用一个索引来选择行。 where 之后出现 between , < , > , in 等操作。 |
| index | index 与 ALL的区别为 index 类型只是遍历了索引树, 通常比ALL 快, ALL 是遍历数据文件。 |
| all | 将遍历全表以找到匹配的行 |
结果值从最好到最坏依次是:要对type进行优化,前提是要有索引才可以
-- 全部的类型:
NULL > system > const > eq_ref > ref > fulltext > ref_or_null > index_merge > unique_subquery > index_subquery > range > index > ALL
-- 常用的类型:越往前查询效率越高,system和const为理想情况,基本达不到要求。
system > const > eq_ref > ref > range > index > ALL
一般来说, 我们需要保证查询至少达到 range 级别, 最好达到ref 。
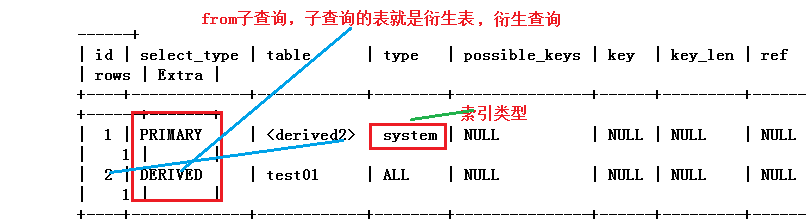
1、system:只有一条数据的系统表,或者衍生表只有一条数据的主查询(测试为ref,老师为system)
create table test01(
tid int(3),
tname varchar(20)
);
insert into test01 values(1,'a') ;
commit;
增加索引:alter table test01 add constraint tid_pk primary key(tid) ;
衍生表只有一条数据:explain select * from (select * from test01 ) t where tid =1 ;
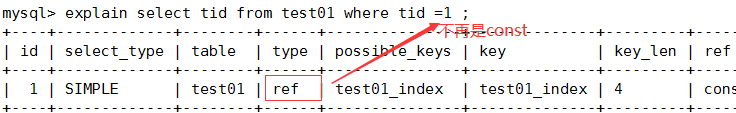
2.const:仅仅能查询到一条数据的SQL,且用于primary key (主键约束)或者unique key (唯一索引)索引(类型和索引类型有关)
explain select tid from test01 where tid =1 ;

-- 删除主键:
alter table test01 drop primary key ;
-- 给tid添加一个普通索引而不是primary key:
create index test01_index on test01(tid) ;
-- 补充点知识:
1.什么是约束:约束就是表中的限制条件、约束的关键字是:constraint
2. 约束的分类:非空约束:not null、唯一性约束:unique、主键约束: primary key、外键约束:foreign key
3、eq_ref:唯一性索引:根据每个索引键的查询,返回匹配唯一行数据(有且只有1个,不能多 、不能0)
常见于唯一索引 和主键索引。 select … from …where name = … .(查询的出的name不能重复是唯一的)
-- 给tid字段创建添加主键约束:Alter table 表名 add constraint 约束名 约束类型(列名)
alter table teacherCard add constraint pk_tcid primary key(tcid);
-- 给tcid字段添加唯一约束:unique index 唯一索引
alter table teacher add constraint uk_tcid unique index(tcid) ;
explain select t.tcid from teacher t,teacherCard tc where t.tcid = tc.tcid ;

以上SQL,用到的索引是 t.tcid,即teacher表中的tcid字段;
如果teacher表的数据个数 和 连接查询的数据个数一致(都是3条数据),则有可能满足eq_ref级别;否则无法满足。
4、ref:非唯一性索引,对于每个索引键的查询,返回匹配的所有行(0,多),与eq_ref条件相反
-- 准备数据:
insert into teacher values(4,'tz',4) ;
insert into teacherCard values(4,'tz222');

根据索引查询,查询的结果可以多个就是ref级别,如果查询的结果只有唯一一个就是eq_ref级别
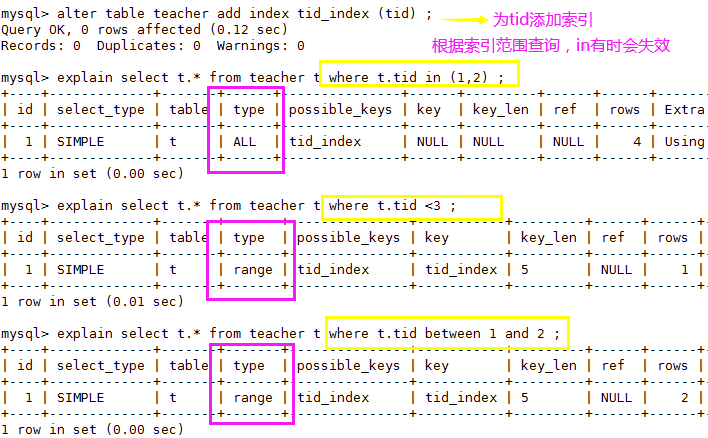
5、range:检索指定范围的行 ,where后面是一个范围查询(between ,> < >=, 特殊:in有时候会失效 ,从而转为 无索引all)
alter table teacher add index tid_index (tid) ;
explain select t.* from teacher t where t.tid in (1,2) ;
explain select t.* from teacher t where t.tid <3 ;
explain select t.* from teacher t where t.tid between 1 and 2 ;
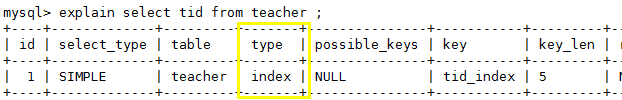
6、index:查询全部索引中数据,扫描索引的那一列(B+树:索引表)
-- tid 是索引,只需要扫描索引表,不需要所有表中的所有数据
explain select tid from teacher ;
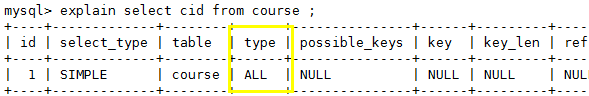
7、all:查询全部表中的数据,因为没有索引,所以扫描整张表
-- cid不是索引,需要全表扫描,即需要扫描所有表中的所有数据
explain select cid from course ;
type索引类型总结:
system/const: 结果只有一条数据
eq_ref:结果多条;但是每条数据是唯一的 ;
ref:结果多条;但是每条数据是是0或多条 ;
4、explain之possible_keys、key
1、possible_keys:可能用到的索引,是一种预测,不准。
2、key:实际使用到的索引
查看各个表中哪些字段中加了索引以及对应索引名称:

explain select t.tname ,tc.tcdesc from teacher t,teacherCard tc
where t.tcid= tc.tcid
and t.tid = (select c.tid from course c where cname = 'sql') ;
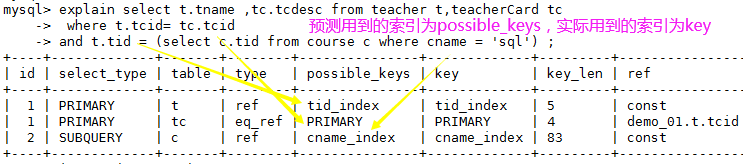
如果 possible_key/key是NULL,则说明没用索引
5、explain之key_len
不同的字符集,latin1,1个字符占1个字节;gbk编码的,1个字符占2个字节;utf8编码的,1个字符占3个字节;utf8mb4编码的,1个字符占4个字节(本文用该字符集)
key_len:索引的长度 ;
作用:用于判断复合索引是否被完全使用 (a,b,c)。
1、如果没用索引长度为0,现在索引长度为80,说明用了索引:char(20)固定字符,与后面的可变varchar(20)不一样
create table test_kl(
-- 创建表,只有一个字段name,有非空约束,字段类型为Char固定长度
name char(20) not null default ''
);
alter table test_kl add index index_name(name) ;
explain select * from test_kl where name ='' ; -- key_len :80
2、 如果索引字段可以为Null,会使用1个字节用于标识:
-- 向表中增加一个字段name1,name1可以为null
alter table test_kl add column name1 char(20) ;
alter table test_kl add index index_name1(name1) ;
explain select * from test_kl where name1 ='';

3、判断复合索引是否被完全使用:
drop index index_name on test_kl ;
drop index index_name1 on test_kl ;
-- 增加一个复合索引
alter table test_kl add index name_name1_index (name,name1) ;
explain select * from test_kl where name1 = '' ; --161
explain select * from test_kl where name = '' ; --80

4、将表的字段添加一个字段:varchar(20)可变字符
-- varchar(20),添加一个字段name2,类型为varchar(20)可变字符
alter table test_kl add column name2 varchar(20) ; --可以为Null
-- 为name2字段添加一个索引
alter table test_kl add index name2_index (name2) ;
explain select * from test_kl where name2 = '' ; --83
20*4=80 + 1(null) +2(用2个字节 标识可变长度) =83
6、explain之ref、rows
1、ref: 注意与type中的ref值区分。
作用: 指明当前表所 参照的 字段。select …where a.c = b.x ;(其中b.x可以是常量,const)
c表参照了t表的tid字段、t表参照了常量为const:
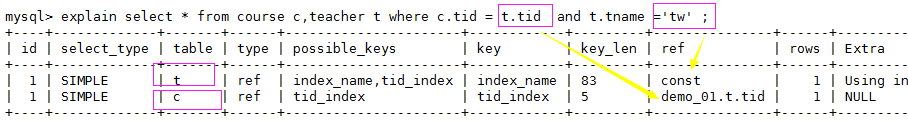
2、rows: 被索引优化查询的 数据个数 (实际通过索引而查询到的 数据个数)
7、explain之Extra
| extra | 含义 |
|---|---|
| using filesort | 说明mysql会对数据使用一个外部的索引排序,而不是按照表内的索引顺序进行读取, 称为 “文件排序”, 效率低。常见于 order by排序 语句中 |
| using temporary | 使用了临时表保存中间结果,MySQL在对查询结果排序时使用临时表。常见于 order by 和 group by分组; 效率低 |
| using index | 表示相应的select操作使用了覆盖索引, 避免访问表的数据行, 效率不错。 |
1、using filesort : 性能消耗大;需要“额外”的一次排序(查询) 。常见于 order by 语句中。
对于单索引:where哪些字段,就order by哪那些字段
create table test02(
a1 char(3),
a2 char(3),
a3 char(3),
index idx_a1(a1),
index idx_a2(a2),
index idx_a3(a3)
);
explain select * from test02 where a1 ='' order by a1 ;
explain select * from test02 where a1 ='' order by a2 ; --using filesort

结论:对于单索引, 如果排序和查找是同一个字段,则不会出现using filesort;如果排序和查找不是同一个字段,则会出现using filesort(排序的字段前需要查询才能排,不同字段要额外查询);避免: where哪些字段,就order by哪那些字段
对于复合索引:不能跨列或无序查询(最佳左前缀)
索引本身就是排序的(B+树),因此只要索引不失效,就说明该索引已经排好序了
drop index idx_a1 on test02;
drop index idx_a2 on test02;
drop index idx_a3 on test02;
-- 创建复合索引
alter table test02 add index idx_a1_a2_a3 (a1,a2,a3) ;
-- 垮了a2列,产生using filesort(导致索引失效,需要重新排序)
explain select *from test02 where a1='' order by a3 ; -- using filesort
-- 垮了a1列,产生using filesort(导致索引失效,需要重新排序)
explain select *from test02 where a2='' order by a3 ; -- using filesort
-- 没有using filesort,(a1,a2)是被复合索引(a1,a2,a3)覆盖,因此索引有效已排好序。
explain select *from test02 where a1='' order by a2 ;-- 复合索引,索引a1后面就是a2
-- 只要包含了a1最左列,并且没有跨列就不会出现using filesort
explain select *from test02 where a2='' order by a1 ;-- using filesort
结论: where和order by 拼接起来按照复合索引的顺序(a1,a2,a3)使用,不要跨列或无序使用。**避免:**按照复合索引的顺序使用。
2、using temporary:性能损耗大 ,用到了临时表。一般出现在group by 语句中。
避免:查询那些列,就根据那些列 group by .
-- SQL解析过程:from..on..join..where..group by..having..select dinstinct..order by limit..
explain select a1 from test02 where a1 in ('1','2','3') group by a1 ;
-- 额外通过a2查询临时表,才能group by a2
explain select a1 from test02 where a1 in ('1','2','3') group by a2 ; -- using temporary
解析过程:
from .. on.. join ..where ..group by ....having ...select dinstinct ..order by limit ...
-- where和group by的列必须一一对应
explain select * from test03 where a2=2 and a4=4 group by a2,a4 ; -- 没有using temporary
-- 出现了临时表,因为分组和where是不一样的列,导致还需要通过a3去查临时表
explain select * from test03 where a2=2 and a4=4 group by a3 ;
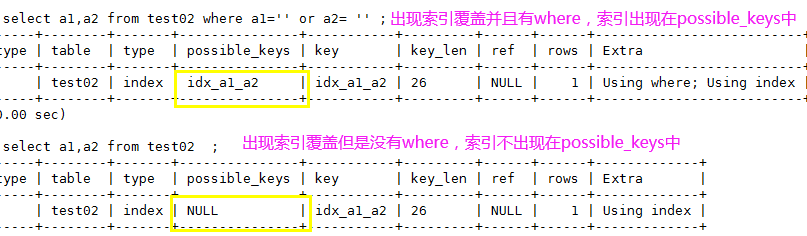
3、 using index :性能提升; 索引覆盖(覆盖索引只在复合索引有效(除了全表只有一个索引外))。原因:不读取原表,只从索引表中获取数据 (不需要回表查询)。只要使用到的列全部都在索引中,就是索引覆盖using index
explain select a1,a2 from test02 where a1='' or a2= '' ; -- using index ,a1与a2都是索引列,要查询数据直接从索引表中查询,不需要回到原表中再查询数据(不需要回表查询)

drop index idx_a1_a2_a3 on test02;
-- 创建复合索引
alter table test02 add index idx_a1_a2(a1,a2) ;
explain select a1,a3 from test02 where a1='' or a3= '' ;

如果用到了索引覆盖(using index时),会对 possible_keys和key造成影响:
a.如果没有where,则索引只出现在key中;
b.如果有where,则索引 出现在key和possible_keys中。
explain select a1,a2 from test02 where a1='' or a2= '' ;
explain select a1,a2 from test02 ;
覆盖索引只在复合索引有效,多个单值索引无效(除了全表只有一个索引外)
------+
| idx_a1 | 1 | a1 |
|
| idx_a2 | 1 | a2 |
|
| idx_a3 | 1 | a3 |
|
-+----------+--------------+-------------+
mysql> explain select a1,a2 from test02 where a1=’’ or a2= ‘’ ;因为在多个单值索引用到or,导致前后a1,a2索引也失效了
±—±------------±-------±-----------±-----±--------------±-----±--------±-----±-----±---------±------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
±—±------------±-------±-----------±-----±--------------±-----±--------±-----±-----±---------±------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | test02 | NULL | ALL | idx_a1,idx_a2 | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using where |
±—±------------±-------±-----------±-----±--------------±-----±--------±-----±-----±---------±------------+
4、using where (需要回表查询)查询不是索引列的要求数据
假设age是索引列
但查询语句select age,name from …where age =…,此语句中name不是索引列,必须回原表查Name,因此会显示using where.
explain select a1,a3 from test02 where a3 = ''; -- a3需要回原表查询

5、 impossible where : where子句永远为false
explain select * from test02 where a1='x' and a1='y';

最后
以上就是虚幻面包最近收集整理的关于【SQL性能问题】explain系列的全部内容,更多相关【SQL性能问题】explain系列内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复