一、RPC原理
- 什么是RPC
RPC(Remote Procedure Call Protocol)——远程过程调用协议,它是一种通过网络从远程计算机程序上请求服务,而不需要了解底层网络技术的协议。RPC协议假定某些传输协议的存在,如TCP或UDP,为通信程序之间携带信息数据。在OSI网络通信模型中,RPC跨越了传输层和应用层。RPC使得开发包括网络分布式多程序在内的应用程序更加容易。
RPC采用客户机/服务器模式。请求程序就是一个客户机,而服务提供程序就是一个服务器。首先,客户机调用进程发送一个有进程参数的调用信息到服务进程,然后等待应答信息。在服务器端,进程保持睡眠状态直到调用信息到达为止。当一个调用信息到达,服务器获得进程参数,计算结果,发送答复信息,然后等待下一个调用信息,最后,客户端调用进程接收答复信息,获得进程结果,然后调用执行继续进行。
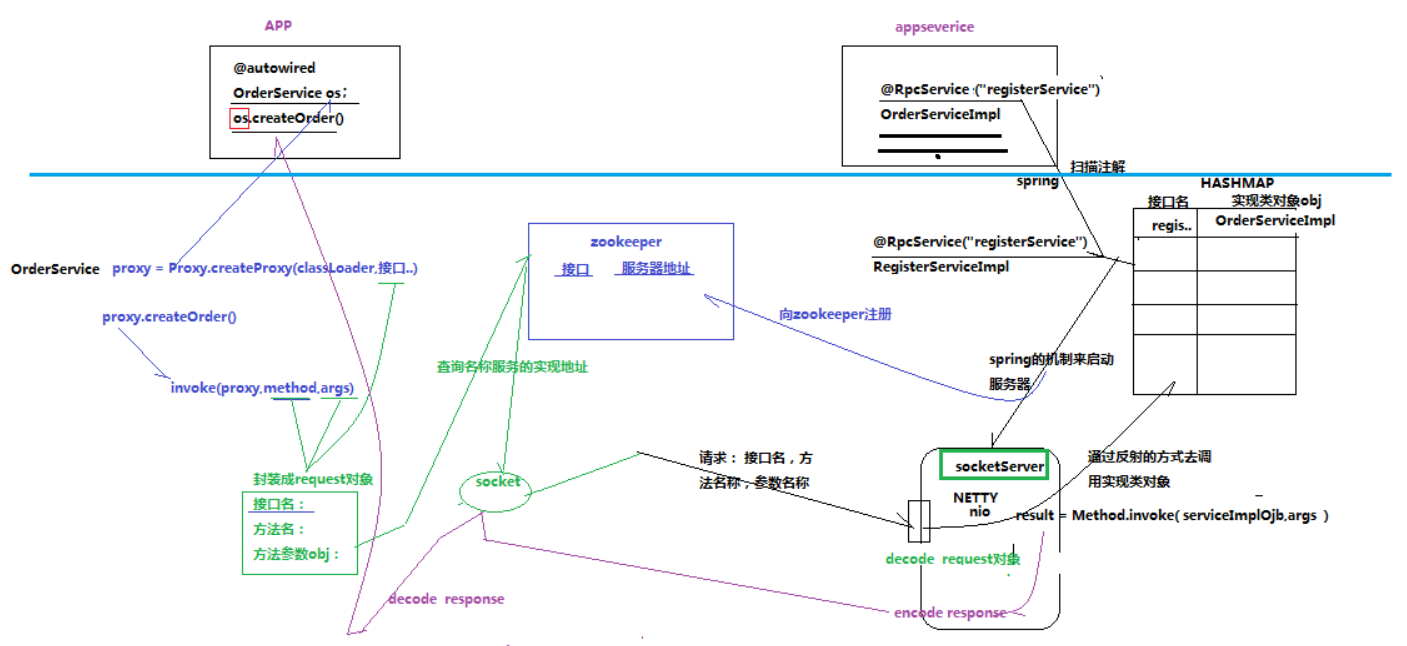
- RPC原理
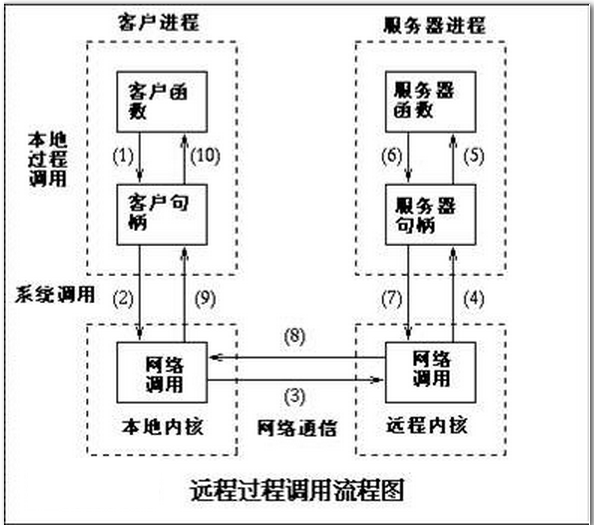
运行时,一次客户机对服务器的RPC调用,其内部操作大致有如下十步:
1.调用客户端句柄;执行传送参数
2.调用本地系统内核发送网络消息
3.消息传送到远程主机
4.服务器句柄得到消息并取得参数
5.执行远程过程
6.执行的过程将结果返回服务器句柄
7.服务器句柄返回结果,调用远程系统内核
8.消息传回本地主机
9.客户句柄由内核接收消息
10.客户接收句柄返回的数据
二、NIO基础
1.简介
nio 是New IO 的简称,在jdk1.4 里提供的新api 。Sun 官方标榜的特性如下: 为所有的原始类型提供(Buffer)缓存支持。字符集编码解码解决方案。 Channel :一个新的原始I/O 抽象。 支持锁和内存映射文件的文件访问接口。 提供多路(non-bloking) 非阻塞式的高伸缩性网络I/O 。
2.传统的I/O与NIO的区别
使用传统的I/O程序读取文件内容, 并写入到另一个文件(或Socket), 如下程序:
File.read(fileDesc, buf, len);
Socket.send(socket, buf, len);
会有较大的性能开销, 主要表现在一下两方面:
① 上下文切换(context switch), 此处有4次用户状态和内核状态的切换
② Buffer内存开销, 一个是应用程序buffer, 另一个是系统读取buffer以及socket buffer
其运行示意图如下
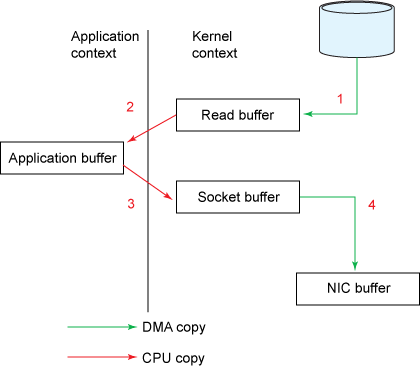
- 先将文件内容从磁盘中拷贝到操作系统buffer
- 再从操作系统buffer拷贝到程序应用buffer
- 从程序buffer拷贝到socket buffer
- 从socket buffer拷贝到协议引擎.
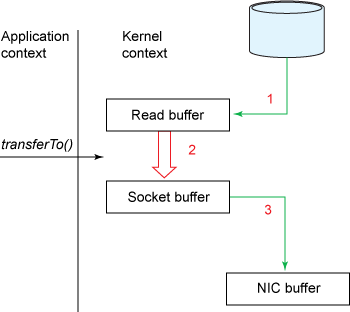
NIO技术省去了将操作系统的read buffer拷贝到程序的buffer, 以及从程序buffer拷贝到socket buffer的步骤, 直接将 read buffer 拷贝到 socket buffer. java 的 FileChannel.transferTo() 方法就是这样的实现, 这个实现是依赖于操作系统底层的sendFile()实现的.
publicvoid transferTo(long position, long count, WritableByteChannel target);
他的底层调用的是系统调用sendFile()方法
sendfile(int out_fd, int in_fd, off_t *offset, size_t count);如下图
NIO相比传统IO的优势不在于数据传送的速度,而是NIO采用轮询+注册的方式,避免的传统IO中获取连接及从socket中读取数据和发送数据时的阻塞情况。
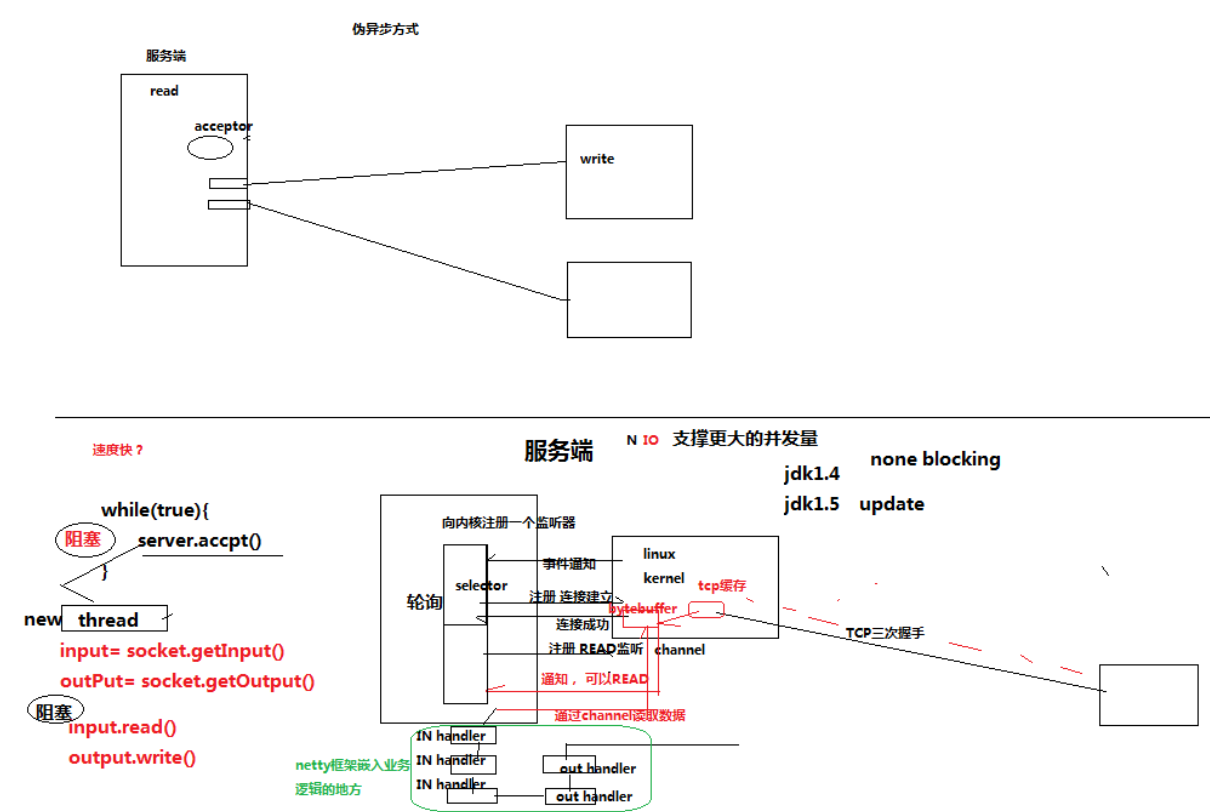
三、netty中handler的执行顺序
Handler与Servlet中的filter很像,通过Handler可以完成通讯报文的解码编码、拦截指定的报文、统一对日志错误进行处理、统一对请求进行计数、控制Handler执行与否。一句话,没有它做不到的只有你想不到的。
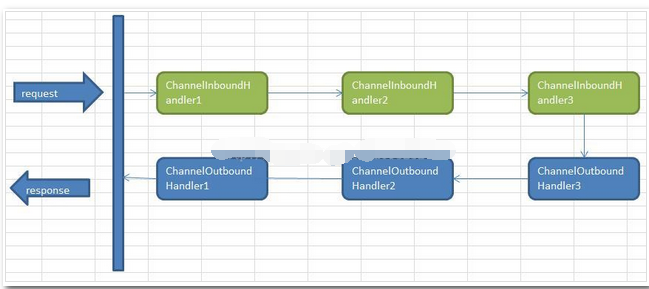
Netty中的所有handler都实现自ChannelHandler接口。按照输出来分,分为ChannelInboundHandler、ChannelOutboundHandler两大类。ChannelInboundHandler对从客户端发往服务器的报文进行处理,一般用来执行解码、读取客户端数据、进行业务处理等;ChannelOutboundHandler对从服务器发往客户端的报文进行处理,一般用来进行编码、发送报文到客户端。
Netty中,可以注册多个handler。ChannelInboundHandler按照注册的先后顺序执行;ChannelOutboundHandler按照注册的先后顺序逆序执行,如下图所示,按照注册的先后顺序对Handler进行排序,request进入Netty后的执行顺序为:
①服务端
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
/**
* • 配置服务器功能,如线程、端口 • 实现服务器处理程序,它包含业务逻辑,决定当有一个请求连接或接收数据时该做什么
*/
public class EchoServer {
private final int port;
public EchoServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void start() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = null;
try {
//server端引导类
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//连接池处理数据
eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
serverBootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//指定通道类型为NioServerSocketChannel,一种异步模式,OIO阻塞模式为OioServerSocketChannel
.localAddress("localhost",port)//设置InetSocketAddress让服务器监听某个端口已等待客户端连接。
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {//设置childHandler执行所有的连接请求
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
// 注册两个InboundHandler,执行顺序为注册顺序,所以应该是InboundHandler1 InboundHandler2
// 注册两个OutboundHandler,执行顺序为注册顺序的逆序,所以应该是OutboundHandler2 OutboundHandler1
//注意:不能将OutboundHandler加载流水线list的最后,否则会导致只会执行到最后一个InboundHandler的地方其后的Handler将不再被执行。
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoInHandler1());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoOutHandler1());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoOutHandler2());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoInHandler2());
}
});
// 最后绑定服务器等待直到绑定完成,调用sync()方法会阻塞直到服务器完成绑定,然后服务器等待通道关闭,因为使用sync(),所以关闭操作也会被阻塞。
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind().sync();
System.out.println("开始监听,端口为:" + channelFuture.channel().localAddress());
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new EchoServer(20000).start();
}
}
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import java.util.Date;
public class EchoInHandler1 extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("in1");
// 通知执行下一个InboundHandler
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();//刷新后才将数据发出到SocketChannel
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
public class EchoInHandler2 extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("in2");
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
String body = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("接收客户端数据:" + body);
//向客户端写数据
System.out.println("server向client发送数据");
String currentTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()).toString();
ByteBuf resp = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(currentTime.getBytes());
ctx.write(resp);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();//刷新后才将数据发出到SocketChannel
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
import java.util.Date;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPromise;
public class EchoOutHandler1 extends ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
// 向client发送消息
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
System.out.println("out1");
/*System.out.println(msg);*/
String currentTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()).toString();
ByteBuf resp = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(currentTime.getBytes());
ctx.write(resp);
ctx.flush();
}
}
public class EchoOutHandler2 extends ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
System.out.println("out2");
// 执行下一个OutboundHandler
/*System.out.println("at first..msg = "+msg);
msg = "hi newed in out2";*/
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
}
②客户端
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
/**
* • 连接服务器 • 写数据到服务器 • 等待接受服务器返回相同的数据 • 关闭连接
*/
public class EchoClient {
private final String host;
private final int port;
public EchoClient(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
public void start() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup nioEventLoopGroup = null;
try {
// 客户端引导类
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
// EventLoopGroup可以理解为是一个线程池,这个线程池用来处理连接、接受数据、发送数据
nioEventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
bootstrap.group(nioEventLoopGroup)//多线程处理
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)//指定通道类型为NioServerSocketChannel,一种异步模式,OIO阻塞模式为OioServerSocketChannel
.remoteAddress(new InetSocketAddress(host, port))//地址
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//业务处理类
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoClientHandler());//注册handler
}
});
// 链接服务器
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect().sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
nioEventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new EchoClient("localhost", 20000).start();
}
}
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
public class EchoClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> {
// 客户端连接服务器后被调用
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("客户端连接服务器,开始发送数据……");
byte[] req = "QUERY TIME ORDER".getBytes();//消息
ByteBuf firstMessage = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);//发送类
firstMessage.writeBytes(req);//发送
ctx.writeAndFlush(firstMessage);//flush
}
// • 从服务器接收到数据后调用
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("client 读取server数据..");
// 服务端返回消息后
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
String body = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("服务端数据为 :" + body);
}
// • 发生异常时被调用
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("client exceptionCaught..");
// 释放资源
ctx.close();
}
}
在使用Handler的过程中,需要注意:
1、ChannelInboundHandler之间的传递,通过调用 ctx.fireChannelRead(msg) 实现;调用ctx.write(msg) 将传递到 ChannelOutboundHandler。在ChannelOutboundHandle之间传递信息调用super.write(ctx, msg, promise)实现;
2、ctx.write()方法执行后,需要调用flush()方法才能令它立即执行。
3、流水线pipeline中outhandler不能放在最后,否则不生效
4、Handler的消费处理放在最后一个处理。
四、Netty发送对象
Netty中,通讯的双方建立连接后,会把数据按照ByteBuf的方式进行传输,例如http协议中,就是通过HttpRequestDecoder对ByteBuf数据流进行处理,转换成http的对象。基于这个思路,我自定义一种通讯协议:Server和客户端直接传输java对象。
实现的原理是通过Encoder把java对象转换成ByteBuf流进行传输,通过Decoder把ByteBuf转换成java对象进行处理,处理逻辑如下图所示:
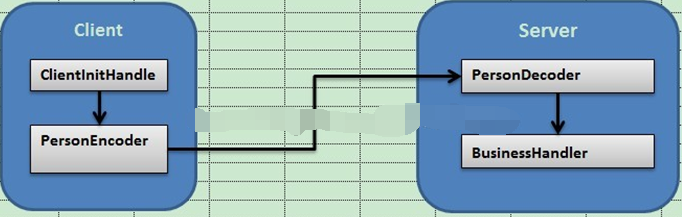
①javabean
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Person implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String name;
private String sex;
private int age;
public String toString() {
return "name:" + name + " sex:" + sex + " age:" + age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
②工具类
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
public class ByteBufToBytes {
/**
* 将ByteBuf转换为byte[]
* @param datas
* @return
*/
public byte[] read(ByteBuf datas) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[datas.readableBytes()];// 创建byte[]
datas.readBytes(bytes);// 将ByteBuf转换为byte[]
return bytes;
}
}
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class ByteObjConverter {
/**
* 使用IO的inputstream流将byte[]转换为object
*/
public static Object byteToObject(byte[] bytes) {
Object obj = null;
ByteArrayInputStream bi = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
ObjectInputStream oi = null;
try {
oi = new ObjectInputStream(bi);
obj = oi.readObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
bi.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
oi.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return obj;
}
/**
* 使用IO的outputstream流将object转换为byte[]
* @param bytes
* @return
*/
public static byte[] objectToByte(Object obj) {
byte[] bytes = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream bo = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oo = null;
try {
oo = new ObjectOutputStream(bo);
oo.writeObject(obj);
bytes = bo.toByteArray();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
bo.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
oo.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return bytes;
}
}
③服务端
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
/**
* • 配置服务器功能,如线程、端口 • 实现服务器处理程序,它包含业务逻辑,决定当有一个请求连接或接收数据时该做什么
*/
public class EchoServer {
private final int port;
public EchoServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void start() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = null;
try {
//创建ServerBootstrap实例来引导绑定和启动服务器
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//创建NioEventLoopGroup对象来处理事件,如接受新连接、接收数据、写数据等等
eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//指定通道类型为NioServerSocketChannel,一种异步模式,OIO阻塞模式为OioServerSocketChannel
//设置InetSocketAddress让服务器监听某个端口已等待客户端连接。
serverBootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).localAddress("localhost",port)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
//设置childHandler执行所有的连接请求
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
//注册解码的handler
ch.pipeline().addLast(new PersonDecoder()); //IN1 反序列化
//添加一个入站的handler到ChannelPipeline
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoServerHandler()); //IN2
}
});
// 最后绑定服务器等待直到绑定完成,调用sync()方法会阻塞直到服务器完成绑定,然后服务器等待通道关闭,因为使用sync(),所以关闭操作也会被阻塞。
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind().sync();
System.out.println("开始监听,端口为:" + channelFuture.channel().localAddress());
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new EchoServer(20000).start();
}
}
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import cn.itcast_03_netty.sendobject.bean.Person;
public class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
Person person = (Person) msg;
System.out.println(person.getName());
System.out.println(person.getAge());
System.out.println(person.getSex());
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("server 读取数据完毕..");
ctx.flush();//刷新后才将数据发出到SocketChannel
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.ByteToMessageDecoder;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 反序列化
* 将Byte[]转换为Object
*/
public class PersonDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
//工具类:将ByteBuf转换为byte[]
ByteBufToBytes read = new ByteBufToBytes();
byte[] bytes = read.read(in);
//工具类:将byte[]转换为object
Object obj = ByteObjConverter.byteToObject(bytes);
out.add(obj);
}
}
④客户端
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
/**
* • 连接服务器 • 写数据到服务器 • 等待接受服务器返回相同的数据 • 关闭连接
*/
public class EchoClient {
private final String host;
private final int port;
public EchoClient(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
public void start() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup nioEventLoopGroup = null;
try {
// 创建Bootstrap对象用来引导启动客户端
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
// 创建EventLoopGroup对象并设置到Bootstrap中,EventLoopGroup可以理解为是一个线程池,这个线程池用来处理连接、接受数据、发送数据
nioEventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
// 创建InetSocketAddress并设置到Bootstrap中,InetSocketAddress是指定连接的服务器地址
bootstrap.group(nioEventLoopGroup)//
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)//
.remoteAddress(new InetSocketAddress(host, port))//
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//
// 添加一个ChannelHandler,客户端成功连接服务器后就会被执行
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws Exception {
// 注册编码的handler
ch.pipeline().addLast(new PersonEncoder()); //out
//注册处理消息的handler
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoClientHandler()); //in
}
});
// • 调用Bootstrap.connect()来连接服务器
ChannelFuture f = bootstrap.connect().sync();
// • 最后关闭EventLoopGroup来释放资源
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
nioEventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new EchoClient("localhost", 20000).start();
}
}
io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
public class EchoClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> {
// 客户端连接服务器后被调用
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("angelababy");
person.setSex("girl");
person.setAge(18);
ctx.write(person);
ctx.flush();
}
// • 从服务器接收到数据后调用
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("client 读取server数据..");
// 服务端返回消息后
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
String body = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("服务端数据为 :" + body);
}
// • 发生异常时被调用
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("client exceptionCaught..");
// 释放资源
ctx.close();
}
}
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToByteEncoder;
/**
* 序列化
* 将object转换成Byte[]
*/
public class PersonEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<Person> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Person msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
//工具类:将object转换为byte[]
byte[] datas = ByteObjConverter.objectToByte(msg);
out.writeBytes(datas);
ctx.flush();
}
}
最后
以上就是冷酷大米最近收集整理的关于轻量级RPC的全部内容,更多相关轻量级RPC内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复