一:为什么要自定义控件?
1.实现自己的style
2.处理特有的用户交互
3.优化布局
4.封装
二:自定义控件有哪些步骤?
1.自定义属性的声明与获取
2.测量onMeasure
3.绘制onDraw
4.状态的存储与恢复
1.自定义属性的声明与获取:
1.1 分析需要的自定义属性(以一个圆形的下载进度条为例)
color:进度条颜色 format:color
Line_width:进度条宽度 format:dimension
radius:进度条半径 format:dimension
progress:进度值(这个可以使用系统提供的类型)
textSize:字体大小
1.2 在res/values/attrs.xml中定义
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="RoundProgressBar">
<attr name="color" format="color"></attr>
<attr name="Line_width" format="dimension"></attr>
<attr name="radius" format="dimension"></attr>
<attr name="android:progress"></attr>
<attr name="android:textSize"></attr>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>1.3 在layout.xml文件中进行使用
<com.example.jiaho.customview.RoundProgressBar
android:id="@+id/roundProgressBar"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="10dp"
android:progress="0"
app:color="#FF00FF00"
app:radius="40dp"
android:textSize="20sp"
app:Line_width="4dp"
/>1.4 在view的构造方法中进行属性获取
public RoundProgressBar(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray ta=context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.RoundProgressBar);
//在构造方法中进行属性获取
mRadius = (int) ta.getDimension(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_radius,dpToPx(30));
mColor = ta.getColor(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_color,0xffff0000);
mLineWidth= (int) ta.getDimension(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_Line_width,dpToPx(3));
mTextSize= (int) ta.getDimension(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_android_textSize,72);
mProgress=ta.getInt(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_android_progress,30);
//资源回收
ta.recycle();
//初始化画笔要在获取属性之后
initPaint();
}
2.测量OnMeasure
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//测量宽度
int widthMode= MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int width=0;
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
width = widthSize;
}else {
int needWidth = measureWidth() + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
width = Math.min(widthSize,needWidth);
}else {
width = needWidth;
}
}
//测量高度
int heightMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int height=0;
//若已经指定视图宽度和高度,直接赋值即可
if(heightMode==MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
height=heightSize;
}else {
int needHeight=measureHeigth()+getPaddingBottom()+getPaddingTop();
//若要求至多,则取最小值
if (heightMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
height=Math.min(needHeight,heightSize);
}else {
//使用自己测量值
height=needHeight;
}
}
//设置获取到的宽度和高度
setMeasuredDimension(width,height);
} //根据View的具体样式使用不同的测量方法
private int measureHeigth() {
return mRadius*2;
}
private int measureWidth() {
return mRadius*2;
}
3.OnDraw
//绘制图形,draw里面最好不要new对象,造成资源浪费
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
//绘制细圆,空心圆要设置为STROKE
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(mLineWidth*1.0f/4);
int width=getWidth();
int height=getHeight();
canvas.drawCircle(width/2,height/2,width/2-getPaddingLeft()-mPaint.getStrokeWidth()/2,mPaint);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(mLineWidth);
canvas.save();
//重新设置canvas画布的中心
canvas.translate(getPaddingLeft(),getPaddingTop());
//将进度转换成角度
float angle=mProgress * 1.0f /100 * 360;
//以矩形作为外框,画一个扇形
canvas.drawArc(mProgressRectF,0,angle,false,mPaint);
canvas.restore();
//绘制文本
String text= mProgress + "%";
//绘制文本不需要设置宽度
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(0);
mPaint.setTextAlign(Paint.Align.CENTER);
mPaint.setTextSize(mTextSize);
int y=getHeight()/2;
//获取字体高度
int textHeight = getTextHeight(text);
canvas.drawText(text,0,text.length(),getWidth()/2,y+textHeight/2,mPaint);
}
//提取出方法
private int getTextHeight(String text) {
//获取字体高度
mPaint.getTextBounds(text,0,text.length(),bound);
return bound.height();
}
4.状态的存储与恢复
private static final String INSTANCE="instence";
private static final String KEY_PROGRESS="key_progress";
//存储状态
@Nullable
@Override
protected Parcelable onSaveInstanceState() {
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putInt(KEY_PROGRESS,mProgress);
bundle.putParcelable(INSTANCE,super.onSaveInstanceState());
return bundle;
}
//恢复状态
@Override
protected void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state) {
if (state instanceof Bundle){
Bundle bundle= (Bundle) state;
mProgress = bundle.getInt(KEY_PROGRESS);
super.onRestoreInstanceState(bundle.getParcelable(INSTANCE));
return;
}
super.onRestoreInstanceState(state);
}
效果图:

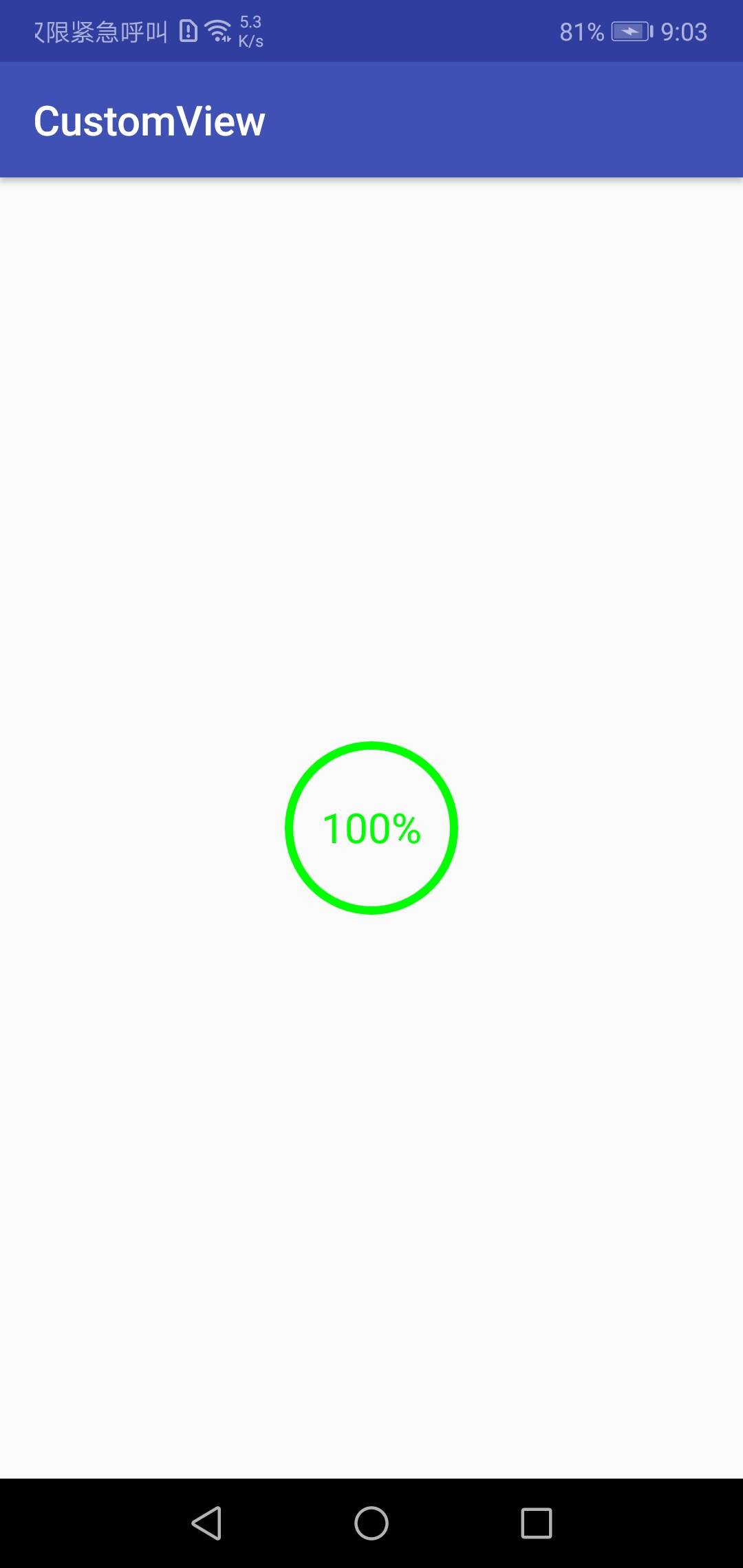
完整代码:
package com.example.jiaho.customview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.graphics.RectF;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Parcelable;
import android.support.annotation.NonNull;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.TypedValue;
import android.view.View;
public class RoundProgressBar extends View{
private int mRadius;
private int mColor;
private int mLineWidth;
private int mTextSize;
private int mProgress;
private RectF mProgressRectF;
private Paint mPaint;
private Rect bound= new Rect();
public RoundProgressBar(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray ta=context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.RoundProgressBar);
//在构造方法中进行属性获取
mRadius = (int) ta.getDimension(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_radius,dpToPx(30));
mColor = ta.getColor(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_color,0xffff0000);
mLineWidth= (int) ta.getDimension(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_Line_width,dpToPx(3));
mTextSize= (int) ta.getDimension(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_android_textSize,72);
mProgress=ta.getInt(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_android_progress,30);
//资源回收
ta.recycle();
//初始化画笔要在获取属性之后
initPaint();
}
//将单位dp转化成px
private float dpToPx(int dpVal) {
return TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP,dpVal,getResources().getDisplayMetrics());
}
private void initPaint() {
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setColor(mColor);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//测量宽度
int widthMode= MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int width=0;
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
width = widthSize;
}else {
int needWidth = measureWidth() + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
width = Math.min(widthSize,needWidth);
}else {
width = needWidth;
}
}
//测量高度
int heightMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int height=0;
//若已经指定视图宽度和高度,直接赋值即可
if(heightMode==MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
height=heightSize;
}else {
int needHeight=measureHeigth()+getPaddingBottom()+getPaddingTop();
//若要求至多,则取最小值
if (heightMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
height=Math.min(needHeight,heightSize);
}else {
//使用自己测量值
height=needHeight;
}
}
//设置获取到的宽度和高度
setMeasuredDimension(width,height);
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
mProgressRectF=new RectF(0,0,w - getPaddingLeft() * 2,h - getPaddingTop() * 2);
}
//根据View的具体样式使用不同的测量方法
private int measureHeigth() {
return mRadius*2;
}
private int measureWidth() {
return mRadius*2;
}
//绘制图形,draw里面最好不要new对象,造成资源浪费
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
//绘制细圆,空心圆要设置为STROKE
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(mLineWidth*1.0f/4);
int width=getWidth();
int height=getHeight();
canvas.drawCircle(width/2,height/2,width/2-getPaddingLeft()-mPaint.getStrokeWidth()/2,mPaint);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(mLineWidth);
canvas.save();
//重新设置canvas画布的中心
canvas.translate(getPaddingLeft(),getPaddingTop());
//将进度转换成角度
float angle=mProgress * 1.0f /100 * 360;
//以矩形作为外框,画一个扇形
canvas.drawArc(mProgressRectF,0,angle,false,mPaint);
canvas.restore();
//绘制文本
String text= mProgress + "%";
//绘制文本不需要设置宽度
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(0);
mPaint.setTextAlign(Paint.Align.CENTER);
mPaint.setTextSize(mTextSize);
int y=getHeight()/2;
//获取字体高度
int textHeight = getTextHeight(text);
canvas.drawText(text,0,text.length(),getWidth()/2,y+textHeight/2,mPaint);
}
//提取出方法
private int getTextHeight(String text) {
//获取字体高度
mPaint.getTextBounds(text,0,text.length(),bound);
return bound.height();
}
public void setProgress(int progress){
mProgress=progress;
//每次设置progress后都要重新绘制
invalidate();
}
public int getProgress(){
return mProgress;
}
private static final String INSTANCE="instence";
private static final String KEY_PROGRESS="key_progress";
//存储状态
@Nullable
@Override
protected Parcelable onSaveInstanceState() {
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putInt(KEY_PROGRESS,mProgress);
bundle.putParcelable(INSTANCE,super.onSaveInstanceState());
return bundle;
}
//恢复状态
@Override
protected void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state) {
if (state instanceof Bundle){
Bundle bundle= (Bundle) state;
mProgress = bundle.getInt(KEY_PROGRESS);
super.onRestoreInstanceState(bundle.getParcelable(INSTANCE));
return;
}
super.onRestoreInstanceState(state);
}
}最后
以上就是爱撒娇母鸡最近收集整理的关于自定义View其实很简单的全部内容,更多相关自定义View其实很简单内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复