文章目录
- 数据分析 第七讲 pandas练习 数据的合并和分组聚合
- 一、pandas-DataFrame
- 练习1
- 对于这一组电影数据,如果我们想runtime(电影时长)的分布情况,应该如何呈现数据?
- 练习2
- 全球食品数据分析
- 二、数据的合并和分组聚合
- 1.字符串离散化
- 2.数据合并
- 3.数据的分组聚合
- 4.索引和复合索引
- Series复合索引
- DateFrame复合索引
- 5.练习
- 1.使用matplotlib呈现出店铺总数排名前10的国家
- 2.使用matplotlib呈现出中国每个城市的店铺数量
- 三、pandas中的时间序列
- 1.时间范围
- 2.DataFrame中使用时间序列
- 3.pandas重采样
- 4.练习
- 练习1:统计出911数据中不同月份的电话次数
- 练习2现在我们有北上广、深圳、和沈阳5个城市空气质量数据,请绘制出5个城市的PM2.5随时间的变化情况
- 四、pandas画图
- 1.折线图
- 2.分组柱状图
- 2.饼图
数据分析 第七讲 pandas练习 数据的合并和分组聚合

一、pandas-DataFrame
练习1
对于这一组电影数据,如果我们想runtime(电影时长)的分布情况,应该如何呈现数据?
数据分析
# 对于这一组电影数据,如果我们想runtime(电影时长)的分布情况,应该如何呈现数据?
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
font = {
'family':'SimHei',
'weight':'bold',
'size':12
}
matplotlib.rc("font", **font)
file_path = './IMDB-Movie-Data.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
# print(df.info())
'''
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 1000 entries, 0 to 999
Data columns (total 12 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Rank 1000 non-null int64
1 Title 1000 non-null object
2 Genre 1000 non-null object
3 Description 1000 non-null object
4 Director 1000 non-null object
5 Actors 1000 non-null object
6 Year 1000 non-null int64
7 Runtime (Minutes) 1000 non-null int64
8 Rating 1000 non-null float64
9 Votes 1000 non-null int64
10 Revenue (Millions) 872 non-null float64
11 Metascore 936 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(3), int64(4), object(5)
memory usage: 93.9+ KB
None
'''
# print(df.head(3))
# runtime_data = df.loc[:,'Runtime (Minutes)'] # 也可以直接取runtime_data = df['Runtime (Minutes)']
# print(type(runtime_data)) # <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
runtime_data = df['Runtime (Minutes)']
print(type(runtime_data)) # <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
print(max(runtime_data)) # 191
print(min(runtime_data)) # 66
# print(runtime_data)
'''
0 121
1 124
2 117
3 108
4 123
...
995 111
996 94
997 98
998 93
999 87
Name: Runtime (Minutes), Length: 1000, dtype: int64
'''
runtime_data = df['Runtime (Minutes)'].values # 变成列表的形式
print(type(runtime_data)) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
print(max(runtime_data)) # 191
print(min(runtime_data)) # 66
# print(runtime_data)
'''
[121 124 117 108 123 103 128 89 141 116 133 127 133 107 109 87 139 123
118 116 120 137 108 92 120 83 159 99 100 115 111 116 144 108 107 147
169 115 132 113 89 111 73 115 99 136 132 91 122 130 136 91 118 101
152 161 88 106 117 96 151 86 112 125 130 129 133 120 106 107 133 124
108 97 108 169 143 153 151 116 148 118 180 149 137 124 129 162 187 128
153 123 146 114 141 116 106 90 105 151 132 115 144 106 116 102 120 110
105 108 89 134 118 117 130 105 118 161 104 97 127 139 98 86 164 106
165 96 108 156 139 125 86 107 130 140 122 143 138 148 127 94 130 118
165 144 104 162 113 121 117 142 88 121 91 94 131 118 112 121 106 90
132 118 144 122 129 109 144 148 118 101 84 126 102 130 130 107 134 117
118 92 105 112 124 135 113 119 100 125 133 94 128 92 140 124 95 148
114 107 113 146 134 126 120 132 99 118 125 111 114 94 144 104 112 126
136 104 100 117 96 117 100 158 110 163 119 107 97 102 118 95 139 131
114 102 100 85 99 125 134 95 90 126 118 158 109 119 119 112 92 94
147 142 112 100 131 105 81 118 119 108 108 117 112 99 102 172 107 85
143 169 110 106 89 124 112 157 117 130 115 128 113 119 98 110 105 127
95 99 118 112 92 107 143 111 94 109 127 158 132 121 95 97 104 148
113 110 104 110 129 180 93 144 138 126 112 81 94 131 104 84 114 109
120 106 110 103 95 133 87 133 117 150 123 97 122 88 126 117 107 119
131 102 139 110 127 138 102 94 89 124 119 96 119 102 118 123 107 123
98 100 132 88 106 120 115 117 136 123 89 113 113 110 111 99 123 133
97 126 86 124 81 142 100 121 105 140 126 132 100 115 122 98 101 112
112 113 85 110 91 91 92 95 118 100 157 100 137 99 93 115 104 130
98 102 108 123 146 101 111 88 108 102 99 166 102 115 104 109 170 102
116 132 102 97 123 114 103 88 130 117 100 112 81 125 95 101 102 100
124 101 108 119 109 115 108 100 117 119 125 97 109 97 103 129 100 91
112 107 157 123 158 153 120 106 137 94 96 113 111 97 115 97 97 94
117 115 105 111 98 118 85 114 108 101 106 112 109 96 131 118 109 124
141 110 131 95 94 91 94 124 91 132 115 92 150 120 161 111 120 117
133 112 106 103 109 100 123 135 117 92 126 89 125 132 130 108 92 108
128 105 107 126 103 112 92 108 98 100 106 123 100 104 106 91 108 92
122 84 103 91 110 101 127 111 154 96 98 98 109 107 121 101 117 106
117 125 146 101 90 103 94 110 133 114 137 110 107 93 152 112 106 105
96 116 110 83 97 95 113 88 129 95 110 95 100 98 139 120 124 162
135 160 90 92 101 139 95 114 103 88 108 97 109 118 104 88 93 98
112 112 120 85 98 129 93 116 83 113 117 122 119 113 85 116 101 133
101 104 116 101 103 87 83 140 165 101 100 96 111 95 114 117 102 129
106 115 129 143 114 137 131 114 98 126 115 102 101 140 123 112 90 130
123 118 96 88 103 122 96 151 104 105 127 93 100 106 128 94 111 106
111 165 98 87 106 88 141 96 150 80 95 131 116 108 104 86 138 97
123 115 102 89 140 113 109 110 117 100 119 104 100 149 104 126 93 128
118 112 99 111 129 110 96 116 86 127 99 106 113 104 107 103 106 111
92 87 113 116 114 114 102 118 85 153 114 122 109 119 106 95 98 110
96 106 102 90 90 108 113 117 120 82 95 134 108 92 89 92 118 111
101 66 102 108 120 98 114 109 88 110 115 105 104 111 116 95 111 128
93 100 123 112 87 129 95 94 99 73 107 123 118 119 90 88 91 108
191 87 102 94 120 112 83 108 128 113 102 115 108 125 135 97 98 138
94 131 108 128 123 104 116 96 92 111 115 123 107 141 113 129 81 85
108 120 110 122 99 126 116 85 93 107 114 100 98 98 110 99 120 125
119 96 101 143 139 101 88 100 104 134 127 145 92 105 123 117 96 89
101 105 98 102 117 110 95 122 95 106 133 87 96 89 122 156 103 91
147 113 97 93 102 103 154 117 110 110 86 144 113 107 97 97 120 108
92 96 108 109 98 124 86 106 119 99 132 91 100 80 105 115 146 95
105 94 100 109 117 110 101 101 115 108 104 180 122 123 83 150 92 105
123 111 124 94 113 92 97 120 109 118 133 104 111 102 92 104 99 128
92 165 97 97 88 111 94 98 93 87]'''
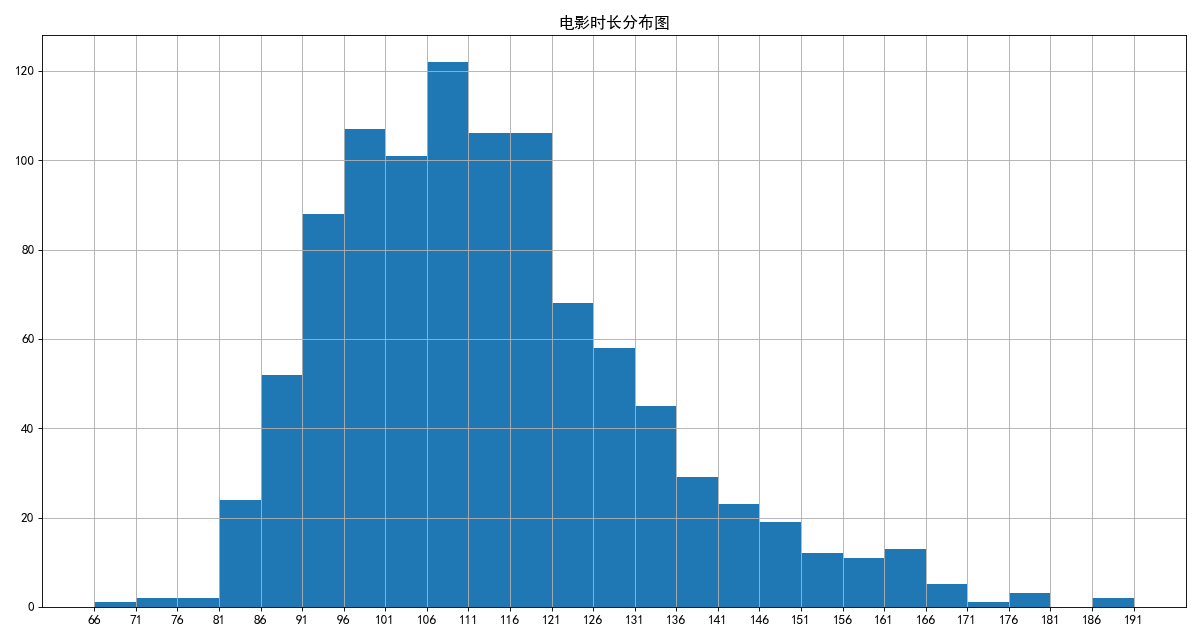
max_runtime = max(runtime_data)
min_runtime = min(runtime_data)
# 直方图
# 组数 = (最大值-最小值)/组距 (191-66)//5 = 25
num_bins = (max_runtime - min_runtime) // 5
# print(num_bins) # 25
plt.figure(figsize=(15,8),dpi=80)
plt.hist(runtime_data,num_bins)
plt.xticks(range(min_runtime,max_runtime+5,5))
plt.title('电影时长分布图')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
练习2
全球食品数据分析
步骤分析
1.数据清洗
2.获取国家列表
3.对各个国家进行统计
4.保存统计结果
import pandas as pd
# df = pd.read_csv('FoodFacts.csv')
# print(df.info())
'''
sys:1: DtypeWarning: Columns (0,3,5,27,36) have mixed types.Specify dtype option on import or set low_memory=False.
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 65503 entries, 0 to 65502
Columns: 159 entries, code to nutrition_score_uk_100g
dtypes: float64(103), object(56)
memory usage: 79.5+ MB
None'''
def get_countries(countries_data):
'''获取国家数据'''
low_countries_data = countries_data.str.lower() # 改为小写
# print(low_countries_data.head(30))
# 很多行包含两个国家france,united kingdom
# contains 模糊查询 ~ 非
low_countries_data = low_countries_data[~low_countries_data.str.contains(',')]
countries = low_countries_data.unique() # 返回列的所有唯一值
# print(countries)
'''
['united kingdom' 'france' 'spain' 'germany' 'united states' 'belgium'
'australia' 'netherlands' 'cuba' 'canada' 'switzerland' 'austria'
'sweden' 'united arab emirates' 'saint pierre and miquelon' 'fr:quebec'
'italy' 'czech republic' 'china' 'cambodia' 'réunion' 'hong kong'
'brazil' 'japan' 'mexico' 'lebanon' 'philippines' 'guadeloupe' 'ireland'
'senegal' "côte d'ivoire" 'togo' 'poland' 'india' 'south korea' 'turkey'
'french guiana' 'portugal' 'south africa' 'romania' 'denmark' 'greece'
'luxembourg' 'new caledonia' 'russia' 'french polynesia' 'tunisia'
'martinique' 'mayotte' 'hungary' 'bulgaria' 'slovenia' 'finland'
'republique-de-chine' 'taiwan' 'lithuania' 'belarus' 'cyprus' 'irlande'
'albania' 'malta' 'iceland' 'polska' 'kenya' 'mauritius' 'algeria' 'iran'
'qatar' 'thailand' 'colombia' 'norway' 'israel' 'venezuela' 'argentina'
'chile' 'new zealand' 'andorra' 'serbia' 'other-turquie' 'iraq'
'nederland' 'singapore' 'indonesia' 'burkina faso']'''
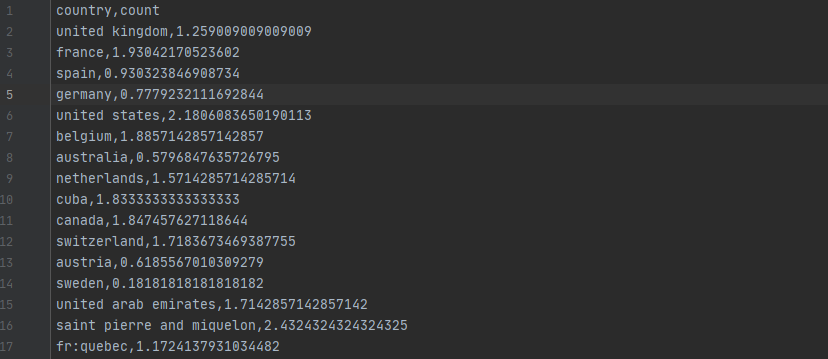
# print("一共有%s个国家"%len(countries)) # 一共有84个国家
return countries
def get_additives_count(countries, data):
count_list = []
for country in countries:
f_data = data[data['countries_en'].str.contains(country, case=False)] # 模糊查找,不区分大小写
# print(f_data.head(10))
# exit()
'''
countries_en additives_n
5 United Kingdom 0.0
10 United Kingdom 5.0
11 United Kingdom 5.0
14 United Kingdom 0.0
17 United Kingdom 0.0
18 United Kingdom 0.0
46 France,United Kingdom 1.0
60 United Kingdom 0.0
84 United Kingdom 0.0
97 United Kingdom 0.0
'''
count = f_data['additives_n'].mean() # 计算平均值
count_list.append(count)
# print(count_list)
'''
[1.259009009009009, 1.93042170523602, 0.930323846908734, 0.7779232111692844, 2.1806083650190113, 1.8857142857142857, 0.5796847635726795, 1.5714285714285714, 1.8333333333333333, 1.847457627118644, 1.7183673469387755, 0.6185567010309279, 0.18181818181818182, 1.7142857142857142, 2.4324324324324325, 1.1724137931034482, 0.9190751445086706, 1.2666666666666666, 1.2, 0.2222222222222222, 2.0625, 1.375, 0.898876404494382, 0.8666666666666667, 1.75, 0.6, 0.8, 1.6748466257668713, 0.7142857142857143, 1.9166666666666667, 0.0, 8.0, 2.310810810810811, 2.0, 2.0, 0.3, 1.7954545454545454, 1.8299492385786802, 1.7272727272727273, 1.7692307692307692, 1.5912408759124088, 1.1111111111111112, 2.1923076923076925, 1.3333333333333333, 0.125, 2.0, 2.246153846153846, 1.5454545454545454, 0.0, 0.5384615384615384, 1.25, 0.25, 0.4166666666666667, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.2857142857142857, 1.3333333333333333, 0.6666666666666666, 0.0, 1.5, 2.1666666666666665, 2.857142857142857, 0.0, 4.4, 0.6896551724137931, 0.5, 1.5714285714285714, 1.0, 0.0, 1.9090909090909092, 3.5, 2.6607142857142856, 0.2, 2.0, 0.0, 1.5, 0.0, 1.0, 2.125, 1.6666666666666667]
'''
# print(len(count_list)) # 84
result_df = pd.DataFrame()
result_df['country'] = countries
result_df['count'] = count_list
return result_df
def main():
'''主函数'''
# 读取数据
df1 = pd.read_csv('FoodFacts.csv', usecols=['countries_en', 'additives_n'])
# print(df1.info())
'''
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 65503 entries, 0 to 65502
Data columns (total 2 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 countries_en 65292 non-null object
1 additives_n 43664 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(1), object(1)
memory usage: 1023.6+ KB
None'''
# 数据清洗 删除缺失数据
data = df1.dropna()
# print(data.info())
'''<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
Int64Index: 43616 entries, 5 to 65501
Data columns (total 2 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 countries_en 43616 non-null object
1 additives_n 43616 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(1), object(1)
memory usage: 1022.2+ KB
None'''
# print(data.head())
''' countries_en additives_n
5 United Kingdom 0.0
6 France 0.0
8 France 0.0
10 United Kingdom 5.0
11 United Kingdom 5.0'''
countries = get_countries(data['countries_en'])
# print(countries)
# 获取每个国家添加剂的数量
additives = get_additives_count(countries, data)
additives.to_csv('result.csv', index=False) # 保存,不加索引
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
二、数据的合并和分组聚合
1.字符串离散化
- 字符串离散化的案例
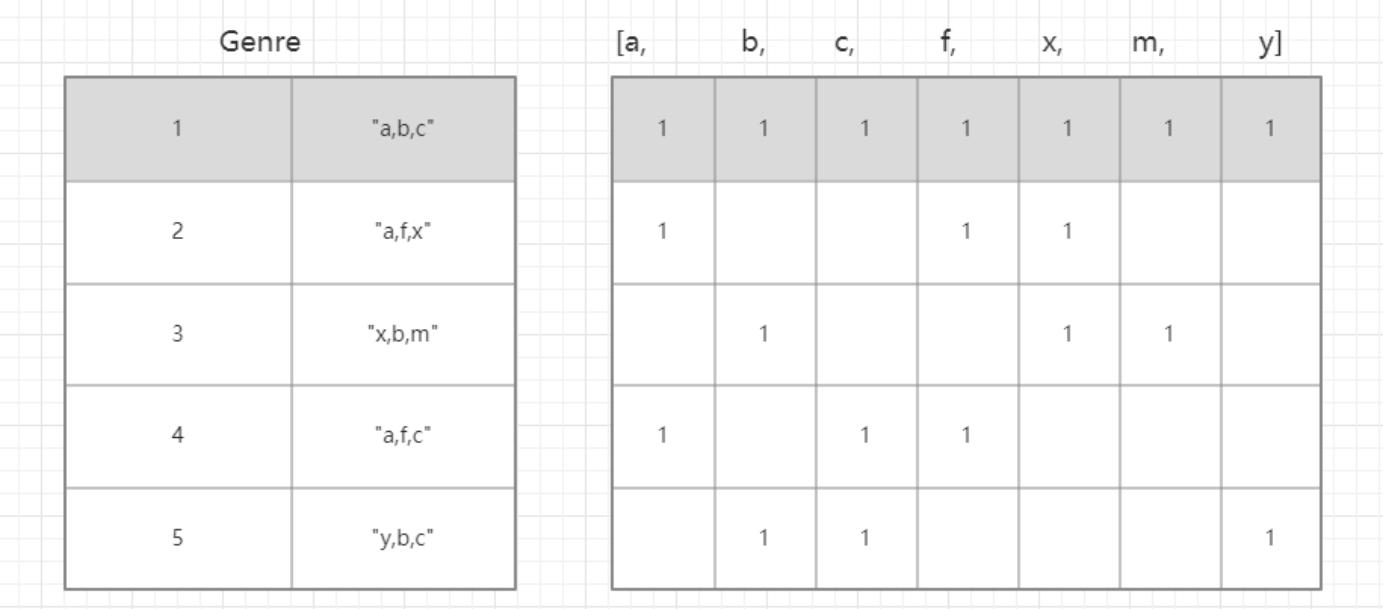
对于这一组电影数据,如果我们希望统计电影分类(genre)的情况,应该如何处理数据? - 思路:重新构造一个全为0的数组,列名为分类,如果某一条数据中分类出现过,就让0变为1
# 字符串离散化的案例
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
font = {
'family': 'SimHei',
'weight': 'bold',
'size': 12
}
matplotlib.rc("font", **font)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 5) # 只看5行
pd.set_option('max_colwidth', 200)
file_path = './IMDB-Movie-Data.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
# print(df)
# print(df.info())
# print(df.head(3))
g_list = df.loc[:, 'Genre'] # 获取分类列
# print(g_list)
'''
0 Action,Adventure,Sci-Fi
1 Adventure,Mystery,Sci-Fi
...
998 Adventure,Comedy
999 Comedy,Family,Fantasy
Name: Genre, Length: 1000, dtype: object'''
g_list = df["Genre"].str.split(",").tolist() # [[],...,[]]
# print(g_list)
# temp_list = []
# for i in g_list:
# for j in i:
# # print(j)
# temp_list.append(j)
# print(set(temp_list))
genre_list = list(set([j for i in g_list for j in i])) # 电影分类类名
# print(genre_list)
'''['Action', 'Crime', 'Biography', 'Adventure', 'Thriller', 'Music', 'Romance', 'Sport', 'Family', 'Horror', 'Western', 'War', 'Animation', 'Mystery', 'Sci-Fi', 'History', 'Drama', 'Musical', 'Fantasy', 'Comedy']'''
# 构造全为0的数组
zeros_data = pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((df.shape[0], len(genre_list))), columns=genre_list)
# print(zeros_data)
'''
Action Horror Family Thriller Animation History Romance Fantasy
0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
998 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
999 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
Biography Western Drama Comedy Sci-Fi Crime War Sport Mystery
0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
998 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
999 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
Musical Music Adventure
0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 0.0
.. ... ... ...
998 0.0 0.0 0.0
999 0.0 0.0 0.0
[1000 rows x 20 columns]'''
# 给每个电影出现的位置赋值1
# print(df) # [1000 rows x 12 columns]
for i in range(df.shape[0]):
# zeros_data[0,[Action,Musical]] = 1
zeros_data.loc[i, g_list[i]] = 1
# print(zeros_data.head(3))
'''
Music Sport Mystery Adventure Musical Comedy Horror Fantasy Action
0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
1 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0
Biography Family Sci-Fi War Thriller Romance Drama Crime Animation
0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
Western History
0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0
'''
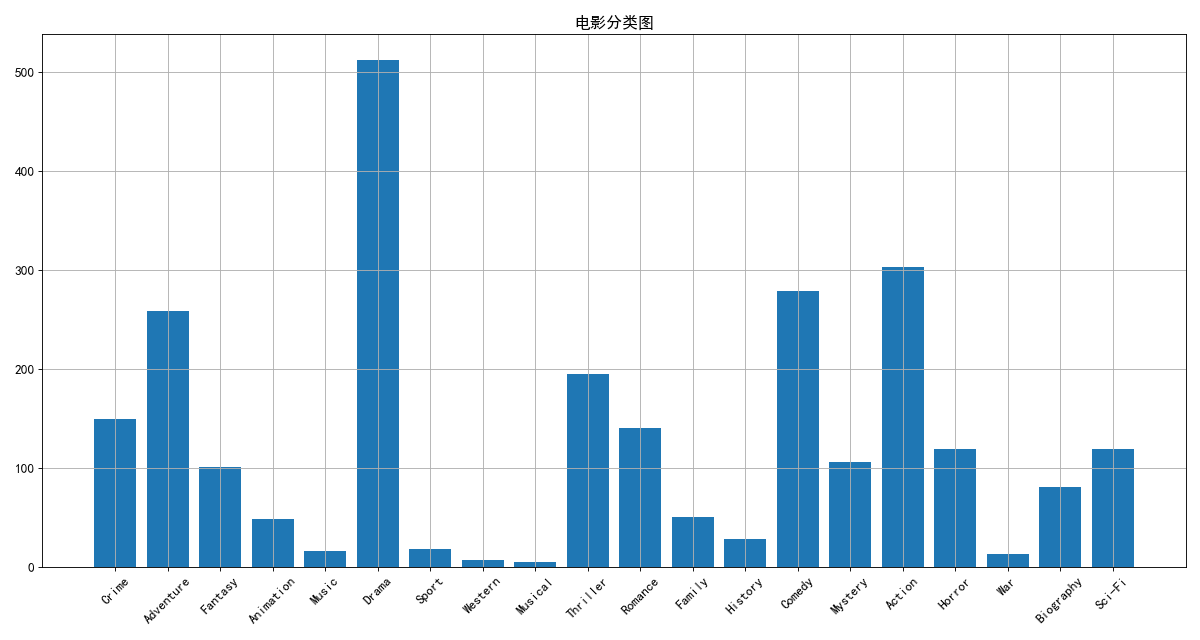
genre_count = zeros_data.sum(axis=0) # 对0轴进行求和
# print(genre_count)
'''
Thriller 195.0
Biography 81.0
...
Action 303.0
Sci-Fi 120.0
Length: 20, dtype: float64'''
x = genre_count.index
y = genre_count.values
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 8), dpi=80)
plt.bar(x, y)
plt.xticks(range(len(x)), x, rotation=45)
plt.title("电影分类图")
plt.grid()
plt.show()
2.数据合并
- join:默认情况下它是把行索引相同的数据合并到一起
- merge:按照指定的列把数据按照一定的方式合并到一起
- 示例1
# 数据合并
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
t1 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4),index=list('ABC'),columns=list('DEFG'))
t2 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(10).reshape(2,5),index=list('AB'),columns=list('VWXYZ'))
print(t1)
'''
D E F G
A 0 1 2 3
B 4 5 6 7
C 8 9 10 11'''
print(t2)
'''
V W X Y Z
A 0 1 2 3 4
B 5 6 7 8 9'''
print(t1 + t2)
'''
D E F G V W X Y Z
A NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
B NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
C NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN'''
print(t1.join(t2)) # join:以t1为基础,默认情况下它是把行索引相同的数据合并到一起
'''
D E F G V W X Y Z
A 0 1 2 3 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0
B 4 5 6 7 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0
C 8 9 10 11 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN'''
print(t2.join(t1)) # join:以t2为基础,默认情况下它是把行索引相同的数据合并到一起
'''
V W X Y Z D E F G
A 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3
B 5 6 7 8 9 4 5 6 7'''
t3 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4),index=list('ABC'),columns=list('DEFG'))
t4 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(10).reshape(2,5),index=list('AC'),columns=list('VWXYZ'))
print(t3)
'''
D E F G
A 0 1 2 3
B 4 5 6 7
C 8 9 10 11'''
print(t4)
'''
V W X Y Z
A 0 1 2 3 4
C 5 6 7 8 9'''
print(t3.join(t4)) # join:以t3为基础,默认情况下它是把行索引相同的数据合并到一起
'''
D E F G V W X Y Z
A 0 1 2 3 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0
B 4 5 6 7 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
C 8 9 10 11 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0'''
print(t4.join(t3)) # join:以t4为基础,默认情况下它是把行索引相同的数据合并到一起
'''
V W X Y Z D E F G
A 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3
C 5 6 7 8 9 8 9 10 11'''
t5 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4),index=list('ABC'),columns=list('DEFG'))
t6 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(10).reshape(2,5),index=list('DE'),columns=list('VWXYZ'))
print(t5.join(t6)) # join:以t5为基础,没有相同的索引,后面拼接的都为NaN
'''
D E F G V W X Y Z
A 0 1 2 3 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
B 4 5 6 7 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
C 8 9 10 11 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN'''
print(t6.join(t5)) # join:以t6为基础,没有相同的索引,后面拼接的都为NaN
'''
V W X Y Z D E F G
D 0 1 2 3 4 NaN NaN NaN NaN
E 5 6 7 8 9 NaN NaN NaN NaN'''
- 示例2
# 数据合并
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
t1 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4), index=list('ABC'), columns=list('DEFG'))
t2 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(10).reshape(2, 5), index=list('AB'), columns=list('DWXYZ'))
print(t1)
'''
D E F G
A 0 1 2 3
B 4 5 6 7
C 8 9 10 11'''
print(t2)
'''
D W X Y Z
A 0 1 2 3 4
B 5 6 7 8 9'''
print(t1 + t2)
'''
D E F G W X Y Z
A 0.0 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
B 9.0 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
C NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN'''
print(t1.merge(t2)) # merge:至少要有一个相同的列索引,相同的列下有相同的元素,就把该元素所在的行(去除相同的元素)合并到一行
'''
D E F G W X Y Z
0 0 1 2 3 1 2 3 4'''
t1.iloc[2, 0] = 5
print(t1)
'''
D E F G
A 0 1 2 3
B 4 5 6 7
C 5 9 10 11'''
print(t2)
'''
D W X Y Z
A 0 1 2 3 4
B 5 6 7 8 9'''
print(t1.merge(t2)) # 以t1为主,merge:至少要有一个相同的列索引,相同的列下有相同的元素,就把该元素所在的行(去除相同的元素)合并到一行,合并后的数据行索引从0开始
'''
D E F G W X Y Z
0 0 1 2 3 1 2 3 4
1 5 9 10 11 6 7 8 9'''
print(t2.merge(t1)) # 以t2为主,merge:至少要有一个相同的列索引,相同的列下有相同的元素,就把该元素所在的行(去除相同的元素)合并到一行,合并后的数据行索引从0开始
'''
D W X Y Z E F G
0 0 1 2 3 4 1 2 3
1 5 6 7 8 9 9 10 11'''
t1.iloc[[0, 1, 2], 0] = 1
print(t1)
'''
D E F G
A 1 1 2 3
B 1 5 6 7
C 1 9 10 11'''
print(t2)
'''
D W X Y Z
A 0 1 2 3 4
B 5 6 7 8 9'''
print(t2.merge(t1)) # 以t2为主,merge:至少要有一个相同的列索引,相同的列下没有相同的元素,Empty DataFrame
'''
Empty DataFrame
Columns: [D, W, X, Y, Z, E, F, G]
Index: []'''
t1.iloc[[0, 1, 2], 0] = 0
print(t1)
'''
D E F G
A 0 1 2 3
B 0 5 6 7
C 0 9 10 11'''
print(t2)
'''
D W X Y Z
A 0 1 2 3 4
B 5 6 7 8 9'''
print(t2.merge(t1)) # 以t2为主,merge:至少要有一个相同的列索引,相同的列下有相同的元素,就把该元素所在的行(去除相同的元素)合并到一行,合并后的数据行索引从0开始
'''
D W X Y Z E F G
0 0 1 2 3 4 1 2 3
1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
2 0 1 2 3 4 9 10 11'''
print(t2.merge(t1,
how='left')) # 以t2为主,merge:至少要有一个相同的列索引,相同的列下有相同的元素,就把该元素所在的行(去除相同的元素)合并到一行,合并后的数据行索引从0开始 how='left'保留t2的原数据,后面用NaN填充
'''
D W X Y Z E F G
0 0 1 2 3 4 1.0 2.0 3.0
1 0 1 2 3 4 5.0 6.0 7.0
2 0 1 2 3 4 9.0 10.0 11.0
3 5 6 7 8 9 NaN NaN NaN'''
print(t2.merge(t1, on='D', how='outer'))
'''
D W X Y Z E F G
0 0 1 2 3 4 1.0 2.0 3.0
1 0 1 2 3 4 5.0 6.0 7.0
2 0 1 2 3 4 9.0 10.0 11.0
3 5 6 7 8 9 NaN NaN NaN'''
t3 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4), index=list('abc'), columns=list('MNOP'))
t4 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(10).reshape(2, 5), index=list('de'), columns=list('MWXYZ'))
print(t3)
'''
M N O P
a 0 1 2 3
b 4 5 6 7
c 8 9 10 11'''
print(t4)
'''
M W X Y Z
d 0 1 2 3 4
e 5 6 7 8 9
'''
print(t3.merge(t4,left_on='N',right_on='Z'))
'''
M_x N O P M_y W X Y Z
0 8 9 10 11 5 6 7 8 9'''
3.数据的分组聚合
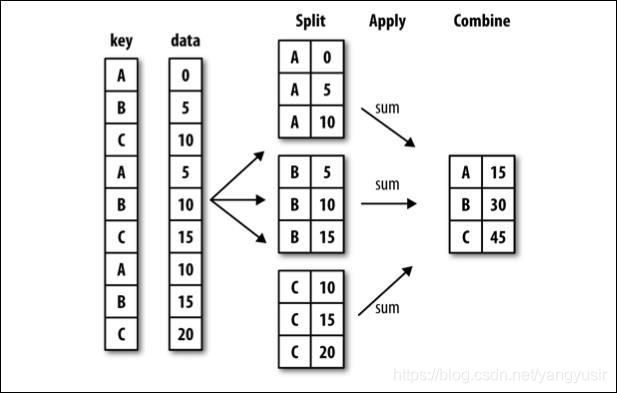
df.groupby(by=“columns_name”)
dict_obj = {
‘key1’ : [‘a’, ‘b’, ‘a’, ‘b’,‘a’, ‘b’, ‘a’, ‘a’],
‘key2’ : [‘one’, ‘one’, ‘two’, ‘three’,‘two’, ‘two’, ‘one’, ‘three’],
‘data1’: np.arange(8),
‘data2’: np.arange(8)
}
# 分组聚合
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
dict_obj = {
'key1': ['a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'a'],
'key2': ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'two', 'two', 'one', 'three'],
'data1': np.arange(8),
'data2': np.arange(8)
}
df = pd.DataFrame(dict_obj)
print(df)
'''
key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one 0 0
1 b one 1 1
2 a two 2 2
3 b three 3 3
4 a two 4 4
5 b two 5 5
6 a one 6 6
7 a three 7 7
'''
# 分组 groupby
df.groupby(by="key1")
print(df.groupby(by="key1")) # <pandas.core.groupby.generic.DataFrameGroupBy object at 0x0000000002CB9208>
for i in df.groupby(by="key1"):
print(i)
'''
('a', key1 key2 data1 data2
0 a one 0 0
2 a two 2 2
4 a two 4 4
6 a one 6 6
7 a three 7 7)
('b', key1 key2 data1 data2
1 b one 1 1
3 b three 3 3
5 b two 5 5)
'''
print(df.groupby(by="key1").mean()) # 求平均值,key2不是数字类型直接忽略掉
'''
data1 data2
key1
a 3.8 3.8
b 3.0 3.0'''
print(df.groupby(by="key1").sum()) # 求和,key2不是数字类型直接忽略掉
'''
data1 data2
key1
a 19 19
b 9 9'''
print(df.groupby(by="key1").count()) # 记录个数
'''
key2 data1 data2
key1
a 5 5 5
b 3 3 3'''
- 练习
现在我们有一组关于全球星巴克店铺的统计数据,如果我想知道美国的星巴克数量和中国的哪个多,或者我想知道中国每个省份星巴克的数量的情况,那么应该怎么办?
# 现在我们有一组关于全球星巴克店铺的统计数据,如果我想知道美国的星巴克数量和
# 中国的哪个多,或者我想知道中国每个省份星巴克的数量的情况,那么应该怎么办?
# 思路:根据国家分组,统计每个国家的总数进行对比,取出中国的数据,按省份分组统计每个省份的总数进行对比
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
file_path = './starbucks_store_worldwide.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
print(df.info())
'''
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 25600 entries, 0 to 25599
Data columns (total 13 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Brand 25600 non-null object
1 Store Number 25600 non-null object
2 Store Name 25600 non-null object
3 Ownership Type 25600 non-null object
4 Street Address 25598 non-null object
5 City 25585 non-null object
6 State/Province 25600 non-null object
7 Country 25600 non-null object
8 Postcode 24078 non-null object
9 Phone Number 18739 non-null object
10 Timezone 25600 non-null object
11 Longitude 25599 non-null float64
12 Latitude 25599 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(2), object(11)
memory usage: 2.5+ MB
None'''
print(df.head())
'''
Brand Store Number ... Longitude Latitude
0 Starbucks 47370-257954 ... 1.53 42.51
1 Starbucks 22331-212325 ... 55.47 25.42
2 Starbucks 47089-256771 ... 55.47 25.39
3 Starbucks 22126-218024 ... 54.38 24.48
4 Starbucks 17127-178586 ... 54.54 24.51
'''
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 10)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 13)
print(df)
'''
City State/Province Country Postcode Phone Number
0 Andorra la Vella 7 AD AD500 376818720
1 Ajman AJ AE NaN NaN
2 Ajman AJ AE NaN NaN
3 Abu Dhabi AZ AE NaN NaN
4 Abu Dhabi AZ AE NaN NaN
... ... ... ... ... ...
25595 Thành Phố Hồ Chí Minh SG VN 70000 08 3824 4668
25596 Thành Phố Hồ Chí Minh SG VN 70000 08 5413 8292
25597 Johannesburg GT ZA 2194 27873500159
25598 Menlyn GT ZA 181 NaN
25599 Midrand GT ZA 1682 27873500215
Timezone Longitude Latitude
0 GMT+1:00 Europe/Andorra 1.53 42.51
1 GMT+04:00 Asia/Dubai 55.47 25.42
2 GMT+04:00 Asia/Dubai 55.47 25.39
3 GMT+04:00 Asia/Dubai 54.38 24.48
4 GMT+04:00 Asia/Dubai 54.54 24.51
... ... ... ...
25595 GMT+000000 Asia/Saigon 106.70 10.78
25596 GMT+000000 Asia/Saigon 106.71 10.72
25597 GMT+000000 Africa/Johannesburg 28.04 -26.15
25598 GMT+000000 Africa/Johannesburg 28.28 -25.79
25599 GMT+000000 Africa/Johannesburg 28.11 -26.02
[25600 rows x 13 columns]
'''
grouped = df.groupby(by='Country').count()['Brand']
print(type(grouped)) # <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
print(grouped)
'''
AD 1
AE 144
AR 108
AT 18
AU 22
...
TT 3
TW 394
US 13608
VN 25
ZA 3
Name: Brand, Length: 73, dtype: int64'''
us_count = grouped['US'] # us_count = grouped.loc['US']也可以
print(us_count) # 13608
cn_count = grouped['CN'] # cn_count = grouped.loc['CN']也可以
print(cn_count) # 2734
print("美国的星巴克总数位%s,中国的星巴克为%s" % (us_count, cn_count))
'''美国的星巴克总数位13608,中国的星巴克为2734'''
# 布尔索引
china_data = df[df['Country'] == 'CN']
print(china_data)
'''
Brand Store Number Store Name Ownership Type
2091 Starbucks 22901-225145 北京西站第一咖啡店 Company Owned
2092 Starbucks 32320-116537 北京华宇时尚店 Company Owned
2093 Starbucks 32447-132306 北京蓝色港湾圣拉娜店 Company Owned
2094 Starbucks 17477-161286 北京太阳宫凯德嘉茂店 Company Owned
2095 Starbucks 24520-237564 北京东三环北店 Company Owned
... ... ... ... ...
4820 Starbucks 17872-186929 Sands Licensed
4821 Starbucks 24126-235784 Wynn II Licensed
4822 Starbucks 28490-242269 Wynn Palace BOH Licensed
4823 Starbucks 22210-218665 Sands Cotai Central Licensed
4824 Starbucks 17108-179449 One Central Licensed
Street Address City State/Province
2091 丰台区, 北京西站通廊7-1号, 中关村南大街2号 北京市 11
2092 海淀区, 数码大厦B座华宇时尚购物中心内, 蓝色港湾国际商区1座C1-3单元首层、 北京市 11
2093 朝阳区朝阳公园路6号, 二层C1-3单元及二层阳台, 太阳宫中路12号 北京市 11
2094 朝阳区, 太阳宫凯德嘉茂一层01-44/45号, 东三环北路27号 北京市 11
2095 朝阳区, 嘉铭中心大厦A座B1层024商铺, 金融大街7号 北京市 11
... ... ... ...
4820 Portion of Shop 04, Ground Floor, Sands, Largo... Macau 92
4821 Wynn Macau, Rua Cidada de Sintra, NAPE Macau 92
4822 Employee Entrance Outlet, Wynn Cotai, Resort Macau 92
4823 Shop K201 & K202, Level 02, Parcela 5&6, Estra... Macau 92
4824 Promenade Rd, Open Area, 2/F Macau 92
Country Postcode Phone Number Timezone Longitude
2091 CN 100073 NaN GMT+08:00 Asia/Beijing 116.32
2092 CN 100086 010-51626616 GMT+08:00 Asia/Beijing 116.32
2093 CN 100020 010-59056343 GMT+08:00 Asia/Beijing 116.47
2094 CN 100028 010-84150945 GMT+08:00 Asia/Beijing 116.45
2095 CN NaN NaN GMT+08:00 Asia/Beijing 116.46
... ... ... ... ... ...
4820 CN NaN (853)28782773 GMT+08:00 Asia/Beijing 113.55
4821 CN NaN 85328723516 GMT+08:00 Asia/Beijing 113.55
4822 CN NaN NaN GMT+08:00 Asia/Beijing 113.54
4823 CN NaN 85328853439 GMT+08:00 Asia/Beijing 113.56
4824 CN NaN NaN GMT+08:00 Asia/Beijing 113.55
Latitude
2091 39.90
2092 39.97
2093 39.95
2094 39.97
2095 39.93
... ...
4820 22.19
4821 22.19
4822 22.20
4823 22.15
4824 22.19
[2734 rows x 13 columns]
'''
china_province_data = china_data.groupby(by='State/Province').count()
print(china_province_data['Brand'])
'''
State/Province
11 236
12 58
13 24
14 8
15 8
...
62 3
63 3
64 2
91 162
92 13
Name: Brand, Length: 31, dtype: int64'''
- DataFrameGroupBy对象方法
方法 说明
count 分组中非NA值的数量
sum 非NA值的和
mean 非NA值的平均值
min,max 非NA值的最小值和最大值
4.索引和复合索引
- 简单的索引操作: t.index
- 指定index: t.index = [‘a’,‘b’,‘c’]
- 重新设置index : t.reindex([“a”,“e”])
- 指定某一列作为index : t.set_index(“M”,drop=False)
- 返回index的唯一值: t.set_index(“M”).index.unique()
- 设置两个索引的时候会是什么样子呢?
- 示例
# 索引和复合索引
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
t1 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4), index=list('ABC'), columns=list('WXYZ'))
print(t1)
'''
W X Y Z
A 0 1 2 3
B 4 5 6 7
C 8 9 10 11'''
print(t1.index) # Index(['A', 'B', 'C'], dtype='object')
# 重置索引
print(t1.reindex(['a','e']))
'''
W X Y Z
a NaN NaN NaN NaN
e NaN NaN NaN NaN'''
print(t1.reindex(['A','e']))
'''
W X Y Z
A 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0
e NaN NaN NaN NaN'''
# 指定某一列作为索引
print(t1.set_index('W')) # 默认删除W列,以W作为行索引
'''
X Y Z
W
0 1 2 3
4 5 6 7
8 9 10 11'''
print(t1.set_index('W',drop=False)) # 不删除W列,以W作为行索引
'''
W X Y Z
W
0 0 1 2 3
4 4 5 6 7
8 8 9 10 11'''
# 返回index的唯一值: t.set_index("M").index.unique()
print(t1.set_index('W').index)
'''Int64Index([0, 4, 8], dtype='int64', name='W')'''
print(t1.set_index('W').index.unique())
'''Int64Index([0, 4, 8], dtype='int64', name='W')'''
t1.loc['B','W'] = 8
print(t1)
'''
W X Y Z
A 0 1 2 3
B 8 5 6 7
C 8 9 10 11'''
print(t1.set_index('W').index.unique())
'''Int64Index([0, 8], dtype='int64', name='W')'''
# 设置两个索引 复合索引
t2 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4), index=list('ABC'), columns=list('WXYZ'))
print(t2)
'''
W X Y Z
A 0 1 2 3
B 4 5 6 7
C 8 9 10 11'''
print(t2.set_index(['W','X']))
'''
Y Z
W X
0 1 2 3
4 5 6 7
8 9 10 11'''
print(type(t2.set_index(['W','X']))) # <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
Series复合索引
a = pd.DataFrame({‘a’: range(7),‘b’: range(7, 0, -1),‘c’: [‘one’,‘one’,‘one’,‘two’,‘two’,‘two’, ‘two’],‘d’:
list(“hjklmno”)})
设置c,d为索引
# 索引和复合索引
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
a = pd.DataFrame({'a': range(7), 'b': range(7, 0, -1), 'c': ['one', 'one', 'one', 'two', 'two', 'two', 'two'], 'd':
list("hjklmno")})
print(type(a)) # <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
print(a)
'''
a b c d
0 0 7 one h
1 1 6 one j
2 2 5 one k
3 3 4 two l
4 4 3 two m
5 5 2 two n
6 6 1 two o'''
b = a.set_index(['c','d'])
print(b)
'''
a b
c d
one h 0 7
j 1 6
k 2 5
two l 3 4
m 4 3
n 5 2
o 6 1
'''
print(b.loc['one'])
'''
a b
d
h 0 7
j 1 6
k 2 5'''
print(b.loc['one'].loc['j'])
'''
a 1
b 6
Name: j, dtype: int64'''
print(b.loc['one'].loc['j']['a']) # 1
c = b['a']
print(type(c)) # <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
print(c)
'''
c d
one h 0
j 1
k 2
two l 3
m 4
n 5
o 6
Name: a, dtype: int64'''
print(c['one']['j']) # 1
print(c['one','j']) # 1
设置d,c为索引
# 索引和复合索引
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
a = pd.DataFrame({'a': range(7), 'b': range(7, 0, -1), 'c': ['one', 'one', 'one', 'two', 'two', 'two', 'two'], 'd':
list("hjklmno")})
print(type(a)) # <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
print(a)
'''
a b c d
0 0 7 one h
1 1 6 one j
2 2 5 one k
3 3 4 two l
4 4 3 two m
5 5 2 two n
6 6 1 two o'''
b = a.set_index(['d','c'])
print(b)
'''
a b
d c
h one 0 7
j one 1 6
k one 2 5
l two 3 4
m two 4 3
n two 5 2
o two 6 1
'''
print(b.loc['j'])
'''
a b
c
one 1 6'''
print(b.loc['j'].loc['one'])
'''
a 1
b 6
Name: one, dtype: int64'''
print(b.loc['j'].loc['one']['a']) # 1
print(b.loc['j'].loc['one','a']) # 1
# 复合索引交换
print(b.swaplevel())
'''
a b
c d
one h 0 7
j 1 6
k 2 5
two l 3 4
m 4 3
n 5 2
o 6 1'''
DateFrame复合索引
# 索引和复合索引
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
a = pd.DataFrame({'a': range(7), 'b': range(7, 0, -1), 'c': ['one', 'one', 'one', 'two', 'two', 'two', 'two'], 'd':
list("hjklmno")})
print(type(a)) # <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
print(a)
'''
a b c d
0 0 7 one h
1 1 6 one j
2 2 5 one k
3 3 4 two l
4 4 3 two m
5 5 2 two n
6 6 1 two o'''
b = a.set_index(['c','d'])
print(b)
'''
a b
c d
one h 0 7
j 1 6
k 2 5
two l 3 4
m 4 3
n 5 2
o 6 1
'''
# 从外层开始取值
print(b.loc['one'].loc['j','b']) # 6
# 从内层开始取值
print(b.swaplevel().loc['j'].loc['one','b']) # 6
5.练习
1.使用matplotlib呈现出店铺总数排名前10的国家
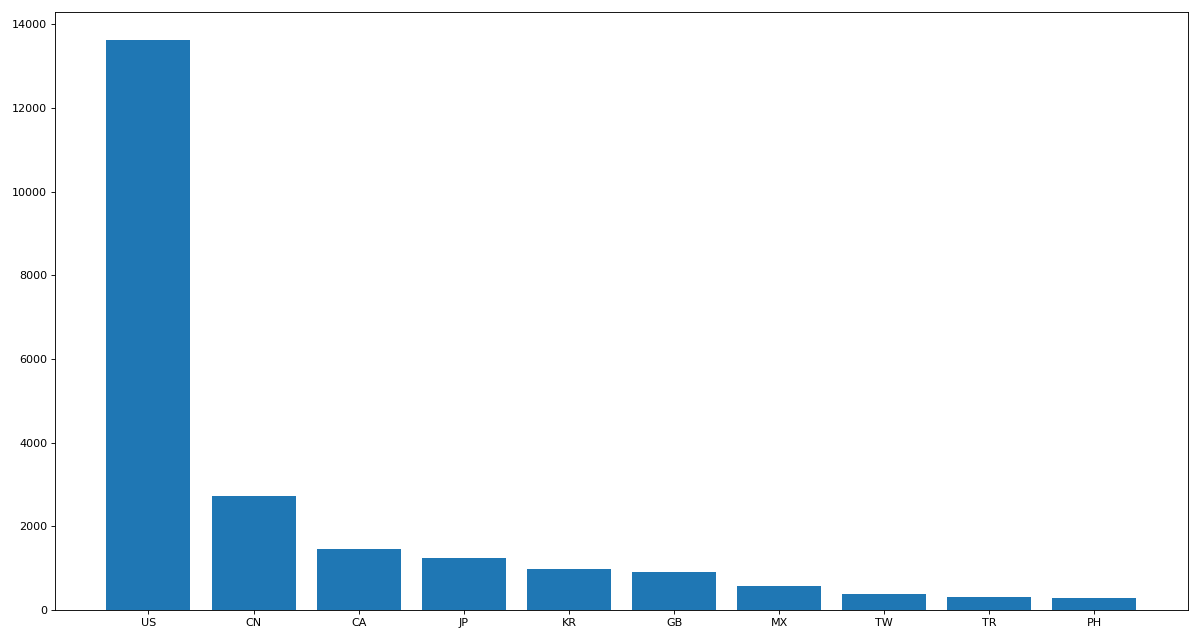
# # 1.使用matplotlib呈现出店铺总数排名前10的国家 # sort_values groupby
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
file_path = './starbucks_store_worldwide.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
print(df.info())
'''
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 25600 entries, 0 to 25599
Data columns (total 13 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Brand 25600 non-null object
1 Store Number 25600 non-null object
2 Store Name 25600 non-null object
3 Ownership Type 25600 non-null object
4 Street Address 25598 non-null object
5 City 25585 non-null object
6 State/Province 25600 non-null object
7 Country 25600 non-null object
8 Postcode 24078 non-null object
9 Phone Number 18739 non-null object
10 Timezone 25600 non-null object
11 Longitude 25599 non-null float64
12 Latitude 25599 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(2), object(11)
memory usage: 2.5+ MB
None'''
data = df.groupby(by='Country').count()
print(data.head(3))
'''
Brand Store Number Store Name ... Timezone Longitude Latitude
Country ...
AD 1 1 1 ... 1 1 1
AE 144 144 144 ... 144 144 144
AR 108 108 108 ... 108 108 108
[3 rows x 12 columns]'''
data_sort = data.sort_values(by='Brand', ascending=False)[0:10] # 倒序
print(data_sort['Brand'])
# data = df.groupby(by='Country').count()['Brand'].sort_values(ascending=False)[0:10]
# print(data) # 这样写也可以
'''
Country
US 13608
CN 2734
CA 1468
JP 1237
KR 993
GB 901
MX 579
TW 394
TR 326
PH 298
Name: Brand, dtype: int64'''
x = data_sort['Brand'].index
y = data_sort['Brand'].values
# 设置图片大小
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 8), dpi=80)
# 直方图
plt.bar(x, y)
plt.show()
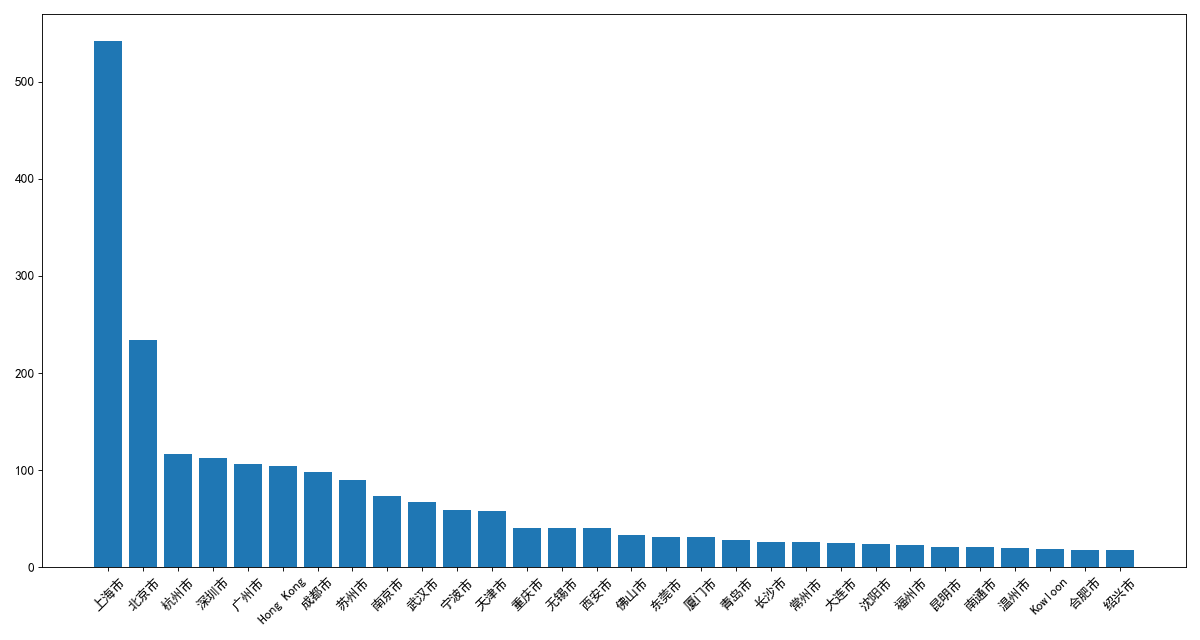
2.使用matplotlib呈现出中国每个城市的店铺数量
# 2.使用matplotlib呈现出中国每个城市的店铺数量
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
font = {
'family': 'SimHei',
'weight': 'bold',
'size': 12
}
matplotlib.rc("font", **font)
file_path = './starbucks_store_worldwide.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
# print(df.info())
'''
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Brand 25600 non-null object
1 Store Number 25600 non-null object
2 Store Name 25600 non-null object
3 Ownership Type 25600 non-null object
4 Street Address 25598 non-null object
5 City 25585 non-null object
6 State/Province 25600 non-null object
7 Country 25600 non-null object
8 Postcode 24078 non-null object
9 Phone Number 18739 non-null object
10 Timezone 25600 non-null object
11 Longitude 25599 non-null float64
12 Latitude 25599 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(2), object(11)
memory usage: 2.5+ MB
None'''
df = df[df['Country'] == 'CN']
# print(df.head(3))
'''
Brand Store Number ... Longitude Latitude
2091 Starbucks 22901-225145 ... 116.32 39.90
2092 Starbucks 32320-116537 ... 116.32 39.97
2093 Starbucks 32447-132306 ... 116.47 39.95
[3 rows x 13 columns]'''
data = df.groupby(by='City').count()['Brand'].sort_values(ascending=False)[0:30]
x = data.index
y = data.values
# 设置图片大小
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 8), dpi=80)
# 直方图
plt.bar(x, y)
# 设置x轴刻度
plt.xticks(rotation=45)
plt.show()
三、pandas中的时间序列
1.时间范围
时间范围
pd.date_range(start=None, end=None, periods=None, freq=‘D’)
periods 时间范围的个数
freq 频率,以天为单位还是以月为单位
关于频率的更多缩写

- 示例
# 时间序列
import pandas as pd
d = pd.date_range(start='20210101', end='20210201')
print(d) # freq='D' 频率默认是天
'''DatetimeIndex(['2021-01-01', '2021-01-02', '2021-01-03', '2021-01-04',
'2021-01-05', '2021-01-06', '2021-01-07', '2021-01-08',
'2021-01-09', '2021-01-10', '2021-01-11', '2021-01-12',
'2021-01-13', '2021-01-14', '2021-01-15', '2021-01-16',
'2021-01-17', '2021-01-18', '2021-01-19', '2021-01-20',
'2021-01-21', '2021-01-22', '2021-01-23', '2021-01-24',
'2021-01-25', '2021-01-26', '2021-01-27', '2021-01-28',
'2021-01-29', '2021-01-30', '2021-01-31', '2021-02-01'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D')'''
m = pd.date_range(start='20210101', end='20211231',freq='M') # 频率是1月
print(m)
'''
DatetimeIndex(['2021-01-31', '2021-02-28', '2021-03-31', '2021-04-30',
'2021-05-31', '2021-06-30', '2021-07-31', '2021-08-31',
'2021-09-30', '2021-10-31', '2021-11-30', '2021-12-31'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='M')'''
d10 = pd.date_range(start='20210101', end='20210201',freq='10D')
print(d10) # freq='10D' 频率是10天
'''
DatetimeIndex(['2021-01-01', '2021-01-11', '2021-01-21', '2021-01-31'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='10D')'''
d3 = pd.date_range(start='20210101', end='20210201',freq='3D')
print(d3) # freq='10D' 频率是3天
'''
DatetimeIndex(['2021-01-01', '2021-01-04', '2021-01-07', '2021-01-10',
'2021-01-13', '2021-01-16', '2021-01-19', '2021-01-22',
'2021-01-25', '2021-01-28', '2021-01-31'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='3D')'''
d3 = pd.date_range(start='20210101', periods=5, freq='3D')
print(d3) # freq='10D' 频率是3天 periods和end不要同时用
'''
DatetimeIndex(['2021-01-01', '2021-01-04', '2021-01-07', '2021-01-10',
'2021-01-13'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='3D')'''
2.DataFrame中使用时间序列
index=pd.date_range(“20190101”,periods=10)
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(10),index=index) 作为行索引
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(10).reshape(1,10),columns=index) 作为列索引
- 示例
# 使用时间序列
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# 时间序列当行索引
dindex = pd.date_range(start='20210101', periods=10)
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(10),index=dindex)
print(df)
'''
0
2021-01-01 0
2021-01-02 1
2021-01-03 2
2021-01-04 3
2021-01-05 4
2021-01-06 5
2021-01-07 6
2021-01-08 7
2021-01-09 8
2021-01-10 9
'''
# 时间序列当列索引
d_index = pd.date_range(start='20210101', periods=10)
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(10).reshape(1,10),columns=d_index)
print(df1)
'''
2021-01-01 2021-01-02 2021-01-03 ... 2021-01-08 2021-01-09 2021-01-10
0 0 1 2 ... 7 8 9
[1 rows x 10 columns]'''
3.pandas重采样
- 重采样:指的是将时间序列从一个频率转化为另一个频率进行处理的过程,将高频率数据转化为低频率数据为降采样,低频率转化为高频率为升采样
- pandas提供了一个resample的方法来帮助我们实现频率转化
- 示例
# 使用时间序列
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
dindex = pd.date_range(start='2021-01-01',end='2021-02-24')
t = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(55).reshape(55,1),index=dindex)
print(t)
'''
0
2021-01-01 0
2021-01-02 1
2021-01-03 2
2021-01-04 3
2021-01-05 4
2021-01-06 5
2021-01-07 6
2021-01-08 7
2021-01-09 8
2021-01-10 9
2021-01-11 10
2021-01-12 11
2021-01-13 12
2021-01-14 13
2021-01-15 14
2021-01-16 15
2021-01-17 16
2021-01-18 17
2021-01-19 18
2021-01-20 19
2021-01-21 20
2021-01-22 21
2021-01-23 22
2021-01-24 23
2021-01-25 24
2021-01-26 25
2021-01-27 26
2021-01-28 27
2021-01-29 28
2021-01-30 29
2021-01-31 30
2021-02-01 31
2021-02-02 32
2021-02-03 33
2021-02-04 34
2021-02-05 35
2021-02-06 36
2021-02-07 37
2021-02-08 38
2021-02-09 39
2021-02-10 40
2021-02-11 41
2021-02-12 42
2021-02-13 43
2021-02-14 44
2021-02-15 45
2021-02-16 46
2021-02-17 47
2021-02-18 48
2021-02-19 49
2021-02-20 50
2021-02-21 51
2021-02-22 52
2021-02-23 53
2021-02-24 54
'''
print(t.resample('M').mean())
'''
0
2021-01-31 15.0
2021-02-28 42.5'''
print(t.resample('10D').mean())
'''
0
2021-01-01 4.5
2021-01-11 14.5
2021-01-21 24.5
2021-01-31 34.5
2021-02-10 44.5
2021-02-20 52.0'''
4.练习
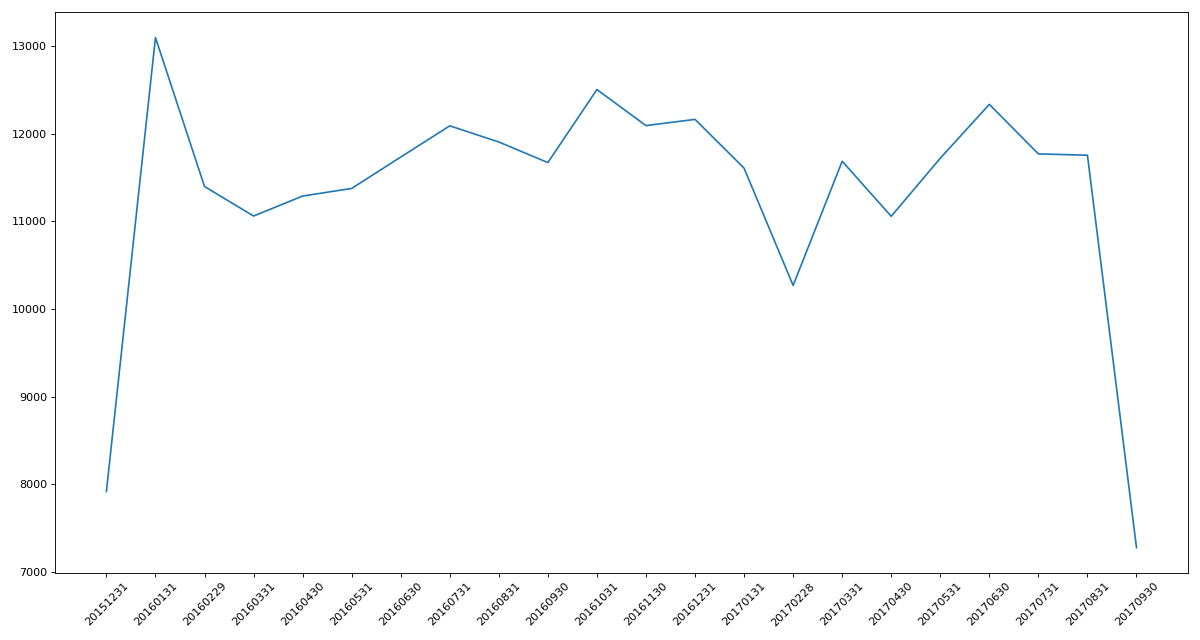
练习1:统计出911数据中不同月份的电话次数
# 练习1:统计出911数据中不同月份的电话次数
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
file_path = './911.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 30)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 9)
# print(df.info())
'''
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 249737 entries, 0 to 249736
Data columns (total 9 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 lat 249737 non-null float64
1 lng 249737 non-null float64
2 desc 249737 non-null object
3 zip 219391 non-null float64
4 title 249737 non-null object
5 timeStamp 249737 non-null object
6 twp 249644 non-null object
7 addr 249737 non-null object
8 e 249737 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(3), int64(1), object(5)
memory usage: 17.1+ MB
None
'''
# print(df['timeStamp'])
'''0 2015-12-10 17:10:52
...
249736 2017-09-20 19:42:29
Name: timeStamp, Length: 249737, dtype: object'''
df['timeStamp'] = pd.to_datetime(df['timeStamp']) # 把时间字符串转为索引
# print(df['timeStamp'])
'''
0 2015-12-10 17:10:52
...
249736 2017-09-20 19:42:29
Name: timeStamp, Length: 249737, dtype: datetime64[ns]'''
df.set_index('timeStamp', inplace=True)
# print(df)
'''
lat lng
timeStamp
2015-12-10 17:10:52 40.297876 -75.581294
... ... ...
2017-09-20 19:42:29 40.095206 -75.410735
desc
timeStamp
2015-12-10 17:10:52 REINDEER CT & DEAD END; NEW HANOVER; Station ...
... ...
2017-09-20 19:42:29 1ST AVE & MOORE RD; UPPER MERION; 2017-09-20 @...
zip title twp
timeStamp
2015-12-10 17:10:52 19525.0 EMS: BACK PAINS/INJURY NEW HANOVER
... ... ... ...
2017-09-20 19:42:29 19406.0 Traffic: VEHICLE ACCIDENT - UPPER MERION
addr e
timeStamp
2015-12-10 17:10:52 REINDEER CT & DEAD END 1
... ... ..
2017-09-20 19:42:29 1ST AVE & MOORE RD 1
[249737 rows x 8 columns]
'''
count_by_month = df.resample('M').count()['lat']
print(count_by_month)
'''
timeStamp
2015-12-31 7916
2016-01-31 13096
2016-02-29 11396
2016-03-31 11059
2016-04-30 11287
2016-05-31 11374
2016-06-30 11732
2016-07-31 12088
2016-08-31 11904
2016-09-30 11669
2016-10-31 12502
2016-11-30 12091
2016-12-31 12162
2017-01-31 11605
2017-02-28 10267
2017-03-31 11684
2017-04-30 11056
2017-05-31 11719
2017-06-30 12333
2017-07-31 11768
2017-08-31 11753
2017-09-30 7276
Freq: M, Name: lat, dtype: int64
'''
# 绘制折线图分析变化趋势
x = count_by_month.index
y = count_by_month.values
x = [i.strftime("%Y%m%d") for i in x] # 转化为时间日期格式。
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 8), dpi=80)
plt.plot(range(len(x)), y)
plt.xticks(range(len(x)), x, rotation=45)
plt.show()
https://www.kaggle.com/uciml/pm25-data-for-five-chinese-cities
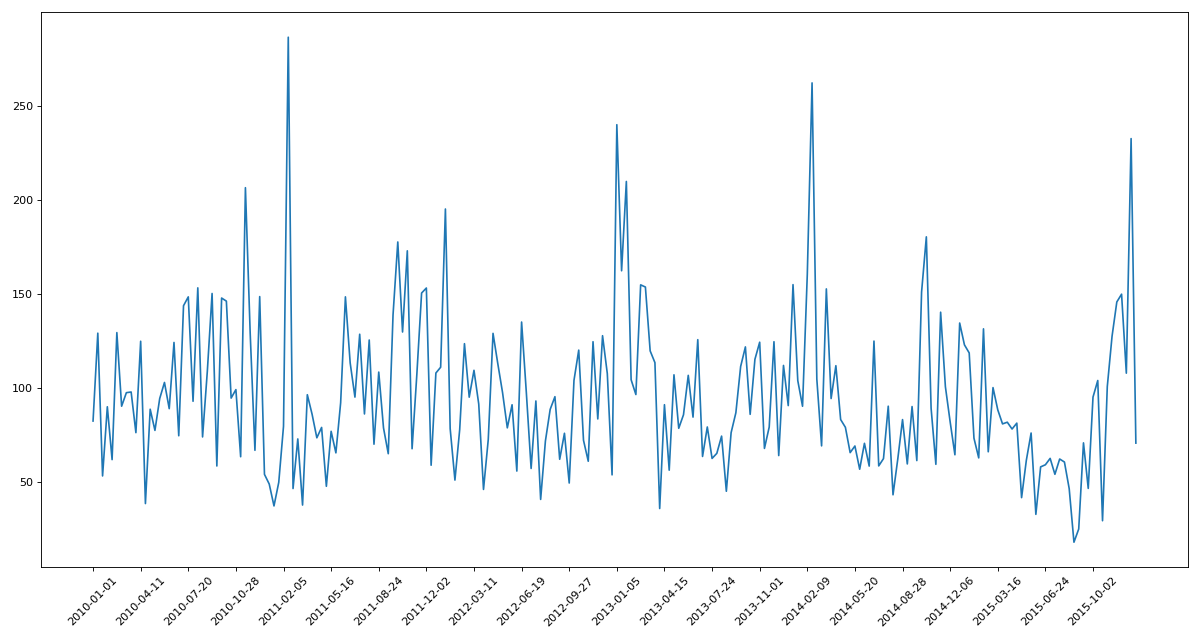
练习2现在我们有北上广、深圳、和沈阳5个城市空气质量数据,请绘制出5个城市的PM2.5随时间的变化情况
数据来源:https://www.kaggle.com/uciml/pm25-data-for-five-chinese-cities
观察这组数据中的时间结构,并不是字符串,这个时候我们应该怎么办?
之前所学习的DatetimeIndex可以理解为时间戳
那么现在我们要学习的PeriodIndex可以理解为时间段
periods = pd.PeriodIndex(year=df[“year”],month=df[“month”],day=df[“day”],hour=df[“hour”],freq=“H”)
那么如果给这个时间段降采样呢?
data = df.set_index(periods).resample(“10D”).mean()
# 现在我们有北上广、深圳、和沈阳5个城市空气质量数据,请绘制出5个城市的PM2.5随时间的变化情况
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
df = pd.read_csv('./PM2.5/BeijingPM20100101_20151231.csv')
# print(df.info())
'''
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 52584 entries, 0 to 52583
Data columns (total 18 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 No 52584 non-null int64
1 year 52584 non-null int64
2 month 52584 non-null int64
3 day 52584 non-null int64
4 hour 52584 non-null int64
5 season 52584 non-null int64
6 PM_Dongsi 25052 non-null float64
7 PM_Dongsihuan 20508 non-null float64
8 PM_Nongzhanguan 24931 non-null float64
9 PM_US Post 50387 non-null float64
10 DEWP 52579 non-null float64
11 HUMI 52245 non-null float64
12 PRES 52245 non-null float64
13 TEMP 52579 non-null float64
14 cbwd 52579 non-null object
15 Iws 52579 non-null float64
16 precipitation 52100 non-null float64
17 Iprec 52100 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(11), int64(6), object(1)
memory usage: 7.2+ MB
None'''
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 30)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 18)
# print(df.head())
'''
No year month day hour season PM_Dongsi PM_Dongsihuan
0 1 2010 1 1 0 4 NaN NaN
1 2 2010 1 1 1 4 NaN NaN
2 3 2010 1 1 2 4 NaN NaN
3 4 2010 1 1 3 4 NaN NaN
4 5 2010 1 1 4 4 NaN NaN
PM_Nongzhanguan PM_US Post DEWP HUMI PRES TEMP cbwd Iws
0 NaN NaN -21.0 43.0 1021.0 -11.0 NW 1.79
1 NaN NaN -21.0 47.0 1020.0 -12.0 NW 4.92
2 NaN NaN -21.0 43.0 1019.0 -11.0 NW 6.71
3 NaN NaN -21.0 55.0 1019.0 -14.0 NW 9.84
4 NaN NaN -20.0 51.0 1018.0 -12.0 NW 12.97
precipitation Iprec
0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0
3 0.0 0.0
4 0.0 0.0
'''
# pd.PeriodIndex 把分开的时间字符串通过PeriodIndex的方法转换为pandas的时间类型
periods = pd.PeriodIndex(year=df["year"], month=df["month"], day=df["day"], hour=df["hour"], freq="H")
# print(periods)
'''
PeriodIndex(['2010-01-01 00:00', '2010-01-01 01:00', '2010-01-01 02:00',
'2010-01-01 03:00', '2010-01-01 04:00', '2010-01-01 05:00',
'2010-01-01 06:00', '2010-01-01 07:00', '2010-01-01 08:00',
'2010-01-01 09:00',
...
'2015-12-31 14:00', '2015-12-31 15:00', '2015-12-31 16:00',
'2015-12-31 17:00', '2015-12-31 18:00', '2015-12-31 19:00',
'2015-12-31 20:00', '2015-12-31 21:00', '2015-12-31 22:00',
'2015-12-31 23:00'],
dtype='period[H]', length=52584, freq='H')
'''
df['datetime'] = periods
df.set_index('datetime',inplace=True)
# print(df.head())
'''
No year month day hour season PM_Dongsi
datetime
2010-01-01 00:00 1 2010 1 1 0 4 NaN
2010-01-01 01:00 2 2010 1 1 1 4 NaN
2010-01-01 02:00 3 2010 1 1 2 4 NaN
2010-01-01 03:00 4 2010 1 1 3 4 NaN
2010-01-01 04:00 5 2010 1 1 4 4 NaN
PM_Dongsihuan PM_Nongzhanguan PM_US Post DEWP HUMI
datetime
2010-01-01 00:00 NaN NaN NaN -21.0 43.0
2010-01-01 01:00 NaN NaN NaN -21.0 47.0
2010-01-01 02:00 NaN NaN NaN -21.0 43.0
2010-01-01 03:00 NaN NaN NaN -21.0 55.0
2010-01-01 04:00 NaN NaN NaN -20.0 51.0
PRES TEMP cbwd Iws precipitation Iprec
datetime
2010-01-01 00:00 1021.0 -11.0 NW 1.79 0.0 0.0
2010-01-01 01:00 1020.0 -12.0 NW 4.92 0.0 0.0
2010-01-01 02:00 1019.0 -11.0 NW 6.71 0.0 0.0
2010-01-01 03:00 1019.0 -14.0 NW 9.84 0.0 0.0
2010-01-01 04:00 1018.0 -12.0 NW 12.97 0.0 0.0
'''
# 进行降采样
df = df.resample('10D').mean()
# 处理缺失数据
data = df['PM_US Post'].dropna()
# print(data)
'''
datetime
2010-01-01 23:00 129.0
2010-01-02 00:00 148.0
2010-01-02 01:00 159.0
2010-01-02 02:00 181.0
2010-01-02 03:00 138.0
...
2015-12-31 19:00 133.0
2015-12-31 20:00 169.0
2015-12-31 21:00 203.0
2015-12-31 22:00 212.0
2015-12-31 23:00 235.0
Freq: H, Name: PM_US Post, Length: 50387, dtype: float64
'''
x = data.index
y = data.values
plt.figure(figsize=(15,8),dpi=80)
plt.plot(range(len(x)),y)
plt.xticks(range(0,len(x),10),list(x)[::10],rotation=45)
plt.show()
四、pandas画图
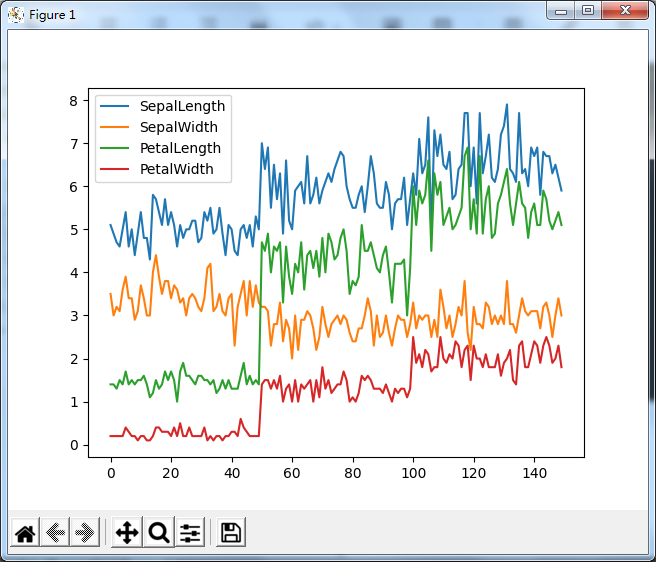
1.折线图
# pandas绘图
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
iris_data = pd.read_csv('iris.csv')
# print(iris_data.info())
'''
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 150 entries, 0 to 149
Data columns (total 5 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 SepalLength 150 non-null float64
1 SepalWidth 150 non-null float64
2 PetalLength 150 non-null float64
3 PetalWidth 150 non-null float64
4 Name 150 non-null object
dtypes: float64(4), object(1)
memory usage: 6.0+ KB
None
'''
# 折线图
iris_data.plot()
plt.show()
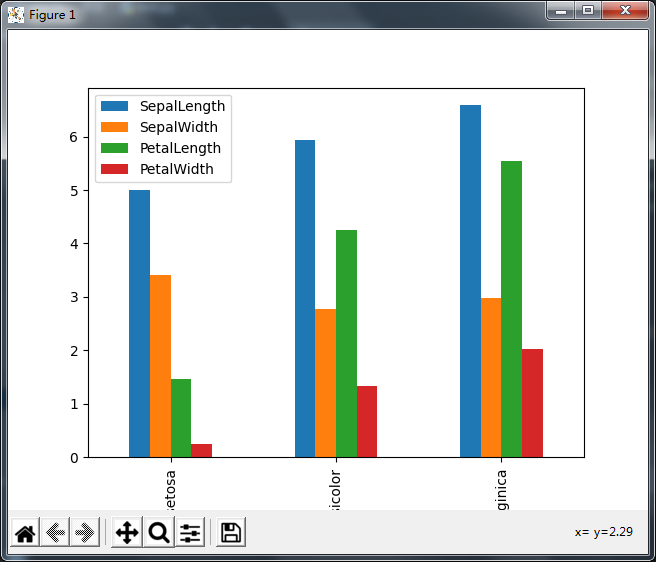
2.分组柱状图
# pandas绘图
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
iris_data = pd.read_csv('iris.csv')
# print(iris_data.info())
# 分组柱状图
iris_data.groupby('Name').mean().plot(kind='bar')
plt.show()
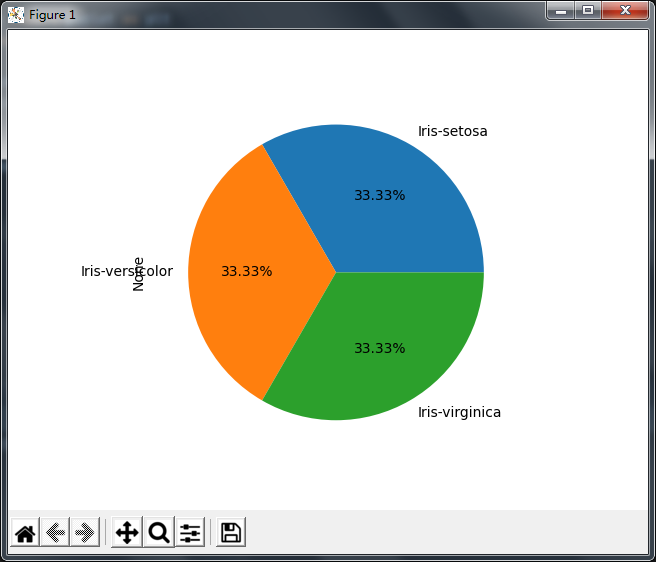
2.饼图
# pandas绘图
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
iris_data = pd.read_csv('iris.csv')
# print(iris_data.info())
# 饼图
iris_data.groupby('Name').size().plot(kind='pie',autopct='%.2f%%')
plt.show()
最后
以上就是安详鲜花最近收集整理的关于数据分析 第七讲 pandas练习 数据的合并、分组聚合、时间序列、pandas绘图数据分析 第七讲 pandas练习 数据的合并和分组聚合的全部内容,更多相关数据分析内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复