摘自:Guava 缓存Cache用法介绍_自知自省的博客-CSDN博客_guavacache使用
1. 前言
Guava Cache是在内存中缓存数据,相比较于数据库或redis存储,访问内存中的数据会更加高效。Guava官网介绍,下面的这几种情况可以考虑使用Guava Cache:
- 愿意消耗一些内存空间来提升速度。
- 预料到某些键会被多次查询。
- 缓存中存放的数据总量不会超出内存容量。
所以,可以将程序频繁用到的少量数据存储到Guava Cache中,以改善程序性能。下面对Guava Cache的用法进行详细的介绍。
2. 构建缓存对象
接口Cache代表一块缓存,它有如下方法:
public interface Cache<K, V> {
V get(K key, Callable<? extends V> valueLoader) throws ExecutionException;
ImmutableMap<K, V> getAllPresent(Iterable<?> keys);
void put(K key, V value);
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m);
void invalidate(Object key);
void invalidateAll(Iterable<?> keys);
void invalidateAll();
long size();
CacheStats stats();
ConcurrentMap<K, V> asMap();
void cleanUp();
}
可以通过CacheBuilder类构建一个缓存对象,CacheBuilder类采用builder设计模式,它的每个方法都返回CacheBuilder本身,直到build方法被调用。构建一个缓存对象代码如下:
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().build();
cache.put("word","Hello Guava Cache");
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("word"));
}
}
上面的代码通过CacheBuilder.newBuilder().build()这句代码创建了一个Cache缓存对象,并在缓存对象中存储了key为word,value为Hello Guava Cache的一条记录。可以看到Cache非常类似于JDK中的Map,但是相比于Map,Guava Cache提供了很多更强大的功能。
3. 设置最大存储
Guava Cache可以在构建缓存对象时指定缓存所能够存储的最大记录数量。当Cache中的记录数量达到最大值后再调用put方法向其中添加对象,Guava会先从当前缓存的对象记录中选择一条删除掉,腾出空间后再将新的对象存储到Cache中。
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(2)
.build();
cache.put("key1","value1");
cache.put("key2","value2");
cache.put("key3","value3");
System.out.println("第一个值:" + cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
System.out.println("第二个值:" + cache.getIfPresent("key2"));
System.out.println("第三个值:" + cache.getIfPresent("key3"));
}
}
上面代码在构造缓存对象时,通过CacheBuilder类的maximumSize方法指定Cache最多可以存储两个对象,然后调用Cache的put方法向其中添加了三个对象。程序执行结果如下图所示,可以看到第三条对象记录的插入,导致了第一条对象记录被删除:
4. 设置过期时间
在构建Cache对象时,可以通过CacheBuilder类的expireAfterAccess和expireAfterWrite两个方法为缓存中的对象指定过期时间,过期的对象将会被缓存自动删除。其中,expireAfterWrite方法指定对象被写入到缓存后多久过期,expireAfterAccess指定对象多久没有被访问后过期。
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(2)
.expireAfterWrite(3,TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
cache.put("key1","value1");
int time = 1;
while(true) {
System.out.println("第" + time++ + "次取到key1的值为:" + cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
上面的代码在构造Cache对象时,通过CacheBuilder的expireAfterWrite方法指定put到Cache中的对象在3秒后会过期。在Cache对象中存储一条对象记录后,每隔1秒读取一次这条记录。程序运行结果如下图所示,可以看到,前三秒可以从Cache中获取到对象,超过三秒后,对象从Cache中被自动删除。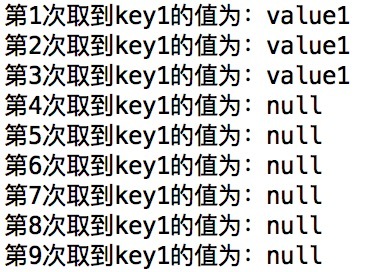
下面代码是expireAfterAccess的例子:
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(2)
.expireAfterAccess(3,TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
cache.put("key1","value1");
int time = 1;
while(true) {
Thread.sleep(time*1000);
System.out.println("睡眠" + time++ + "秒后取到key1的值为:" + cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
}
}
}
通过CacheBuilder的expireAfterAccess方法指定Cache中存储的对象如果超过3秒没有被访问就会过期。while中的代码每sleep一段时间就会访问一次Cache中存储的对象key1,每次访问key1之后下次sleep的时间会加长一秒。程序运行结果如下图所示,从结果中可以看出,当超过3秒没有读取key1对象之后,该对象会自动被Cache删除。
5. 弱引用
可以通过weakKeys和weakValues方法指定Cache只保存对缓存记录key和value的弱引用。这样当没有其他强引用指向key和value时,key和value对象就会被垃圾回收器回收。
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Cache<String,Object> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(2)
.weakValues()
.build();
Object value = new Object();
cache.put("key1",value);
value = new Object();//原对象不再有强引用
System.gc();
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
}
}
上面代码的打印结果是null。构建Cache时通过weakValues方法指定Cache只保存记录值的一个弱引用。当给value引用赋值一个新的对象之后,就不再有任何一个强引用指向原对象。System.gc()触发垃圾回收后,原对象就被清除了。
6. 显式清除
可以调用Cache的invalidateAll或invalidate方法显示删除Cache中的记录。invalidate方法一次只能删除Cache中一个记录,接收的参数是要删除记录的key。invalidateAll方法可以批量删除Cache中的记录,当没有传任何参数时,invalidateAll方法将清除Cache中的全部记录。invalidateAll也可以接收一个Iterable类型的参数,参数中包含要删除记录的所有key值。下面代码对此做了示例。
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().build();
Object value = new Object();
cache.put("key1","value1");
cache.put("key2","value2");
cache.put("key3","value3");
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("key1");
list.add("key2");
cache.invalidateAll(list);//批量清除list中全部key对应的记录
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key2"));
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key3"));
}
}
代码中构造了一个集合list用于保存要删除记录的key值,然后调用invalidateAll方法批量删除key1和key2对应的记录,只剩下key3对应的记录没有被删除。
7. 移除监听器
可以为Cache对象添加一个移除监听器,这样当有记录被删除时可以感知到这个事件。
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
RemovalListener<String, String> listener = new RemovalListener<String, String>() {
public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification<String, String> notification) {
System.out.println("[" + notification.getKey() + ":" + notification.getValue() + "] is removed!");
}
};
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(3)
.removalListener(listener)
.build();
Object value = new Object();
cache.put("key1","value1");
cache.put("key2","value2");
cache.put("key3","value3");
cache.put("key4","value3");
cache.put("key5","value3");
cache.put("key6","value3");
cache.put("key7","value3");
cache.put("key8","value3");
}
}
removalListener方法为Cache指定了一个移除监听器,这样当有记录从Cache中被删除时,监听器listener就会感知到这个事件。程序运行结果如下图所示: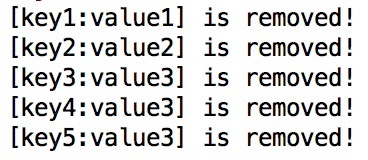
8. 自动加载
Cache的get方法有两个参数,第一个参数是要从Cache中获取记录的key,第二个记录是一个Callable对象。当缓存中已经存在key对应的记录时,get方法直接返回key对应的记录。如果缓存中不包含key对应的记录,Guava会启动一个线程执行Callable对象中的call方法,call方法的返回值会作为key对应的值被存储到缓存中,并且被get方法返回。下面是一个多线程的例子:
public class StudyGuavaCache {
private static Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(3)
.build();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("thread1");
try {
String value = cache.get("key", new Callable<String>() {
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("load1"); //加载数据线程执行标志
Thread.sleep(1000); //模拟加载时间
return "auto load by Callable";
}
});
System.out.println("thread1 " + value);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("thread2");
try {
String value = cache.get("key", new Callable<String>() {
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("load2"); //加载数据线程执行标志
Thread.sleep(1000); //模拟加载时间
return "auto load by Callable";
}
});
System.out.println("thread2 " + value);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
这段代码中有两个线程共享同一个Cache对象,两个线程同时调用get方法获取同一个key对应的记录。由于key对应的记录不存在,所以两个线程都在get方法处阻塞。此处在call方法中调用Thread.sleep(1000)模拟程序从外存加载数据的时间消耗。代码的执行结果如下图: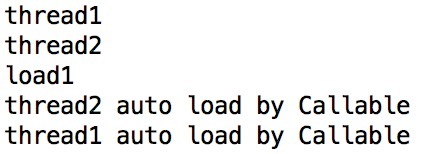
从结果中可以看出,虽然是两个线程同时调用get方法,但只有一个get方法中的Callable会被执行(没有打印出load2)。Guava可以保证当有多个线程同时访问Cache中的一个key时,如果key对应的记录不存在,Guava只会启动一个线程执行get方法中Callable参数对应的任务加载数据存到缓存。当加载完数据后,任何线程中的get方法都会获取到key对应的值。
9. 统计信息
可以对Cache的命中率、加载数据时间等信息进行统计。在构建Cache对象时,可以通过CacheBuilder的recordStats方法开启统计信息的开关。开关开启后Cache会自动对缓存的各种操作进行统计,调用Cache的stats方法可以查看统计后的信息。
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(3)
.recordStats() //开启统计信息开关
.build();
cache.put("key1","value1");
cache.put("key2","value2");
cache.put("key3","value3");
cache.put("key4","value4");
cache.getIfPresent("key1");
cache.getIfPresent("key2");
cache.getIfPresent("key3");
cache.getIfPresent("key4");
cache.getIfPresent("key5");
cache.getIfPresent("key6");
System.out.println(cache.stats()); //获取统计信息
}
}
程序执行结果如下图所示: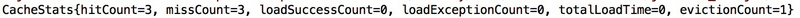
这些统计信息对于调整缓存设置是至关重要的,在性能要求高的应用中应该密切关注这些数据。
10 并发度
Guava Cache可以通过参数concurrencyLevel(5) 设置并发度,即可以同时写缓存的线程数。
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(3)
.concurrencyLevel(5)
.build();
cache.put("key1","value1");
cache.getIfPresent("key1");
}
}
11. LoadingCache
LoadingCache是Cache的子接口,相比较于Cache,当从LoadingCache中读取一个指定key的记录时,如果该记录不存在,则LoadingCache可以自动执行加载数据到缓存的操作。LoadingCache接口的定义如下:
public interface LoadingCache<K, V> extends Cache<K, V>, Function<K, V> {
V get(K key) throws ExecutionException;
V getUnchecked(K key);
ImmutableMap<K, V> getAll(Iterable<? extends K> keys) throws ExecutionException;
V apply(K key);
void refresh(K key);
@Override
ConcurrentMap<K, V> asMap();
}
与构建Cache类型的对象类似,LoadingCache类型的对象也是通过CacheBuilder进行构建,不同的是,在调用CacheBuilder的build方法时,必须传递一个CacheLoader类型的参数,CacheLoader的load方法需要我们提供实现。当调用LoadingCache的get方法时,如果缓存不存在对应key的记录,则CacheLoader中的load方法会被自动调用从外存加载数据,load方法的返回值会作为key对应的value存储到LoadingCache中,并从get方法返回。
public class StudyGuavaCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException {
CacheLoader<String, String> loader = new CacheLoader<String, String> () {
public String load(String key) throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(1000); //休眠1s,模拟加载数据
System.out.println(key + " is loaded from a cacheLoader!");
return key + "'s value";
}
};
LoadingCache<String,String> loadingCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(3)
.build(loader);//在构建时指定自动加载器
loadingCache.get("key1");
loadingCache.get("key2");
loadingCache.get("key3");
}
}
程序执行结果如下图所示:
相应参数解释:
最后
以上就是任性网络最近收集整理的关于Guava 缓存Cache用法介绍的全部内容,更多相关Guava内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复