描述:
花了两天时间写了一个实现企业组织架构的树形数据结构,企业组织架构复杂庞大,这么重要的信息需要统一的数据结构来保存和操作。平时工作中很多业务系统会集成企业集团的组织架构做查询展示等,但是各自实现的方式不同,于是我就想着设计一种通用的数据结构专门适用于企业级的组织架构的数据特点。
企业的组织结构一般是树形,也就是满足以下特点:
1、树里的任意元素一定是唯一(类似于部门,子公司,分公司,总公司,集团本部),一定是唯一的。
2、树中的任意元素只有一个父亲,一个父亲可以有多个儿子(类似于部门只隶属一个公司,子公司只能隶属于一个总公司等,但是对于一个总公司可以有多个部门,多个子公司甚至还会不断更新增加或删除或转移关系)
基于上述的企业组织架构的特点,这个树形其实并非是二叉树,而是一种一对多的“多级树”。
代码:
给出实现企业组织架构的“多级树”代码: LinkedTree.java
(提示:这个代码是我自己纯手写哈,我自己demo测试跑过应该没有大问题,使用的同学可以先自测验证下,代码不是很复杂哈)。
对了,使用我的数据结构的话。对象的equals hashcode尽量复写下,不复写不知道会不会有问题(掩面笑)。
package com.sedt.envoy.yyu;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* @author 何成伟 Hcw
* @date 2022/8/24 19:42
*/
public class LinkedTree<T> implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3423100105373102575L;
private static final String ROOT_IS_NULL = "root element is null";
private final Node<T> root;
private final ArrayList<Node<T>> list = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 必须指定根节点才可以构造
*
* @param rootElement
*/
public LinkedTree(T rootElement) {
if (Objects.isNull(rootElement)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(ROOT_IS_NULL);
}
this.root = new Node<>(null, rootElement);
this.list.add(root);
}
/**
* 增加单个新目标到指定父节点的下面
*
* @param parent
* @param target
* @return
*/
public LinkedTree<T> add(T parent, T target) {
try {
lock.writeLock().lock();
if (this.list.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(ROOT_IS_NULL);
}
if (Objects.isNull(target) || Objects.isNull(parent)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("target/parent element is null");
}
List<T> values = this.list.stream().map(Node::getValue).collect(Collectors.toList());
if (values.contains(target)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("target element is repeated in the tree");
}
int indexParent = values.indexOf(parent);
if (-1 == indexParent) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("parent is not found");
}
Node<T> parentNode = this.list.get(indexParent);
Node<T> targetNode = new Node<>(parentNode, target);
parentNode.addSon(targetNode);
this.list.add(targetNode);
return this;
} finally {
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
/**
* 在父节点和他的儿子(儿子们)中间插入一个元素,当father的儿子,当children的父亲
* 这段调试了将近一小时。。。漏了一个细节,出现的错误和最后导致的原因差的离谱
*
* @param target
* @param father
* @return
*/
public boolean insert(T target, T father) {
try {
lock.writeLock().lock();
if (Objects.isNull(target) || Objects.isNull(father)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("input null");
}
List<T> values = this.list.stream().map(Node::getValue).collect(Collectors.toList());
if (values.contains(target)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("target is repeated in the values");
}
Node<T> fatherNode = getNode(father);
List<Node<T>> sonNodes = fatherNode.getSons();
List<Node<T>> allChildren = new LinkedList<>();
getRangeChildren(fatherNode, allChildren);
Node<T> targetNode = new Node<>(fatherNode, target);
this.list.add(targetNode);
fatherNode.setSons(null);
fatherNode.addSon(targetNode);
targetNode.addSons(sonNodes);
sonNodes.forEach(sonNode -> sonNode.setParent(targetNode));
allChildren.forEach(child -> child.setFloor(child.getFloor() + 1));
return true;
} finally {
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
/**
* 增加批量新目标到指定父节点的下面
* 会按targetList中的排列顺序添加到parent的sons下
*
* @param parent
* @param targetList
* @return
*/
public LinkedTree<T> add(T parent, List<T> targetList) {
try {
lock.writeLock().lock();
if (Objects.isNull(parent) || Objects.isNull(targetList) || targetList.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("parent/target is null or empty");
}
List<T> values = this.list.stream().map(Node::getValue).collect(Collectors.toList());
for (T t : targetList) {
if (values.contains(t)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("the target: " + t + "has repeated in the tree");
}
}
int parentIndex = values.indexOf(parent);
if (-1 == parentIndex) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("parent is not found");
}
Node<T> parentNode = this.list.get(parentIndex);
List<Node<T>> targetNodes = new LinkedList<>();
targetList.forEach(t -> {
Node<T> target = new Node<>(parentNode, t);
targetNodes.add(target);
});
parentNode.addSons(targetNodes);
this.list.addAll(targetNodes);
return this;
} finally {
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
/**
* 删除指定树中的某一个节点,该节点的儿子和儿子的儿子等都会移除
*
* @param target
* @return
*/
public boolean remove(T target) {
try {
lock.writeLock().lock();
Node<T> targetNode = getNode(target);
if (getRoot().equals(targetNode)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("root cannot be removed");
}
List<Node<T>> removeChildren = new LinkedList<>();
getRangeChildren(targetNode, removeChildren);
targetNode.getParent().removeSon(targetNode);
this.list.remove(targetNode);
removeChildren.forEach(Node::setNull);
return true;
} finally {
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
private void checkTargetIfNullAndTreeEmpty(T target) {
try {
lock.readLock().lock();
if (this.list.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(ROOT_IS_NULL);
}
if (Objects.isNull(target)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("target element is null");
}
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
/**
* 修改一个指定节点的值
*
* @param target
* @param source
* @return
*/
public boolean modify(T target, T source) {
try {
lock.writeLock().lock();
if (this.list.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(ROOT_IS_NULL);
}
if (Objects.isNull(target) || Objects.isNull(source)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("target/source element is null");
}
List<T> values = this.list.stream().map(Node::getValue).collect(Collectors.toList());
if (values.contains(target)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("target element is repeated in the tree");
}
int indexSource = values.indexOf(source);
if (-1 == indexSource) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("source is not found");
}
Node<T> sourceNode = this.list.get(indexSource);
sourceNode.setValue(target);
return true;
} finally {
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
/**
* 获取指定father父节点下的所有子节点,包括儿子,儿子的儿子,孙子的儿子....
*
* @param father
* @return
*/
public List<T> getAllChildren(T father) {
try {
lock.readLock().lock();
return getRangeSearch(father);
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
/**
* 获取指定父节点下的所有儿子,不包括儿子们之后的子节点
*
* @param father
* @return
*/
public List<T> getSons(T father) {
try {
lock.readLock().lock();
Node<T> fatherNode = getNode(father);
return fatherNode.getSons().stream().map(Node::getValue).collect(Collectors.toList());
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
/**
* 获取目标节点的父亲节点
*
* @param target
* @return
*/
public T getParent(T target) {
try {
lock.readLock().lock();
return getNode(target).getParent().getValue();
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
private List<T> getRangeSearch(T father) {
try {
lock.readLock().lock();
Node<T> fatherNode = getNode(father);
List<Node<T>> nodes = getRangeChildren(fatherNode, new LinkedList<>());
return nodes.stream().map(Node::getValue).collect(Collectors.toList());
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
private List<Node<T>> getRangeChildren(Node<T> fatherNode, List<Node<T>> collection) {
List<Node<T>> allChildren = this.list.stream().filter(node -> Objects.nonNull(node.getParent())
&& node.getParent().equals(fatherNode)).collect(Collectors.toList());
collection.addAll(allChildren);
for (Node<T> node : allChildren) {
if (Objects.nonNull(node.getSons())) {
getRangeChildren(node, collection);
}
}
return collection;
}
/**
* 交换同一个父亲下的两个儿子排序
* 同一个父亲下的儿子们的排序通过一个linkedList做维护,默认是插入的顺序排序
*
* @param target1
* @param target2
*/
public boolean changeSonSeq(T target1, T target2) {
try {
lock.writeLock().lock();
if (Objects.isNull(target1) || Objects.isNull(target2)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("target1/target2 is null");
}
Node<T> target1Node = getNode(target1);
Node<T> target2Node = getNode(target2);
if (Objects.isNull(target1Node.getParent()) || Objects.isNull(target2Node.getParent())) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("target1Node/target2Node parent is null,maybe contains root");
}
if (!target1Node.getParent().equals(target2Node.getParent())) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("target1Node/target2Node parent is not same");
}
Node<T> parentNode = target1Node.getParent();
Collections.swap(parentNode.getSons(), parentNode.getSons().indexOf(target1Node),
parentNode.getSons().indexOf(target2Node));
return true;
} finally {
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
/**
* 更换该节点的父节点
* 好乱。。。没有注释完全不懂自己在写什么
*
* @param node
* @param fatherTarget
*/
public boolean move(T node, T fatherTarget) {
try {
lock.writeLock().lock();
if (Objects.isNull(node) || Objects.isNull(fatherTarget)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("node/fatherTarget is null");
}
Node<T> nodeNode = getNode(node);
Node<T> fatherTargetNode = getNode(fatherTarget);
Node<T> oriFatherNode = nodeNode.getParent();
Integer oriFloor = nodeNode.getFloor();
if (Objects.isNull(nodeNode.getParent())) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("root cannot move");
}
if (nodeNode.getParent().equals(fatherTargetNode)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("current node's father is already point to fatherTarget");
}
List<Node<T>> oldChildren = new LinkedList<>();
getRangeChildren(nodeNode, oldChildren);
// 父亲不能移到儿子或儿子的儿子等身上
if (oldChildren.contains(fatherTargetNode)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("cannot move to the son");
}
nodeNode.setFloor(fatherTargetNode.getFloor() + 1);
// 原来的父节点删除你
oriFatherNode.removeSon(nodeNode);
// 现在的新父节点加上你
fatherTargetNode.addSon(nodeNode);
// 你的所有子节点都要更新他们的floor
Integer distance = oriFloor - (fatherTargetNode.getFloor() + 1);
oldChildren.forEach(o -> {
Integer oldFloor = o.getFloor();
o.setFloor(oldFloor - distance);
});
return true;
} finally {
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
/**
* 获取当前树的根节点对象
*
* @return
*/
public T getRoot() {
try {
lock.readLock().lock();
if (this.list.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(ROOT_IS_NULL);
}
return this.root.getValue();
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
/**
* 获取当前树在同一个floor上的兄弟们
*
* @param floor
* @return
*/
public List<T> getBrothers(int floor) {
try {
lock.readLock().lock();
if (this.list.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(ROOT_IS_NULL);
}
List<Node<T>> nodeList = this.list.stream()
.filter(node -> node.getFloor().equals(floor)).collect(Collectors.toList());
if (nodeList.isEmpty()) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
return nodeList.stream().map(Node::getValue).collect(Collectors.toList());
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
/**
* 获取指定目标同父亲下的兄弟们(返回会排除目标自己)
*
* @param target
* @return
*/
public List<T> getBrothers(T target) {
try {
lock.readLock().lock();
if (this.list.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(ROOT_IS_NULL);
}
if (Objects.isNull(target)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("target is null");
}
List<Node<T>> nodeList = this.list.stream().filter(node -> Objects.nonNull(node.getParent())
&& node.getParent().getValue().equals(getNode(target).getParent().getValue())
&& !node.getValue().equals(target)).collect(Collectors.toList());
if (nodeList.isEmpty()) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
return nodeList.stream().map(Node::getValue).collect(Collectors.toList());
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
/**
* 获取指定目标的所在的层
*
* @param target
* @return
*/
public int getFloor(T target) {
try {
lock.readLock().lock();
Node<T> targetNode = getNode(target);
return targetNode.getFloor();
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
/**
* 追踪任意两个元素间的父与子路径
* 两个元素间必须有“爷父孙...”的血缘关系,属于旁系无法追踪
*
* @param ori
* @param target
* @return
*/
public List<T> getAnyTraceTarget(T ori, T target) {
try {
lock.readLock().lock();
Node<T> targetNode = getNode(target);
Node<T> oriNode = getNode(ori);
if (oriNode.getFloor().equals(targetNode.getFloor())) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("ori and target cannot be brother");
}
List<Node<T>> trace = new LinkedList<>();
if (oriNode.getFloor() > targetNode.getFloor()) {
// ori在target级别下面
followingTraceToTarget(trace, oriNode, targetNode);
} else {
// ori在target级别之上
followingTraceToTarget(trace, targetNode, oriNode);
Collections.reverse(trace);
}
return trace.stream().map(Node::getValue).collect(Collectors.toList());
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
/**
* 追踪从目标节点出发一路找到root经过的节点路径
*
* @param target
* @return
*/
public List<T> getTargetTraceRoot(T target) {
try {
lock.readLock().lock();
Node<T> targetNode = getNode(target);
if (Objects.isNull(targetNode.getParent())) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("root cannot here");
}
List<Node<T>> trace = new LinkedList<>();
followingTraceToRoot(trace, targetNode);
return trace.stream().map(Node::getValue).collect(Collectors.toList());
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
private void followingTraceToTarget(List<Node<T>> collection, Node<T> node, Node<T> targetNode) {
collection.add(node);
if (node.equals(this.root)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("cannot be traced");
}
if (node.equals(targetNode)) {
return;
}
followingTraceToTarget(collection, node.getParent(), targetNode);
}
private void followingTraceToRoot(List<Node<T>> collection, Node<T> node) {
collection.add(node);
if (node.equals(this.root)) {
return;
}
followingTraceToRoot(collection, node.getParent());
}
/**
* 追踪从root出发一路找到目标节点经过的节点路径
*
* @param target
* @return
*/
public List<T> getRootTraceTarget(T target) {
try {
lock.readLock().lock();
List<T> traceToRoot = getTargetTraceRoot(target);
Collections.reverse(traceToRoot);
return traceToRoot;
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
/**
* 获取目标节点的详情(层级结构)
* 真的有时间要优化下这个代码,写得我也是栓q了
*
* @param target
* @return
*/
public Detail<T> getNodeDetail(T target) {
try {
lock.readLock().lock();
Node<T> targetNode = getNode(target);
List<Node<T>> targetNodeChildren = new LinkedList<>();
getRangeChildren(targetNode, targetNodeChildren);
targetNodeChildren.add(targetNode);
Map<Node<T>, Detail<T>> nodeDetailMap = new HashMap<>();
int floorMax = targetNodeChildren.stream().max(Comparator.comparing(Node::getFloor))
.orElseThrow(() -> new UnsupportedOperationException("max floor is missing")).getFloor();
int floorMin = targetNodeChildren.stream().min(Comparator.comparing(Node::getFloor))
.orElseThrow(() -> new UnsupportedOperationException("min floor is missing")).getFloor();
for (int i = floorMax; i >= floorMin; i--) {
int finalI = i;
targetNodeChildren.stream().filter(child -> child.getFloor().equals(finalI)).forEach(child -> {
List<Detail<T>> detailList = new LinkedList<>();
child.getSons().forEach(son -> {
Detail<T> detail = nodeDetailMap.get(son);
if (Objects.nonNull(detail)) {
detailList.add(detail);
}
});
Detail<T> detail = new Detail<>(child.getValue(), detailList, child.getFloor());
nodeDetailMap.put(child, detail);
});
}
return nodeDetailMap.get(targetNode);
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
private Node<T> getNode(T target) {
try {
lock.readLock().lock();
checkTargetIfNullAndTreeEmpty(target);
List<T> values = this.list.stream().map(Node::getValue).collect(Collectors.toList());
int indexTarget = values.indexOf(target);
if (-1 == indexTarget) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("target is not found");
}
return this.list.get(indexTarget).getNode();
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
private static class Node<T> implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3031742444270186151L;
protected T value;
protected Node<T> parent;
protected LinkedList<Node<T>> sons;
protected Integer floor;
private Node(Node<T> parent, T t) {
this.parent = parent;
this.value = t;
this.sons = null;
if (Objects.isNull(parent)) {
this.floor = 0;
} else {
this.floor = parent.getFloor() + 1;
}
}
protected Node<T> getNode() {
return this;
}
protected Integer getFloor() {
return floor;
}
protected LinkedList<Node<T>> getSons() {
if (Objects.isNull(this.sons)) {
return new LinkedList<>();
}
return this.sons;
}
protected Node<T> getParent() {
return this.parent;
}
protected T getValue() {
return this.value;
}
protected void setValue(T t) {
this.value = t;
}
protected void setParent(Node<T> parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
protected void setSons(LinkedList<Node<T>> sons) {
this.sons = sons;
}
protected void setFloor(Integer floor) {
this.floor = floor;
}
private void addSon(Node<T> son) {
if (Objects.isNull(this.sons) || this.sons.isEmpty()) {
LinkedList<Node<T>> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
linkedList.addLast(son);
this.sons = linkedList;
} else {
getSons().addLast(son);
}
son.setParent(this);
}
private void addSons(List<Node<T>> sons) {
if (Objects.isNull(this.sons) || this.sons.isEmpty()) {
this.sons = new LinkedList<>(sons);
} else {
getSons().addAll(sons);
}
}
private void removeSon(Node<T> node) {
if (Objects.isNull(node)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("input is null");
}
if (Objects.isNull(this.sons) || this.sons.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("tree has no children");
}
int nodeIndex = getSons().indexOf(node);
if (-1 == nodeIndex) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("node is not found in sons");
}
getSons().remove(nodeIndex);
if (getSons().isEmpty()) {
this.sons = null;
}
node.setParent(null);
}
private void setNull() {
setValue(null);
setSons(null);
setParent(null);
setFloor(null);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof Node)) {
return false;
}
Node<?> node = (Node<?>) o;
return Objects.equals(getValue(), node.getValue()) && Objects.equals(getParent(), node.getParent())
&& Objects.equals(getSons(), node.getSons());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(getValue(), getParent());
}
}
public static class Detail<T> implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4208216219090662249L;
private T value;
private Integer floor;
private List<Detail<T>> sons;
public Detail(T value, List<Detail<T>> sons, Integer floor) {
this.value = value;
this.sons = sons;
this.floor = floor;
}
public T getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(T value) {
this.value = value;
}
public List<Detail<T>> getSons() {
return sons;
}
public void setSons(List<Detail<T>> sons) {
this.sons = sons;
}
public Integer getFloor() {
return floor;
}
public void setFloor(Integer floor) {
this.floor = floor;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Detail<?> detail = (Detail<?>) o;
return Objects.equals(value, detail.value) && Objects.equals(sons, detail.sons)
&& Objects.equals(floor, detail.floor);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(value, sons, floor);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Detail{" + "value=" + value + ", sons=" + sons + ", floor=" + floor + '}';
}
}
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
}
这边说明一点,使用了ReentrantReadWriteLock 是一种读写锁,可以提高读读间的并发效率,也就是只读不会互斥,可以并发。但是互斥读写、写写的情况。理由是我不希望我在读取树形遍历的时候有另一个线程进来对正在读的树形变量做写操作,这样会有一定的问题。
例如A线程在读取遍历树形信息,假设正好读完floor=2的元素,此时正好B线程进来做增加树节点操作,在floor=3增加了属于floor=2中元素的几个子节点,那么A线程下一刻便会把floor=3中的新增节点也读进来,但是A线程在floor=2没有拿到B线程增加时对floor=2中涉及到的父节点的更新信息,导致新的floor=3节点找不到floor=2中父节点,于是可能整个遍历就crash(没有试过,大概率空指针)。
以下是我的demo测试:demo测试的组织架构是这样的(示意图)
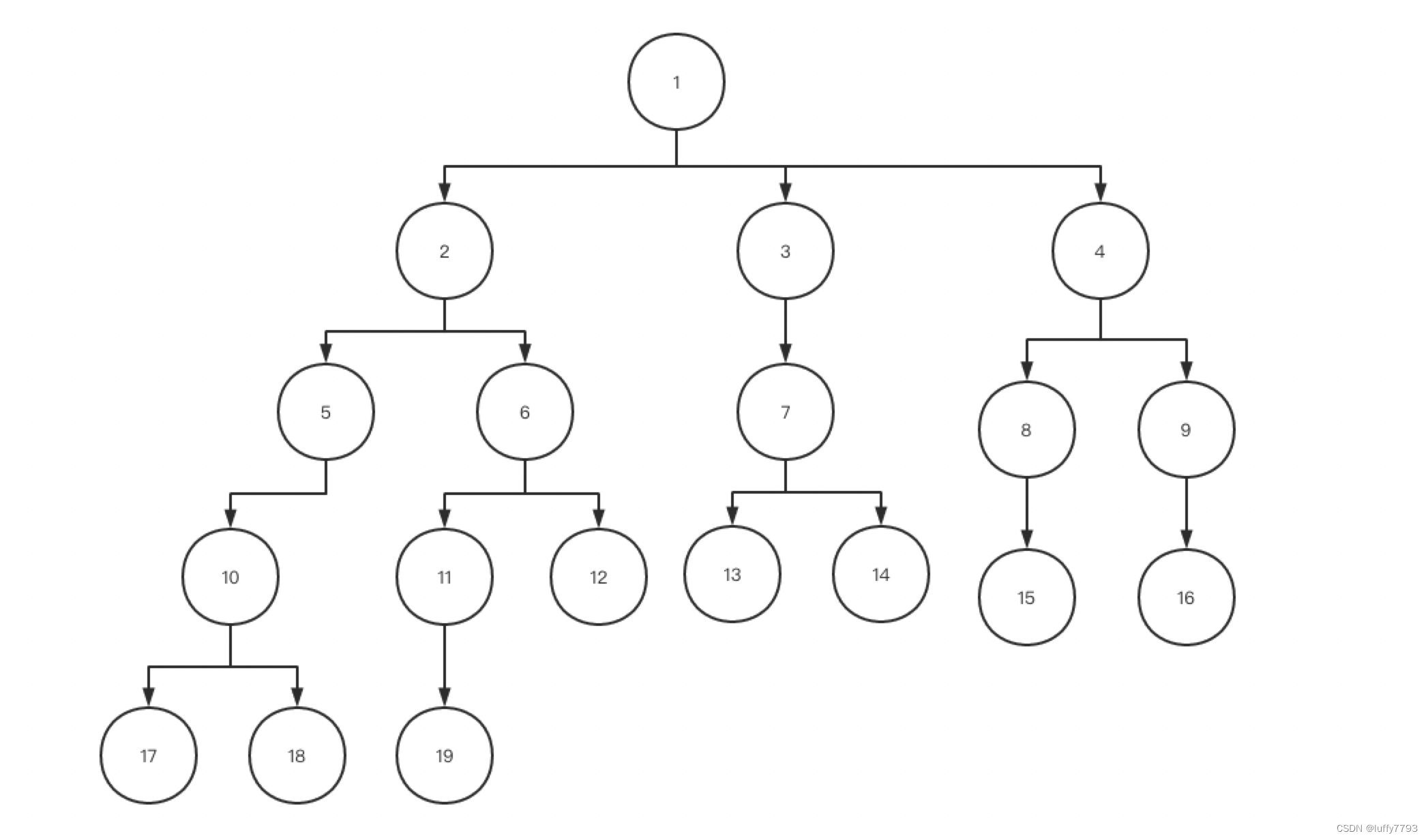
代码:
package com.sedt.envoy.yyu;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 何成伟 Hcw
* @date 2022/8/25 20:33
*/
public class LinkedTreeTest {
public static LinkedTree<Integer> linkedTree;
static {
linkedTree = new LinkedTree<>(1);
// add -> list
// 1-> 2,3,4 // 2->5,6 // 3->7 // 4->8,9
linkedTree.add(1, Arrays.asList(2, 3, 4)).add(2, Arrays.asList(5, 6))
.add(3, 7).add(4, Arrays.asList(8, 9));
// 5->10
linkedTree.add(5, 10);
// 6->11,12
linkedTree.add(6, Arrays.asList(11, 12));
// 7->13,14
linkedTree.add(7, Arrays.asList(13, 14));
// 8->15
linkedTree.add(8, 15);
// 9->16
linkedTree.add(9, 16);
// 10 ->17,18
linkedTree.add(10, Arrays.asList(17, 18));
//11->19
linkedTree.add(11, 19);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// getTargetTraceRoot
List<Integer> targetTraceRoot = linkedTree.getTargetTraceRoot(17);
System.out.println("TargetTraceRoot: " + targetTraceRoot);
// getRootTraceTarget
List<Integer> rootTraceTarget = linkedTree.getRootTraceTarget(19);
System.out.println("RootTraceTarget: " + rootTraceTarget);
// getRoot
Integer root = linkedTree.getRoot();
System.out.println("root: " + root);
// getFloor
int floor = linkedTree.getFloor(3);
System.out.println("floor: " + floor);
// nodeDetail
LinkedTree.Detail<Integer> detail = linkedTree.getNodeDetail(2);
String s = JSONObject.toJSONString(detail);
System.out.println("s: " + s);
JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(s);
System.out.println("JSON: " + jsonObject);
// getParent
Integer parent = linkedTree.getParent(6);
System.out.println("parent: " + parent);
// getBrother(floor)
List<Integer> brothersWithFloor = linkedTree.getBrothers(floor);
System.out.println("brothersWithFloor: " + brothersWithFloor);
// getBrother(target)
List<Integer> brotherWithTarget = linkedTree.getBrothers(Integer.valueOf(3));
System.out.println("brotherWithTarget: " + brotherWithTarget);
// getAllChildren
List<Integer> allChildren = linkedTree.getAllChildren(3);
System.out.println("allChildren: " + allChildren);
// insert
LinkedTree.Detail<Integer> detail1 = linkedTree.getNodeDetail(1);
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(detail1));
linkedTree.insert(20, 1);
LinkedTree.Detail<Integer> detail2 = linkedTree.getNodeDetail(1);
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(detail2));
// getSons
List<Integer> sons = linkedTree.getSons(3);
System.out.println("sons: " + sons);
// modify
linkedTree.modify(100, 2);
List<Integer> mod = linkedTree.getSons(1);
System.out.println("mod: " + mod);
// move
linkedTree.move(3, 4);
LinkedTree.Detail<Integer> move = linkedTree.getNodeDetail(4);
System.out.println("move: " + JSONObject.toJSONString(move));
// changeSonSeq
List<Integer> b = linkedTree.getSons(7);
System.out.println("move before: " + b);
linkedTree.changeSonSeq(13, 14);
List<Integer> a = linkedTree.getSons(7);
System.out.println("move after: " + a);
System.out.println("root allChildren: " + linkedTree.getAllChildren(1));
// remove
linkedTree.remove(100);
System.out.println("root allChildren after remove: " + linkedTree.getAllChildren(1));
}
}
然后假设我们取根节点的“1”对象:linkedTree.getNodeDetail(1); 可以得到返回的json层级结构如下,如果没有子节点那么sons=[],value指的是你塞进去的对象实例,我们这里是Integer对象,当然这个value也可以是一个由类构造的实例。
{
"floor": 0,
"sons": [
{
"floor": 1,
"sons": [
{
"floor": 2,
"sons": [
{
"floor": 3,
"sons": [
{
"floor": 4,
"sons": [],
"value": 17
},
{
"floor": 4,
"sons": [],
"value": 18
}
],
"value": 10
}
],
"value": 5
},
{
"floor": 2,
"sons": [
{
"floor": 3,
"sons": [
{
"floor": 4,
"sons": [],
"value": 19
}
],
"value": 11
},
{
"floor": 3,
"sons": [],
"value": 12
}
],
"value": 6
}
],
"value": 2
},
{
"floor": 1,
"sons": [
{
"floor": 2,
"sons": [
{
"floor": 3,
"sons": [],
"value": 13
},
{
"floor": 3,
"sons": [],
"value": 14
}
],
"value": 7
}
],
"value": 3
},
{
"floor": 1,
"sons": [
{
"floor": 2,
"sons": [
{
"floor": 3,
"sons": [],
"value": 15
}
],
"value": 8
},
{
"floor": 2,
"sons": [
{
"floor": 3,
"sons": [],
"value": 16
}
],
"value": 9
}
],
"value": 4
}
],
"value": 1
}如果上述代码实现无误,那么对于组织架构就有了一个相对很好的数据结构来维护,但是还有一个问题就是同步,由于我工作中采用的是http调用接口的方式去同步增量的组织架构信息(对,就是那样,方便随时一个业务新应用做集成。。。),也就是定时去拉增量接口,然后根据自己是怎么实现组织架构的,写好逻辑,往自己的业务系统更新掉这部分内容。那么就全量(第一次同步,大量的save)和增量(基于区间时间拉取变化的内容可能新增,删除,修改等)而言,也就是需要我们自己做一个“转接头”将这部分接口的信息转化为调用这个数据结构的api,达到保存和更新的效果。这个就要各位同学自己去根据实际情况自定义实现这个“转接头”。只要这些测试下来没问题,且约定的一些接口定义字段不在变化,那么这部分代码就可以作为整个公司开发sdk中的一部分,甚至可以把此组织架构数据放入统一的缓存,只保证缓存和组织架构http接口间的同步正确即可,对于业务系统只管查询就行。而要去主动更新组织架构就涉及到更大的权限,这个我以为一般业务系统不能做到,也就是你不会去调用增删改组织架构的接口,而只查询而已。在这个基础上延伸属于你这个服务该有的功能,比如你是一个管吃饭的服务,a部门11点吃饭,b部门12点吃饭等等此类。
好了,以上就是所有的代码。都是纯手写和自己构思设计,不排除有小bug,各位也可以在我的基础上继续开发,做到自定义(怎么舒服怎么来),也希望大家可以一起帮我做个测试或是代码上的优化等。
感谢您提出的建议,谢谢,希望对正在看这篇文章的你有一定的启发。
最后
以上就是满意帆布鞋最近收集整理的关于【数据结构】实现一种适用于保存和操作企业级组织架构的树形数据结构的全部内容,更多相关【数据结构】实现一种适用于保存和操作企业级组织架构内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。

![mysql数据库原理设计与应用在线pdf_《数据库原理与应用》[51MB]PDF完整版下载-码农之家...](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg12.png)






发表评论 取消回复